Introduction
At the Lenovo new product launch in March of this year, they brought their latest and greatest 2023 notebook, along with the powerful Legion C140W GaN charger. This device is an upgraded version of the already-impressive Lenovo Legion 135W C135 USB-C GaN charger. We've already taken it apart in a previous article, so be sure to check that out for the full breakdown below.
The new charger model is capable of supporting both the 28V5A PD3.1 protocol and the proprietary 20V7A 140W Lenovo protocol. With these advanced capabilities, you can charge your devices at lightning-fast speeds without sacrificing safety or efficiency.
So, without further ado, let's dive into the inner workings of this beastly device. We'll explore all of its internal components and structures, so you can see just how impressive it truly is.
Product Appearance

The product name, both lenovo and LEGION's LOGO are printed on front.

And some major selling points are on the back as always.

The packaging box contains the user manual, charger, and a thick charging cable.

First, let's take a closer look at the cable. The junction between the cable and the connector is protected by a rubber sleeve.

LEGION is engraved on one side.

And 140W is engraved on the other side.
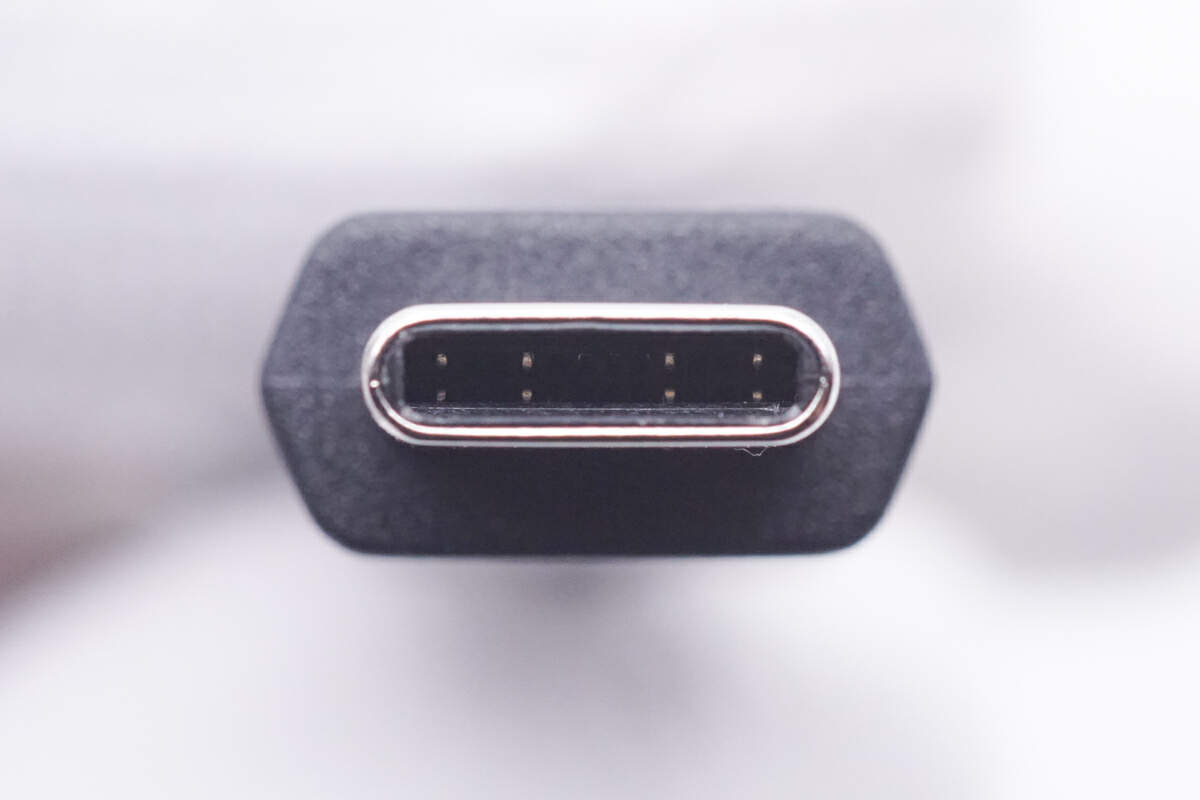

It does not adopt a "full-pin" design, obviously.

The ChargerLAB POWER-Z KM003C shows this cable integrates an E-Marker chip, and it can support 50V 5A 240W EPR charging instead of the 140W marked on the connector. But the data transmission speed only supports USB 2.0.
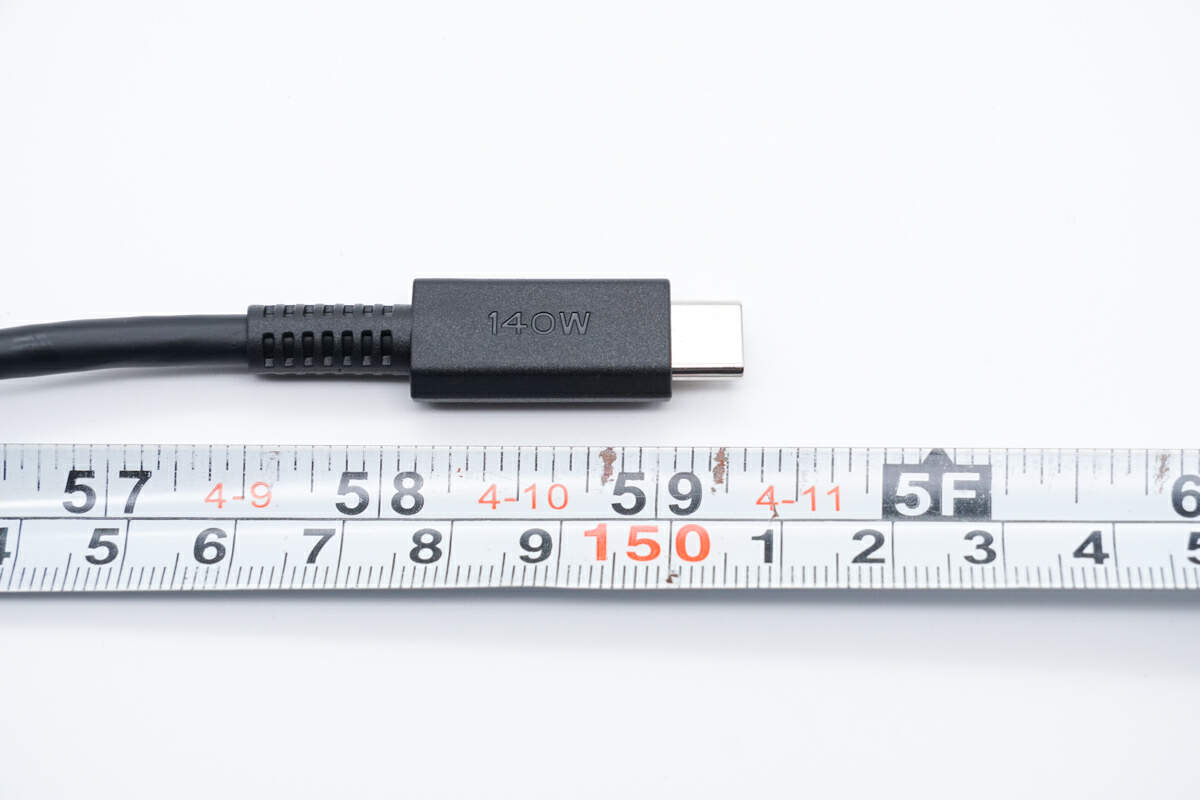

The 1.5 m (4' 11") cable is enough for daily use.
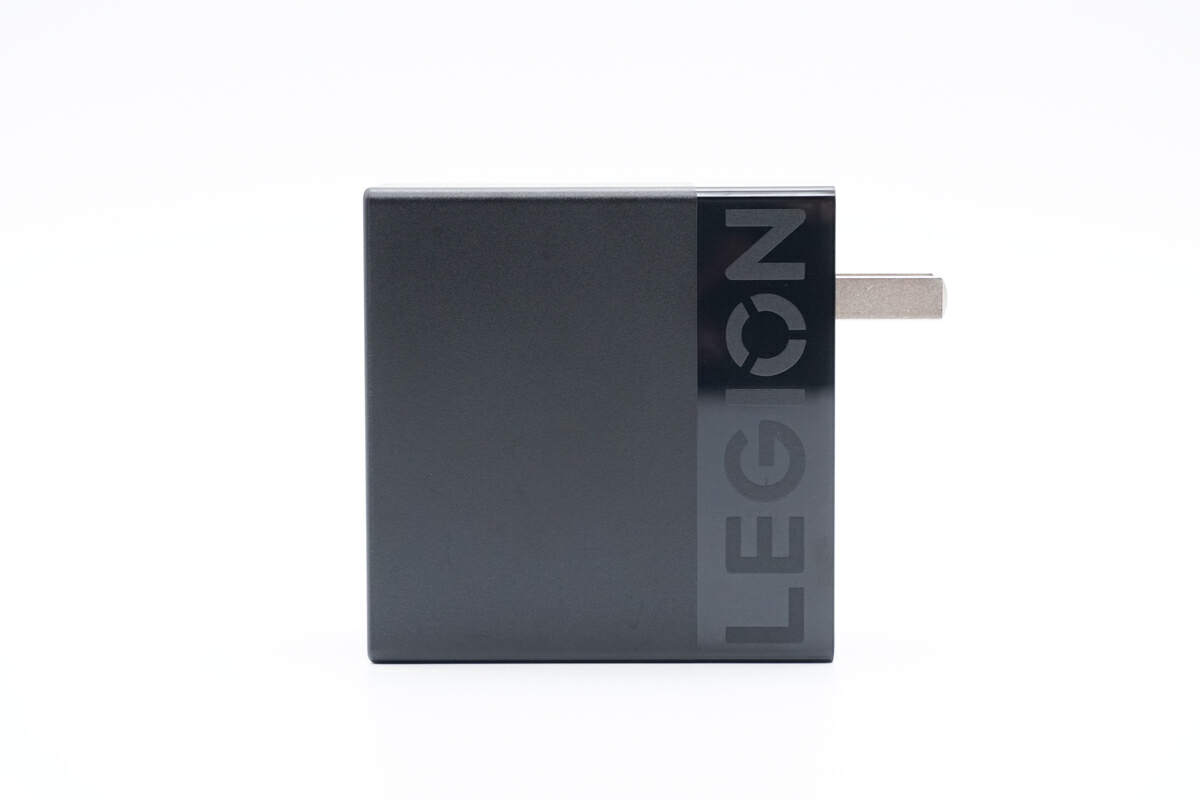

Moving on to the charger. The appearance is pretty much like the 135W charger with Legion LOGO near the input prongs.

And the "140W" is on the opposite side.
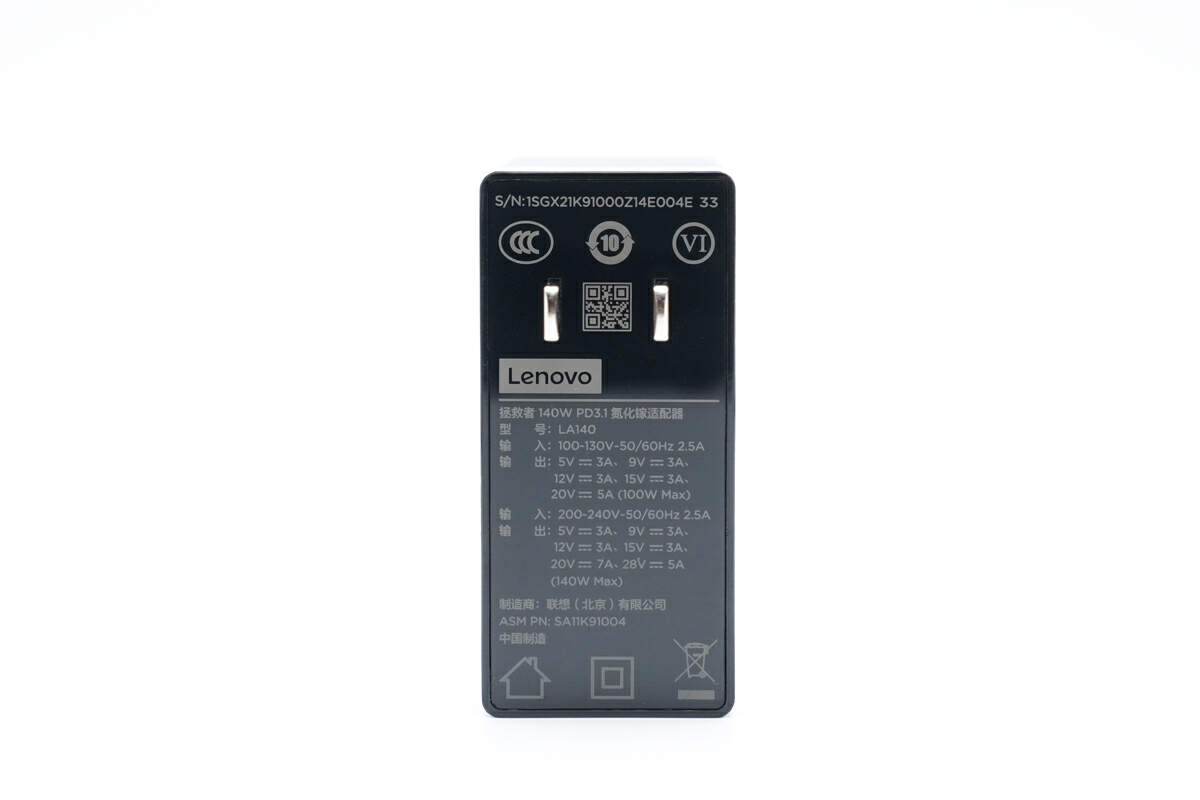

All specs info are printed under the input prongs.

Model is LA140. It can reach 140W output at an input of 200-240V, and it only reaches 100W output at an input of 100-130V.
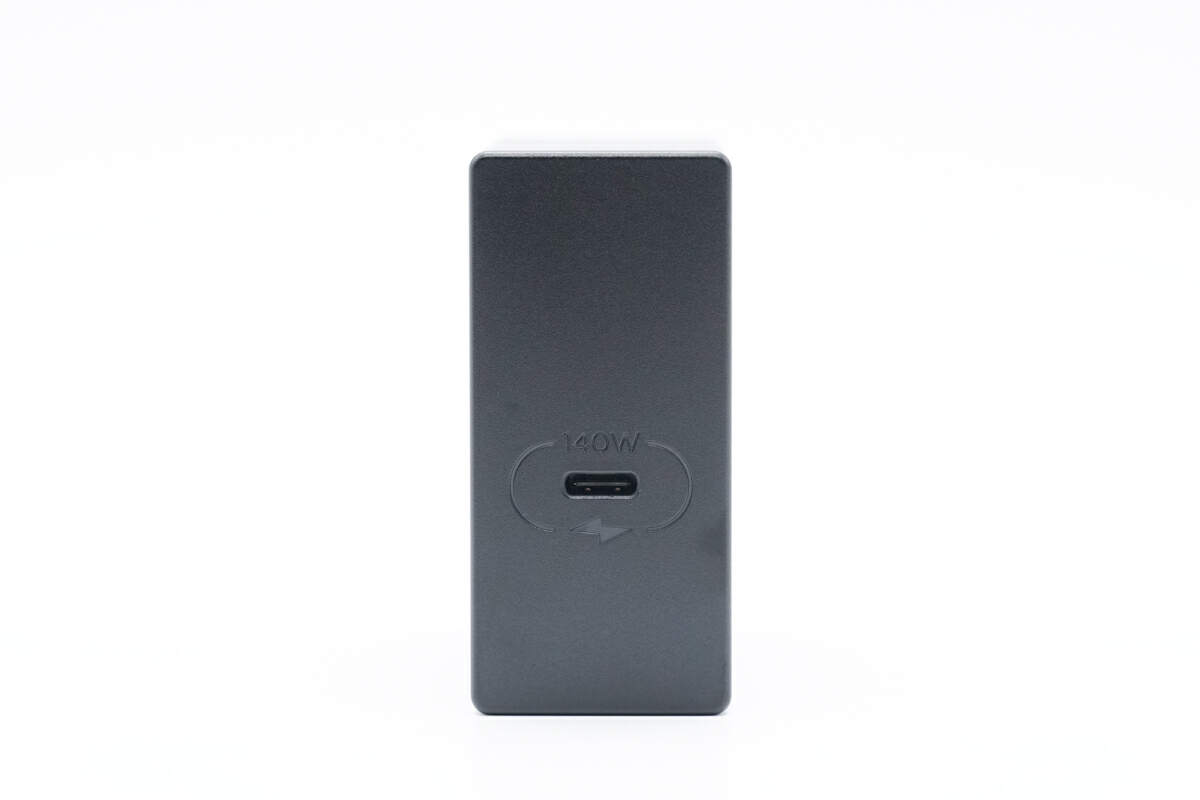

Only a USB-C port is on the output panel.

