Introduction
ChargerLAB this time got a 180W USB-C GaN charger from Infinix. This charger is equipped with European pins and a USB-C port. It can support a charging power of up to 20V9A 180W. It can provide fast charging for phones and laptops.
Next, we are going to take it apart to see its internal components and structure.
Product Appearance
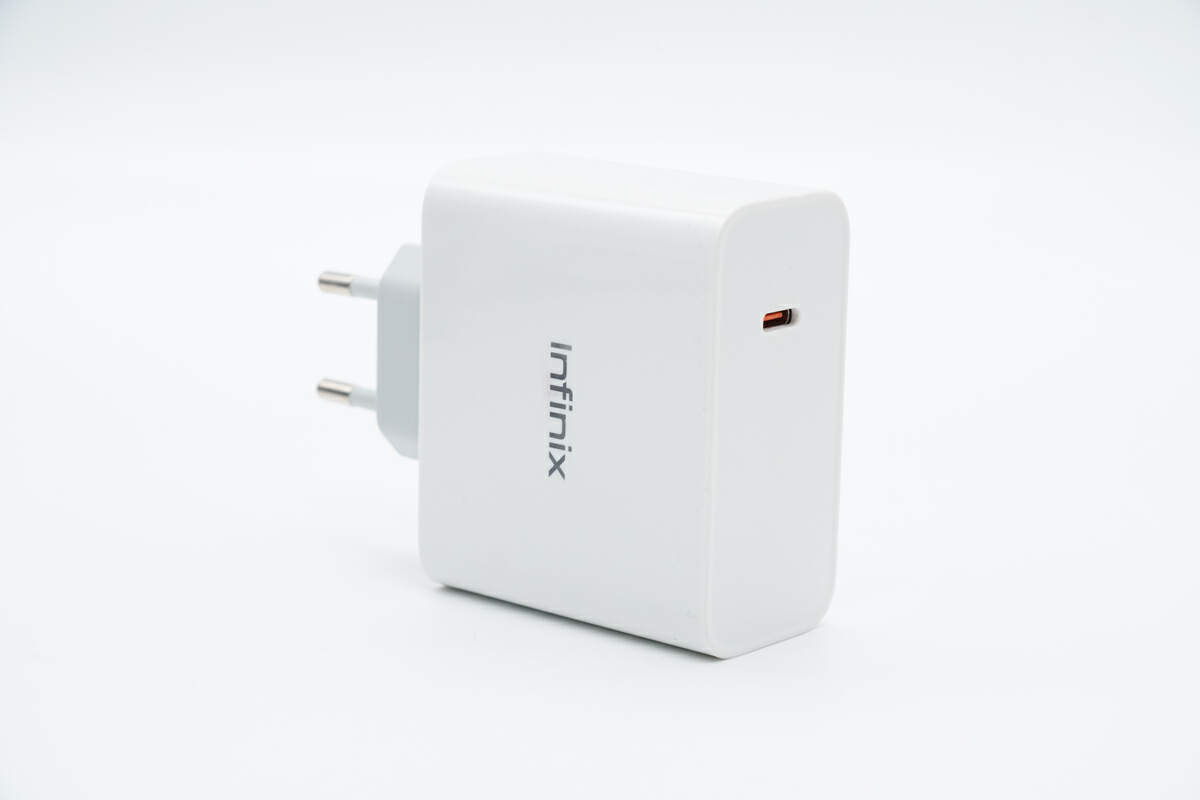

It adopts a one-piece white case.

The "infinix" is printed in the middle.
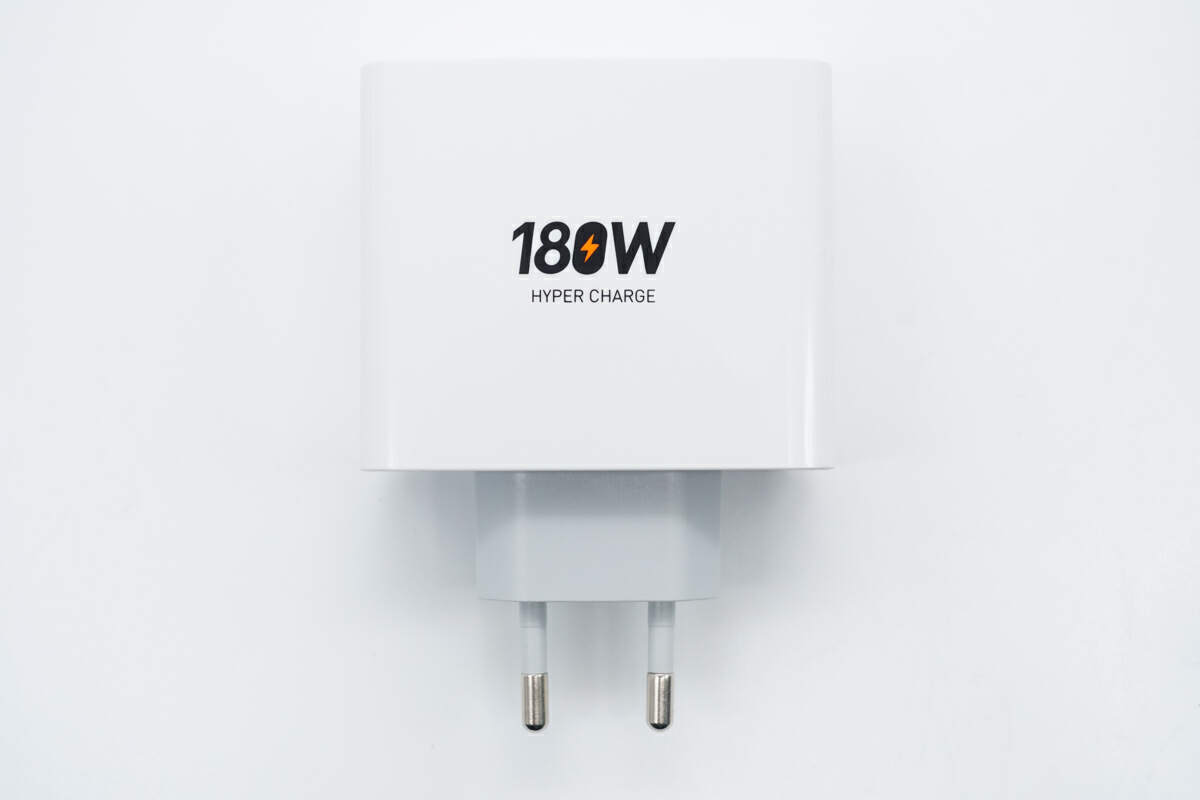

There is "180W HYPER CHARGE" printed on the center of the back.
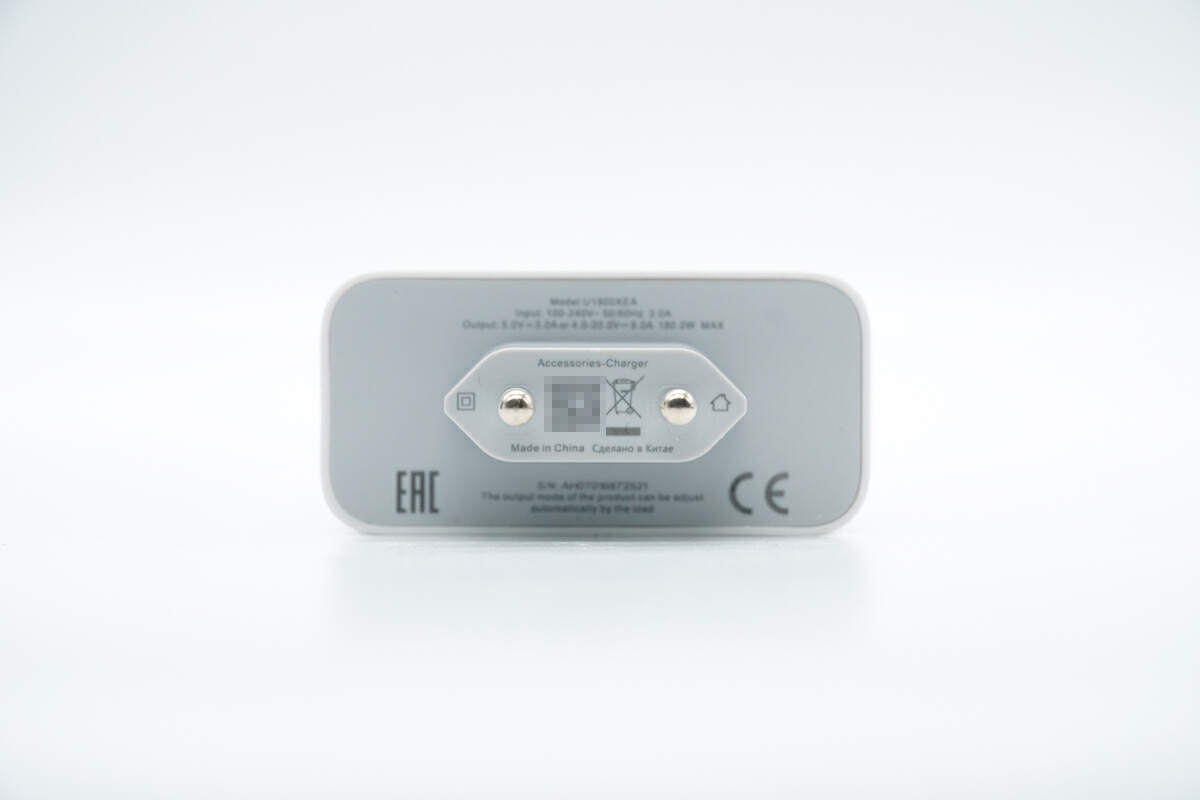

The specs info are printed on the input end. It has passed EAC and CE certifications.

Model is U1800XEA. It can support input of 100-240V~50/60Hz 3A. And it can support output of 5V3A, and 4-20V9A. The maximum output power is 180W.

The charger is equipped with European pins.

