Introduction
In recent years, various handheld game consoles have appeared on the market, such as Steam Deck, ASUS, Switch, etc, and there is a new type of charger with an HDMI port for handheld game consoles. We took apart HAGiBiS 65W and Baseus 67W before, you can click on the links to check them. And today, we want to introduce what HDMI is and how it works to you.

I believe you have seen it on TVs, monitors, and notebooks.
Versions

It was first released in December 2002 by TV manufacturers, like Hitachi, Panasonic, Philips, Sony, and Toshiba. And it was designed specifically for the era's Blu-ray technology, and its primary feature was the simultaneous integration of video and audio transmission. In comparison to the single video transmission of DVI and DP at that time, it was better suited for audiovisual equipment. It had a maximum bandwidth of 4.95Gbps, with 3.96Gbps allocated for video streaming, supporting resolutions of 1080P or 1600*1200. On the audio side, it supported 8-channel LPCM 24bit/192kHz.
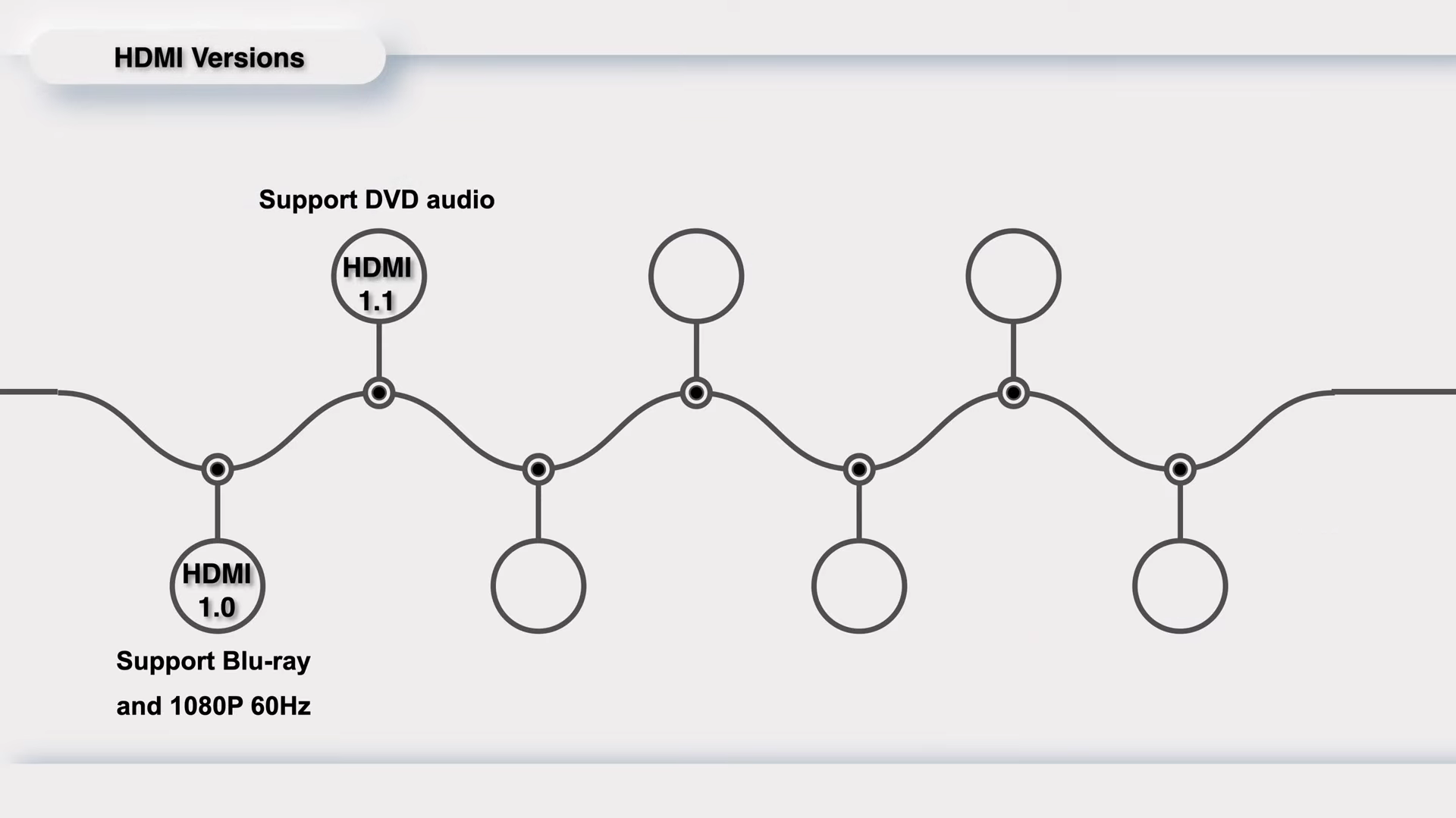
HDMI 1.1 was released in May 2004, adding support for DVD audio based on 1.0.
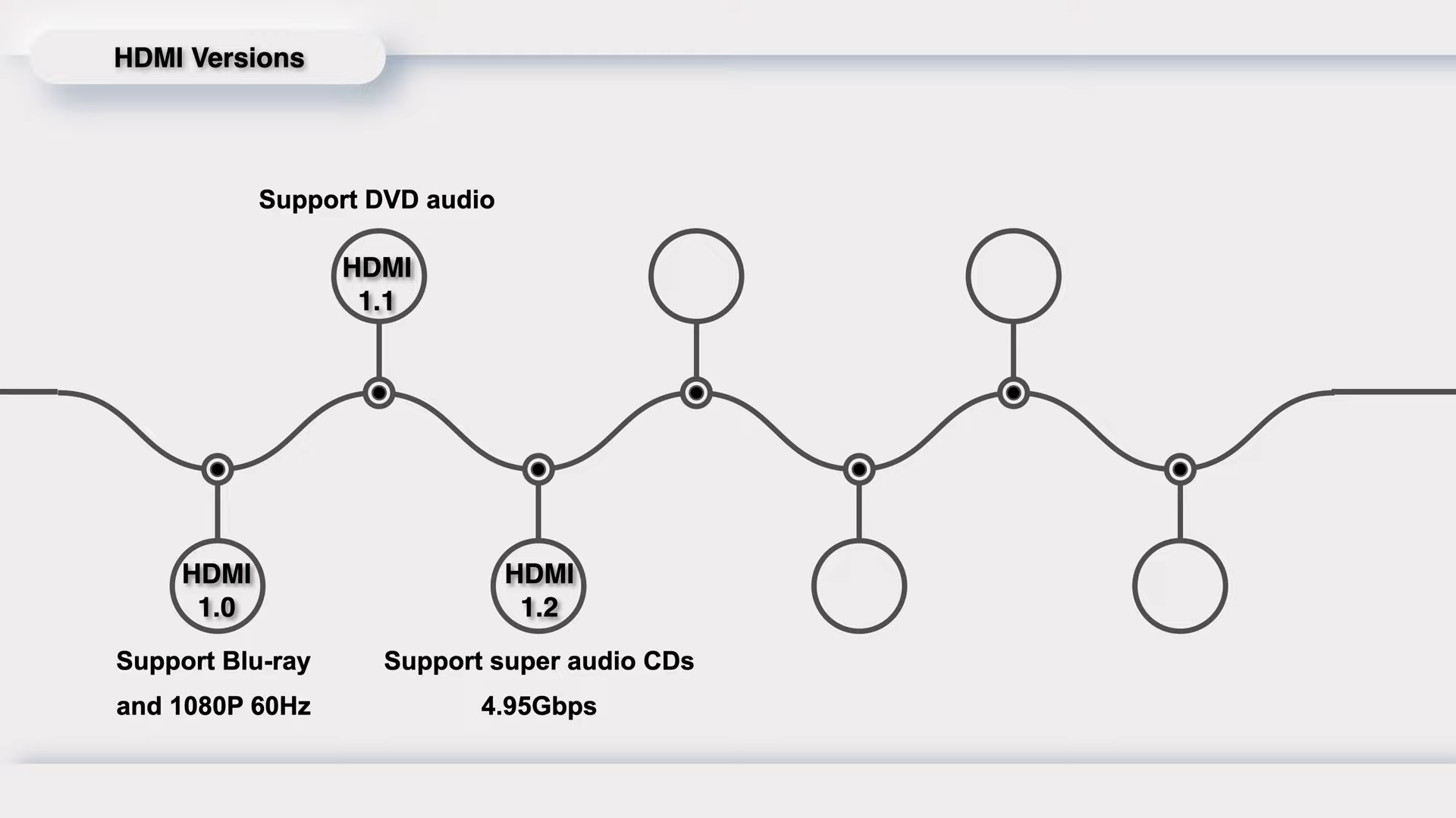
HDMI 1.2 was released in August 2005 and the bandwidth reaches 4.95Gbps.