The little 140W and charging icons clearly show it can do 140W.
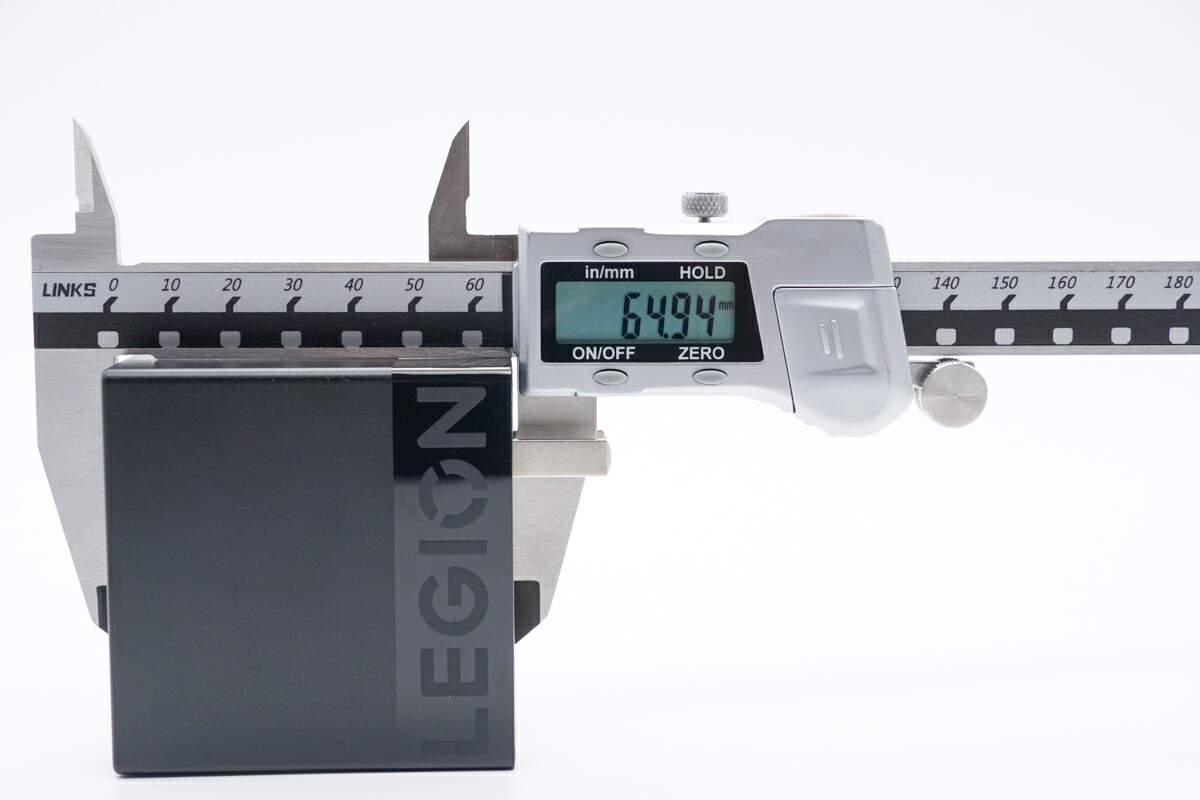

The length of the charger is about 65mm (2.56 inches).
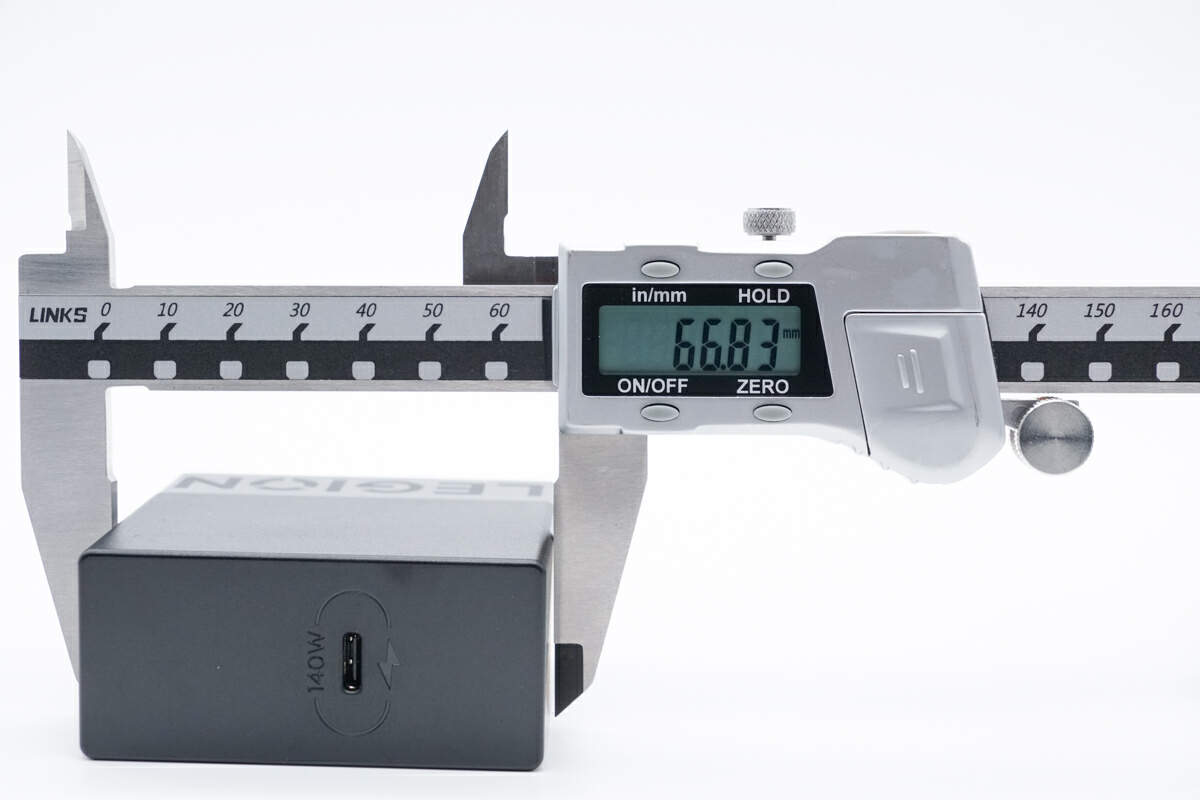

The width is about 67mm (2.64 inches).
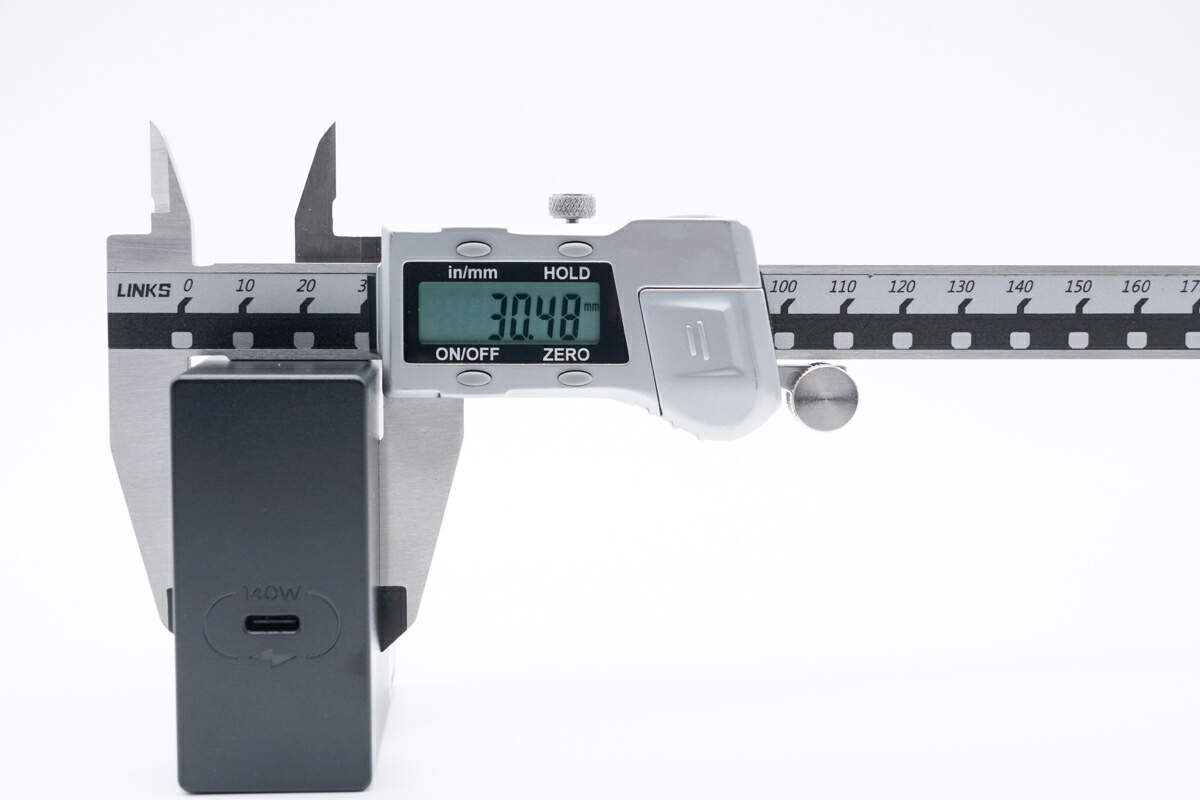

And the height is about 30.5mm (1.20 inches), so the power density is approximately 1.06W/cm³.
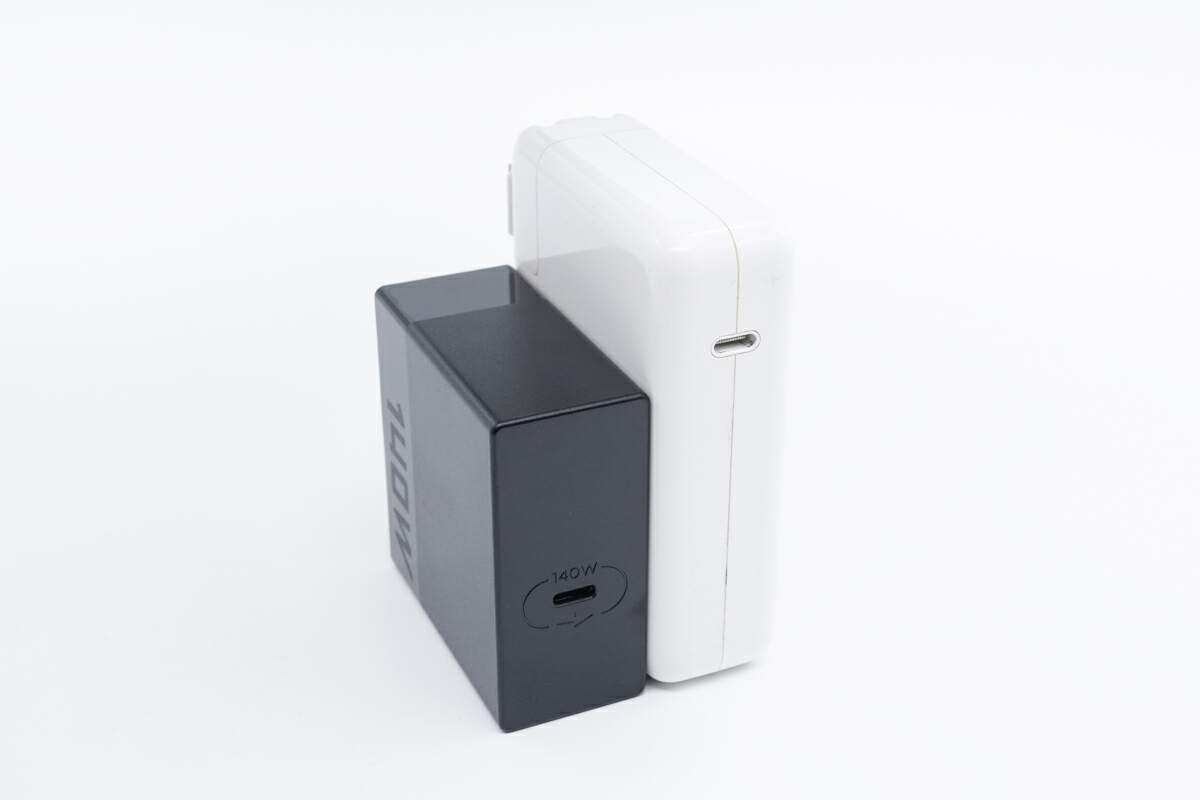

Compared with Apple 140W GaN charger, the size is much smaller.
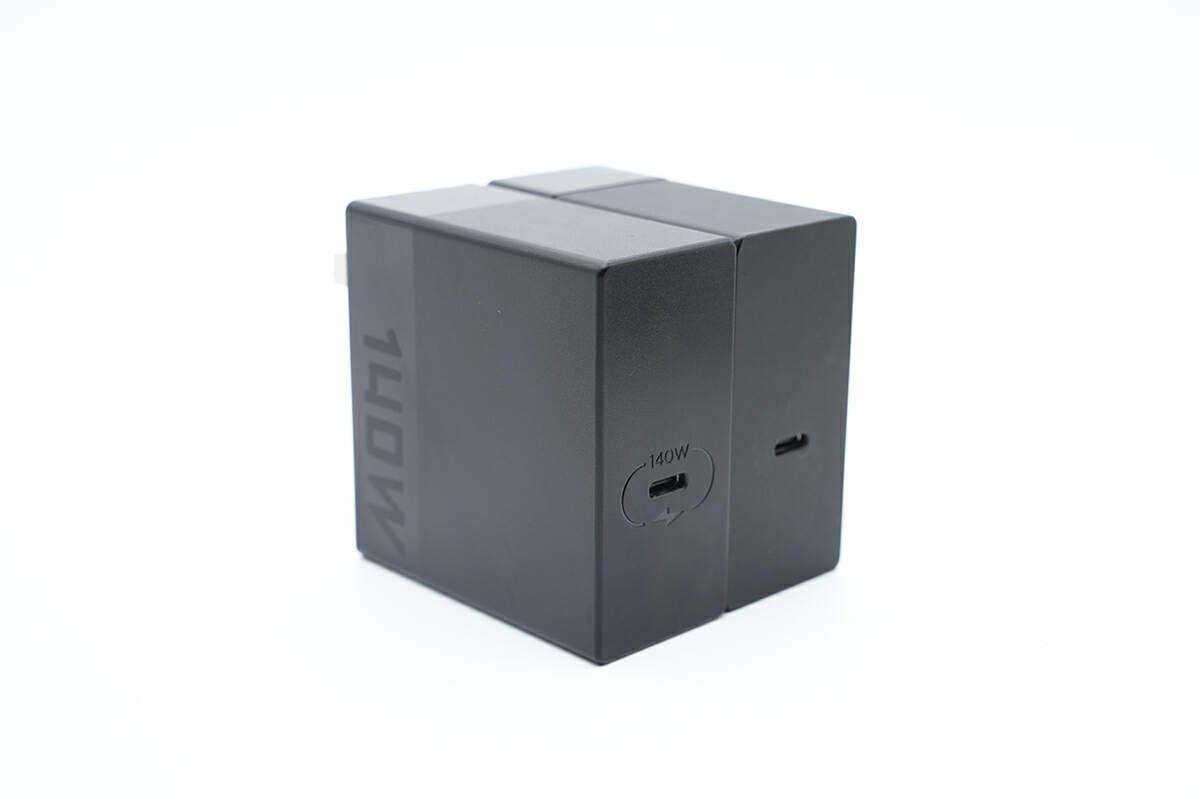

And it's quite similar to the previous 135W version.
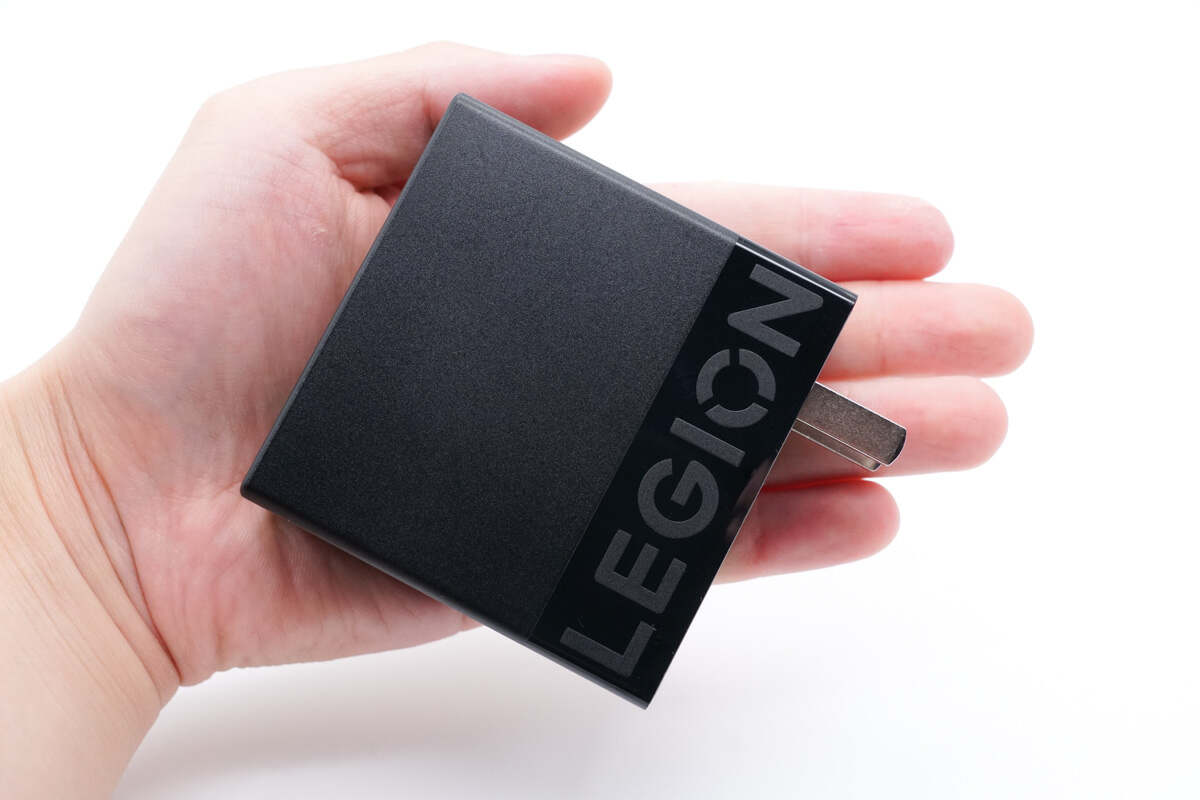