Here is the USB-C port.
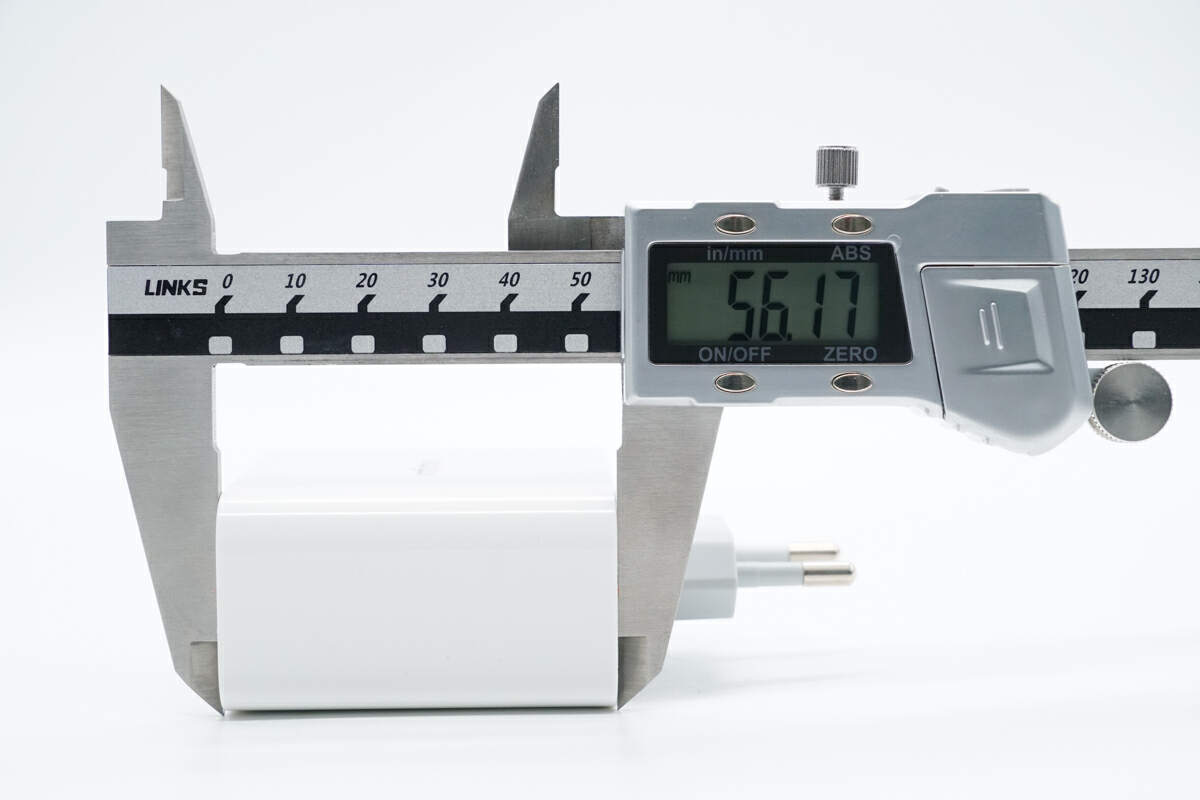

The height of it is about 56 mm (2.2 inches).
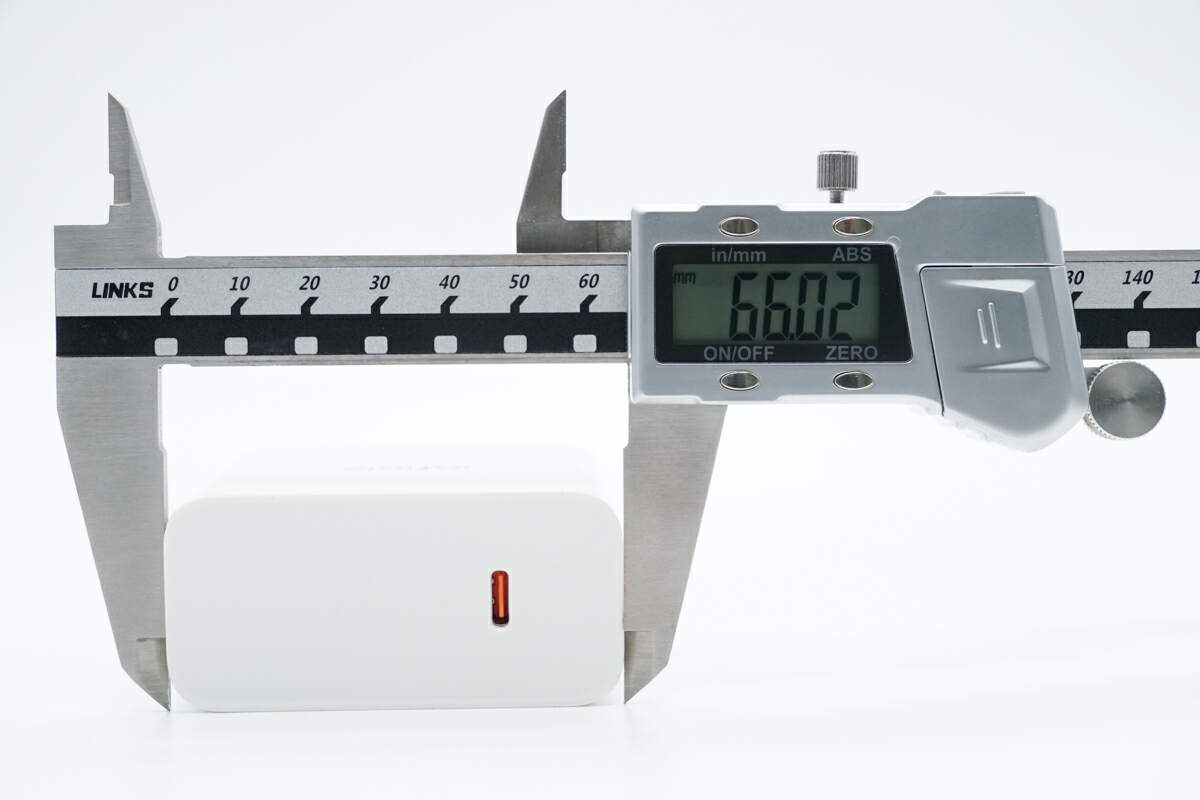

The width is about 66 mm (2.6 inches).
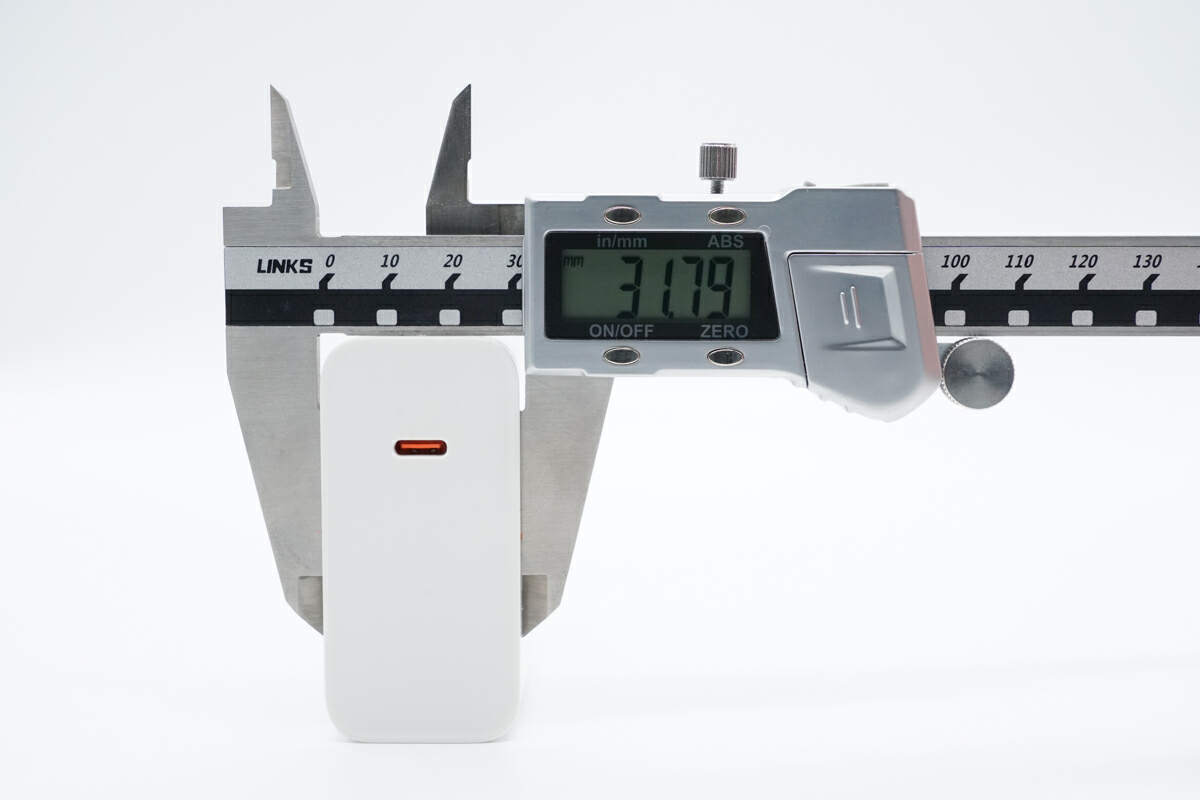

The thickness is about 32 mm (1.26 inches).