It supports super audio CDs and solved the low resolution and poor compatibility of HDMI 1.1.
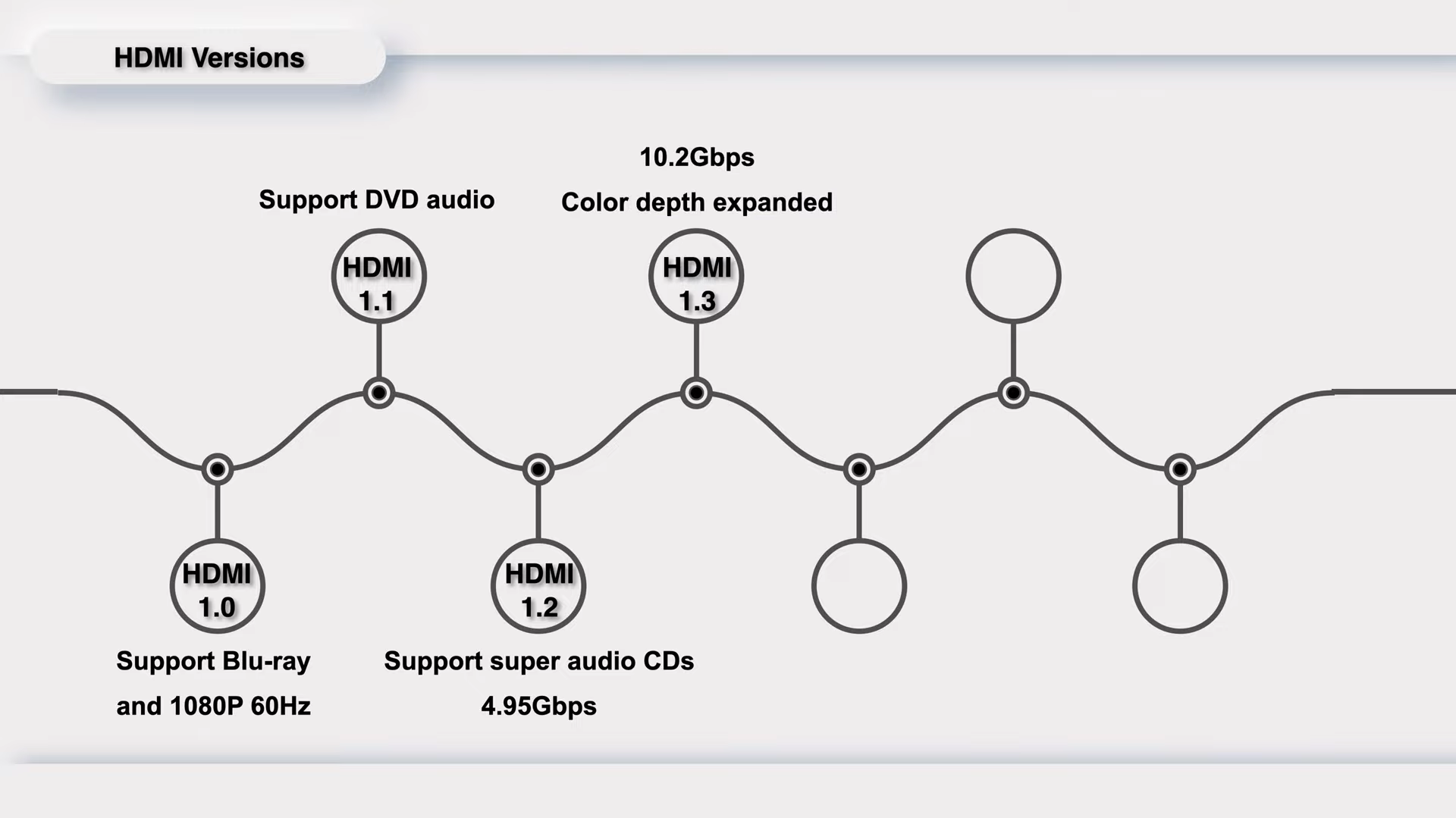
HDMI 1.3 was released in June 2006, doubling the bandwidth to 10.2Gbps. The cable consists of four pairs of transmission channels, with one pair serving as the clock channel, while the remaining three pairs are designated as TMDS channels (Transition Minimized Differential Signaling). And the color depth is greatly expanded to 30 bits, 36 bits, and 48 bits.
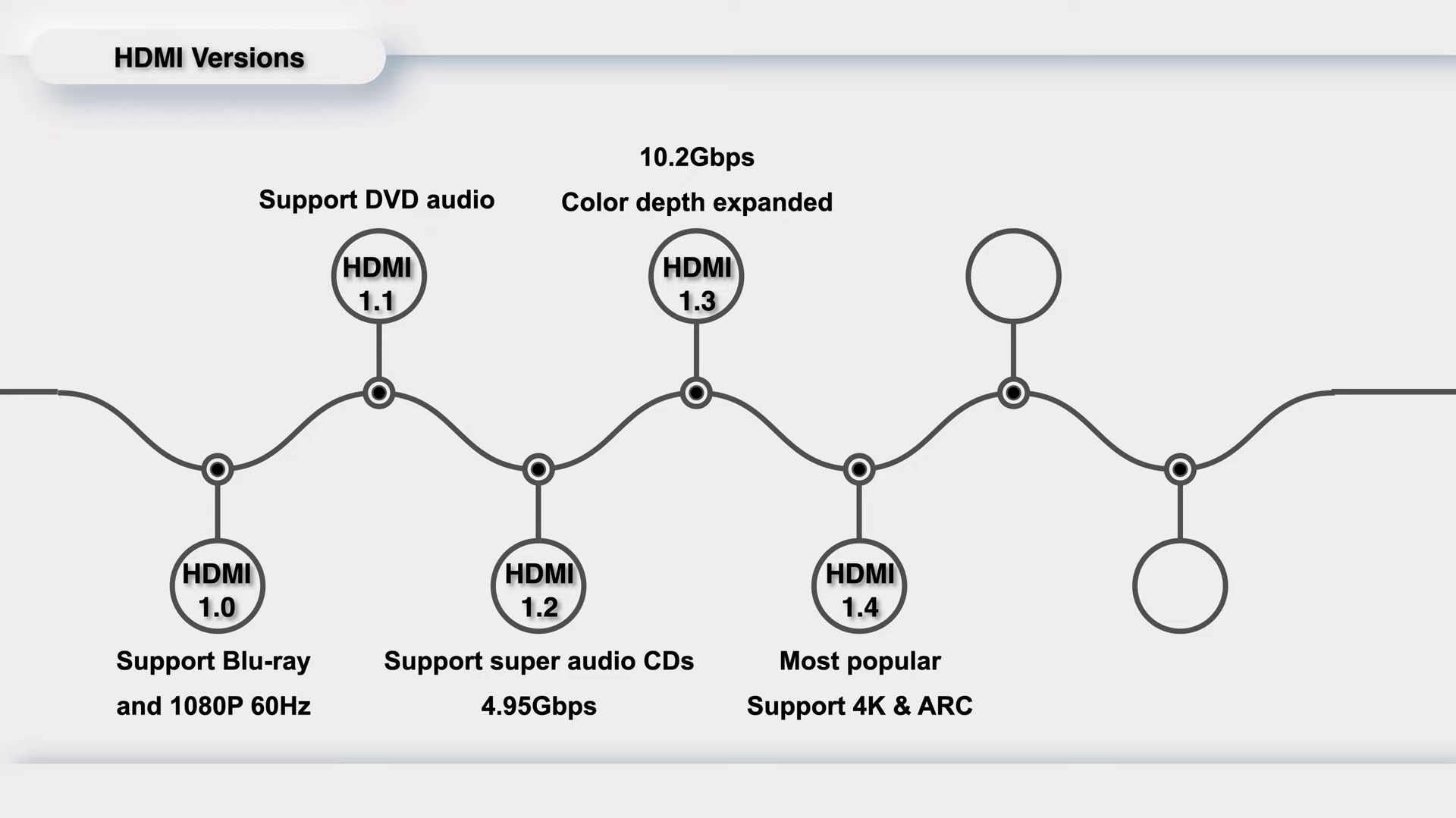
The HDMI 1.4 was released in May 2009 and is the most popular version, because this is the first time the HDMI supports 4K video. And the ARC (Audio Return Channel) makes it possible for HDMI-connected TV to send audio data to the audio output devices, like soundbar. Additionally, it has also introduced a new 100Mbps network transmission capability.