This is how it looks like on my hand.
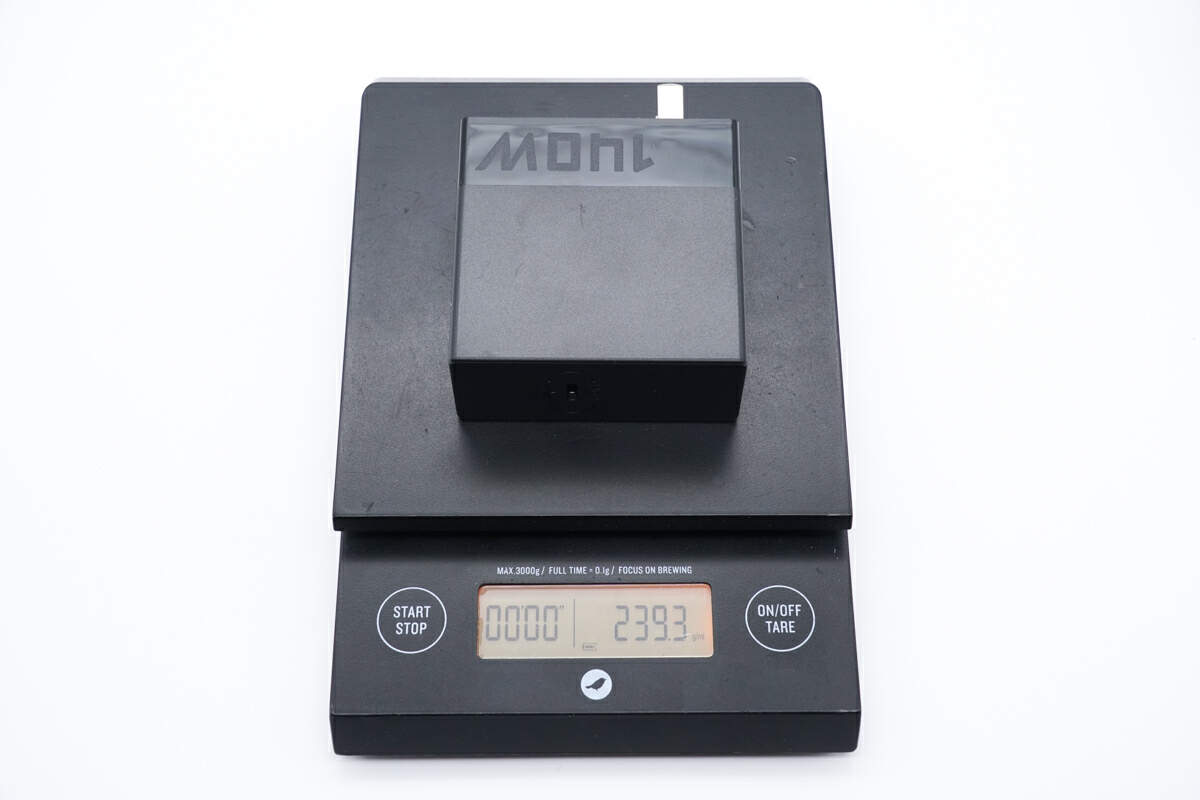

The weight of the charger is about 239g (8.43 oz).
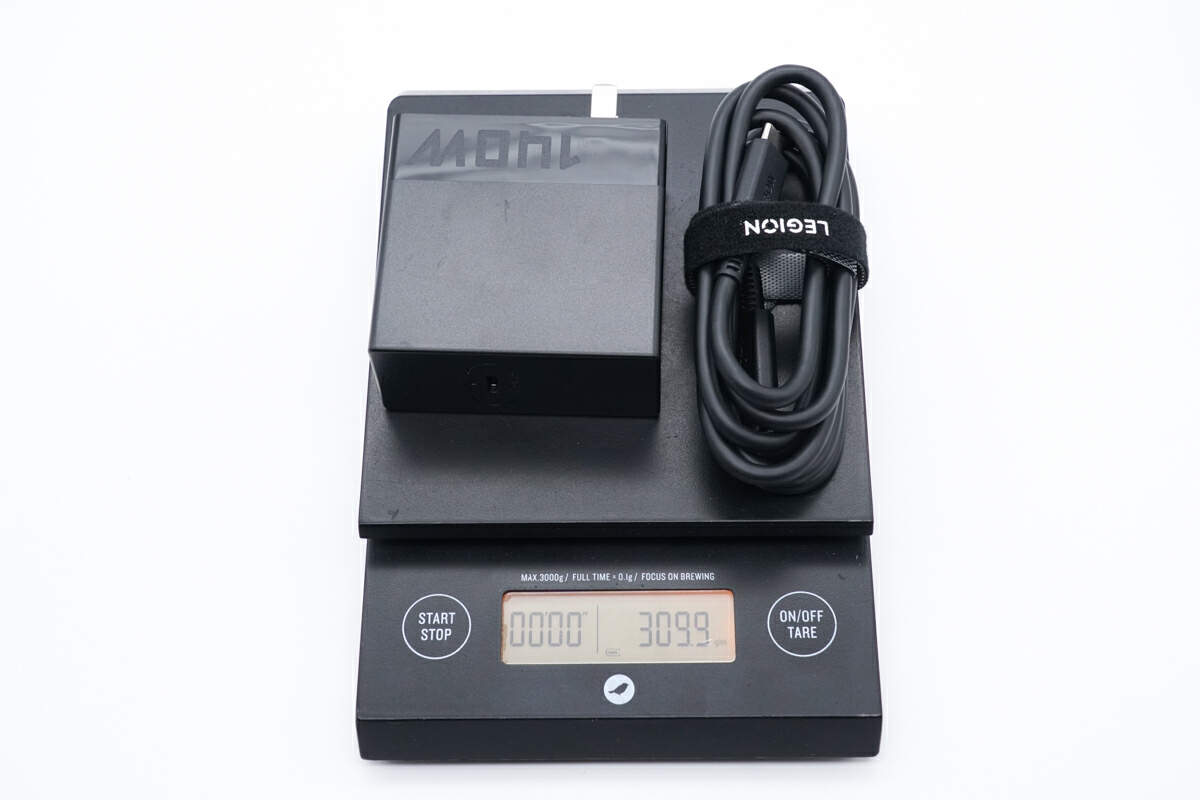

After adding the original cable, the weight is about 310g (10.93 oz).
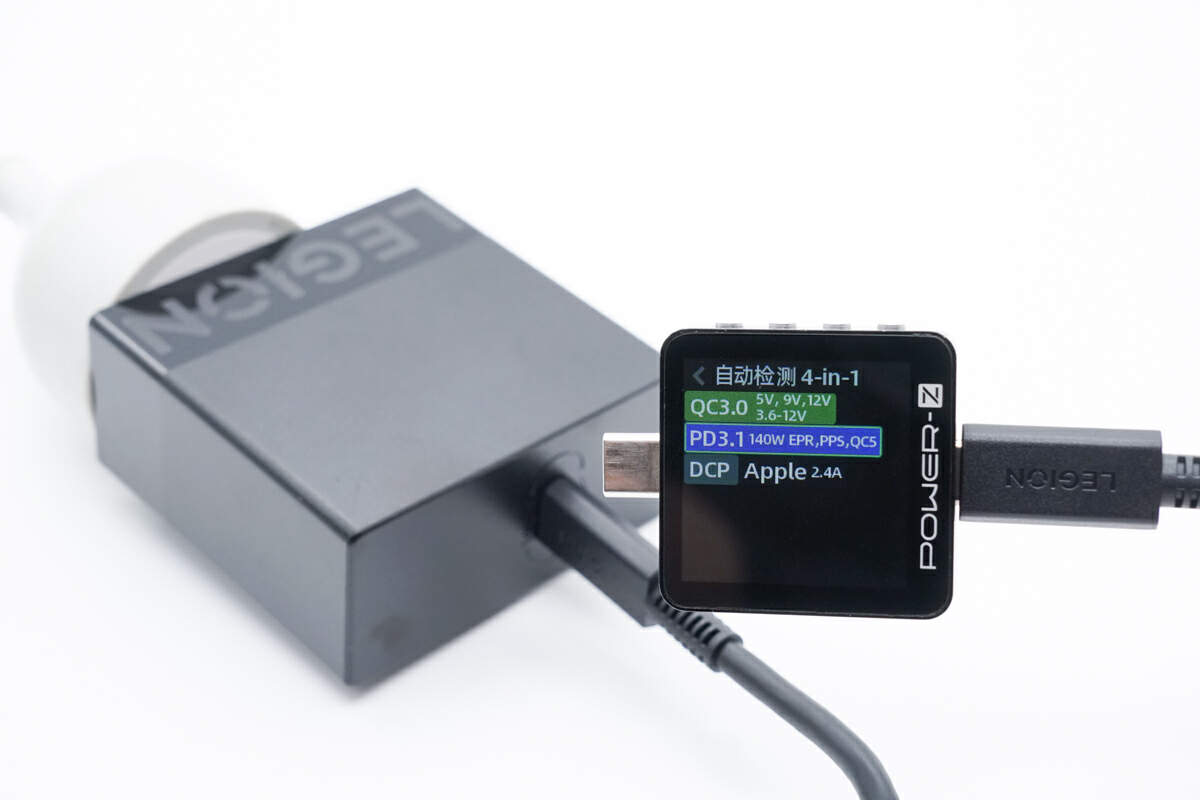

The ChargerLAB POWER-Z KM003C shows it supports QC3.0, PD3.1, PPS, QC5, DCP protocols.

And it also supports six fixed PDOs of 5V/9V/12V/15V 3A, 20V/28V 5A, a set of PPS, and a set of AVS.
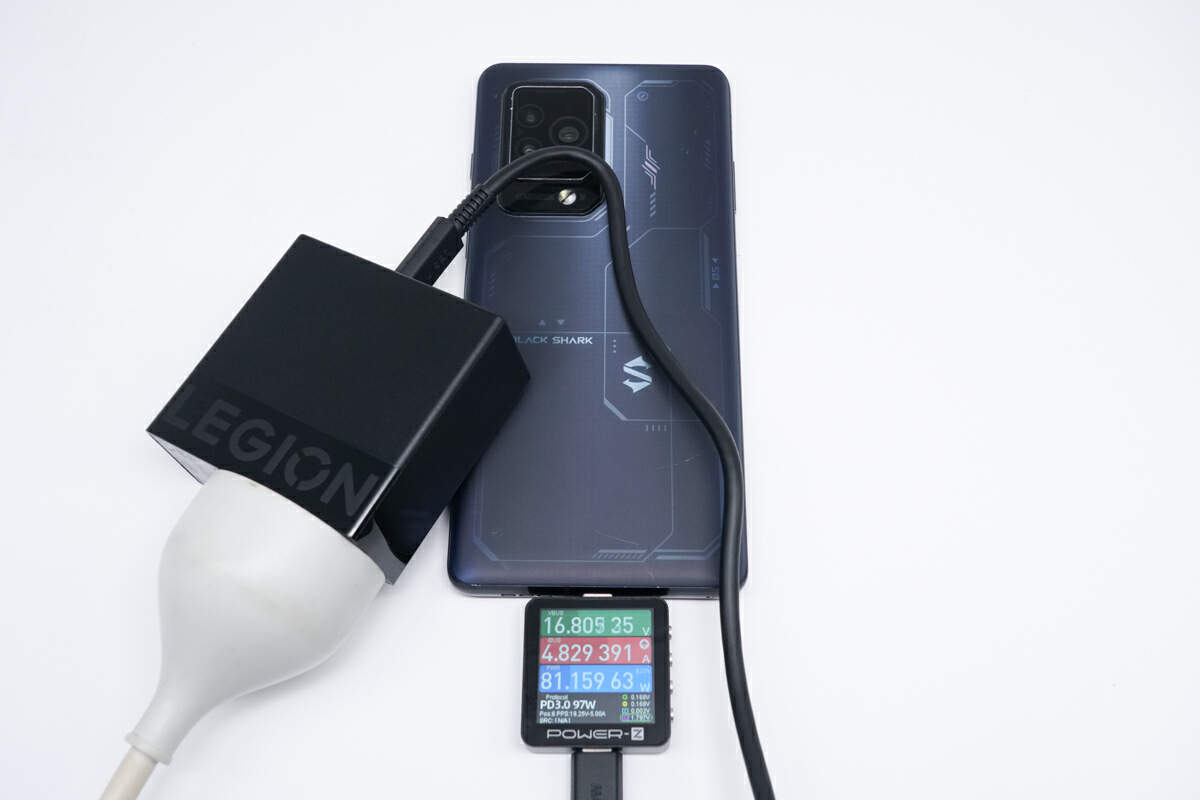

For example, it can provide 16.8V 4.83A 81.16W to the Black Shark 5 Pro.
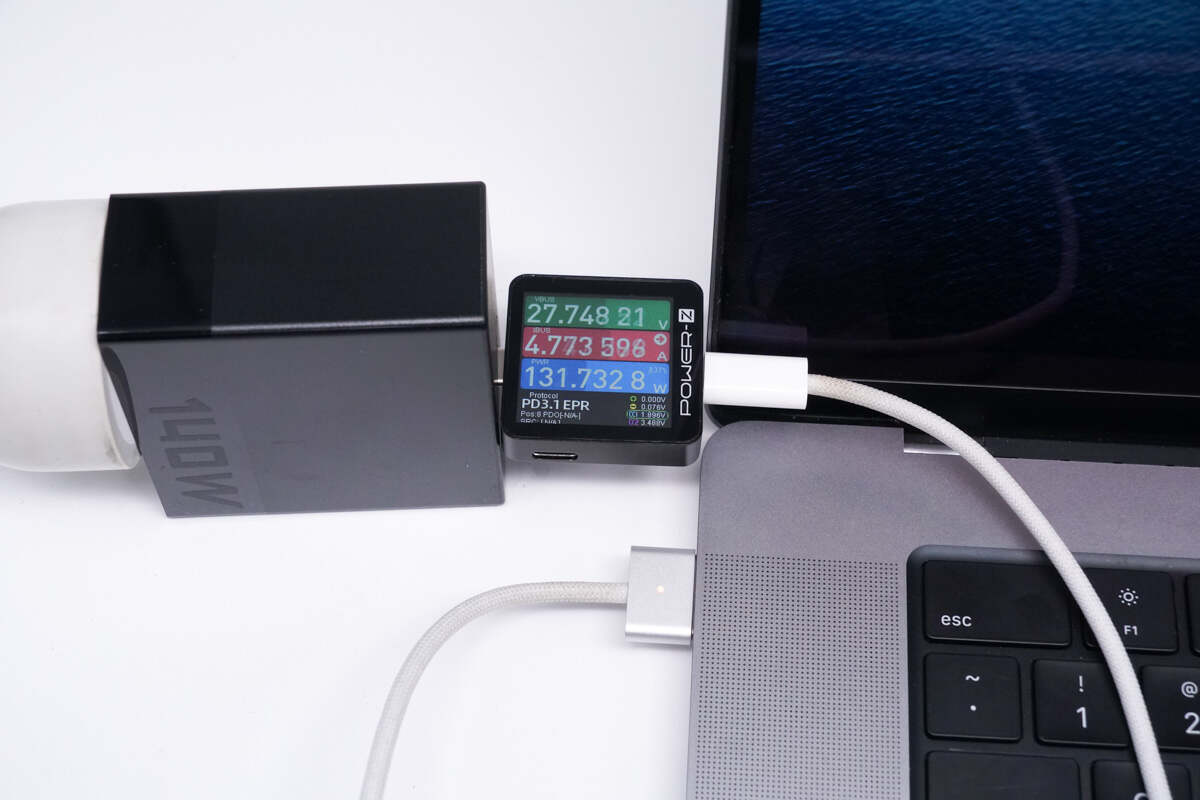

And the power for the 16-inch MacBook Pro M1 Max is 27.75V 4.77A 131.73W.
Teardown
Next, let's take apart the device and examine its internal components and structure.
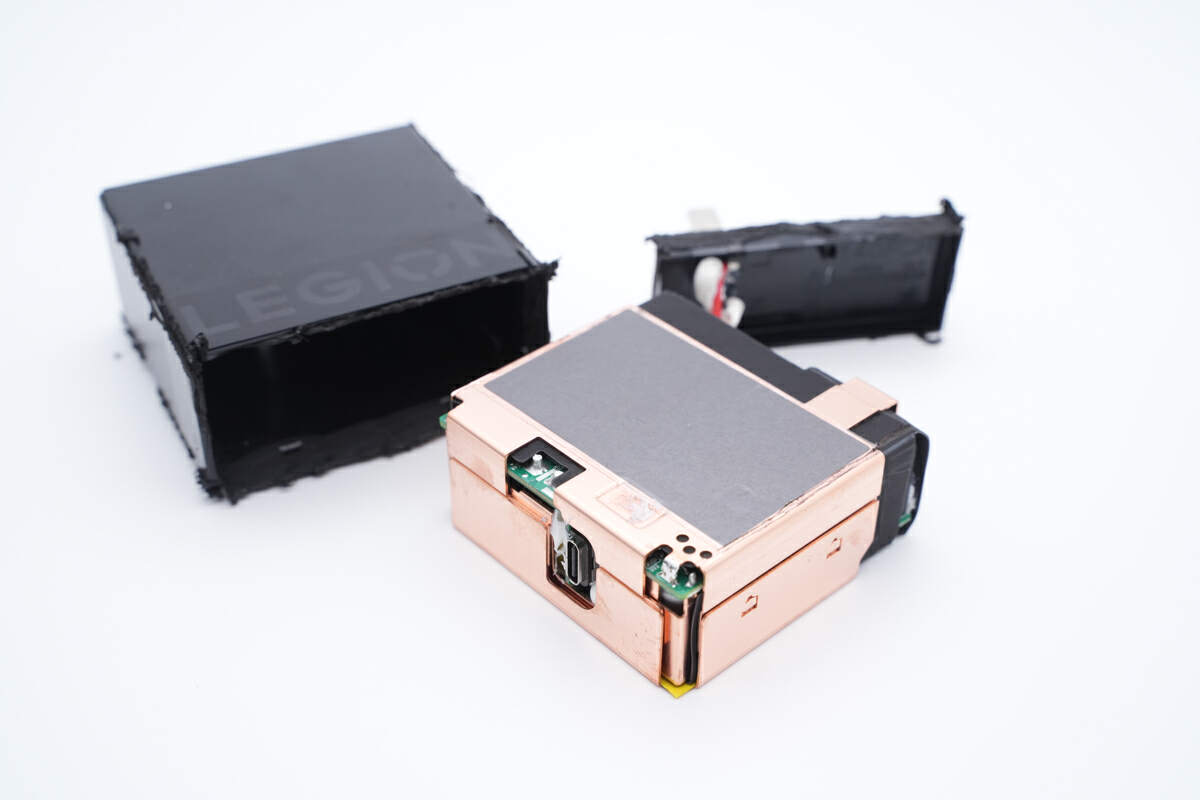

Use the cutting machine to cut off the outer case, and take out the PCBA module.
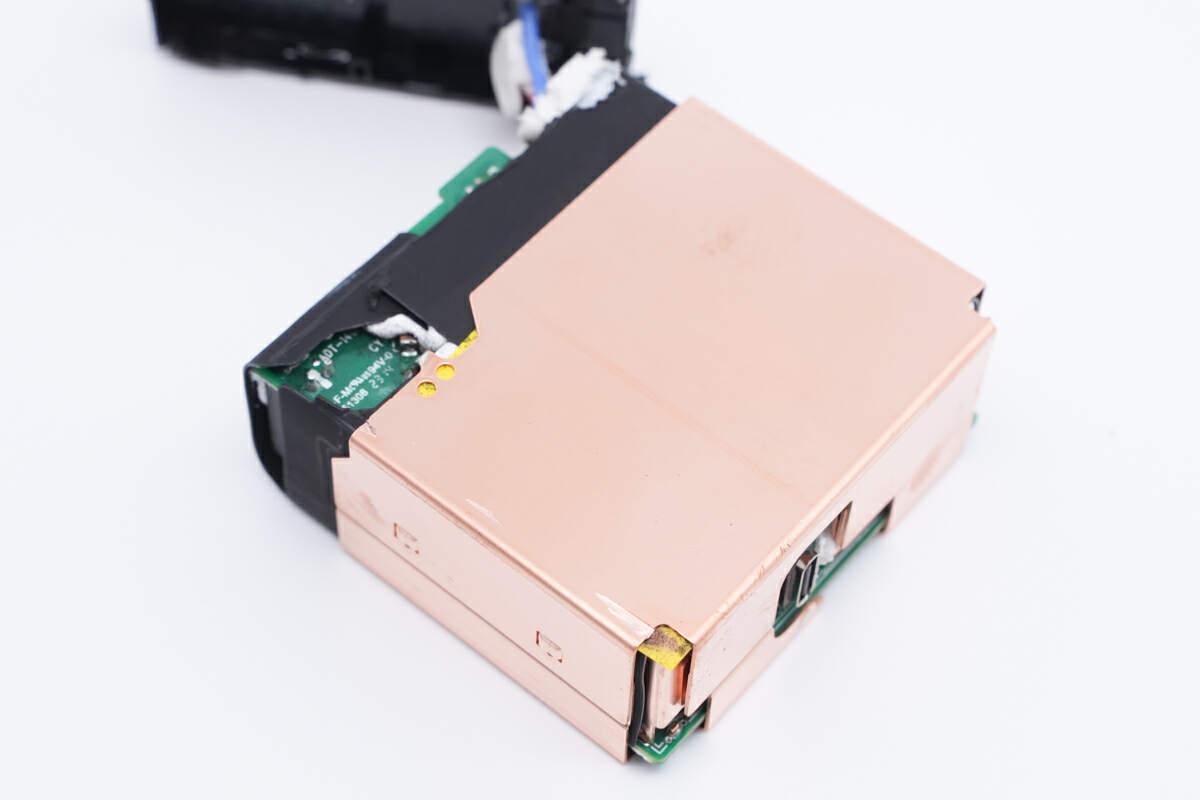