That's how big it is in the hand.
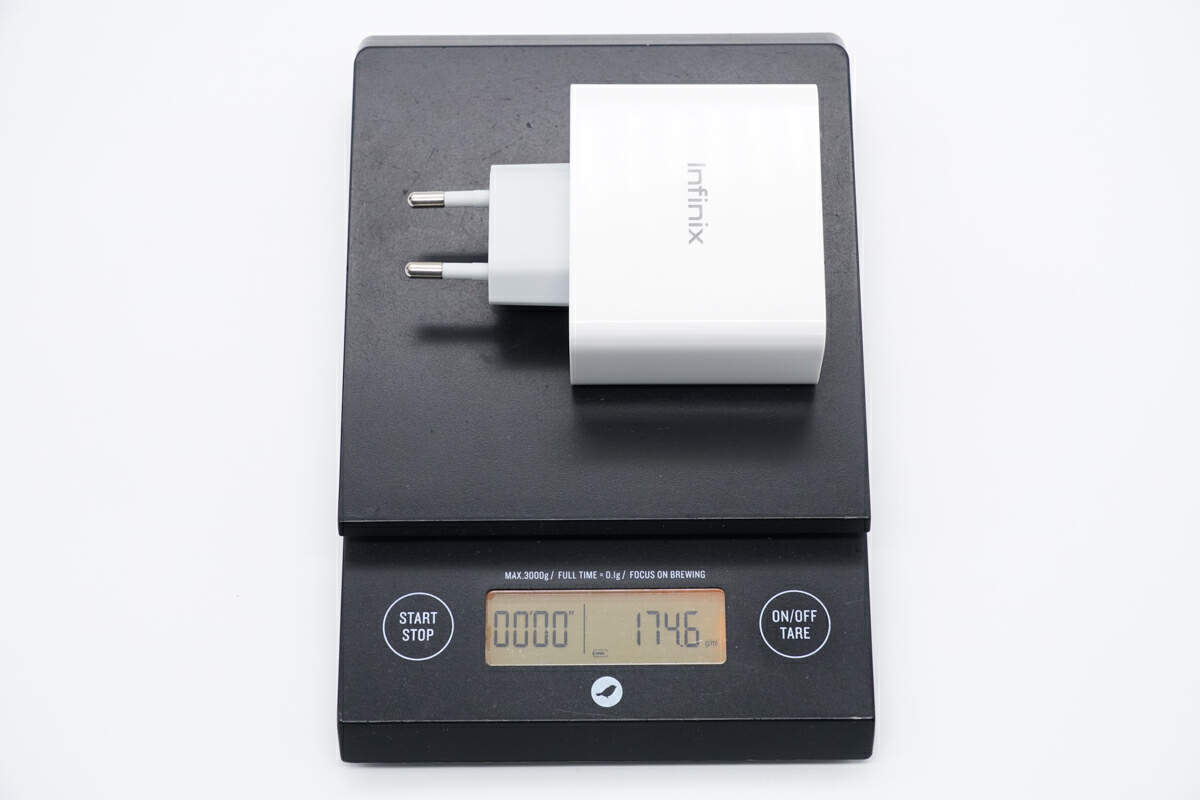

The weight is about 175 g (6.17 oz).
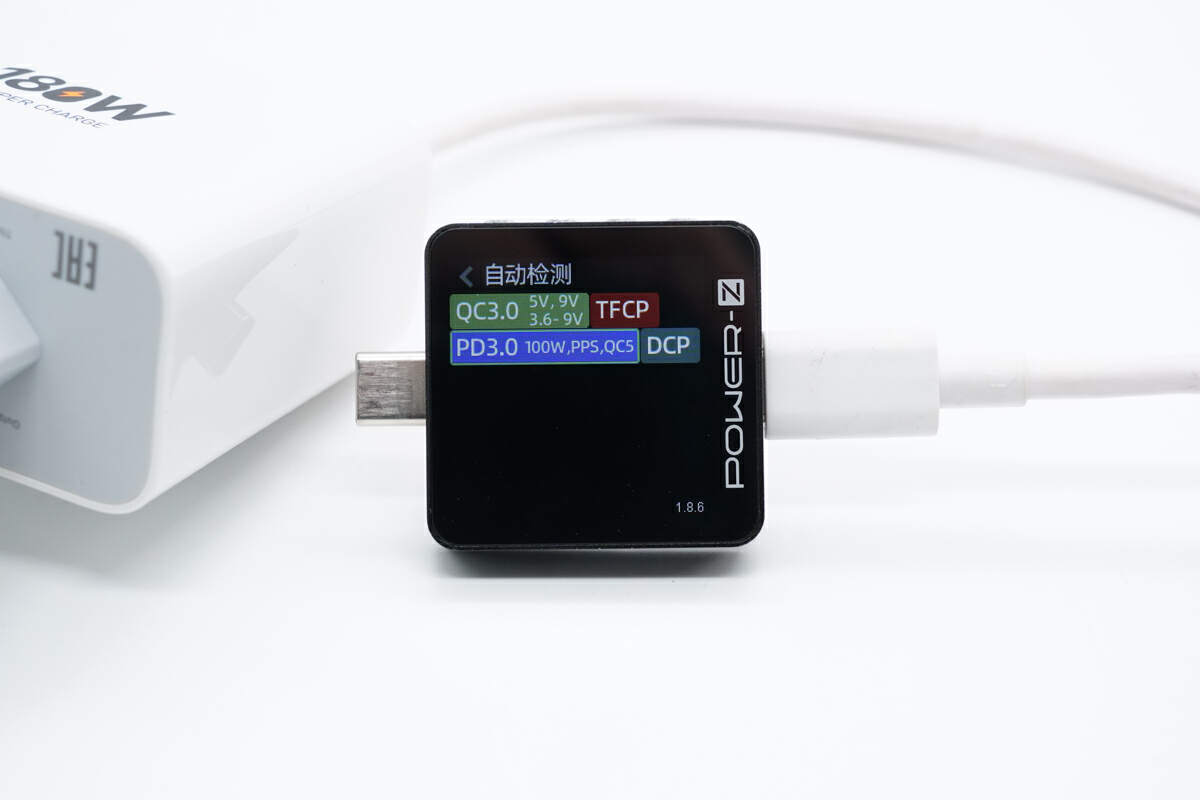

The ChargerLAB POWER-Z KM003C shows the USB-C port can support QC3.0, TFCP, PD3.0, PPS, QC5, and DCP charging protocols.
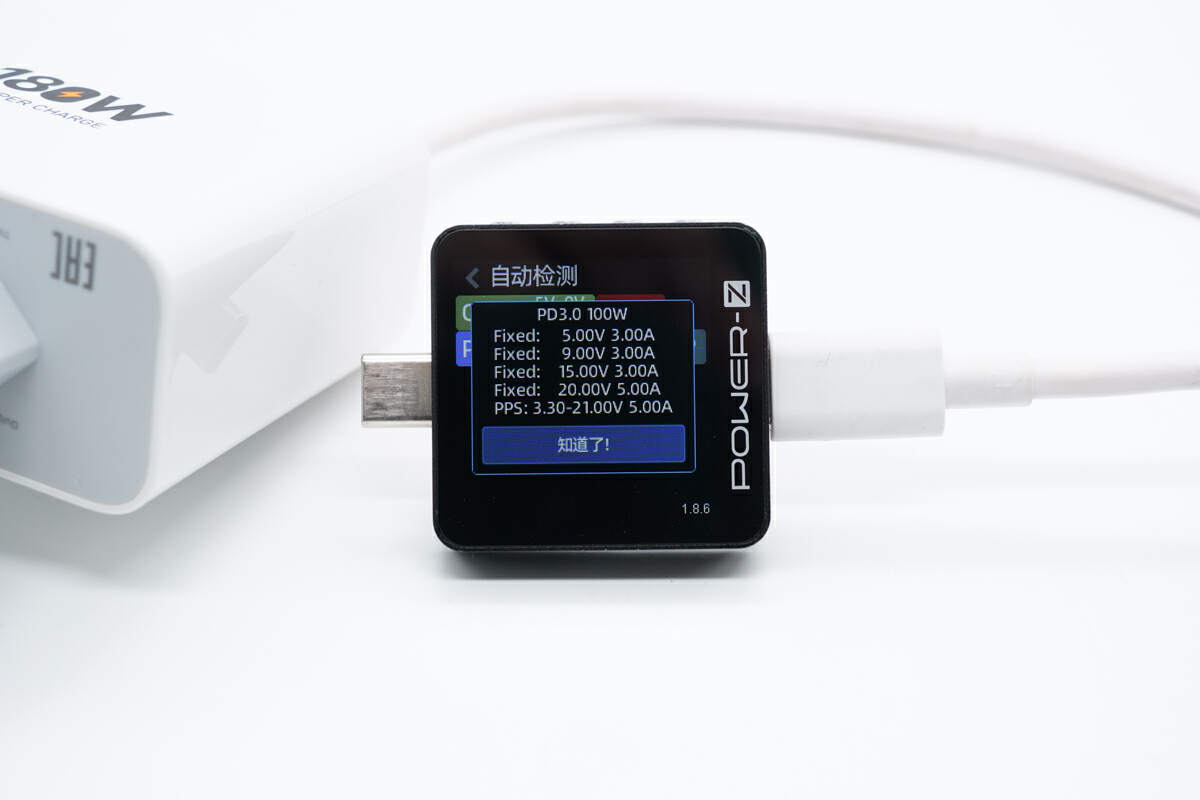

And it has four fixed PDOs of 5V3A, 9V3A, 15V3A, 20V5A, and a set of PPS, which is 3.3-21V5A.
Teardown
After the product's appearance, let's start to take it apart.
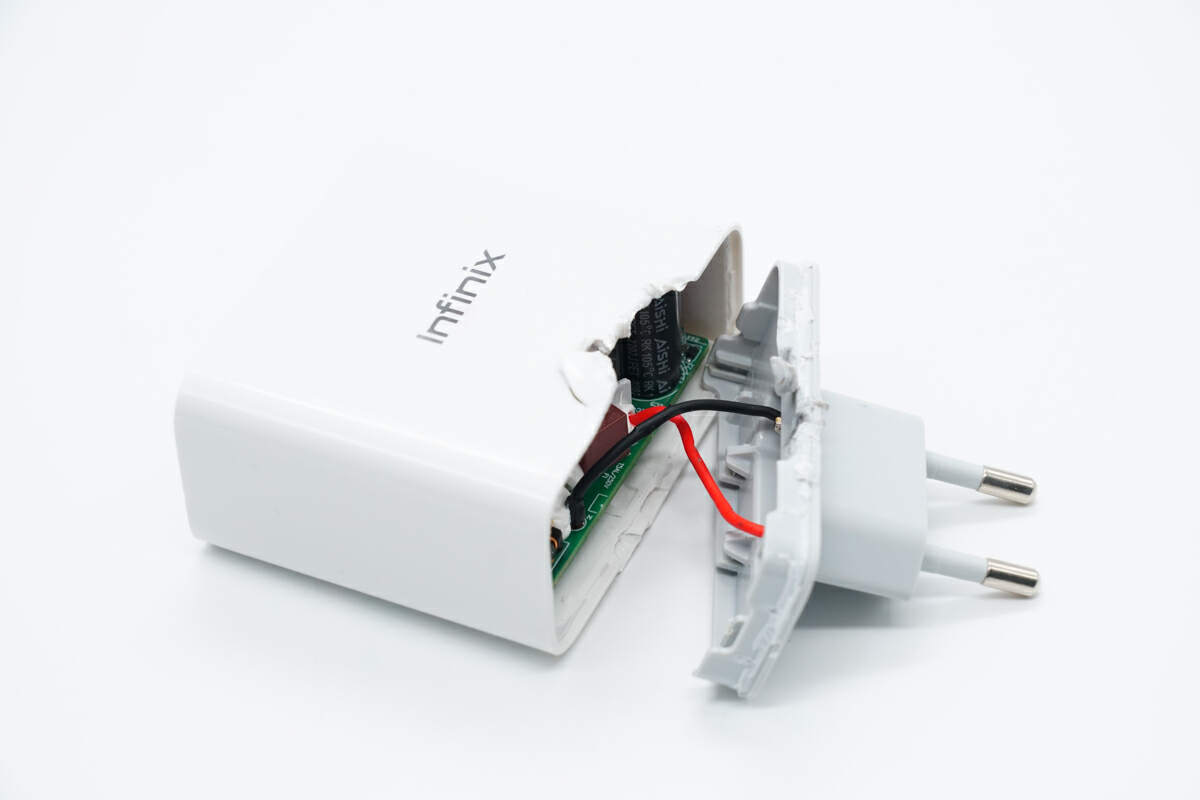
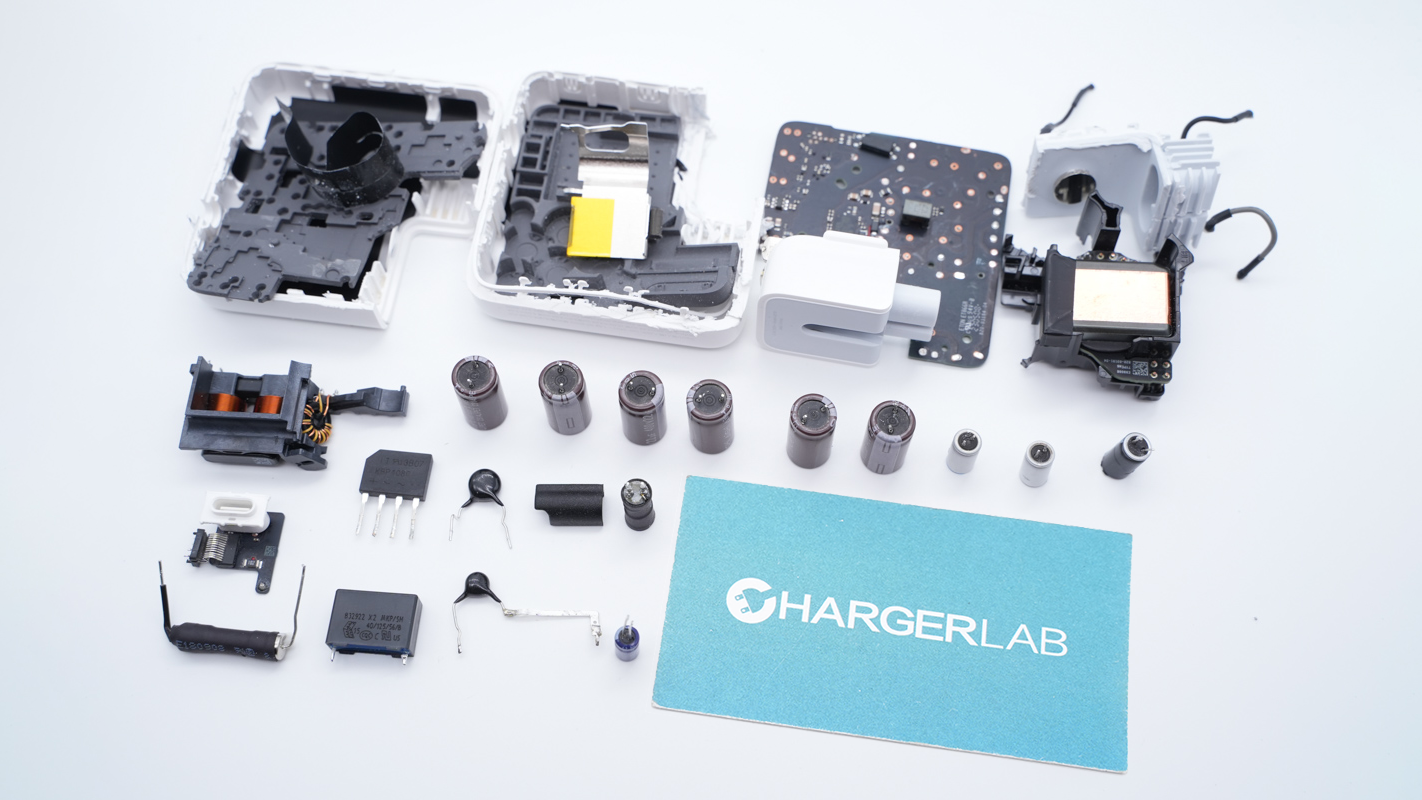
Remove the cover along the gap. The PCBA module and the prongs are connected by wires.
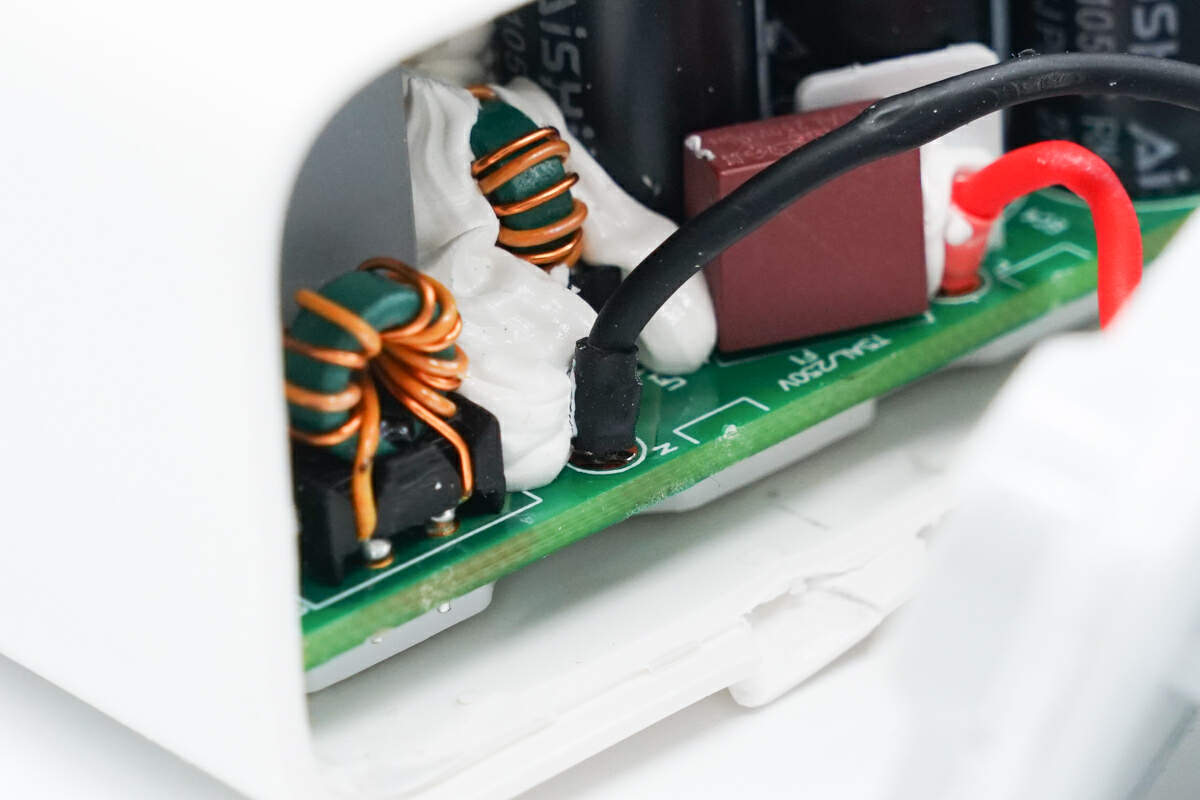