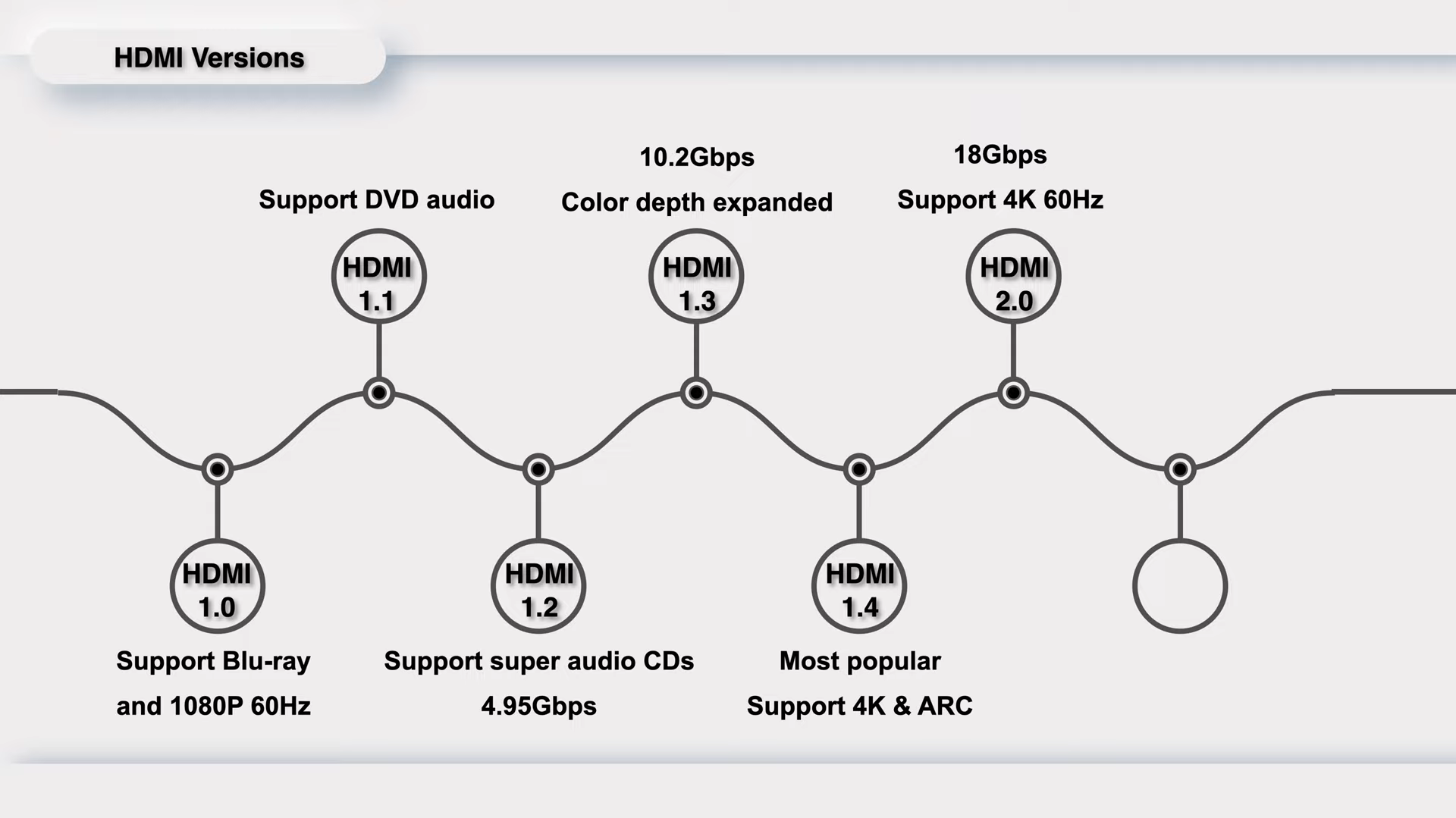
HDMI 2.0, also known as "HDMI UHD," was introduced in September 2013. This iteration saw a bandwidth upgrade to 18Gbps, enabling support for 4K resolution at 60Hz refresh rate. It introduced features like hot plugging and audio support for up to 32 channels, with a maximum sampling rate of 1536kHz.
In terms of compatibility, HDMI 2.0 doesn't replace previous versions but ensures backward compatibility with earlier generations. However, despite these advancements, HDMI 2.0 is not as widely adopted as its predecessor, HDMI 1.4, at present.