The entire module is covered with pure copper heat sink to enhance heat dissipation performance.
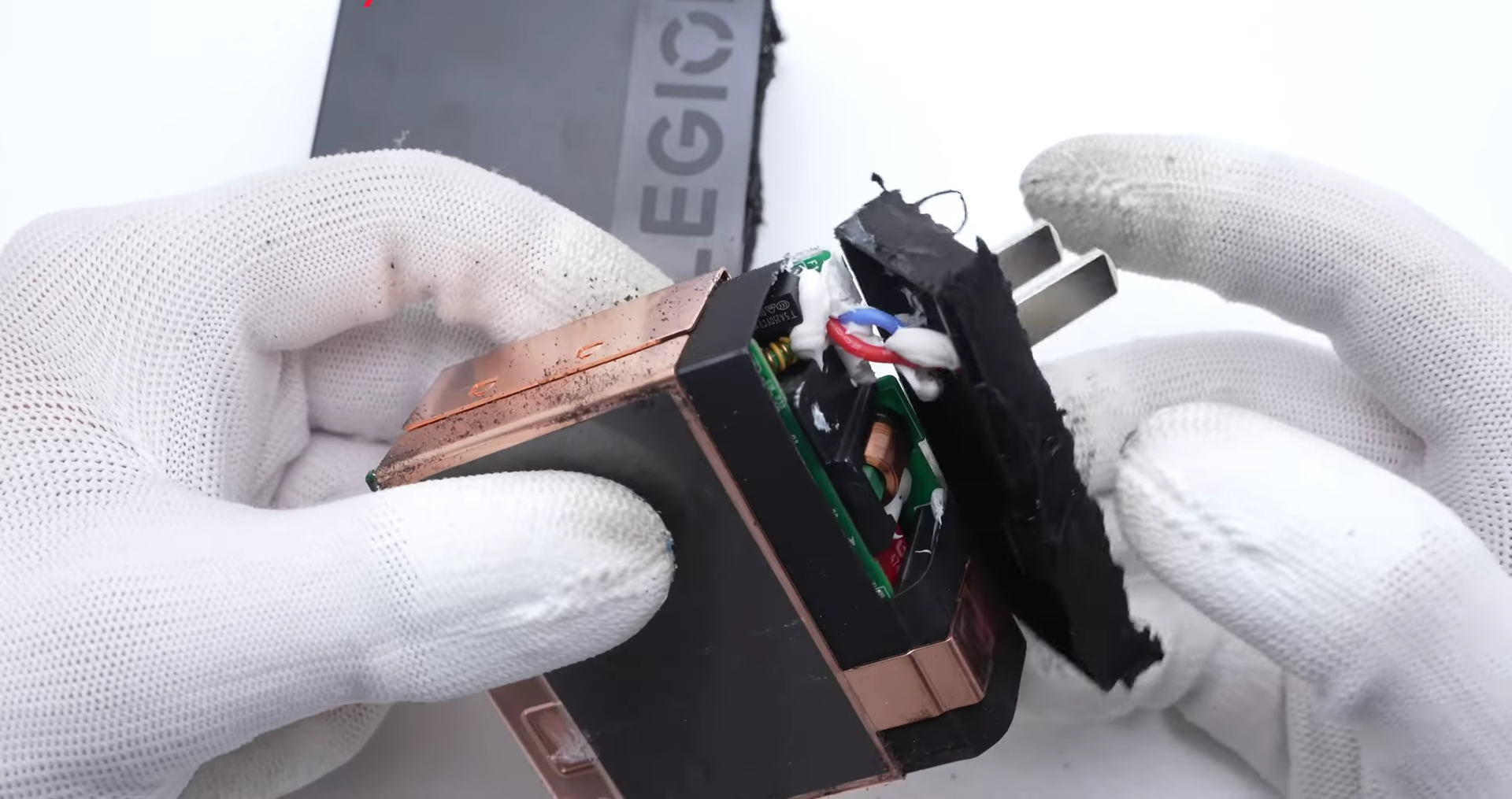

The input prongs are connected to the module through red and blue wires.
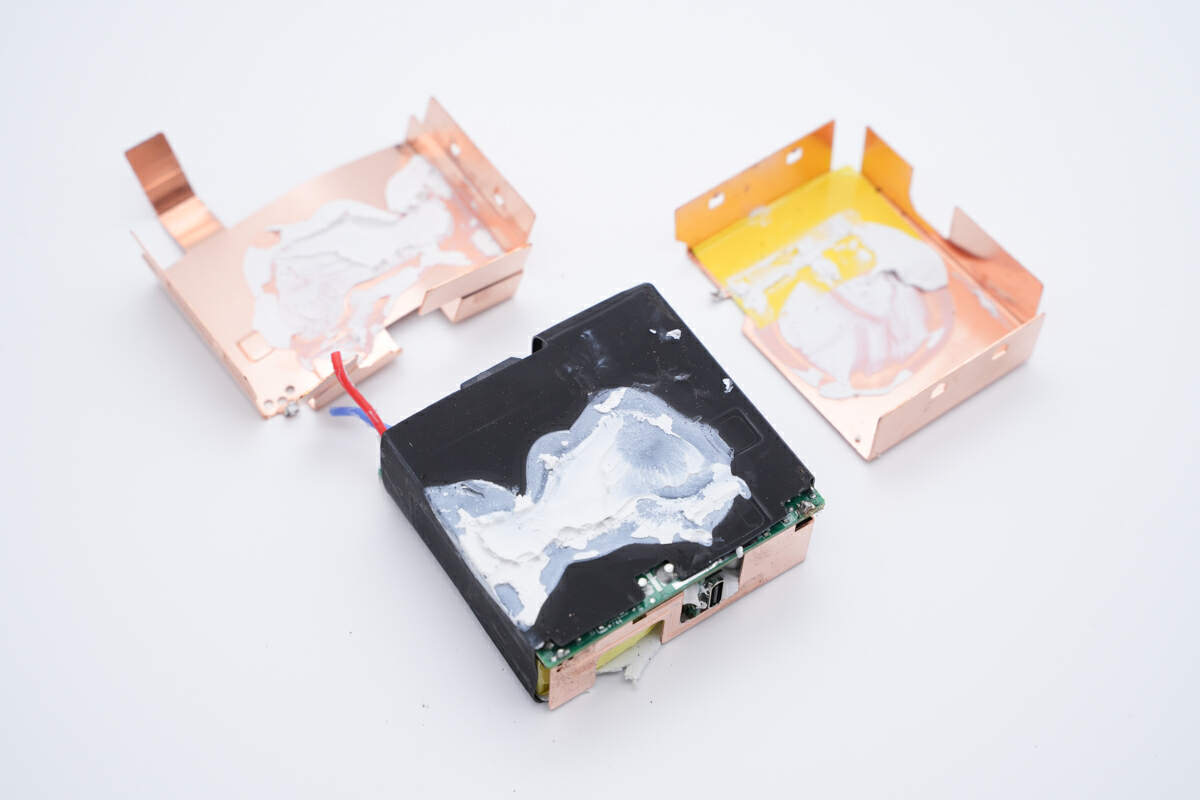

Remove the heat sink, there's another layer of mylar sheet between the PCBA module and the heat sink for insulation. And those white silicone adhesives can dissipate heat and fix the internal components.
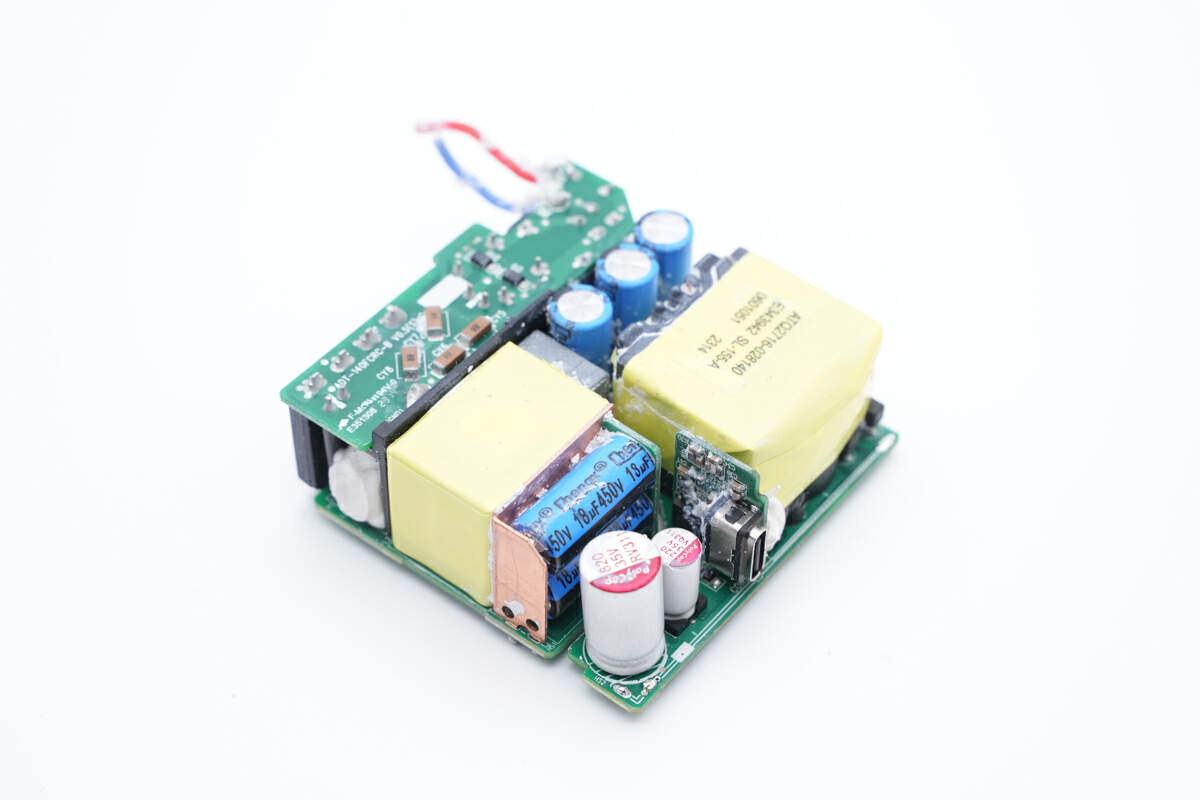

Cleaning up the PCBA module.
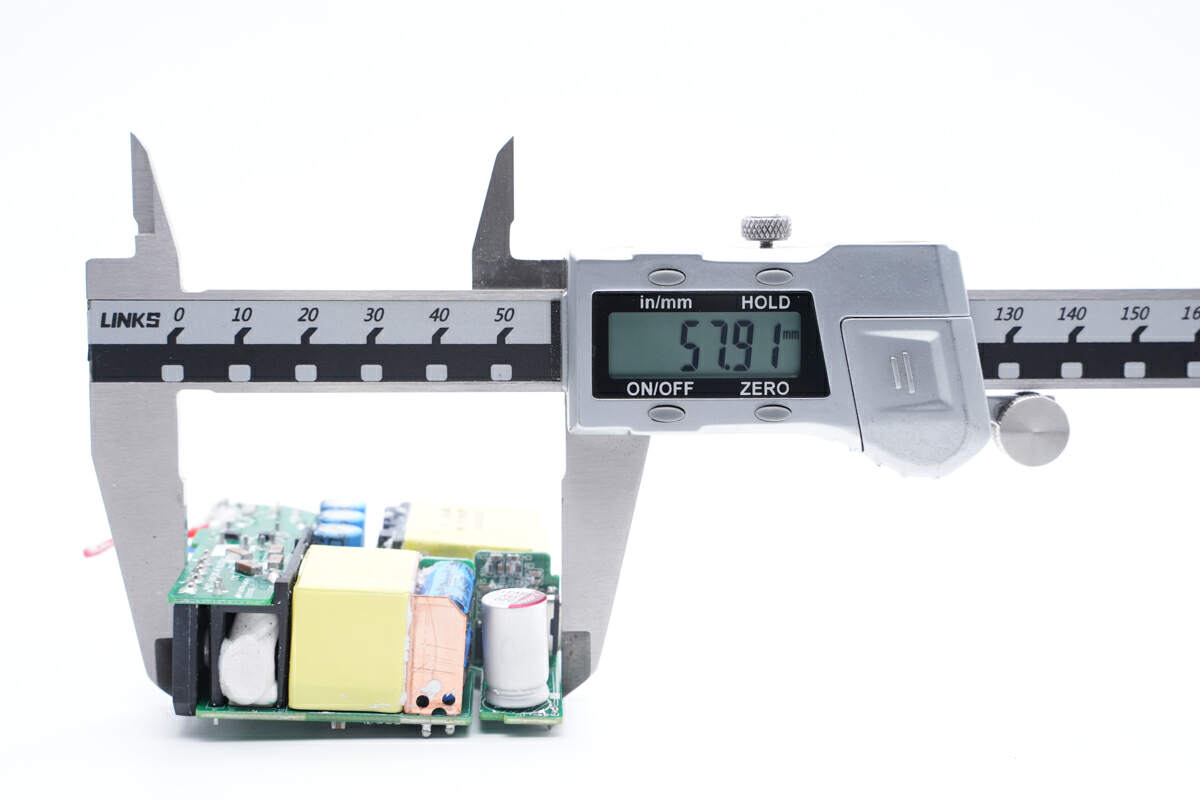

The length of the PCBA is about 58mm (2.28 inches).
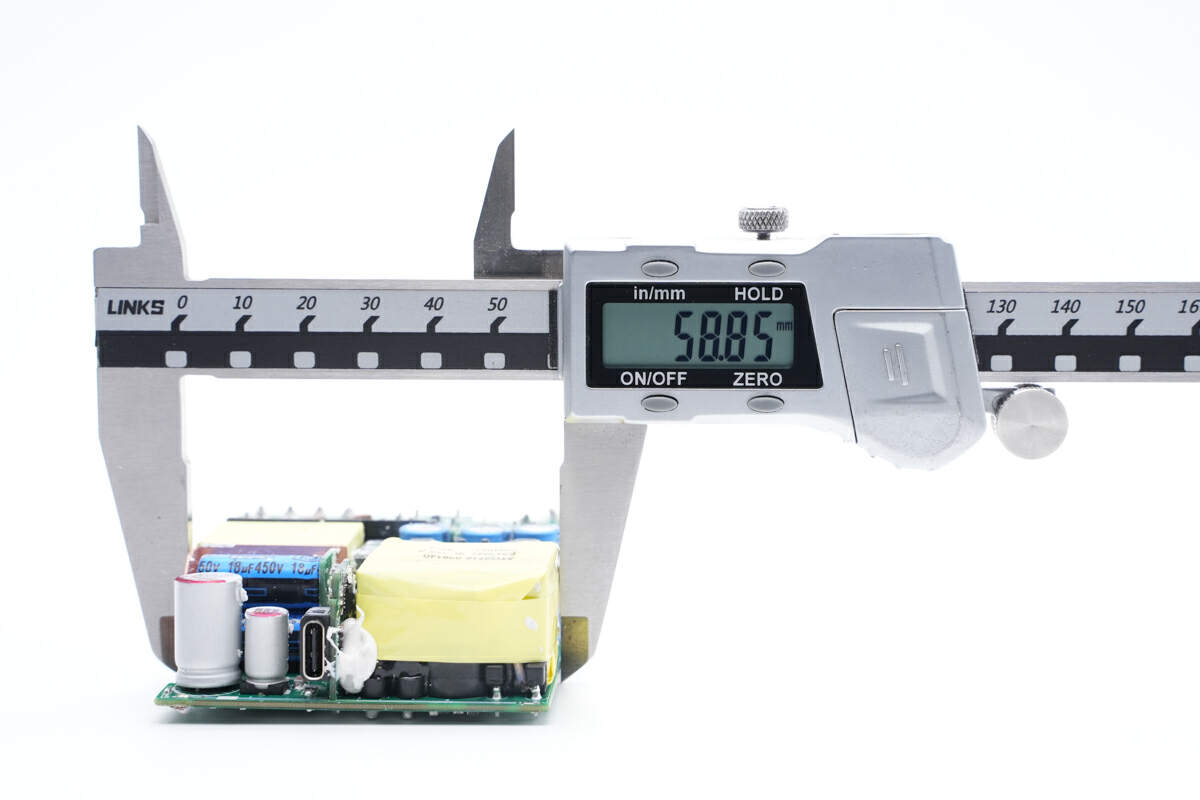

The width is about 58.9mm (2.32 inches).
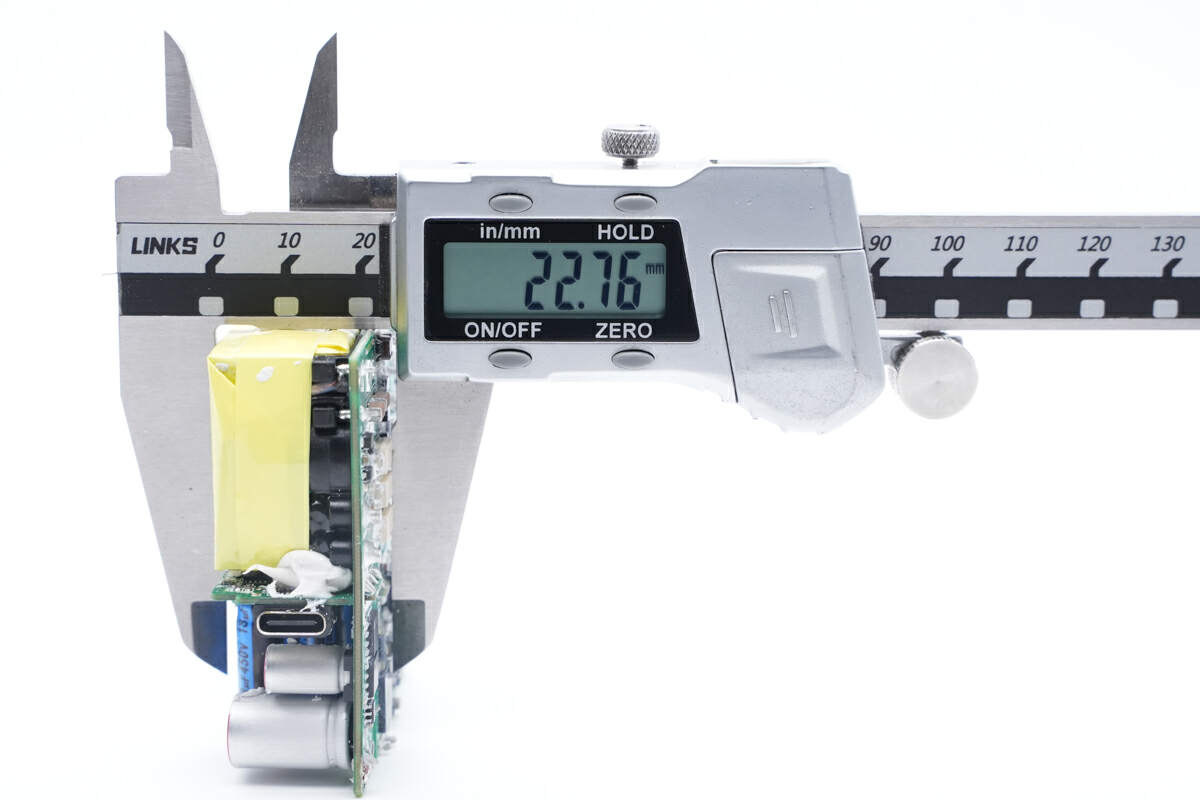