The wires are soldered to the PCBA module.
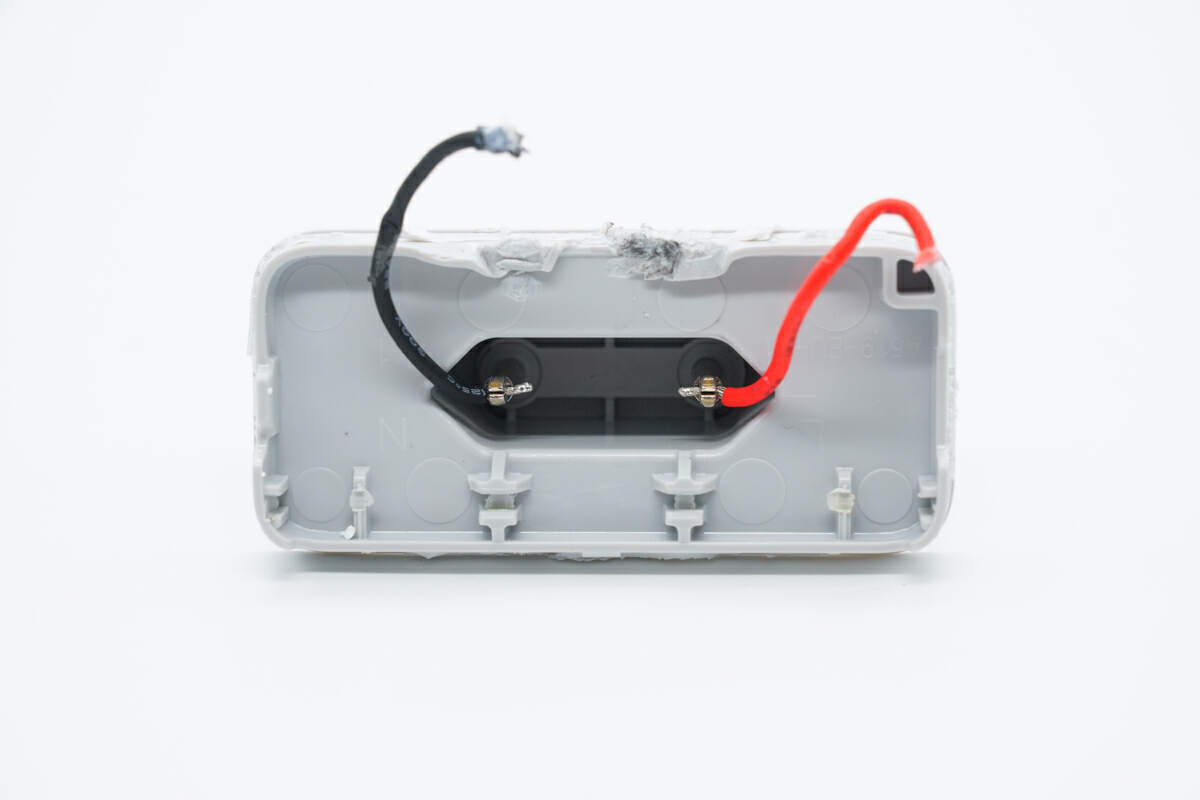

The foldable prongs are connected by crimping.
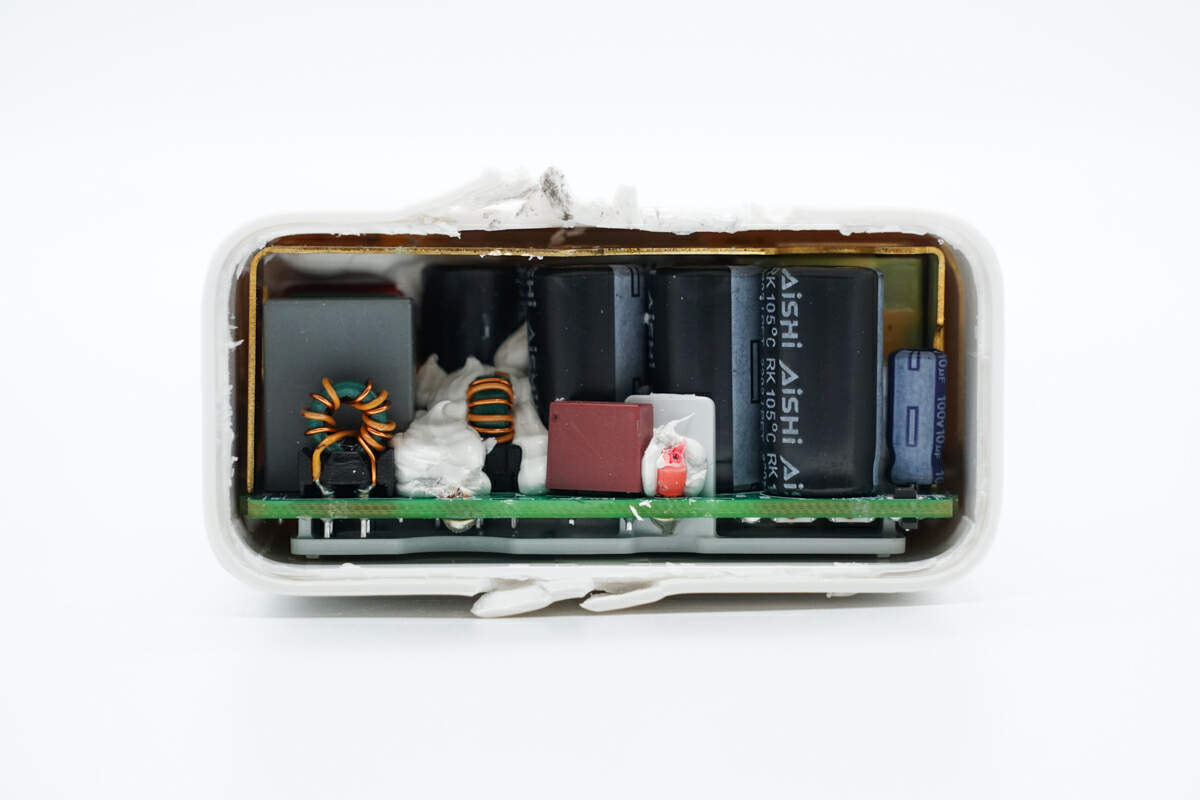