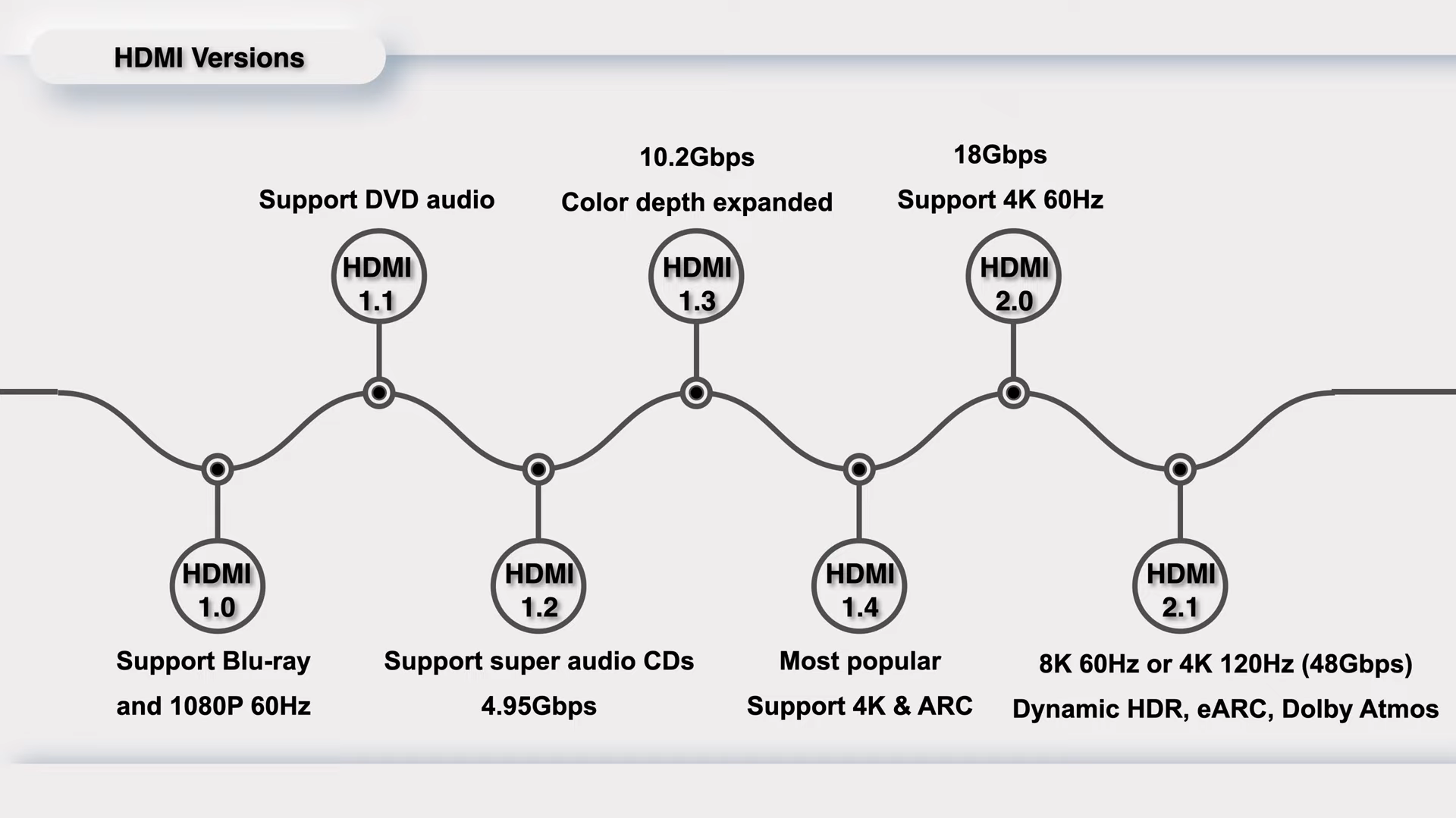
And the latest version of HDMI is 2.1, which was released in January 2017. The bandwidth was greatly increased to 48Gbps, faster than Thunderbolt 4.
It supports up to 8K 60Hz or 4K 120Hz, and many new features have been supported, like dynamic HDR, eARC, Dolby Atmos, etc.
Types
After introducing different versions of HDMI from 1.0 to 2.1, let's take a look at different types of HDMI connectors.
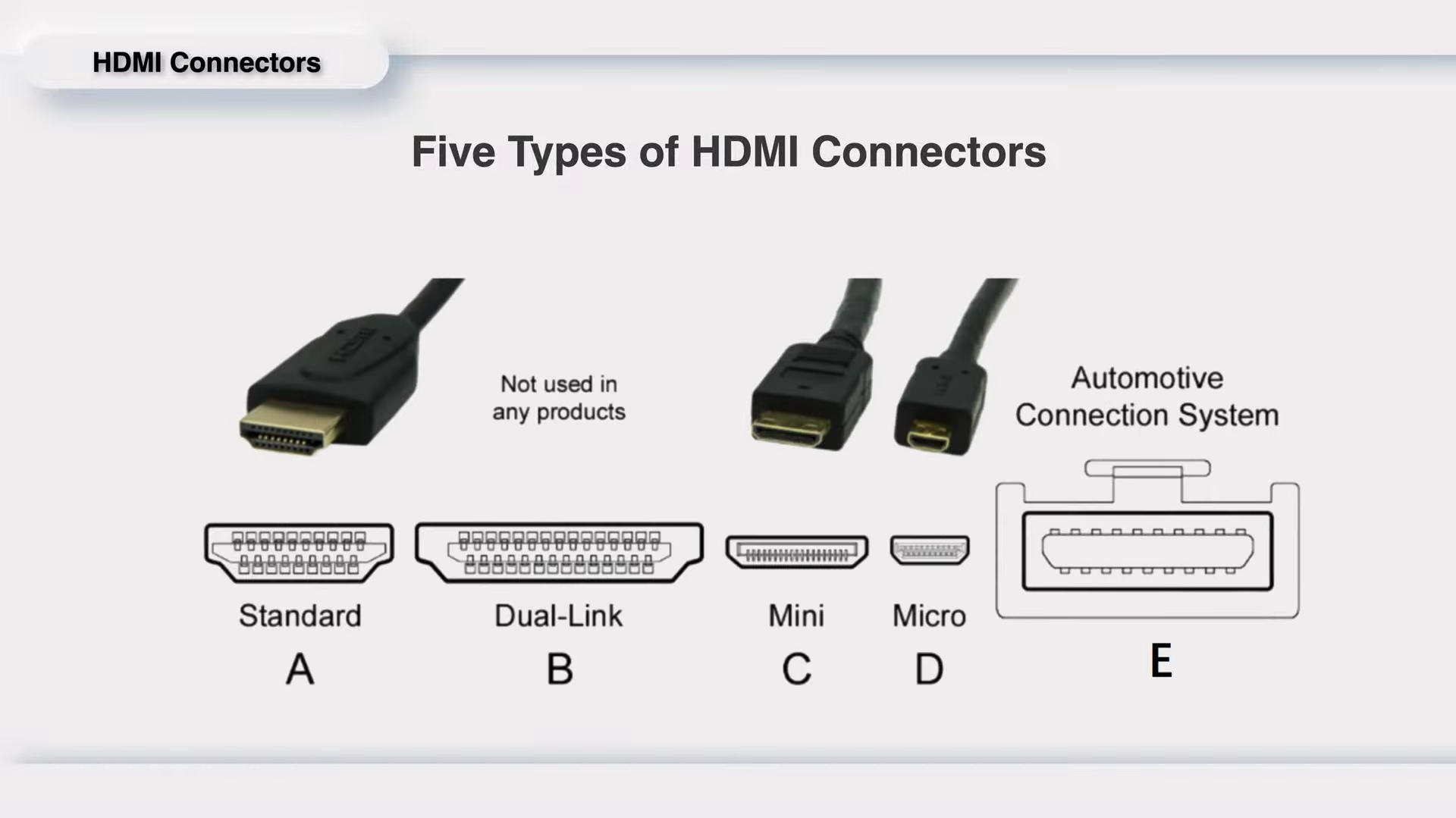
Like USB-A, USB-B, USB-C, there're five types of HDMI connectors, from Type-A to Type-E.

Standard Type-A is the most common connector in our daily life.