And the height is about 22.8mm (0.90 inches).
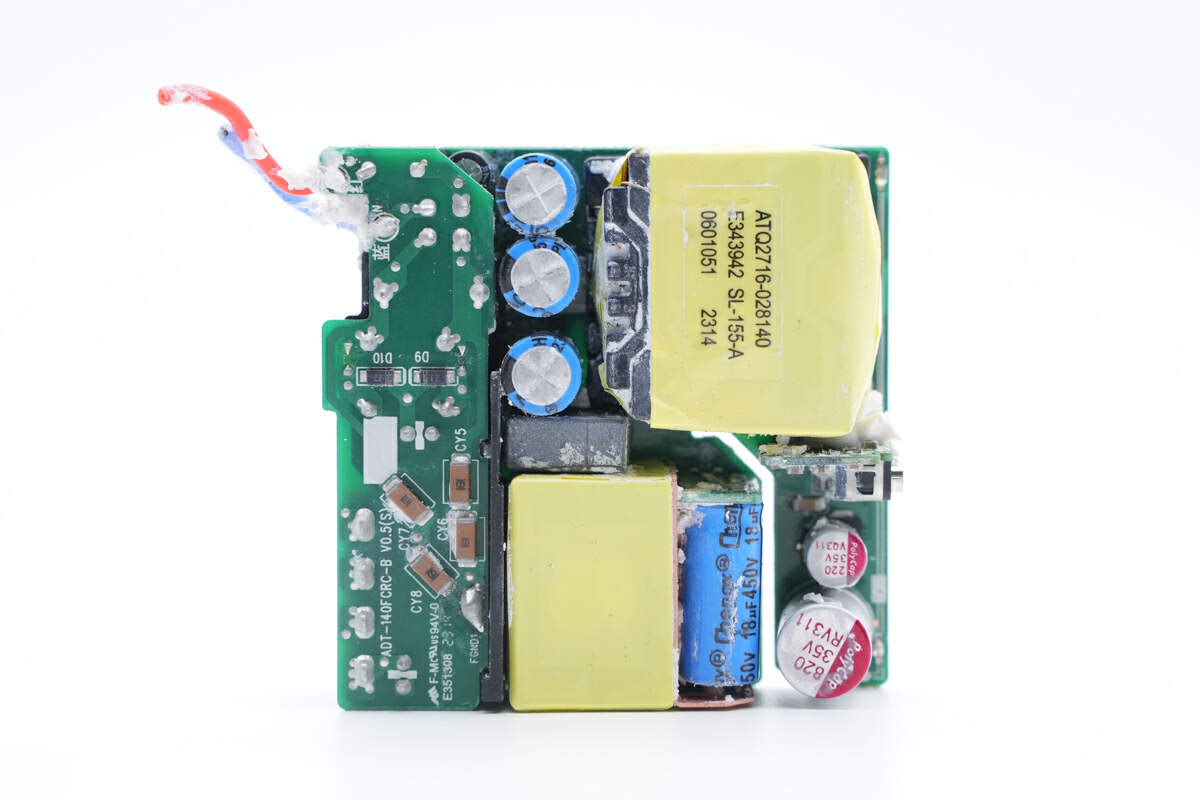

There's a small PCB on the front.
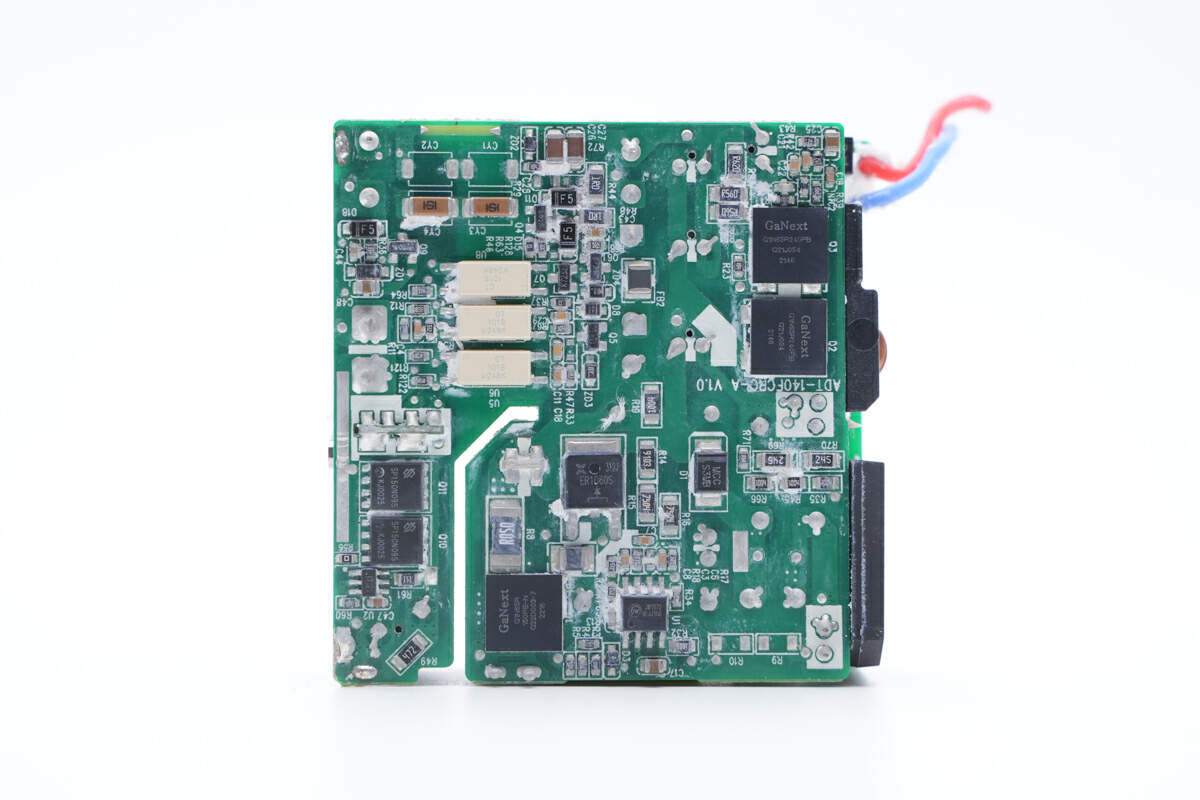

And the main PCB is on the back.
ChargerLAB found it adopts AHB (asymmetrical half bridge) flyback topology and has a PFC circuit. The current will be filtered by synchronous rectification circuit for output. Next, let’s introduce every single component.

The input time-delay fuse is from CONQUER MST series. 5A 250V.
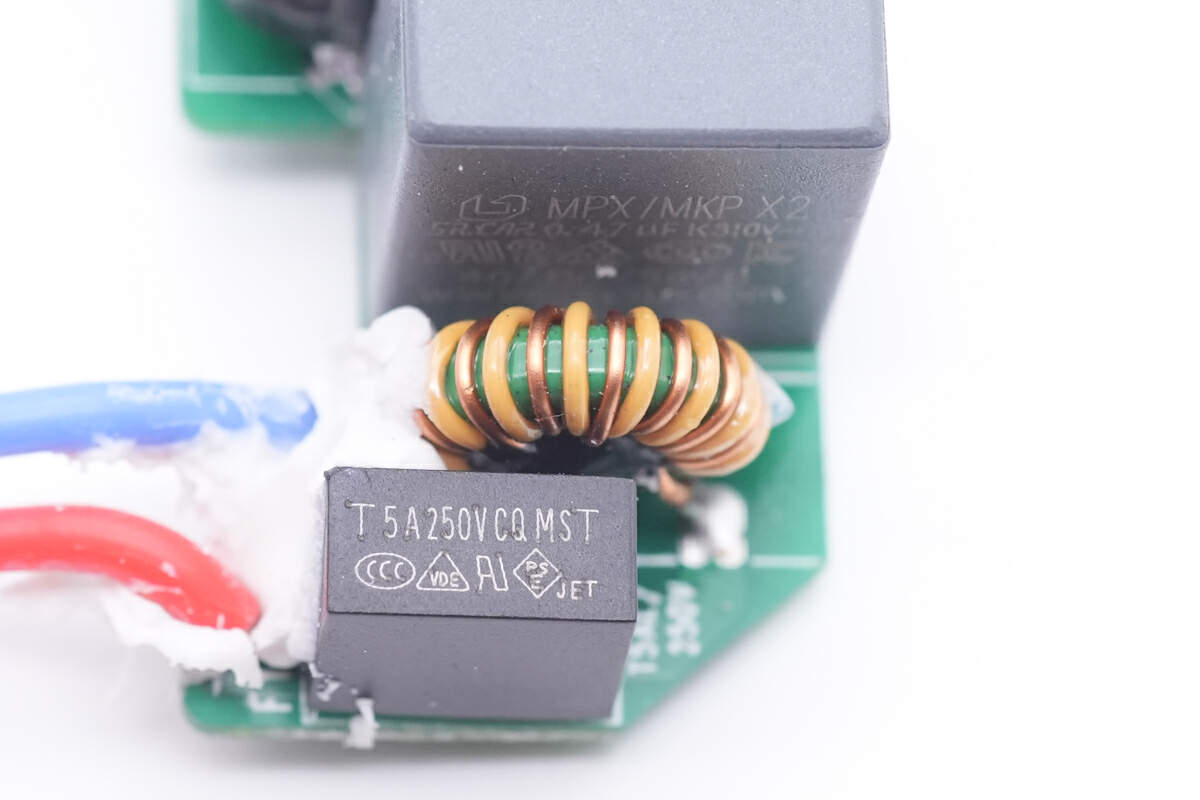
The common mode choke is behind the fuse to filter out EMI interference.
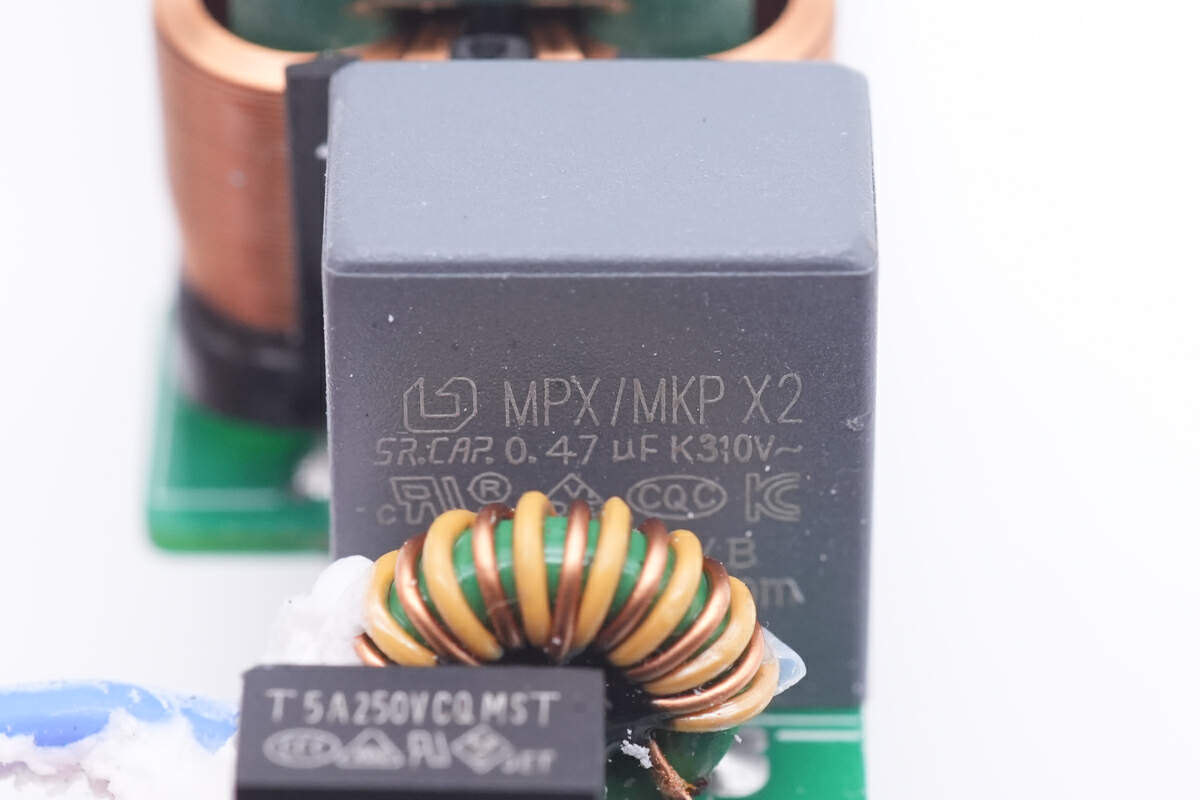

The safety X2 capacitor is from Surong. Capacity is 0.47μF.
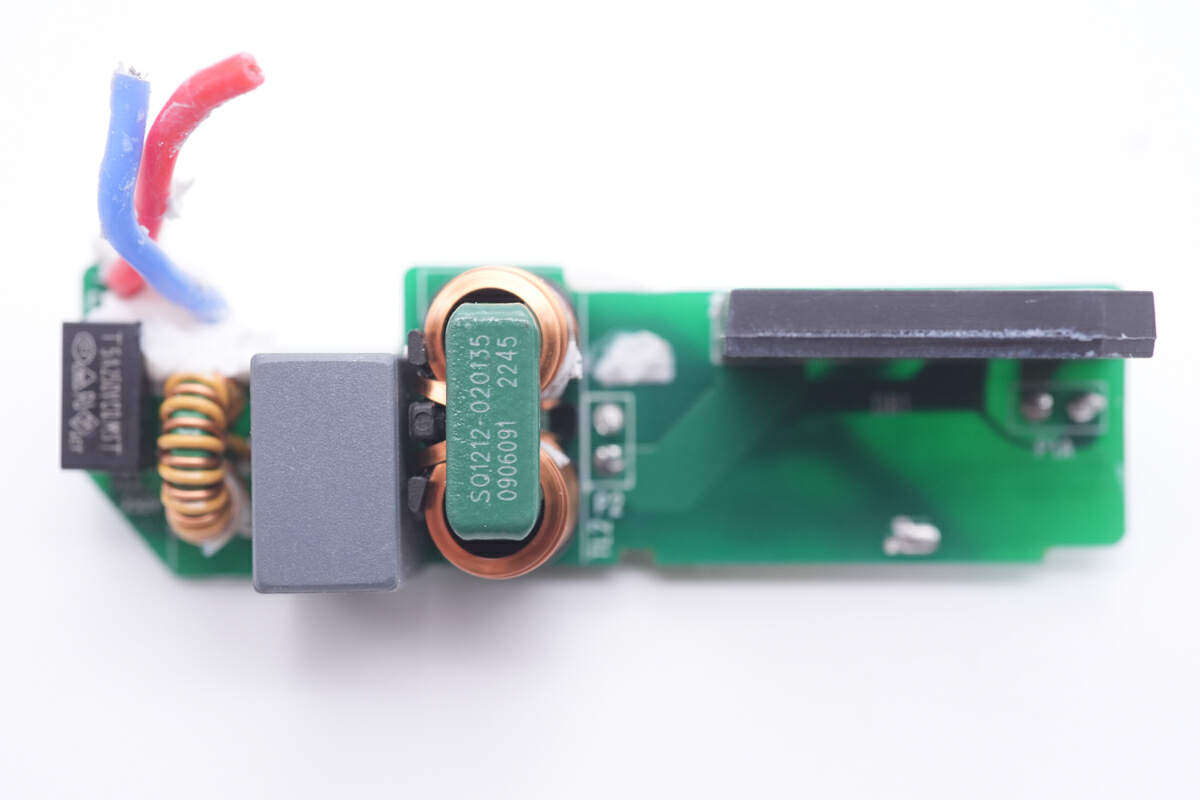
The second common mode choke is obviously larger and different from the first one.
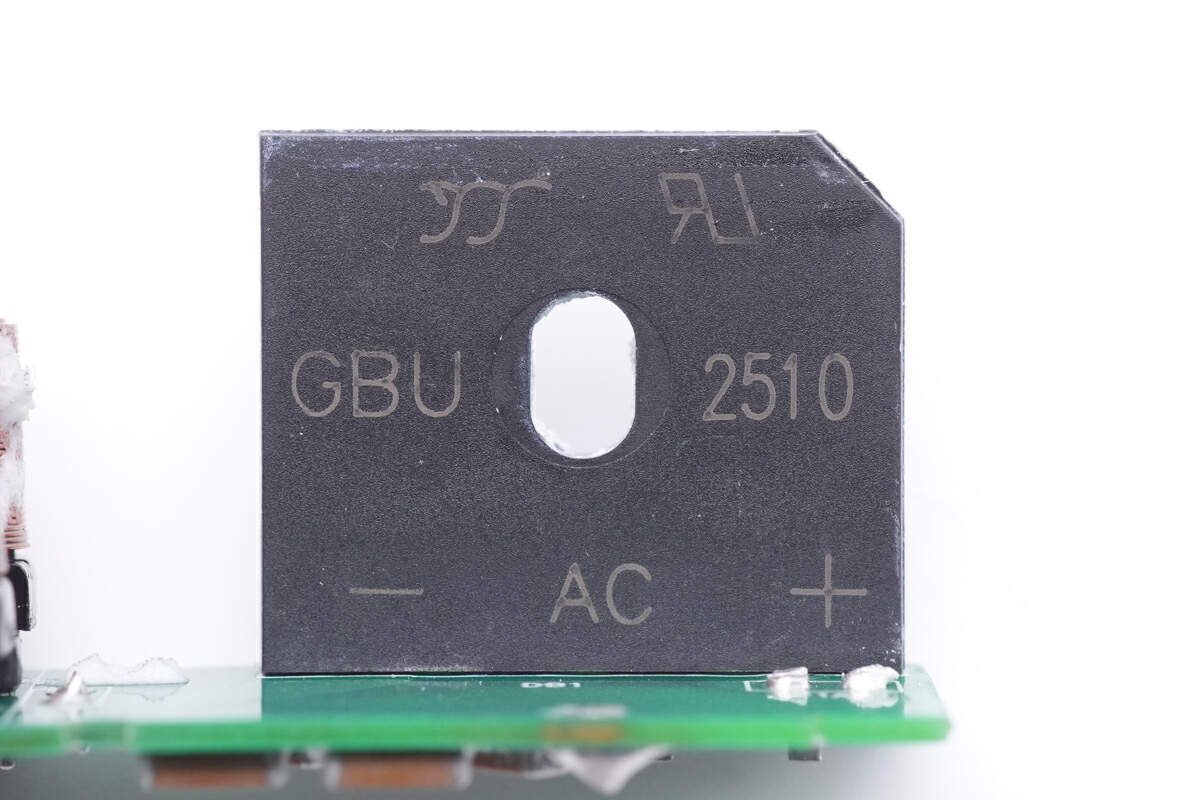
The bridge rectifier is from Yangjie. Model is GBU2510. 1000V 25A.
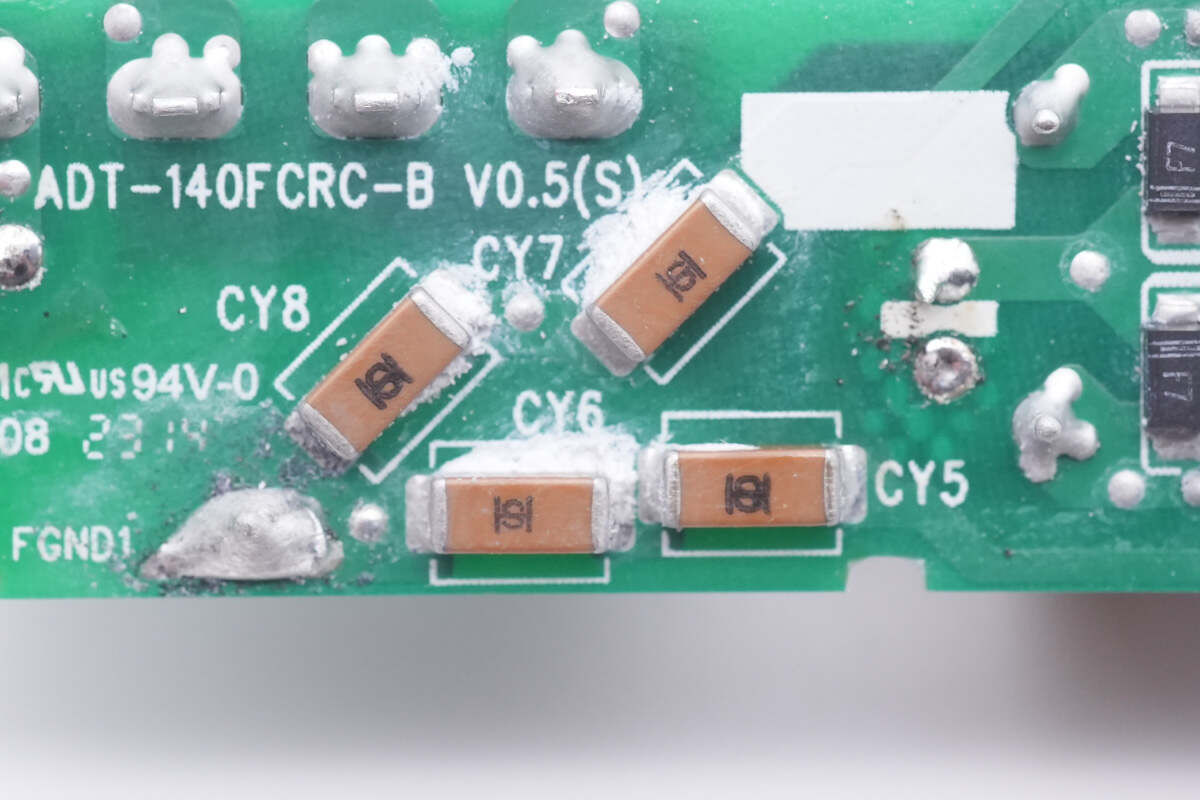
Those four SMD Y capacitors are from Holy Stone. Two capacitors are connected in series to improve the withstand voltage and safety.