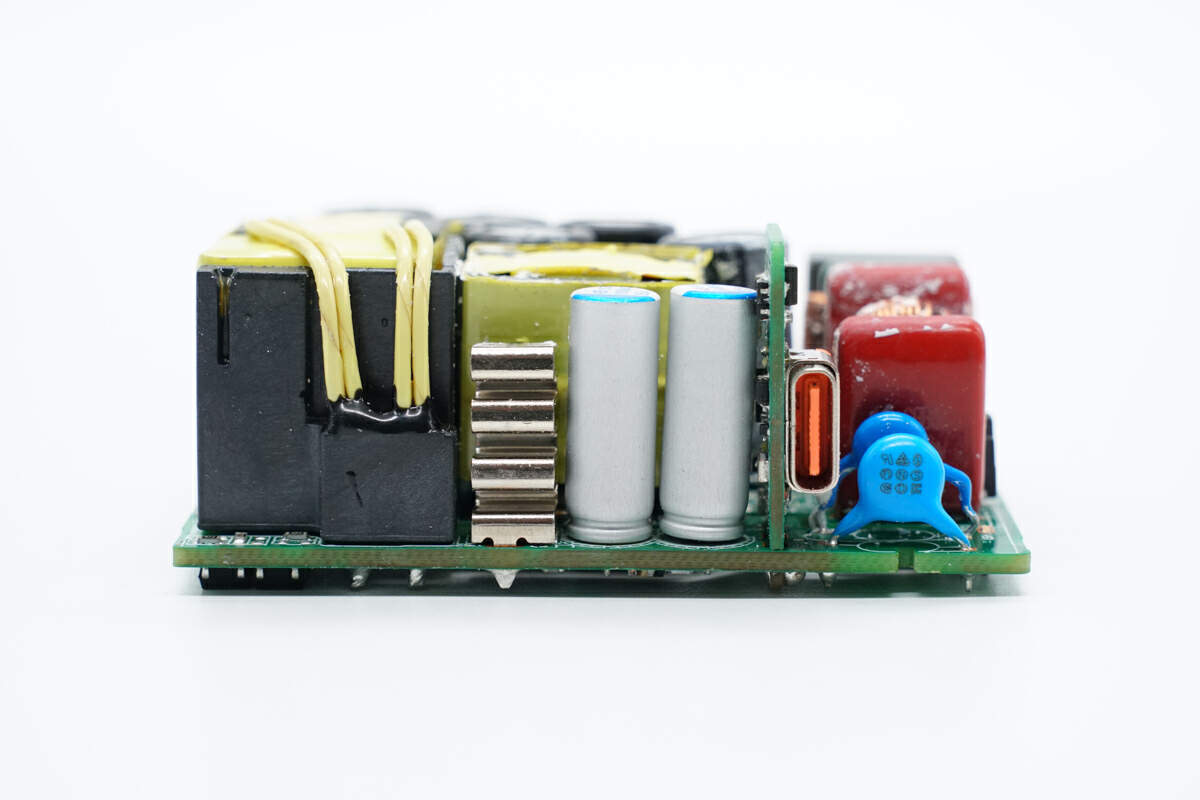
Here is the PCBA module.
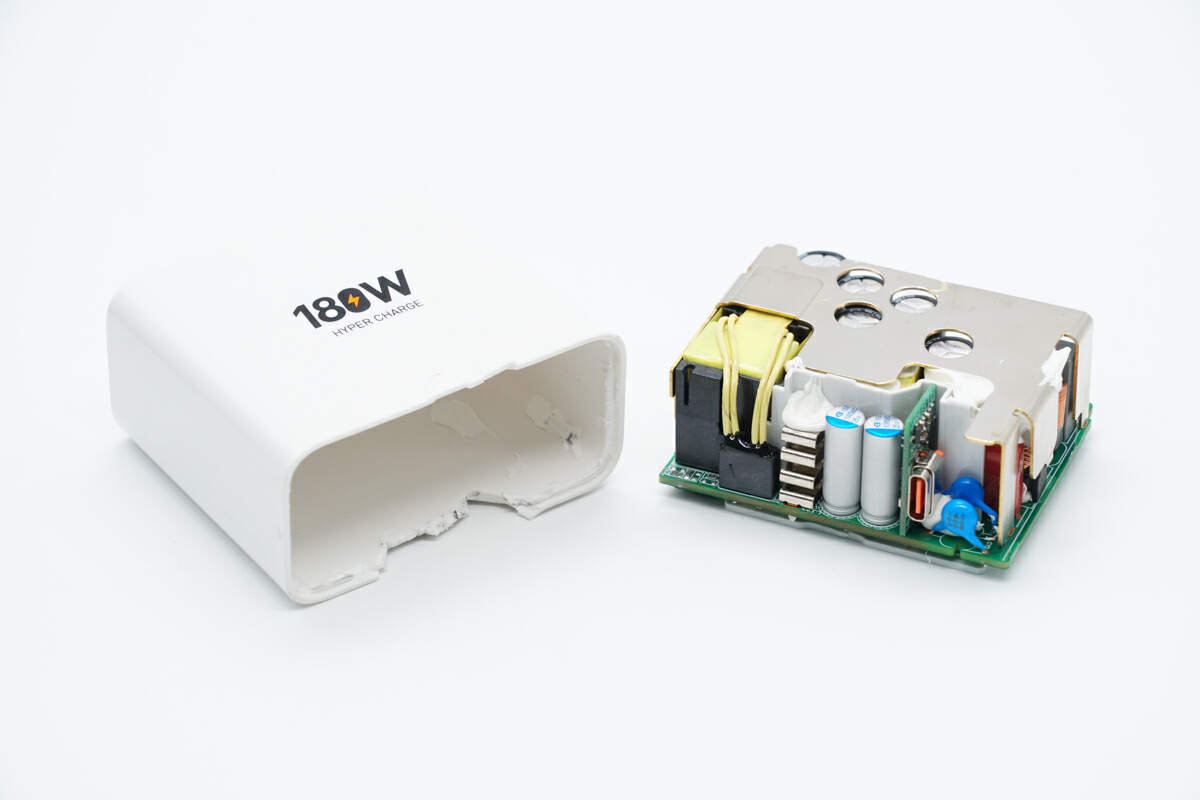

Take out the PCBA module from the case.
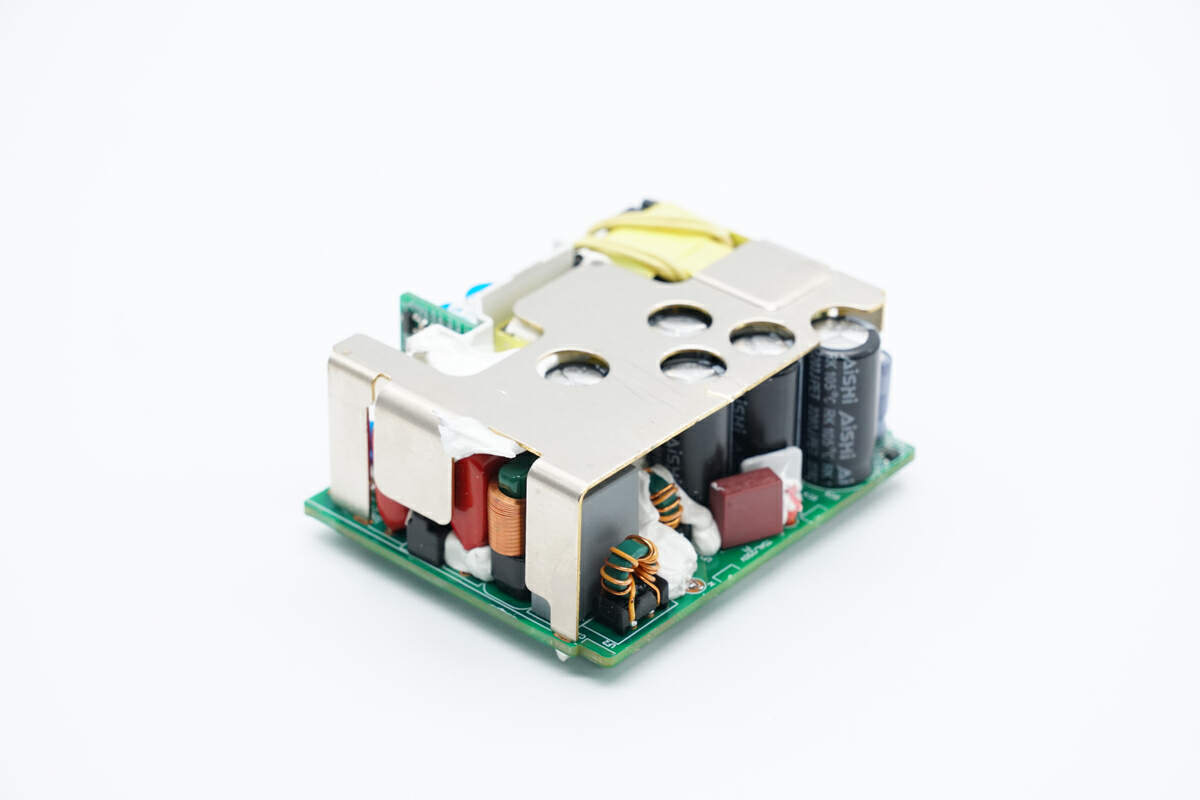

There is a heat sink on the top of the PCBA module.
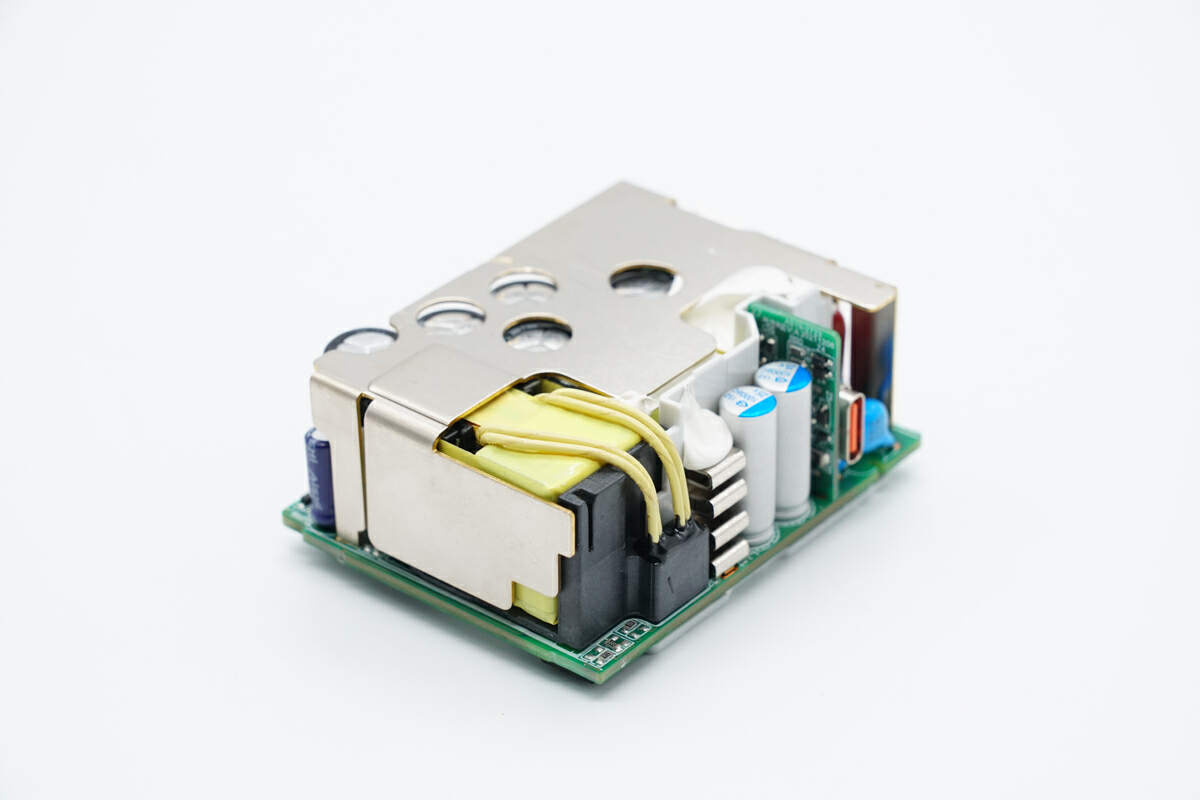