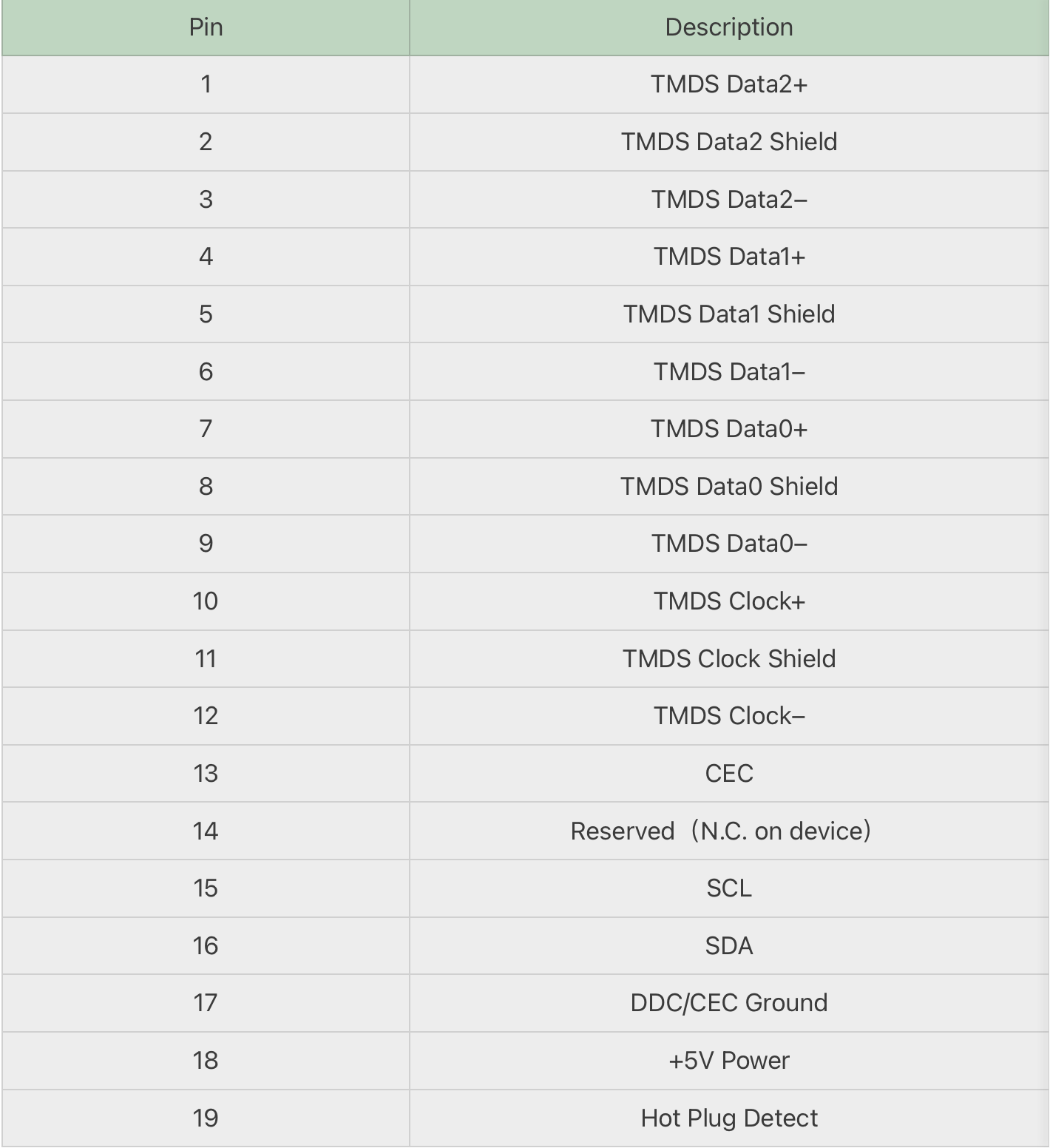
With 19 pins, a width of 13.9mm (0.55 inches), and a thickness of 4.45mm (0.18 inches), it offers compatibility ranging from HDMI 1.0 to 2.1.

Type-B is pretty rare, as you can see we only got this low resolution image for you.
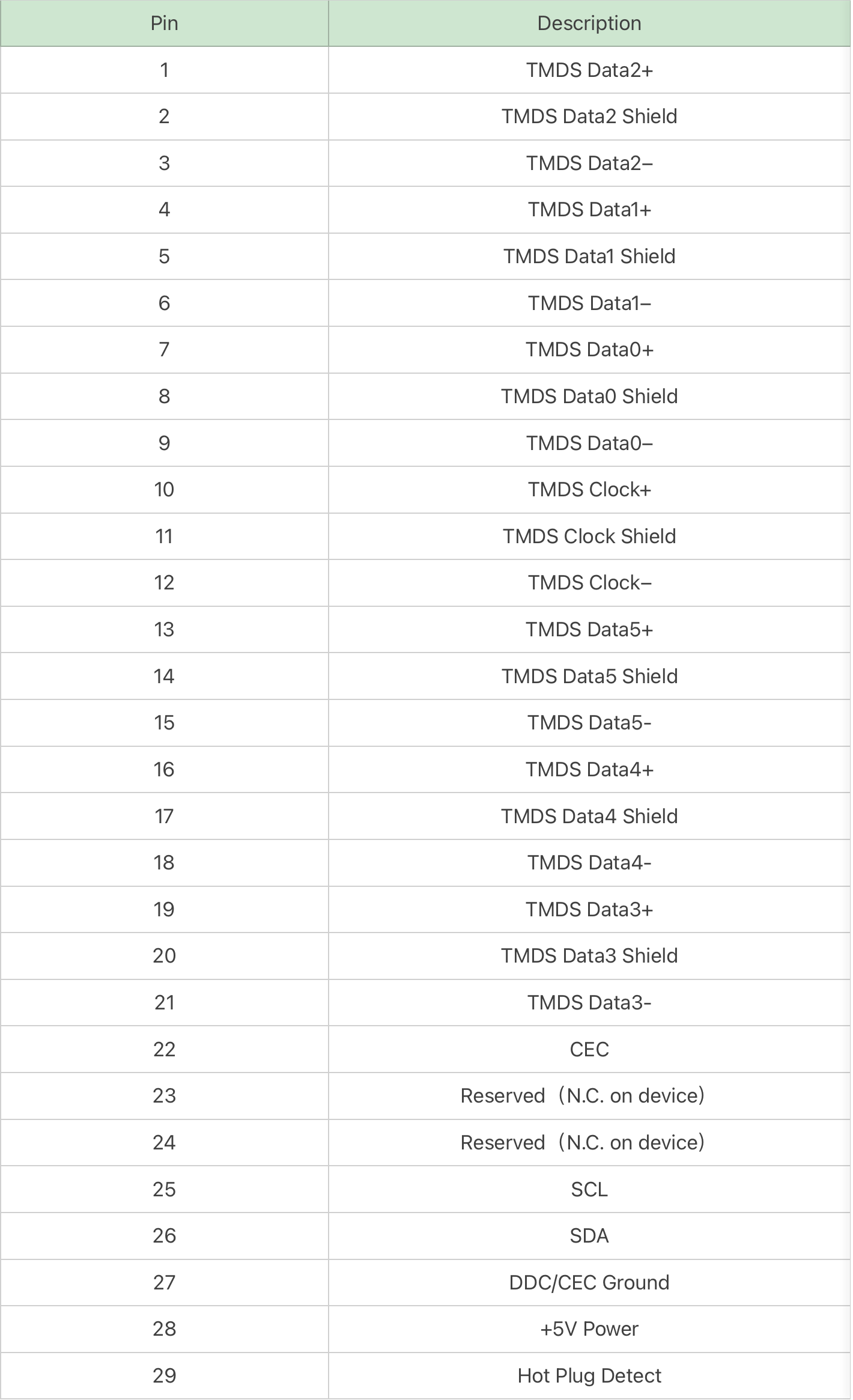
It has 29 pins and can support high-resolution video of 2560×1600 theoretically, but the HDMI chip at that time could not support it, so it gradually faded away.
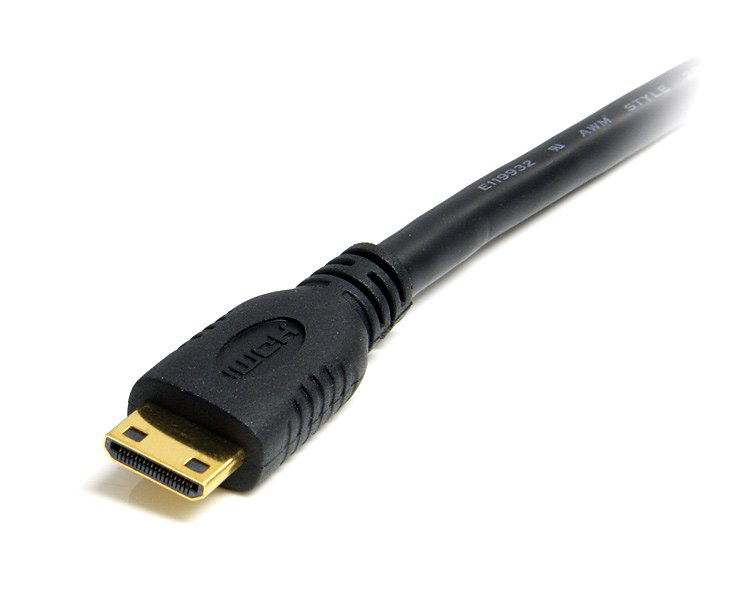

The Type-C is known as mini HDMI connector, which was released after HDMI 1.3.