The red film capacitor is 1μF 450V.

Another CBB film capacitor is smaller. 0.47μF 450V.
Then, let's introduce the PFC circuit.
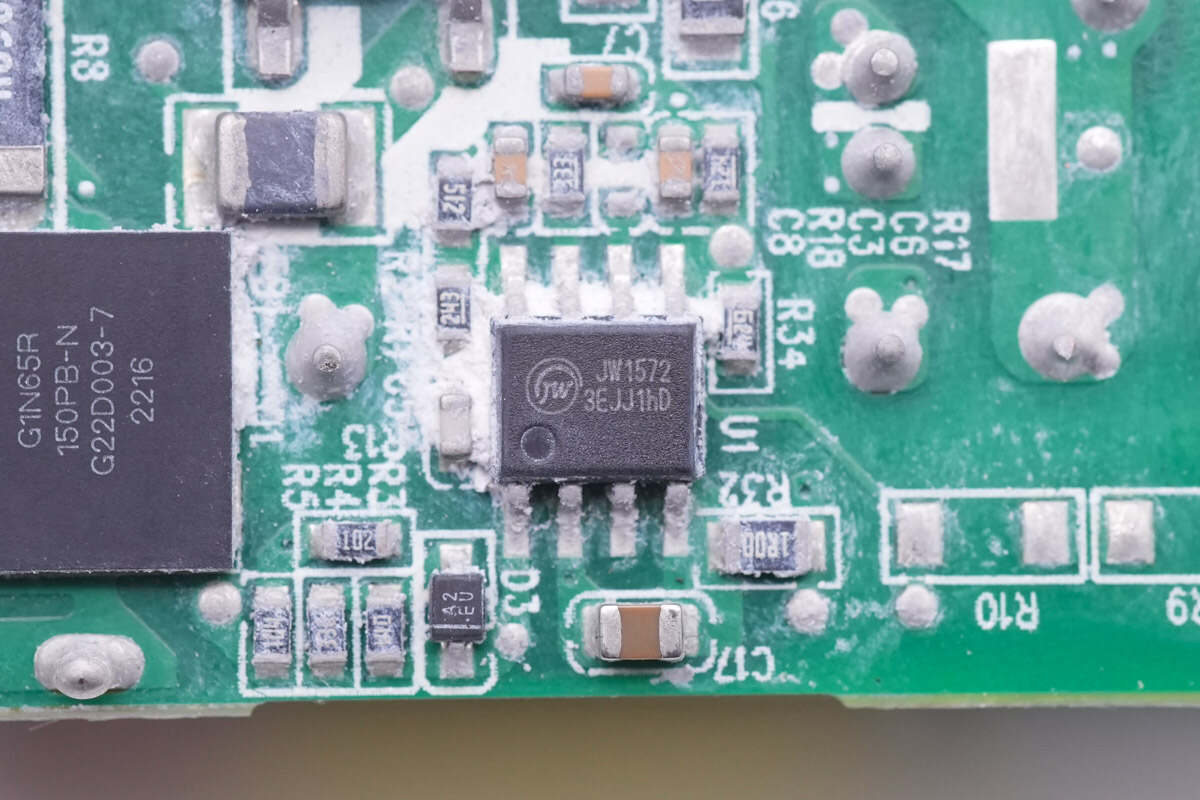
The PFC boost controller is from JoulWatt, model JW1572, it has a high-precision constant voltage output and is suitable for single stage boost power factor correction (PFC). The chip adopts constant on time control strategy to ensure high power factor, and the input voltage detection circuit is not needed, which simplifies the system design and saves the loss.
Here is all the information about JoulWatt JW1572.

The GaN FET for PFC boost is from GaNext, model G1N65R150PB-N, which can be driven by MOSFET.
It does not need for negative gate drive, which can greatly simplify the gate drive circuit. 650V 150mΩ.
Here is all the information about GaNext G1N65R150PB-N.
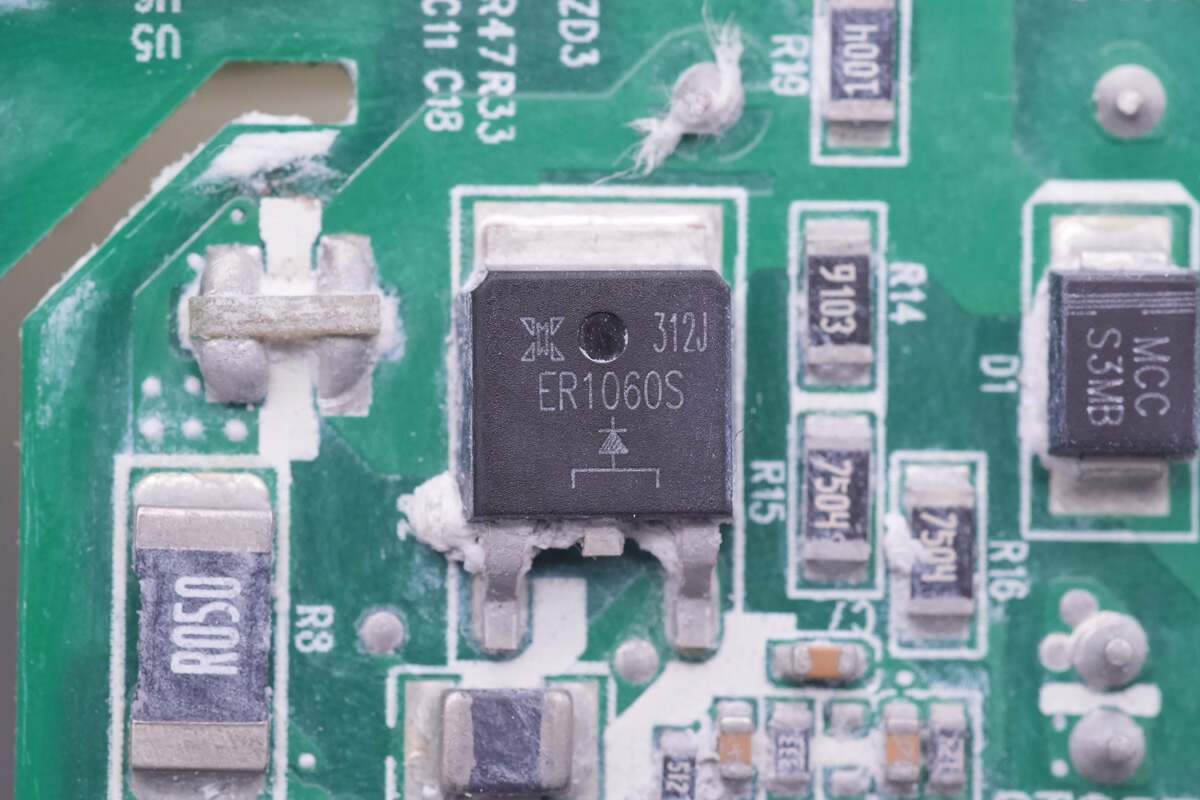
The PFC boost rectifier is marked with ER1060S. 10A 600V.

The PFC boost inductor adopts ATQ23 magnetic core.
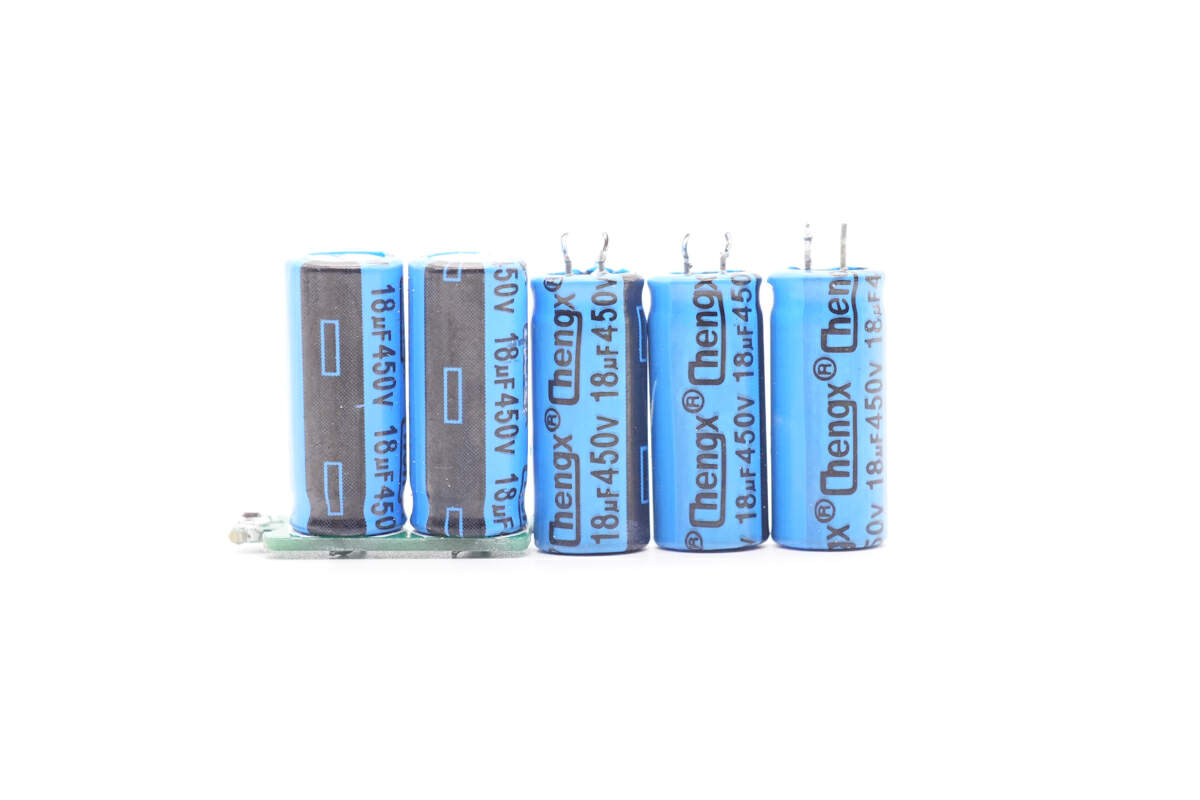