There is a white board between the primary and secondary sides for insulation.
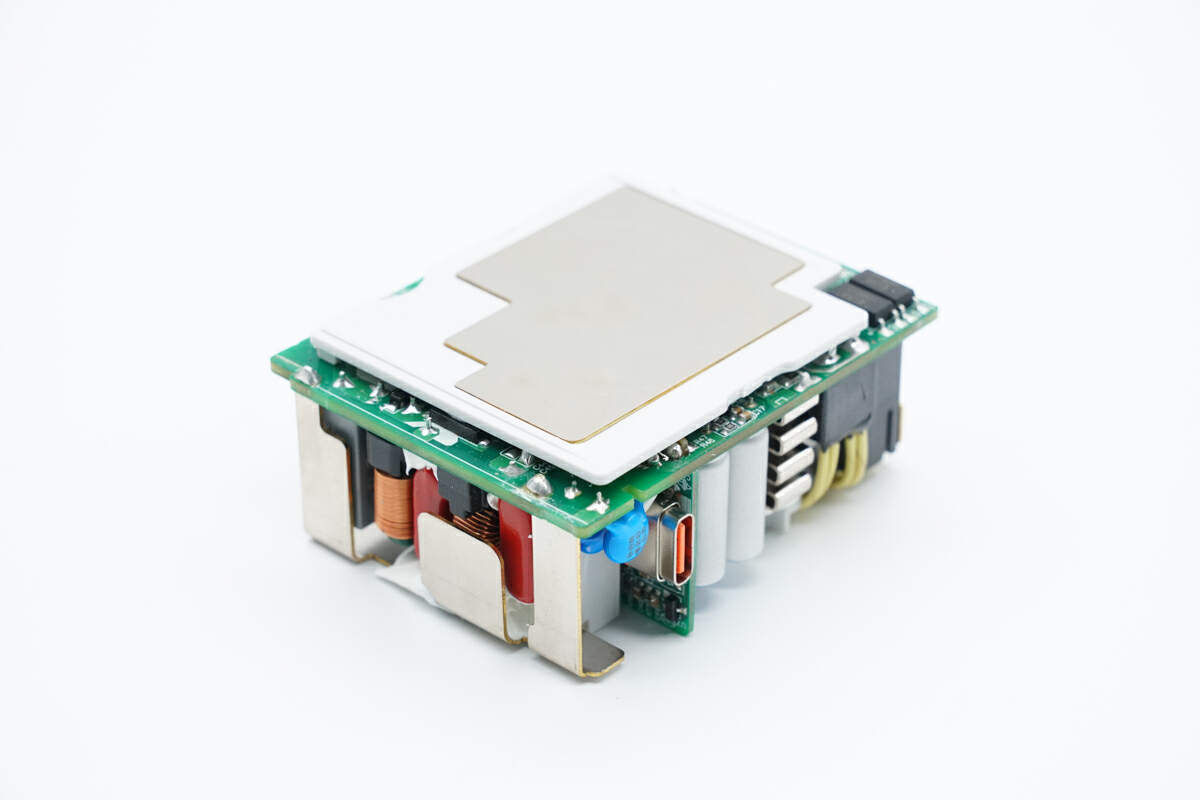

There is also a white plastic board on the back of the PCBA module for isolation. And there is a metal sheet on the board to enhance the heat dissipation.
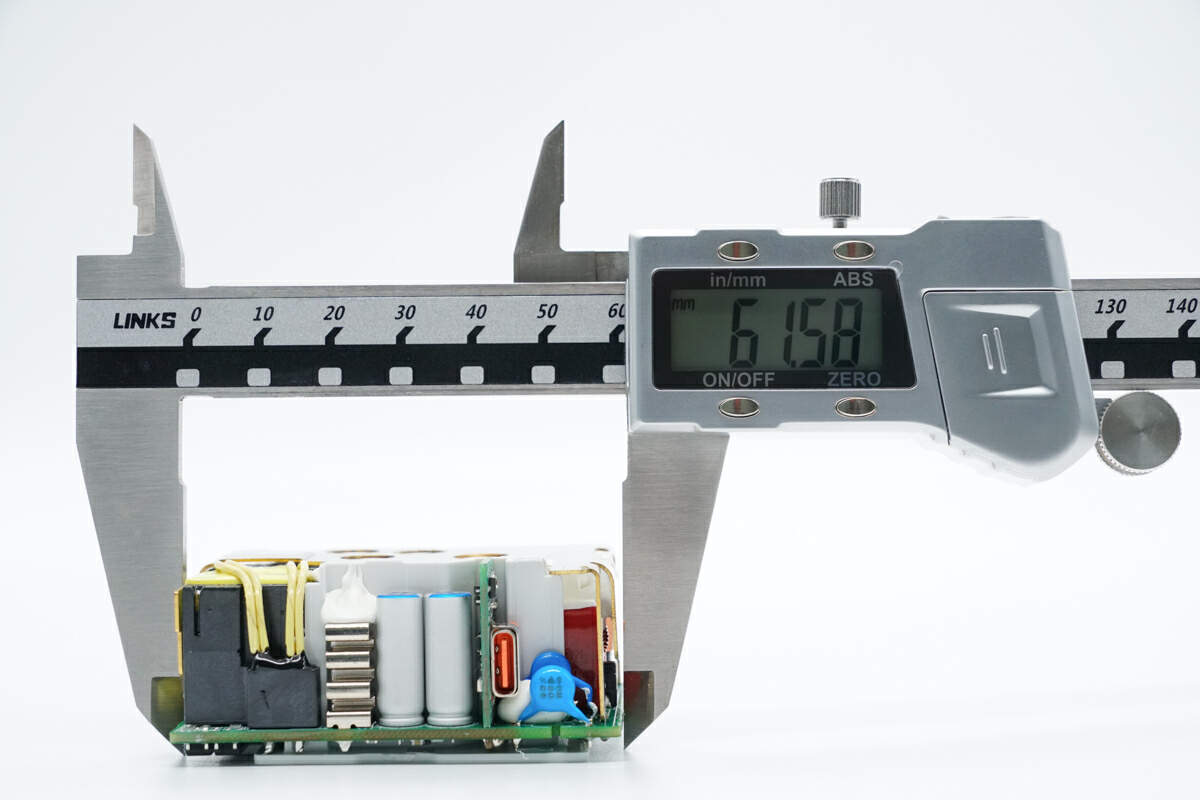
The length of the PCBA module is about 62 mm (2.44 inches).
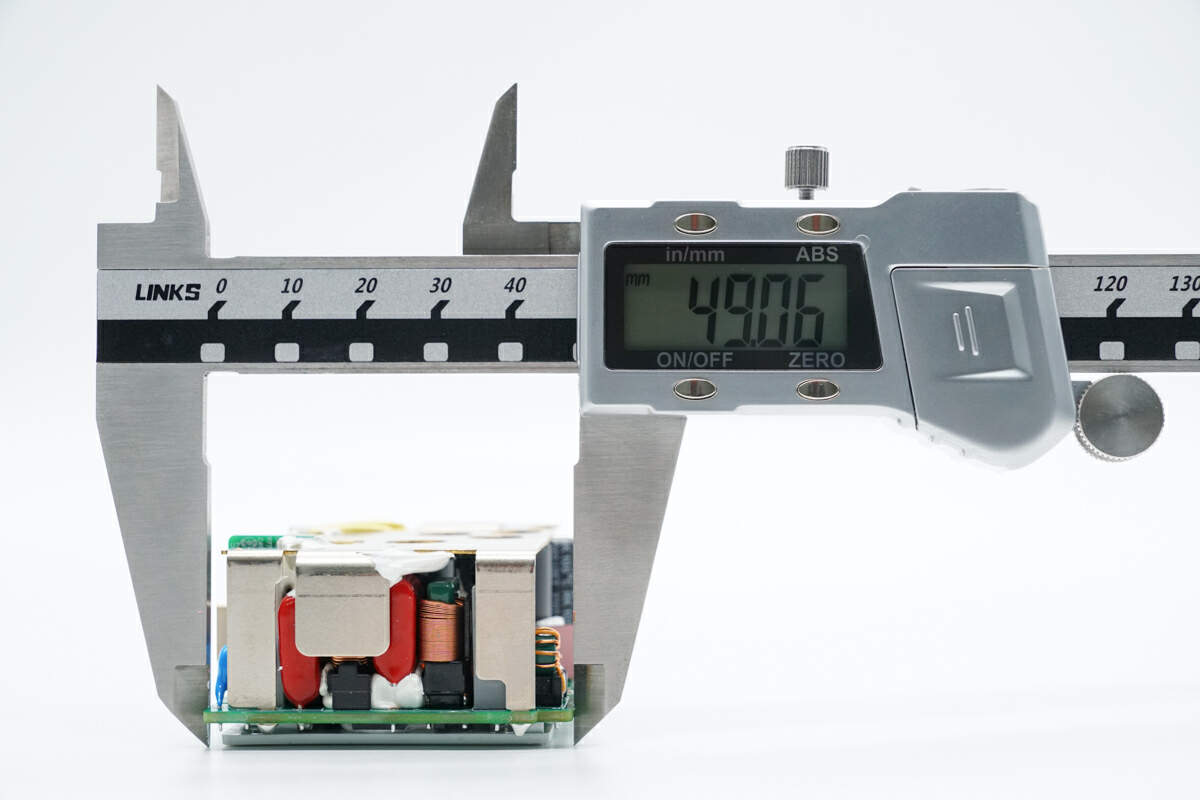
The width is about 49 mm (1.93 inches).
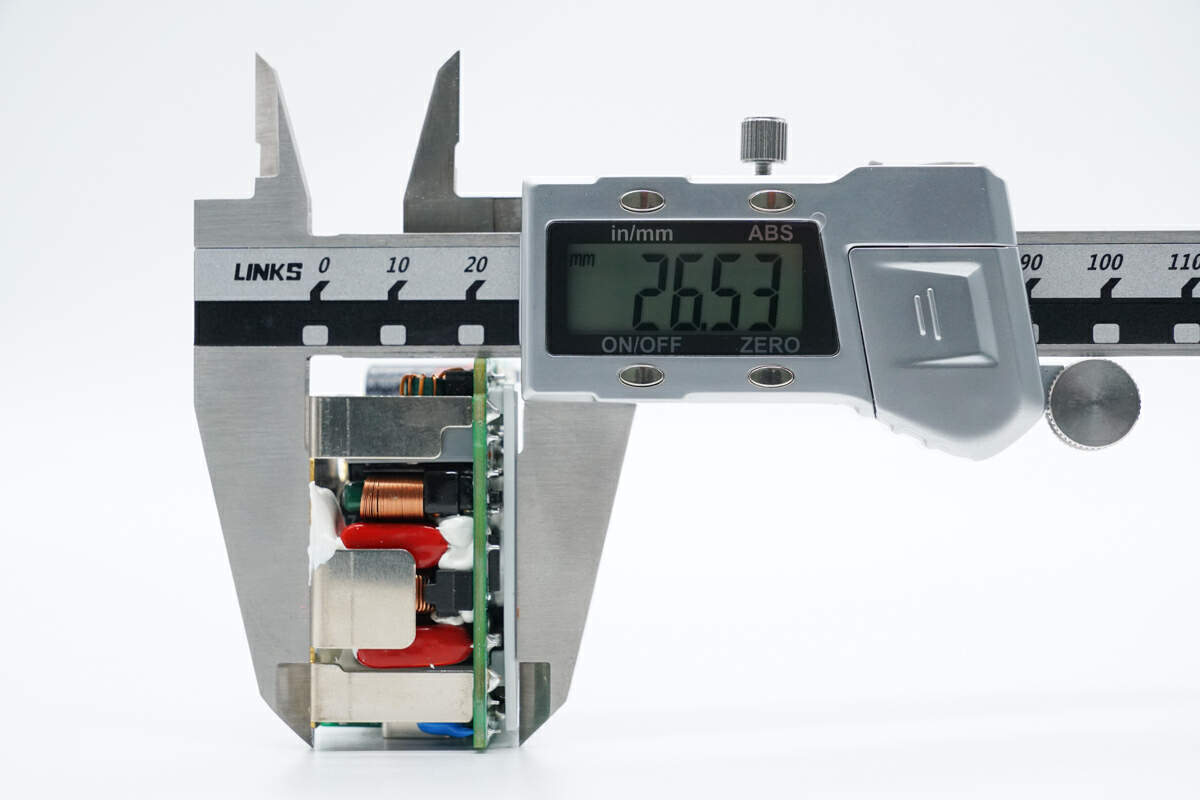