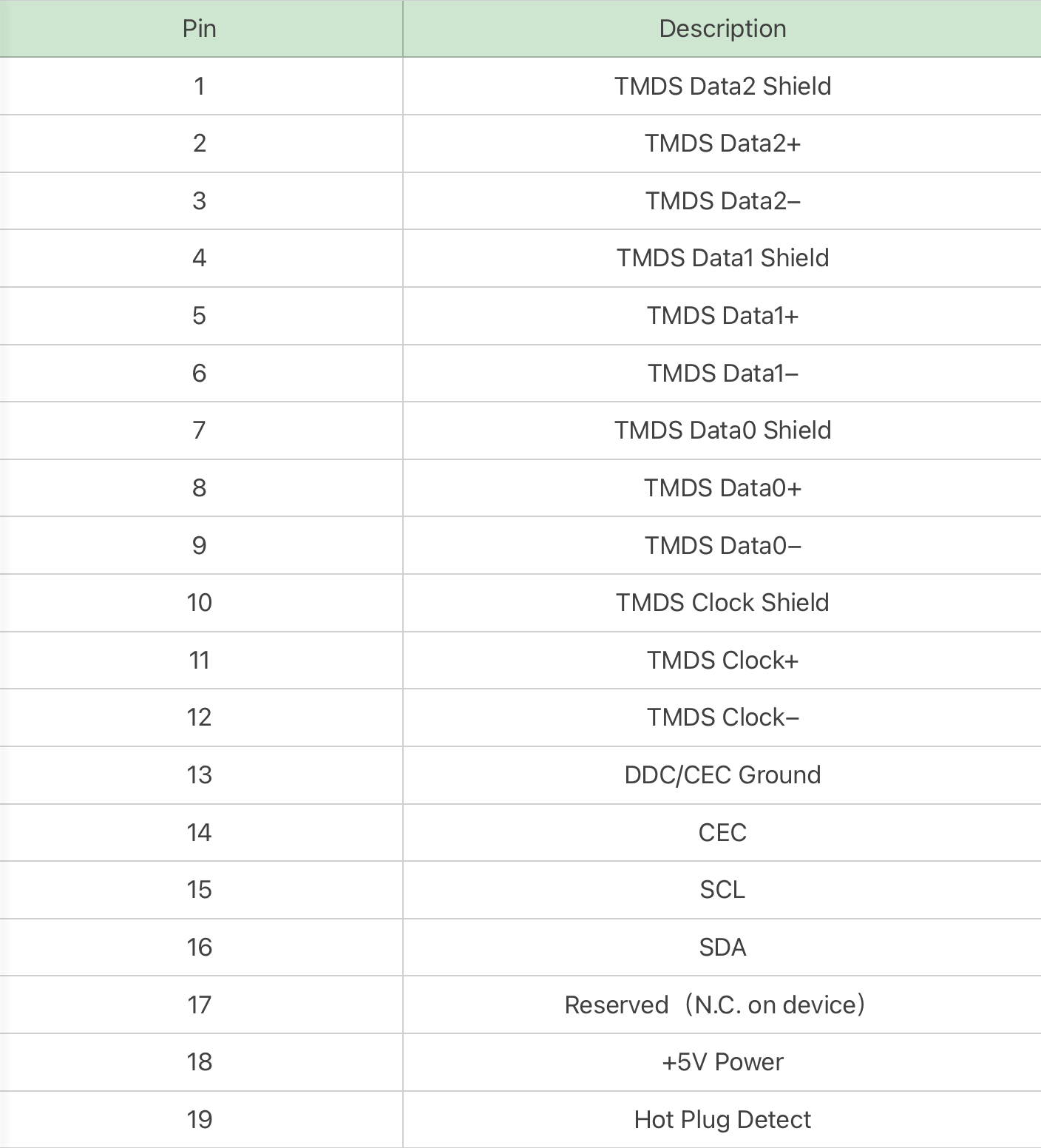
It also has 19 pins, but adopts a single-row design.
The small size makes it suitable for some notebooks or portable displays.
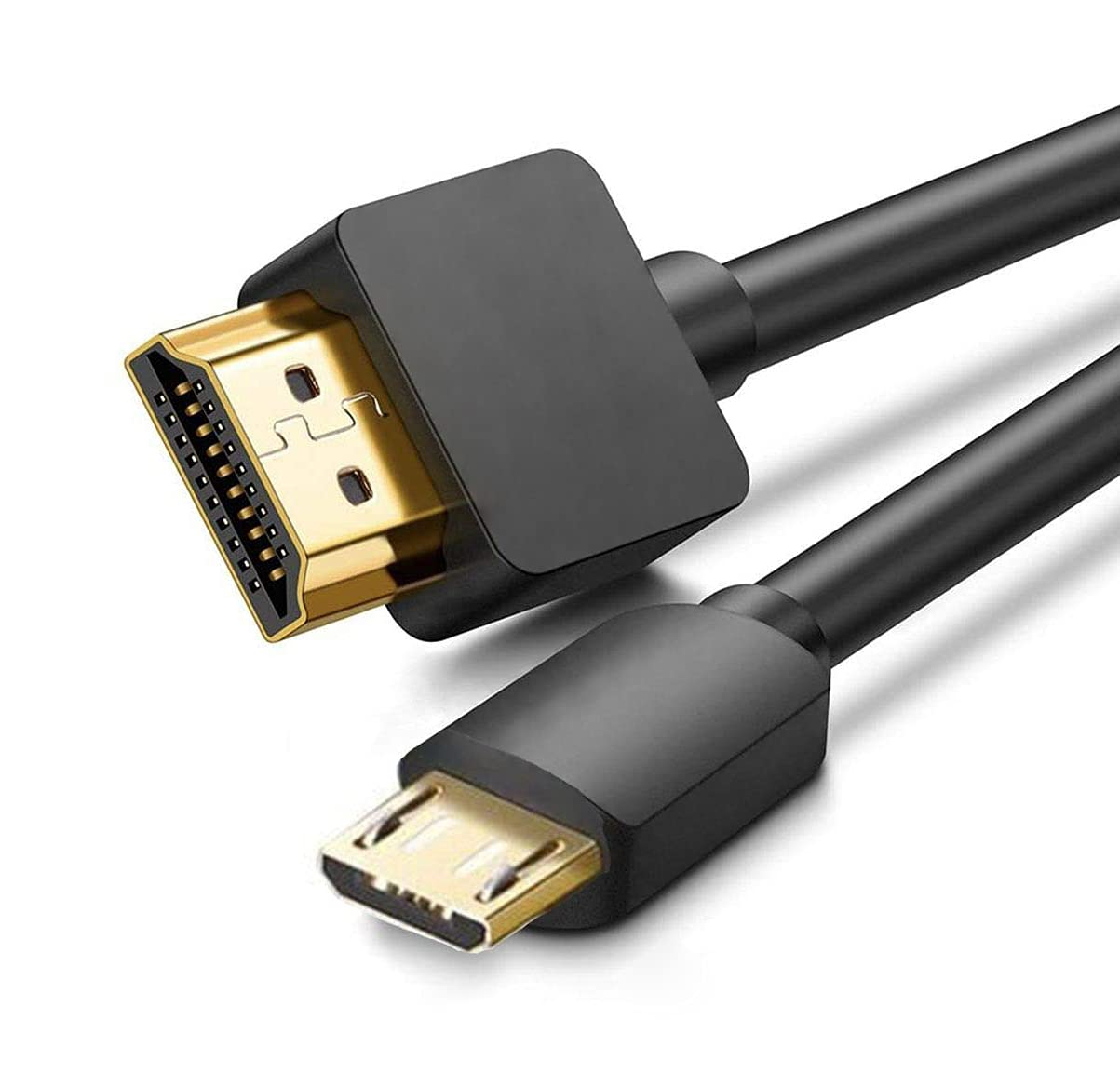

The Type-D is about half smaller than Type-C, called micro HDMI connector.