All those five electrolytic capacitors are from Chengxing. 450V 18μF for each.
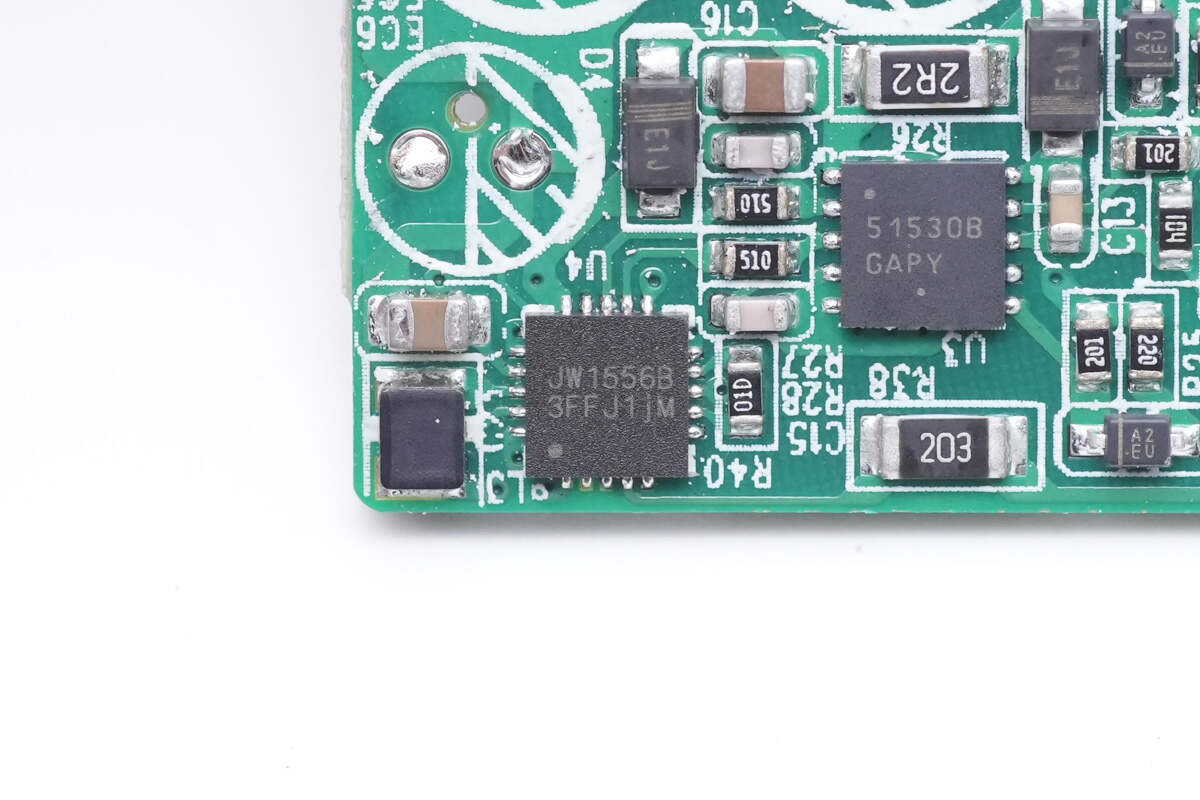
Next, let's talk about the AHB flyback topology.
The AHB controller is also from JoulWatt, model JW1556B, it is an asymmetrical half-bridge flyback controller in a QFN 4x4-20 package, suitable for offline flyback converter applications. The input voltage range is 2.5-38V, the maximum operating frequency is 1.5MHz, and it supports 65-300W fast charging applications. JW1556B is an optimized model specially designed for notebooks. Its peak output power has been optimized and supports 1-2 times the peak power. Therefore, this charger is ideal for laptop adapters.
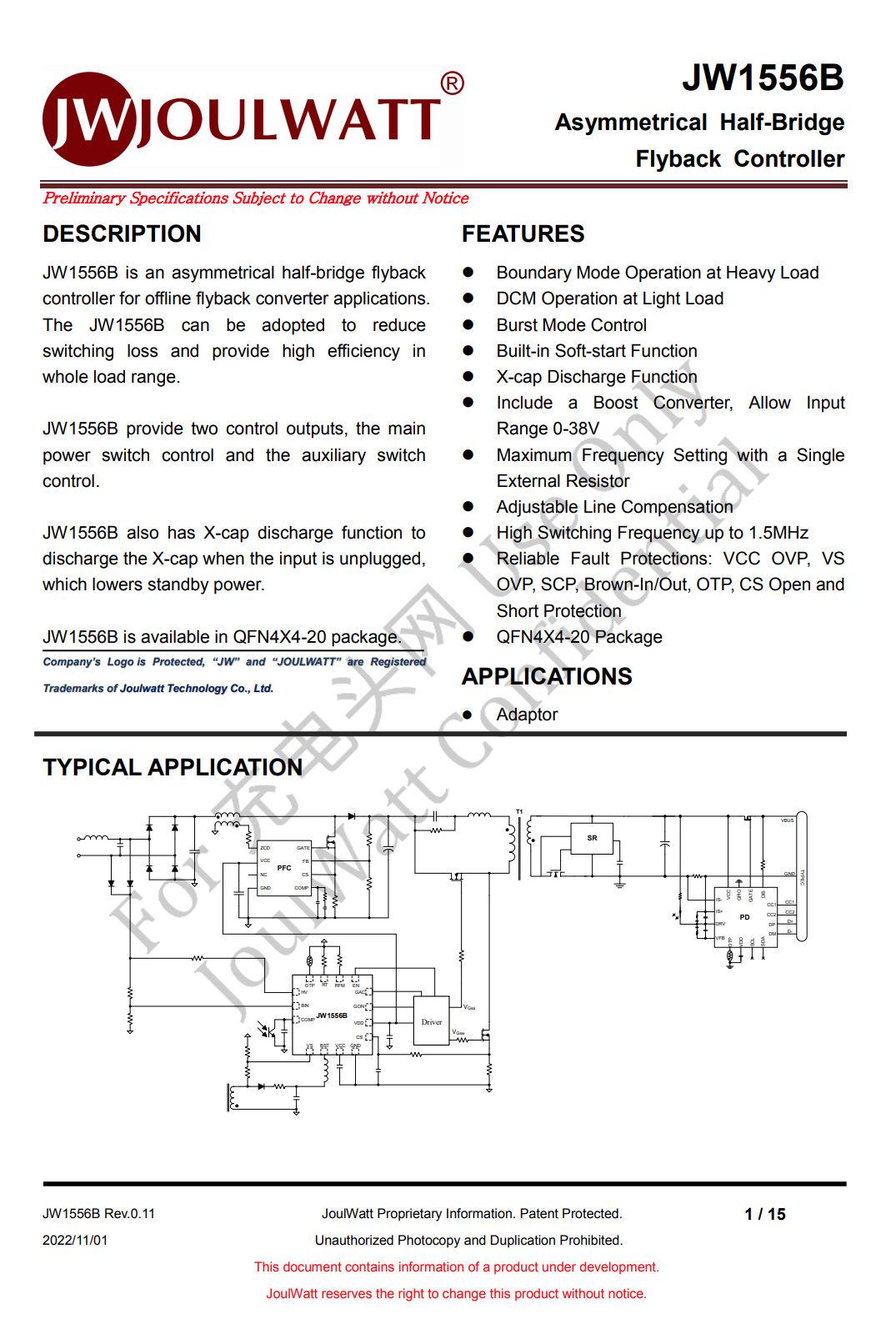
Here is all the information about JoulWatt JW1556B.
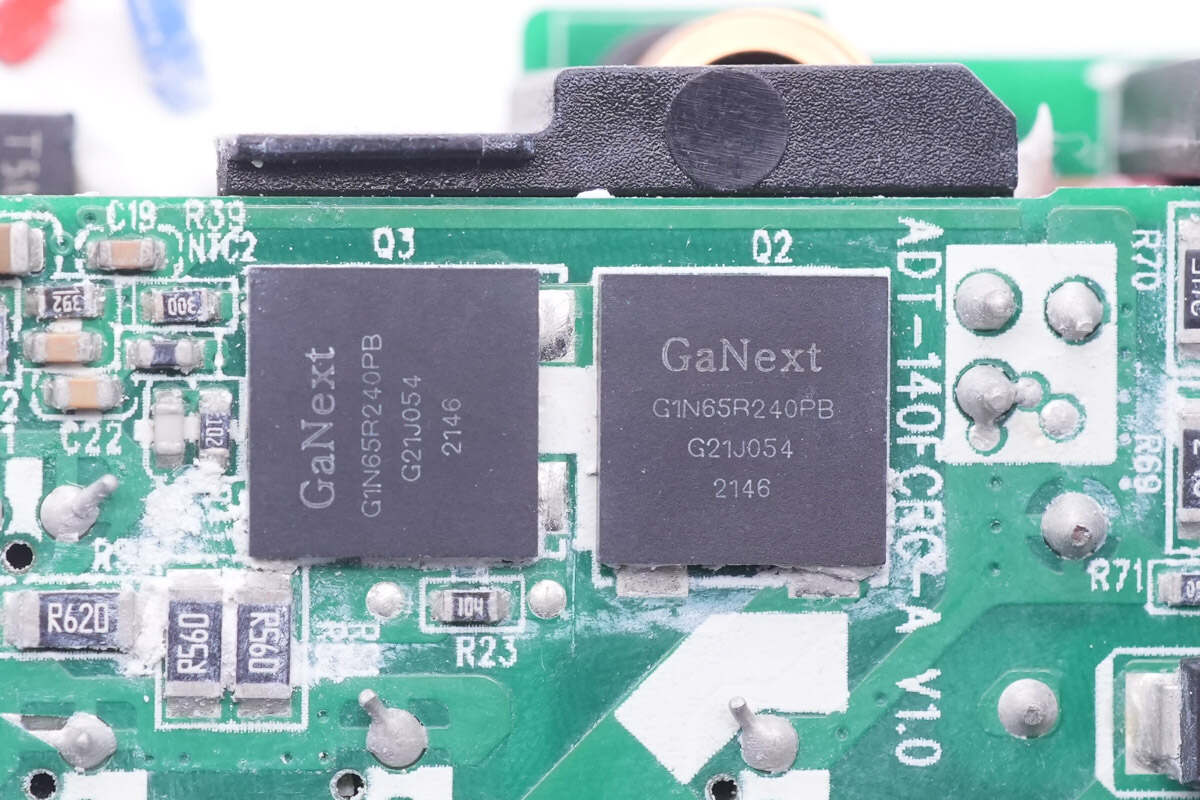
These are two GaN FETs from GaNext. They can form a half-bridge circuit for AHB topology. Model is G1N65R240PB. 650V 240mΩ.
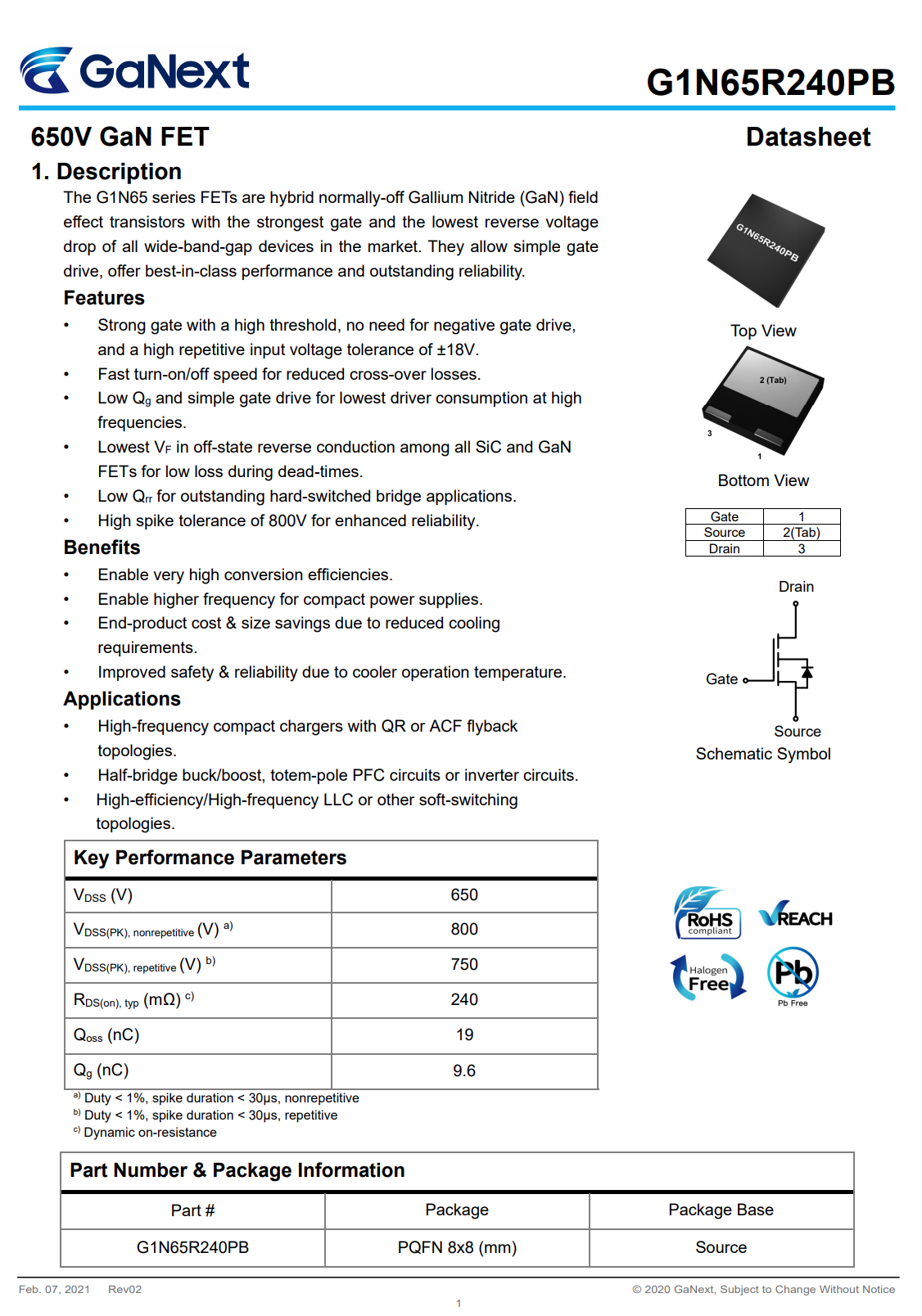
And here is all the information about GaNext G1N65R240PB.
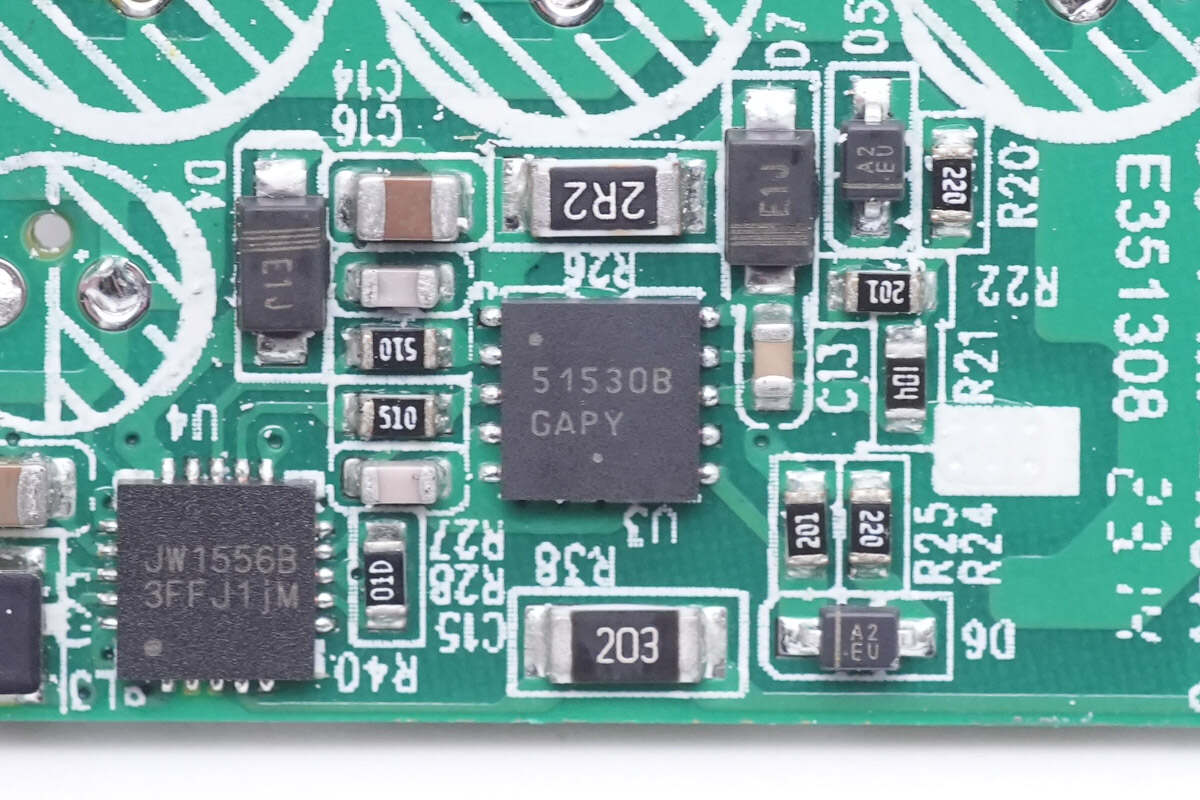
This driver drives two GaN FETs we just mentioned, from ON Semiconductor. The high-voltage side can be up to 700V. Model is NCP51530B.
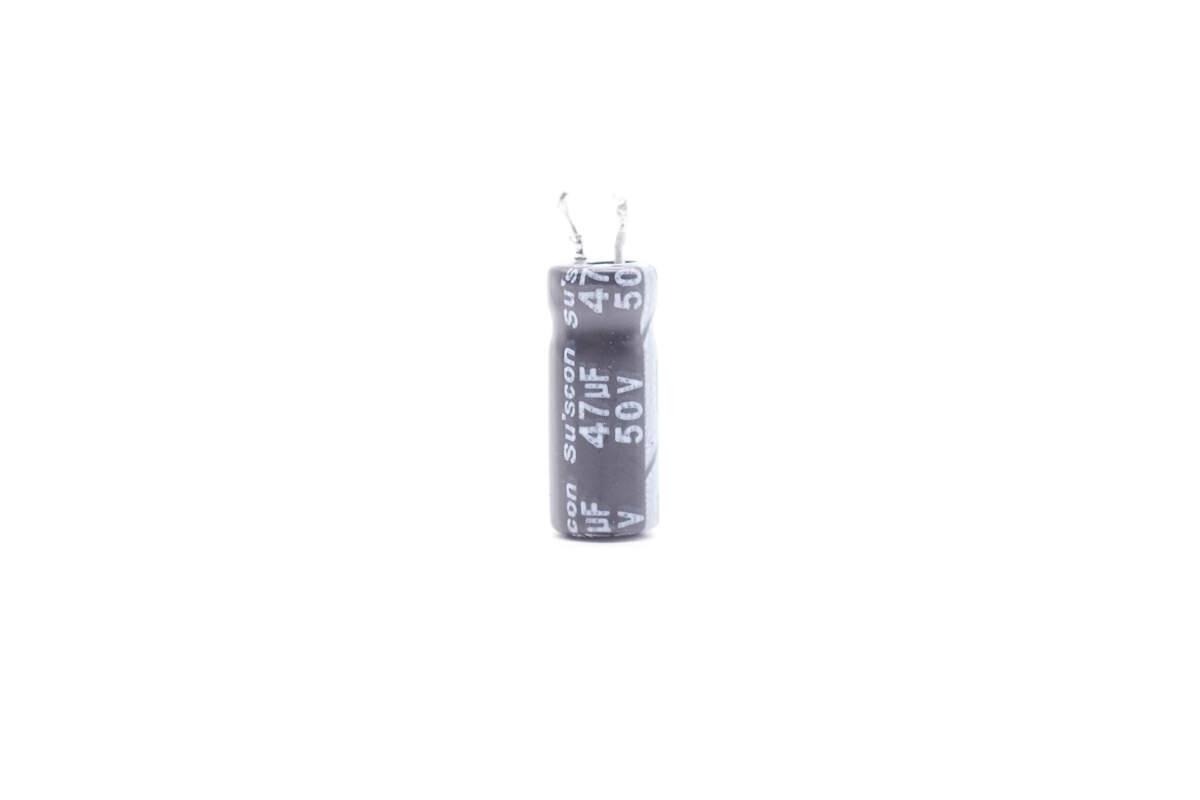

The small capacitor that powers the AHB controller is from Su'scon. 50V 47μF.

The resonant capacitor is 0.47μF 250V.