The thickness is about 27 mm (1.06 inches).
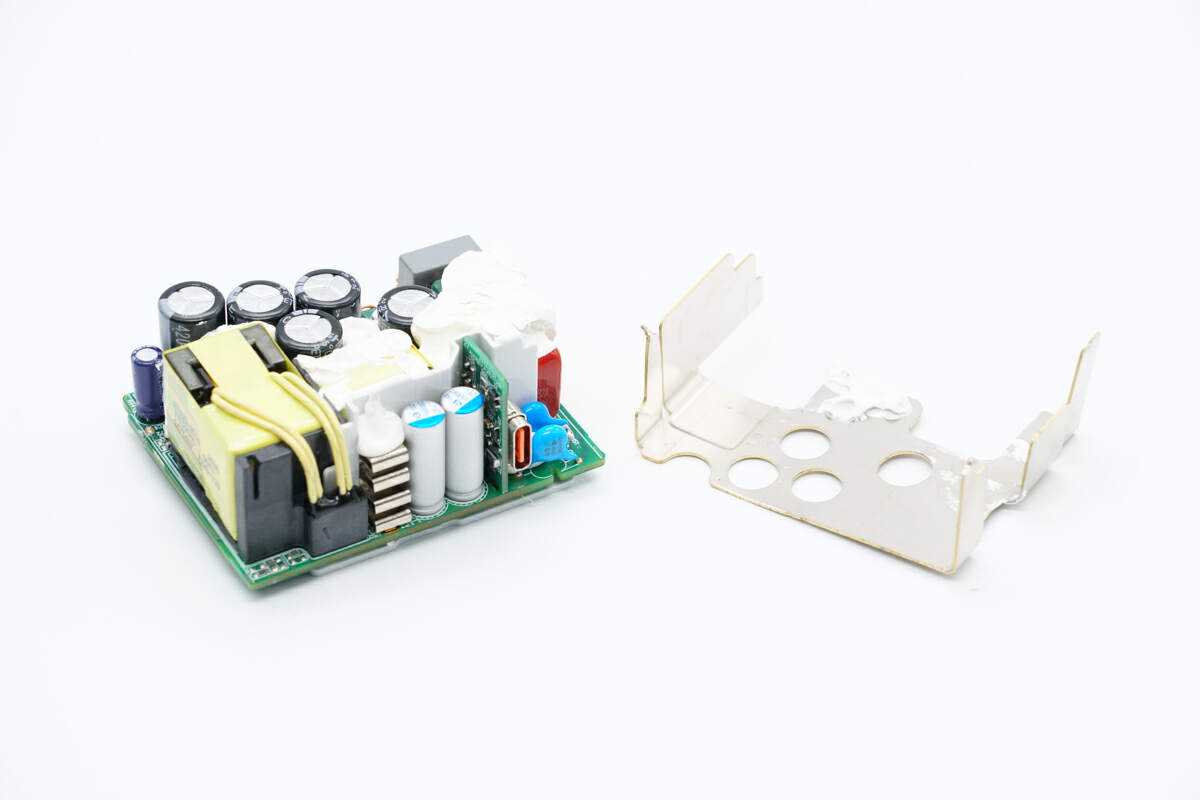

Remove the heat sink. The position corresponding to the PFC boost inductor has potting compound for heat dissipation.
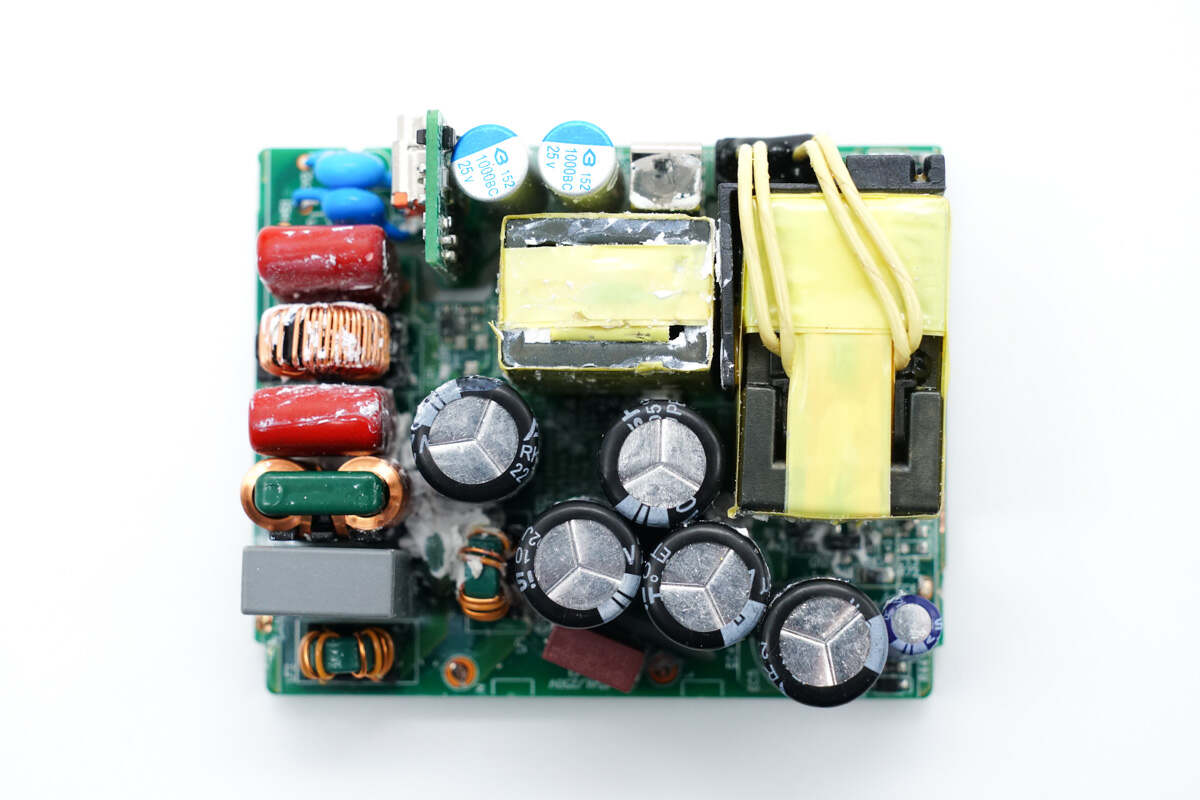

There are fuse, common mode choke, capacitors, inductors, small PCB of USB-C, and transformer on the front.
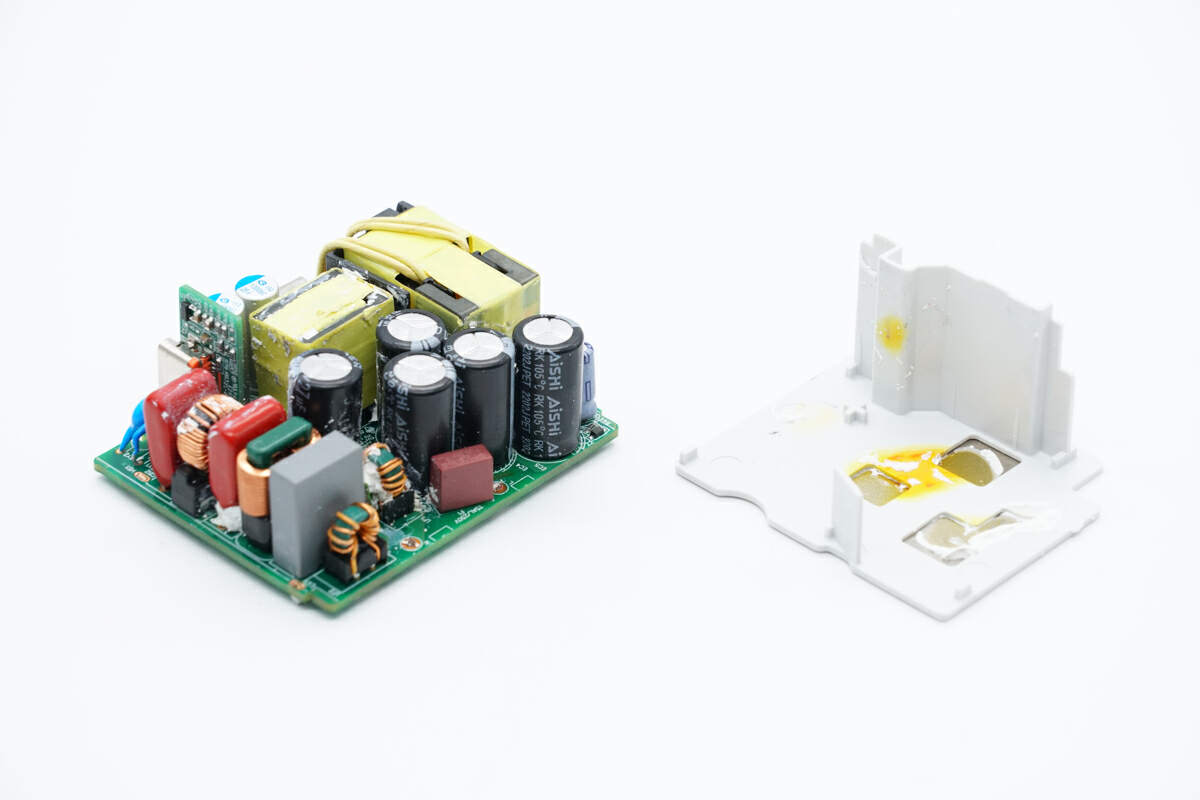