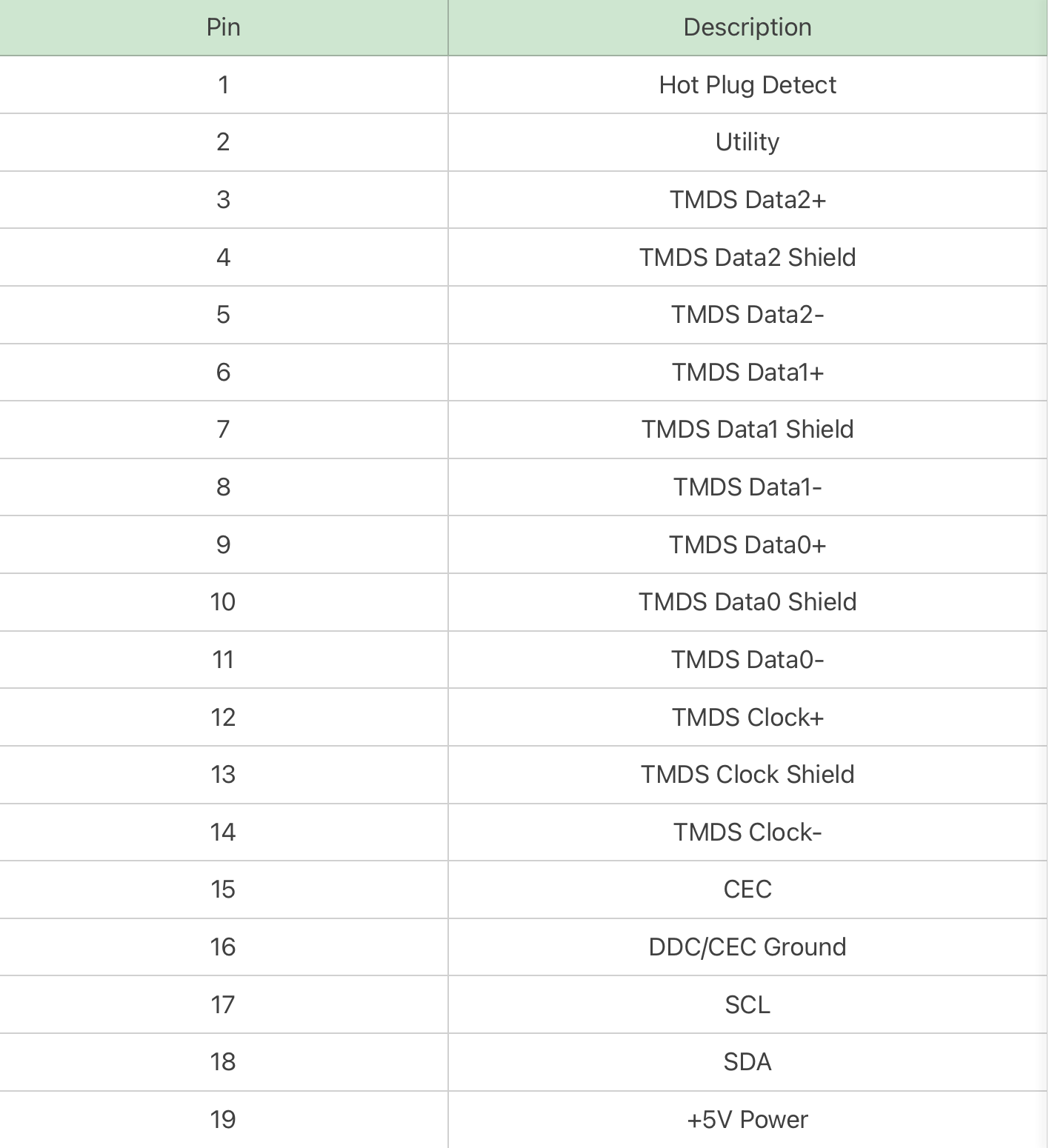
It was released after HDMI 1.3 and adopts a double-row 19-pin design. We can find this kind of port on cameras, tablets. However, let's be honest, those who have used it know that it can be considered one of the most prone-to-failure interfaces out there
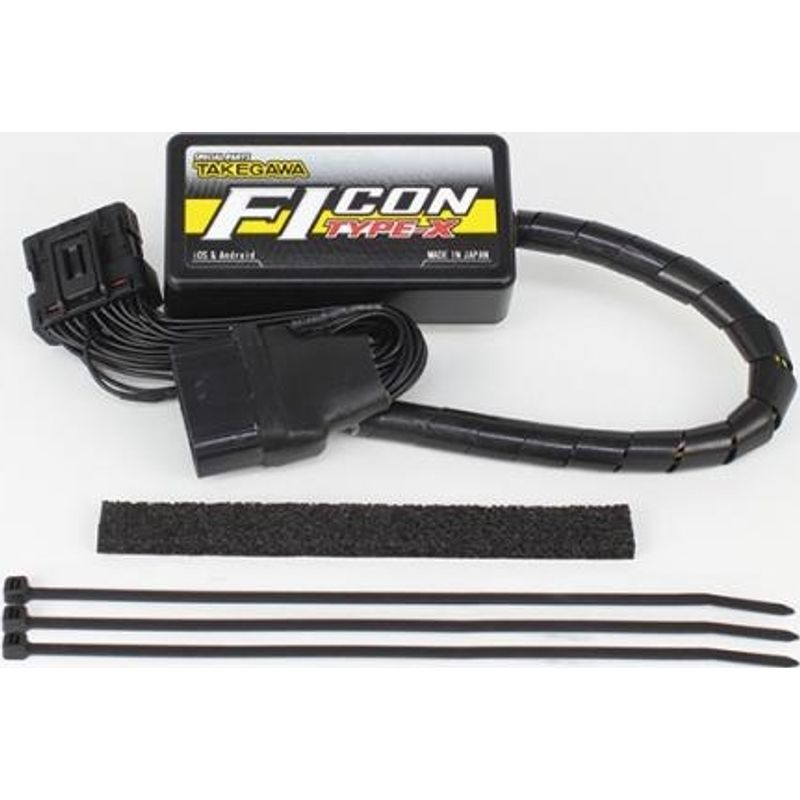

Finally, the Type-E is specially designed for vehicles, which is very rare. And the locking tab can keep the stable connection.