The largest component is a transformer, which adopts ATQ2716 magnetic core.
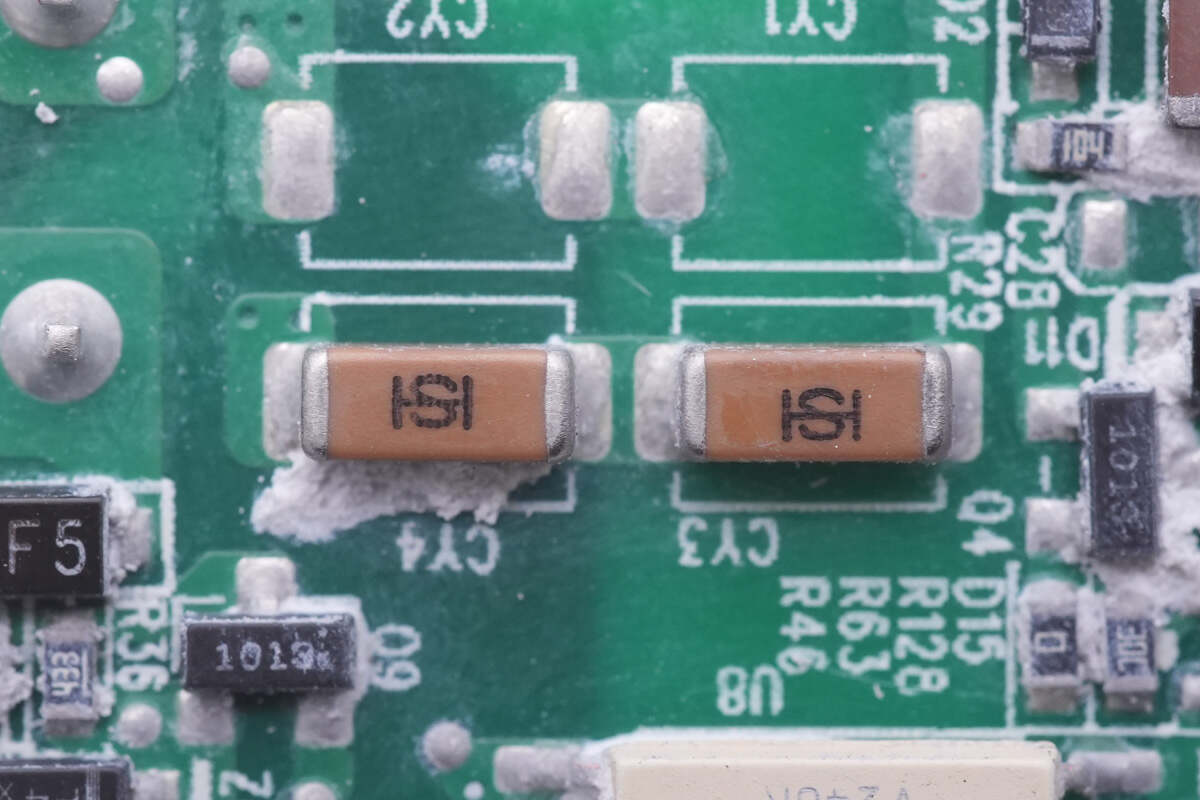
Those two SMD Y capacitors are also from Holy Stone, connected in series.
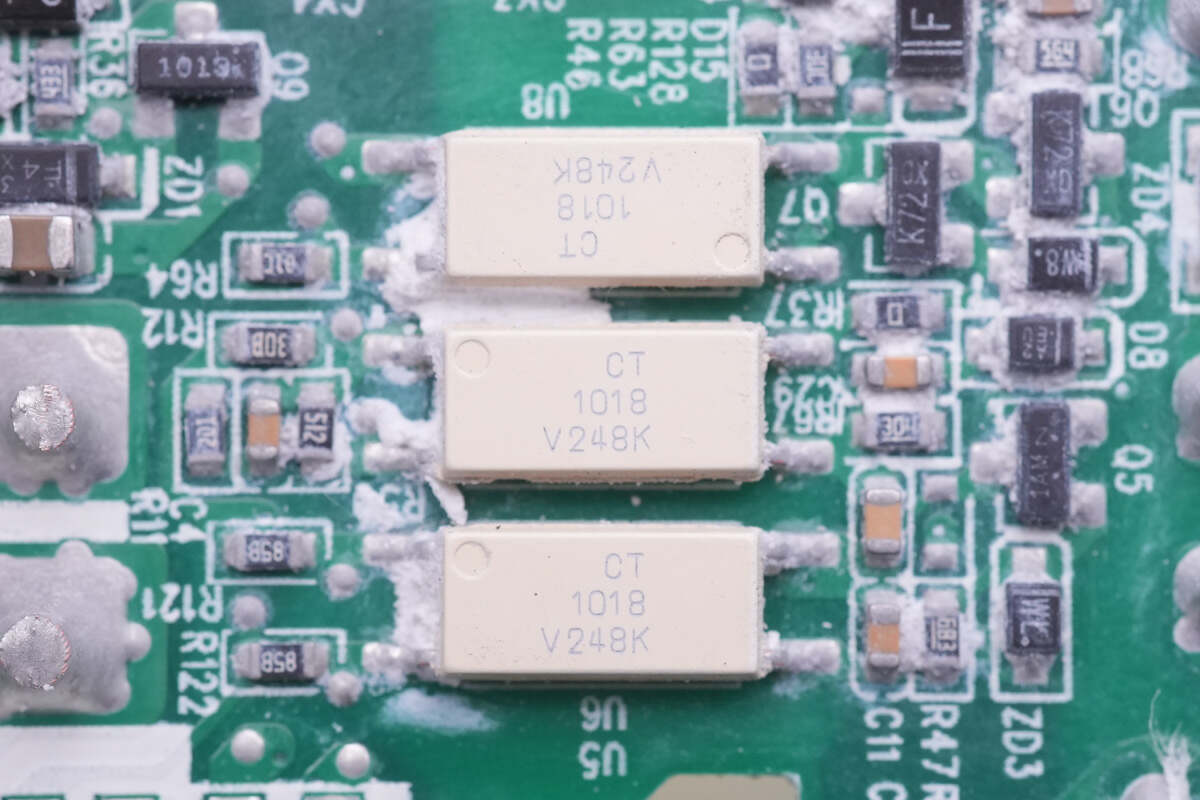
There’re three CT1018 optocouplers between the primary side and the secondary side.
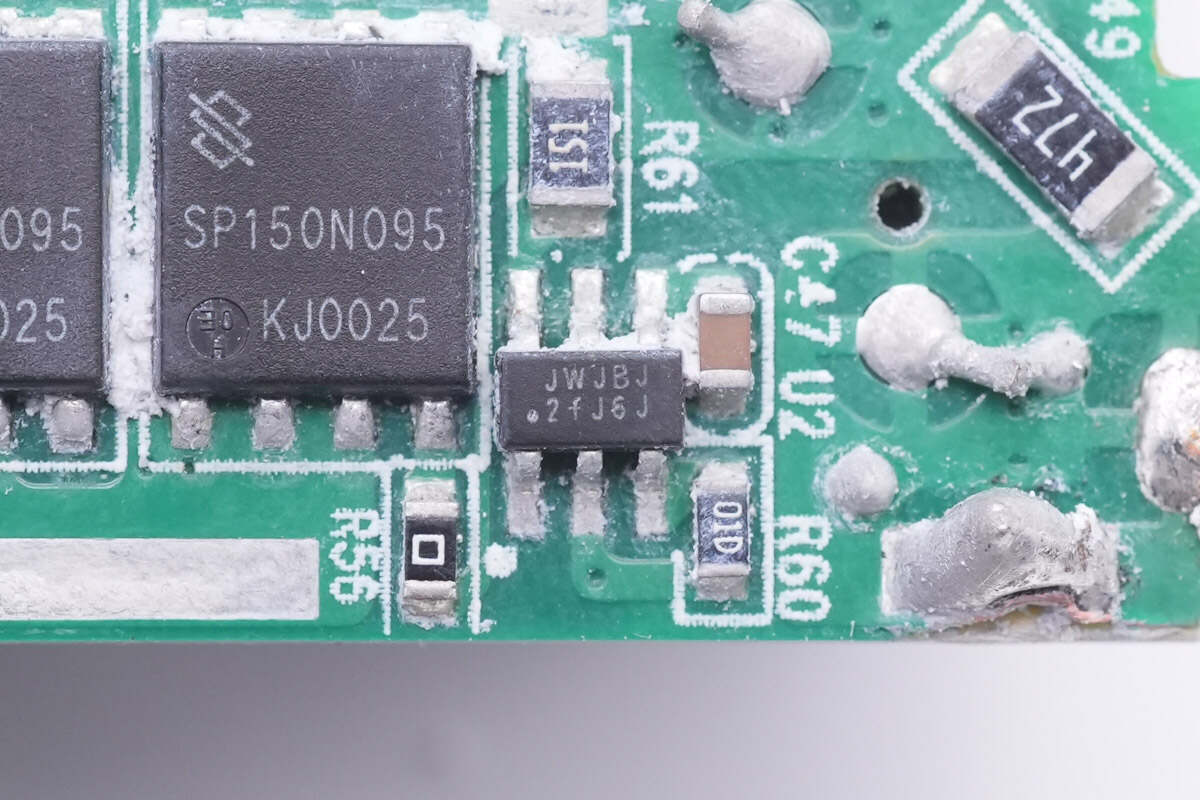
Then, let's see the synchronous rectification circuit.
The controller marked with JWJBJ is from JoulWatt, model is JW7726BL. It supports Active Clamp Flyback, DCM, Quasi-Resonant and CCM Flyback, with fast turn-off capability. It also supports high-side and low-side rectification with low standby current. During the start-up process (before VCC is established), it can effectively prevent the gate from being coupled to the turn-on voltage.
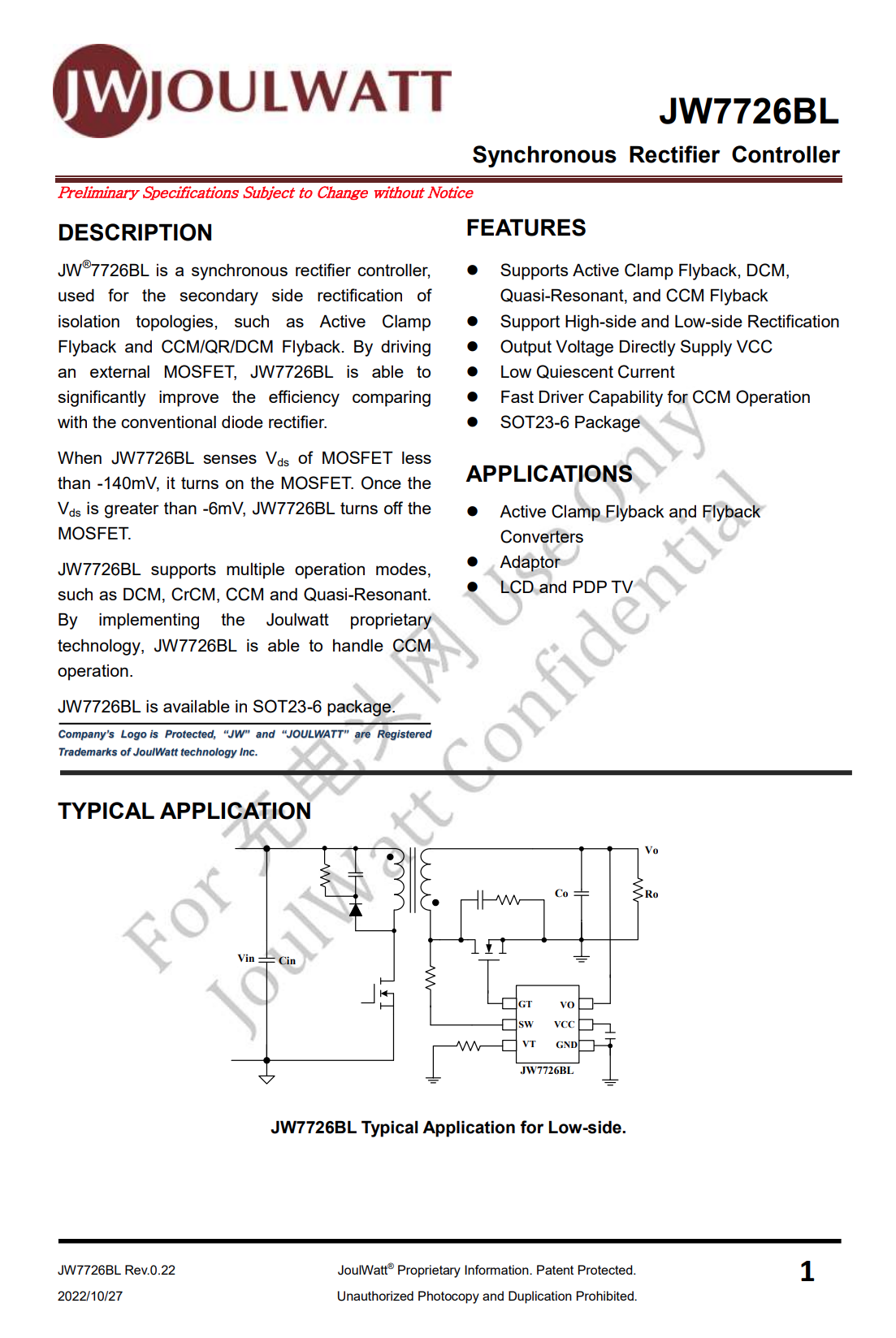
Here is all the information about JoulWatt JW7726BL.
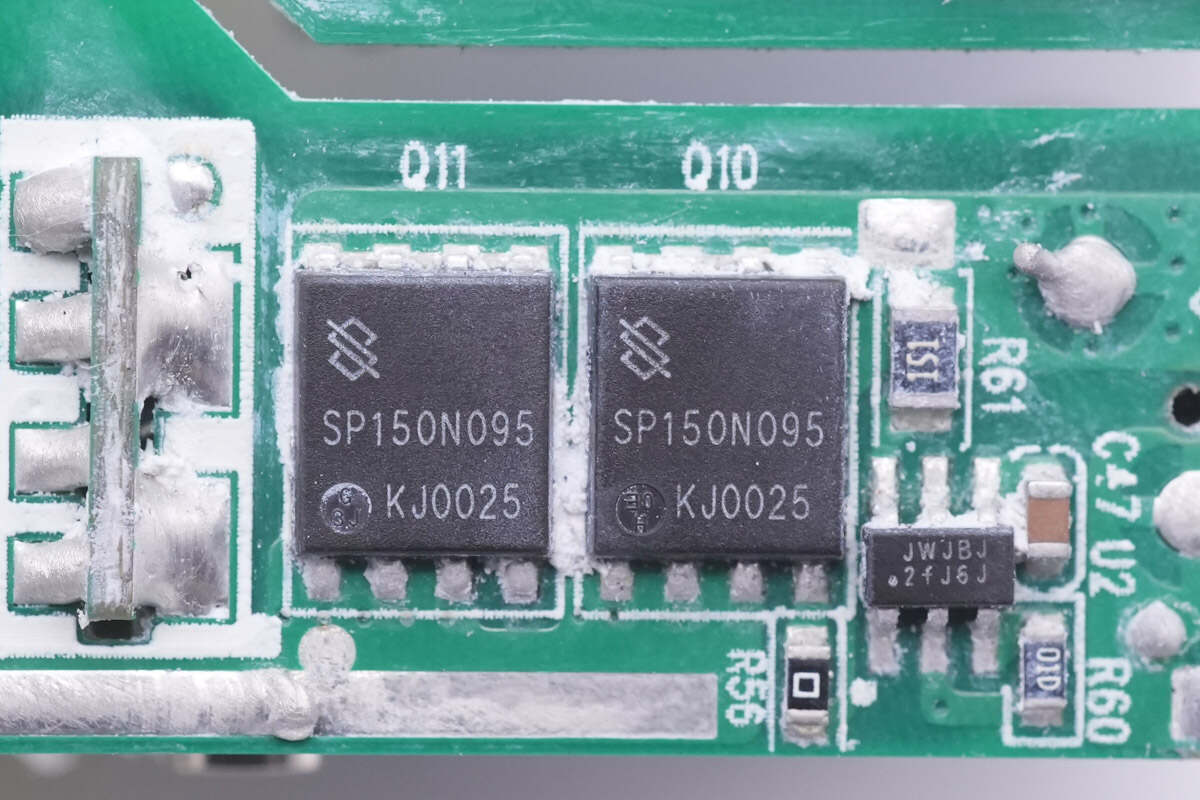
Two synchronous rectifiers are connected in parallel. Model is SP150N095.

This solid capacitor is from PolyCap RV series. 35V 820μF.

And this one is also from PolyCap, but it's VQ series. 35V 220μF.

The protocol chip is from Weltrend and adopts QFN-16 package. It supports USB PD3.1, and the input voltage can reach 45V. Model is WT6676F.
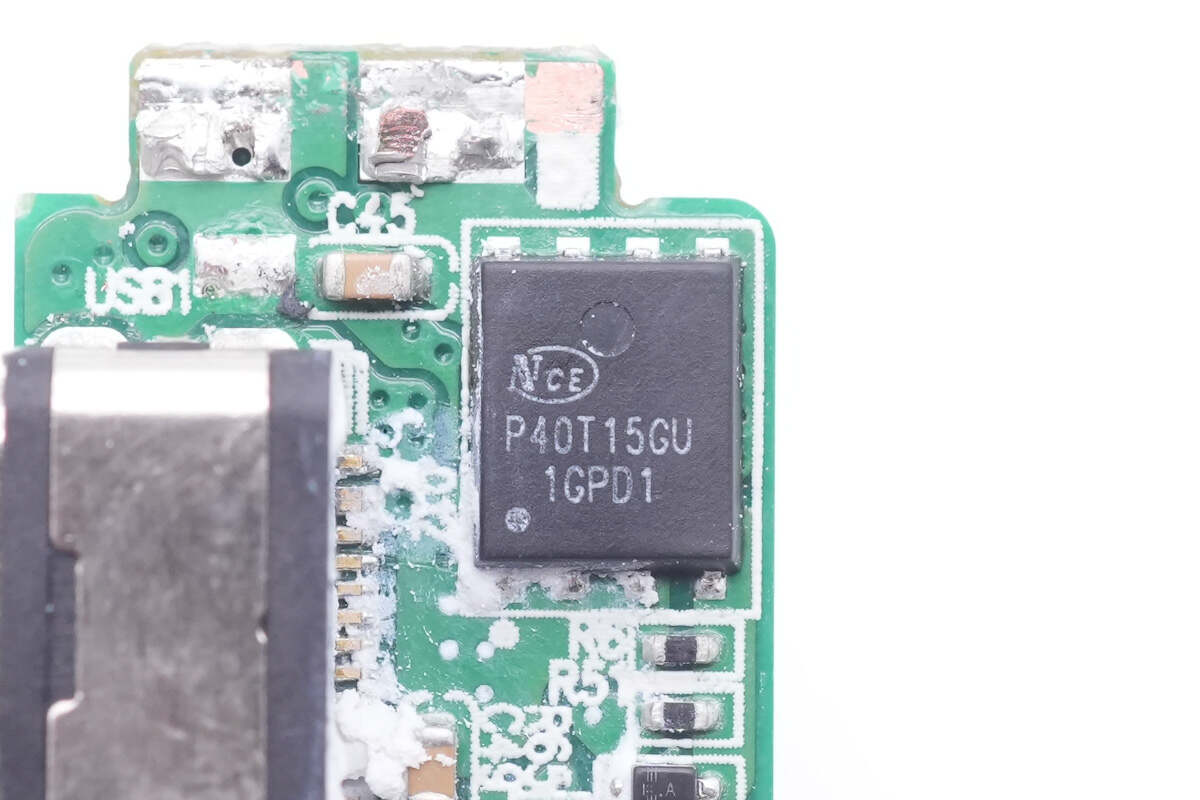

The output VBUS MOSFET is from NCE Power and adopts DFN5*6-8L package. Model is NCEP40T15GU. 40V 1.09mΩ.

The plastic sheet inside the USB-C socket is black.
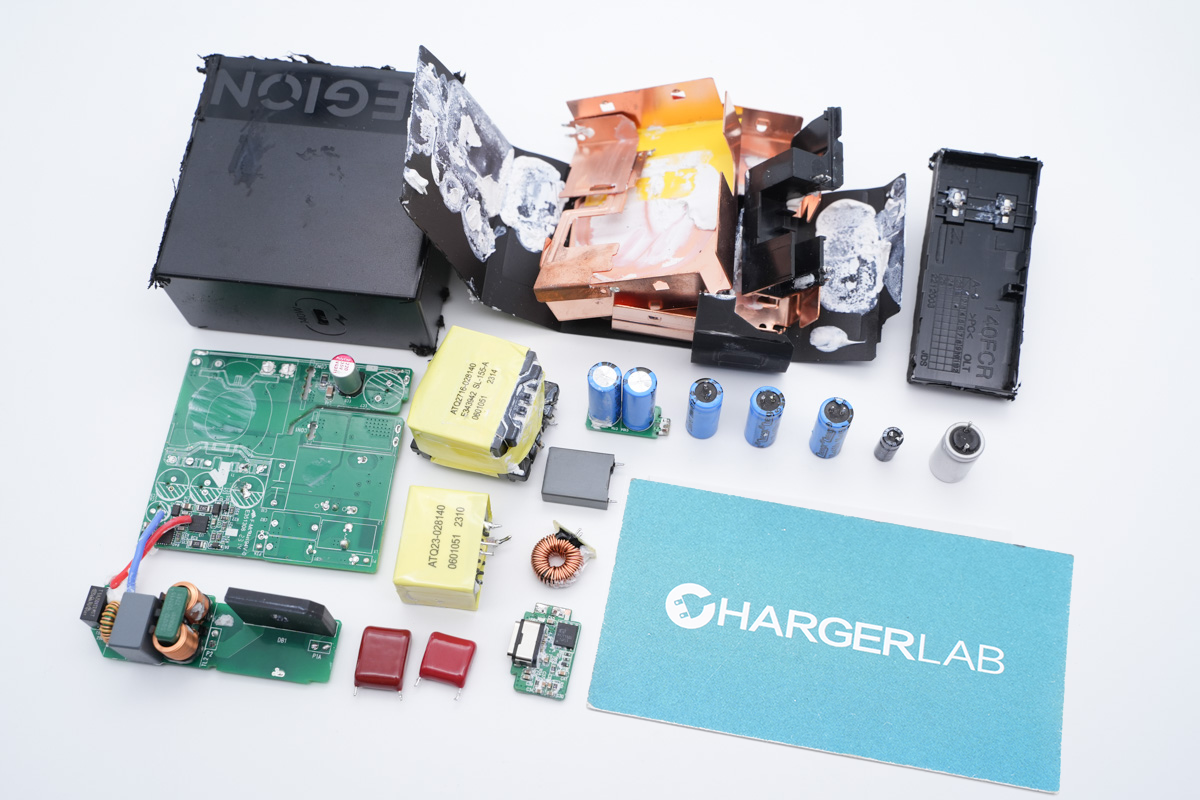

One last look at all the components of this Lenovo Legion 140W PD3.1 USB-C GaN laptop charger.
Summary of ChargerLAB
The Lenovo Legion 140W PD3.1 USB-C GaN laptop charger is designed with a square shape and a fixed plug, making it ideal for carrying in a laptop bag while traveling. Unlike bulky traditional chargers, this charger is compact and lightweight, making it a convenient and hassle-free travel companion. Supporting an impressive 140W fast charging output, this charger is not only compatible with Lenovo's proprietary 20V7A fast charging mode on their laptops, but it also supports 28V5A PD3.1 fast charging and 5A PPS fast charging, which makes it versatile enough to charge a wide range of laptops and Android smartphones from various brands.
It's a pity that Lenovo doesn't ship this charger with the laptop. You have to buy it separately, but the compact size makes it more suitable for use on the go.
Related Articles:
1. Teardown of Lenovo Legion 140W PD3.1 USB-C GaN Laptop Charger (Video)
2. Teardown of Lenovo Legion 135W/C135 USB-C GaN Charger
3. Teardown of Lenovo ThinkPad Stack Power Bank (Modular Design)