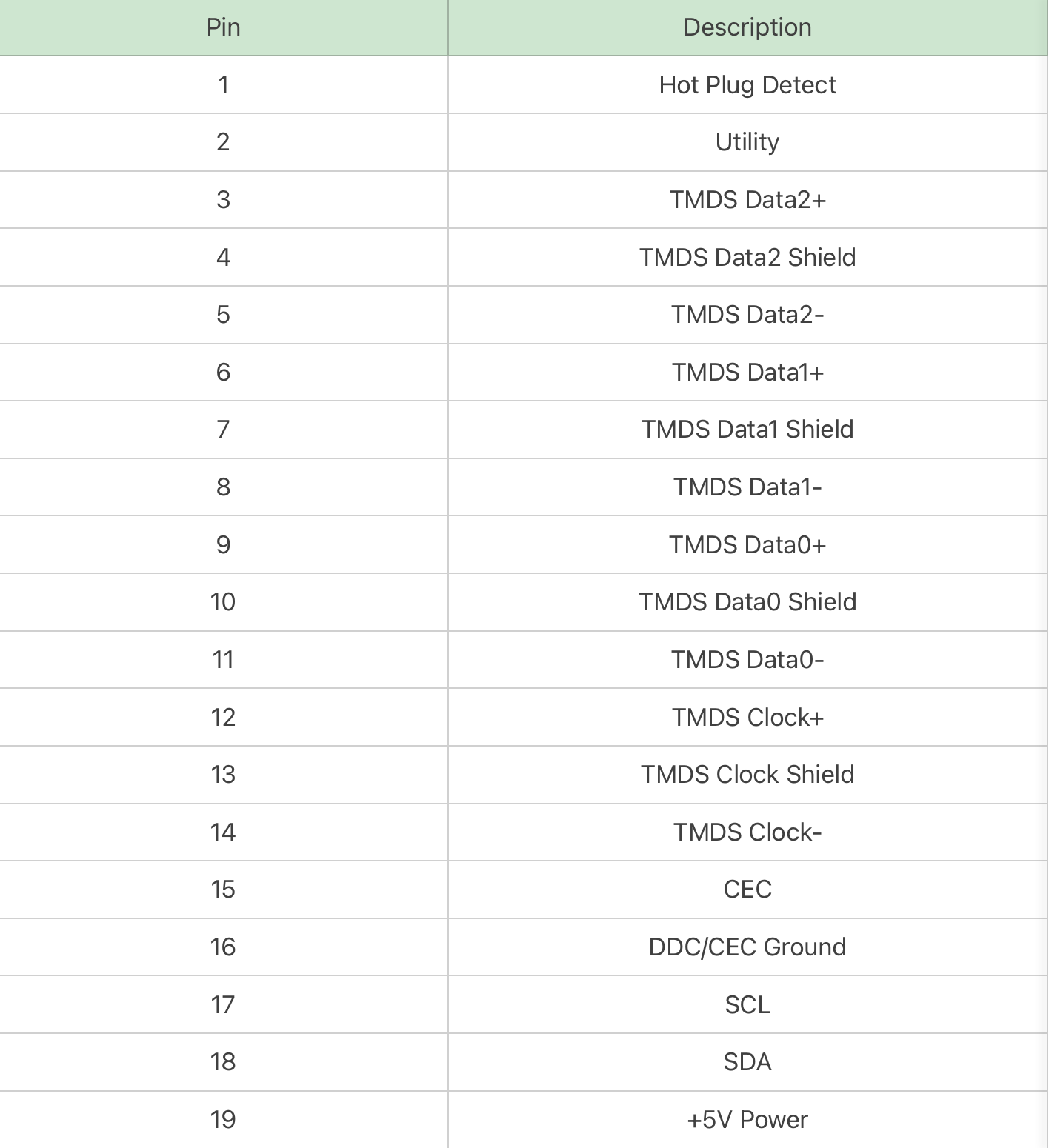
It also has 19 pins.
Furthermore, the suitability of an HDMI cable for real world usage is contingent upon both its "cable" and "connector" components. The cable determines the bandwidth, which translates to the highest supported resolution, while the connector determines the types of devices it can connect to. Based on varying data bandwidths, HDMI cables are categorized into four specifications: Standard, High Speed, Premium High Speed, and Ultra High Speed. The data bandwidth ranges from a starting point of 2.25Gbps to a maximum of 48Gbps.

So, you may find that different types of HDMI connectors can support different types of HDMI versions. We cannot distinguish which video formats it supports from the appearance of the HDMI connector. That's pretty similar to USB-C connector.
Features
After discussing the connector types, let's delve into its special feature: HDCP (High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection). Developed primarily by Intel, this technology aims to prevent users from illegally recording content and protect copyrights. When unauthorized recording is detected, HDCP can reduce the video quality and resolution.
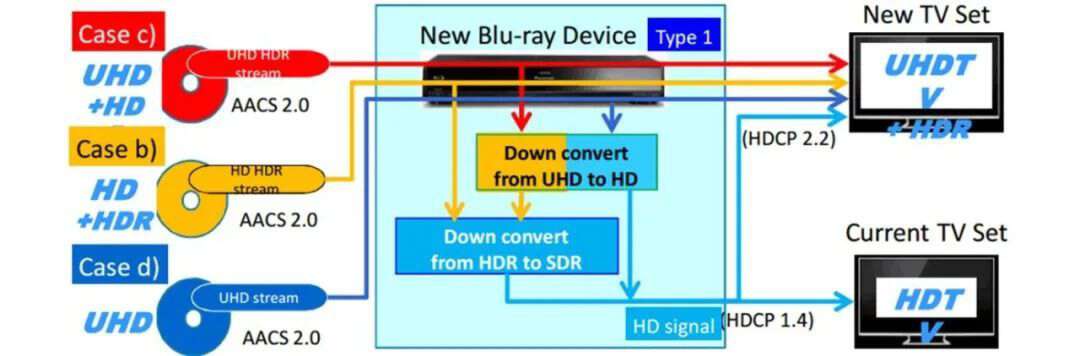
If you've ever noticed that your screen recordings appear blurry, this could very well be the reason.
HDMI vs DP
There's another universal connector for video signal transmission, the DisplayPort. So, what's the difference between HDMI and DP?

As mentioned, HDMI was initiated by TV manufacturers and adopts the TMDS method for transmitting data. After the image is converted by graphics card, it needs to be transmitted to the display line by line.
But the DP was initiated by PC manufacturers, and the image does not need to be converted. It directly packs the images generated by the graphics card into small data packets, known as micro packets, and directly transmits them to the display.
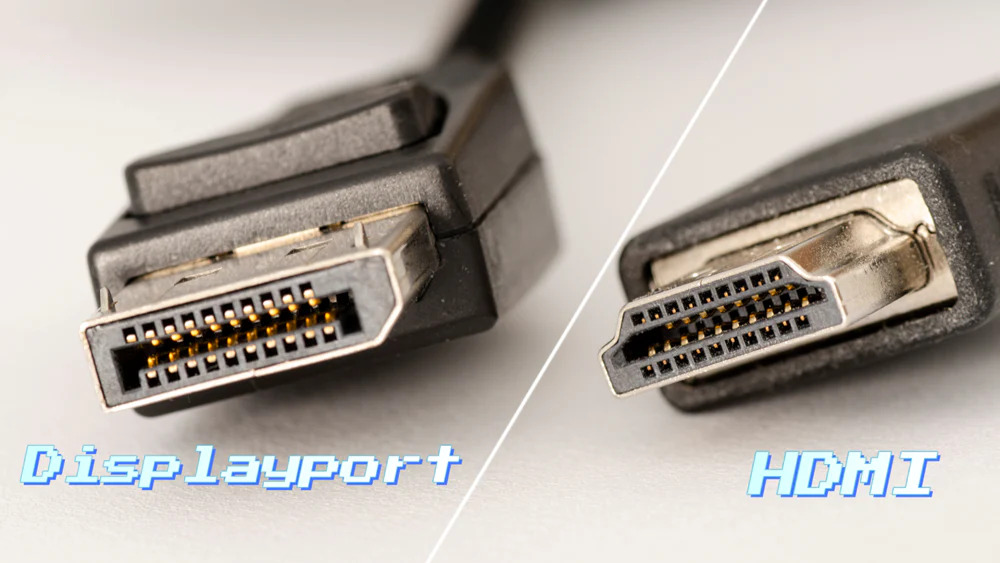

So, the transmission performance of DP is much better than HDMI. The latest DP2.0 can achieve a single output of 16K 60Hz or dual output of 8K 120Hz and supports HDR-10, and the HDMI 2.1 only supports up to 8K 60Hz.
Summary of ChargerLAB
Well, that's a brief introduction to the HDMI standard.
As the most widely used audio and video standard, each new version will bring larger bandwidth, wider color depth, and richer functions.
However, there is not only one competitor in this market. Perhaps in the future, the HDMI, DP, USB4, and Thunderbolt 4 will be integrated into the USB-C connector. We only need a USB-C full-function cable to enjoy a better user experience with different standards.
Related Articles:
1. What is USB-C? All you need to know! - ChargerLAB Explained
2. What's USB Type-B Connector? | Introduction and Explained
3. What's Difference Between 5A Cable and 3A Cable
HAGiBiS 65W and Baseus 67W