Remove the heat sink on the back of the PCBA module. The position corresponding to the GaN FET and rectifier has potting compound for heat dissipation.
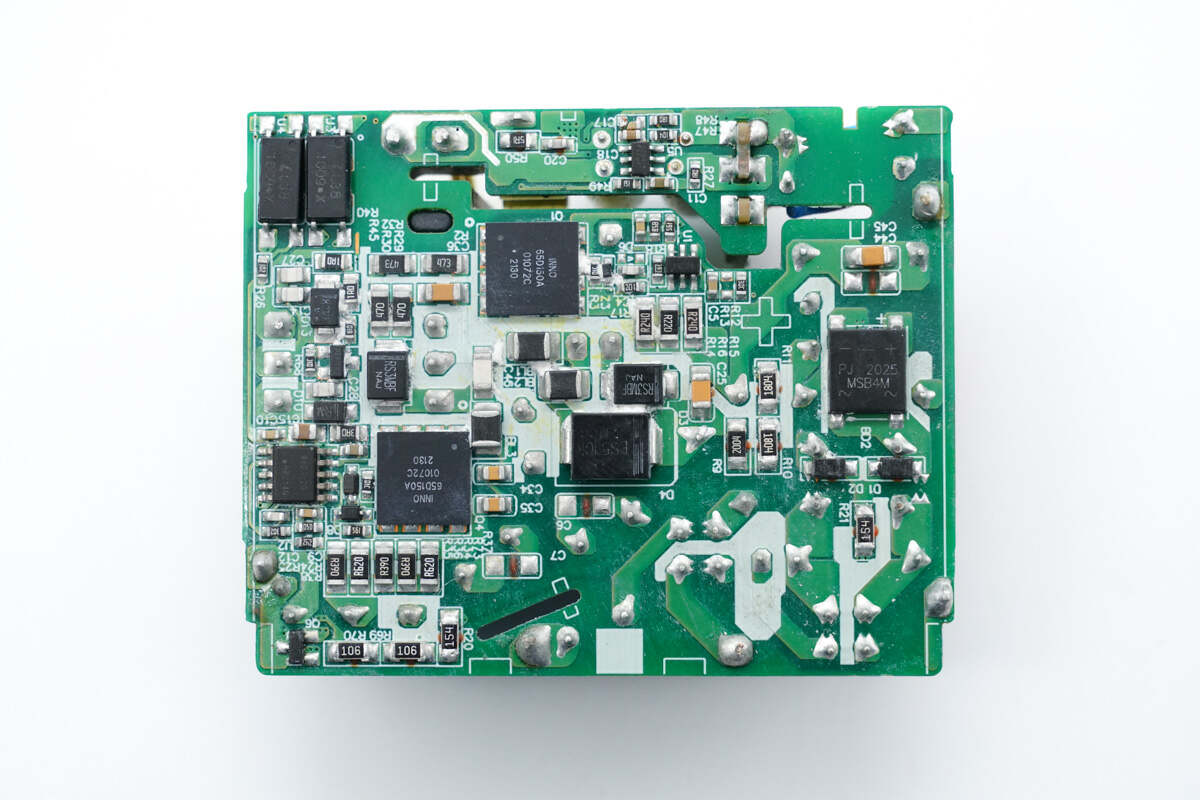
The PFC controller, PFC rectifier, flyback controller, optocouplers, SMD Y capacitor, and synchronous rectifier controller are on the back.
ChargerLAB found it adopts a PFC circuit and flyback topology with synchronous rectification.
Next, we will take a look at each component starting from the input end.
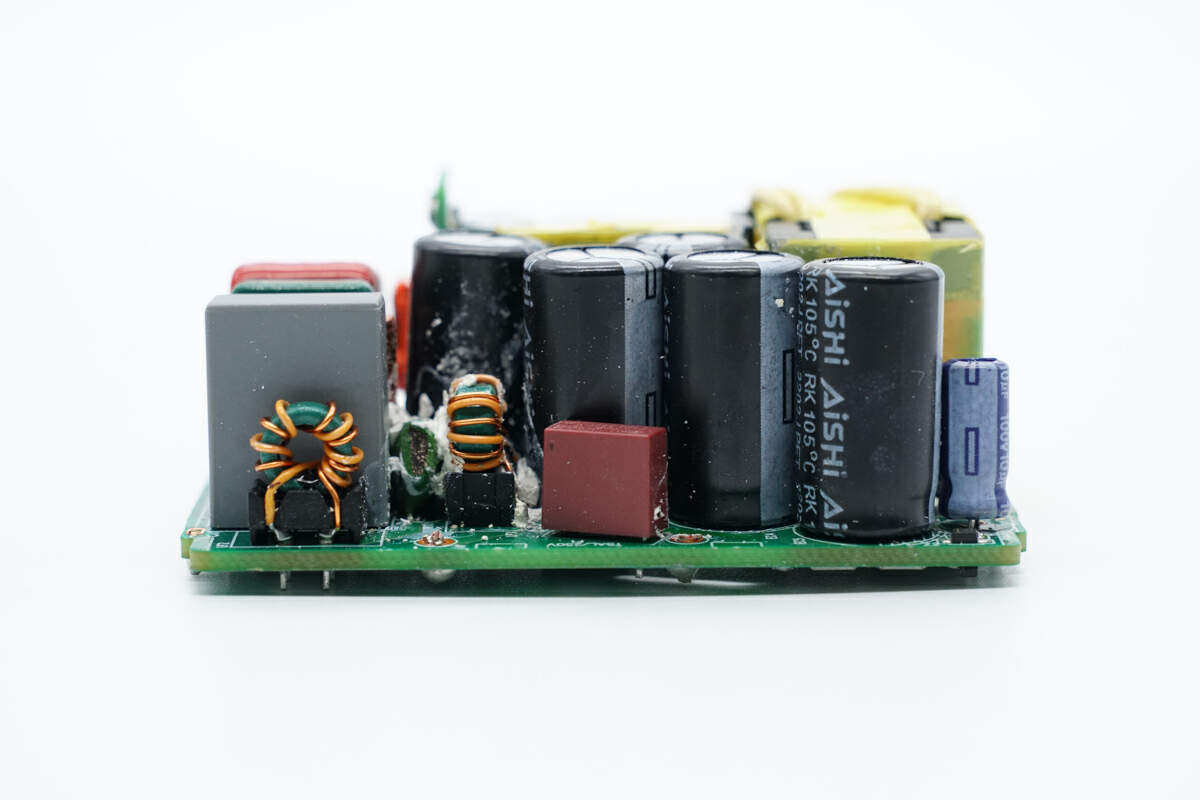
There are fuse, common mode choke, and safety X2 capacitor at the input end.
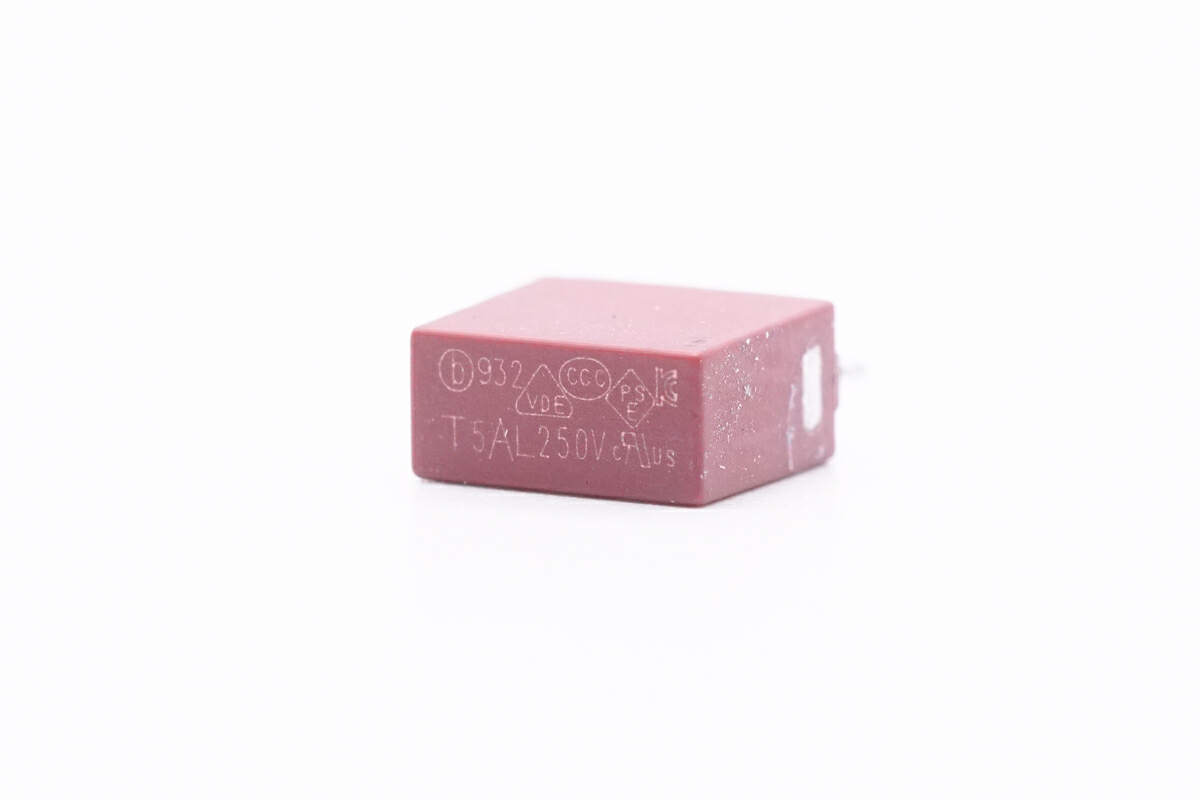

The input fuse marked with 932 is from Betterfuse. 5A 250V.
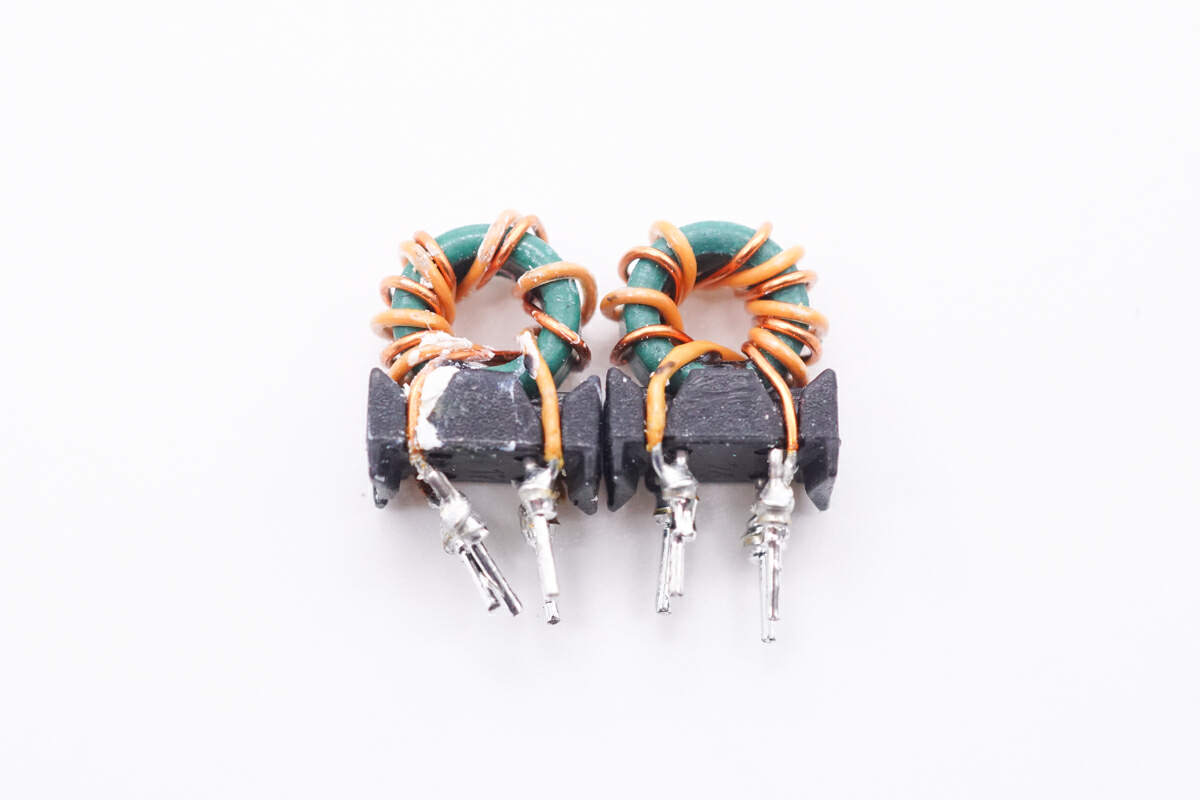

The common mode chokes are wound with magnets and insulated wires, and they're also insulated with frames.
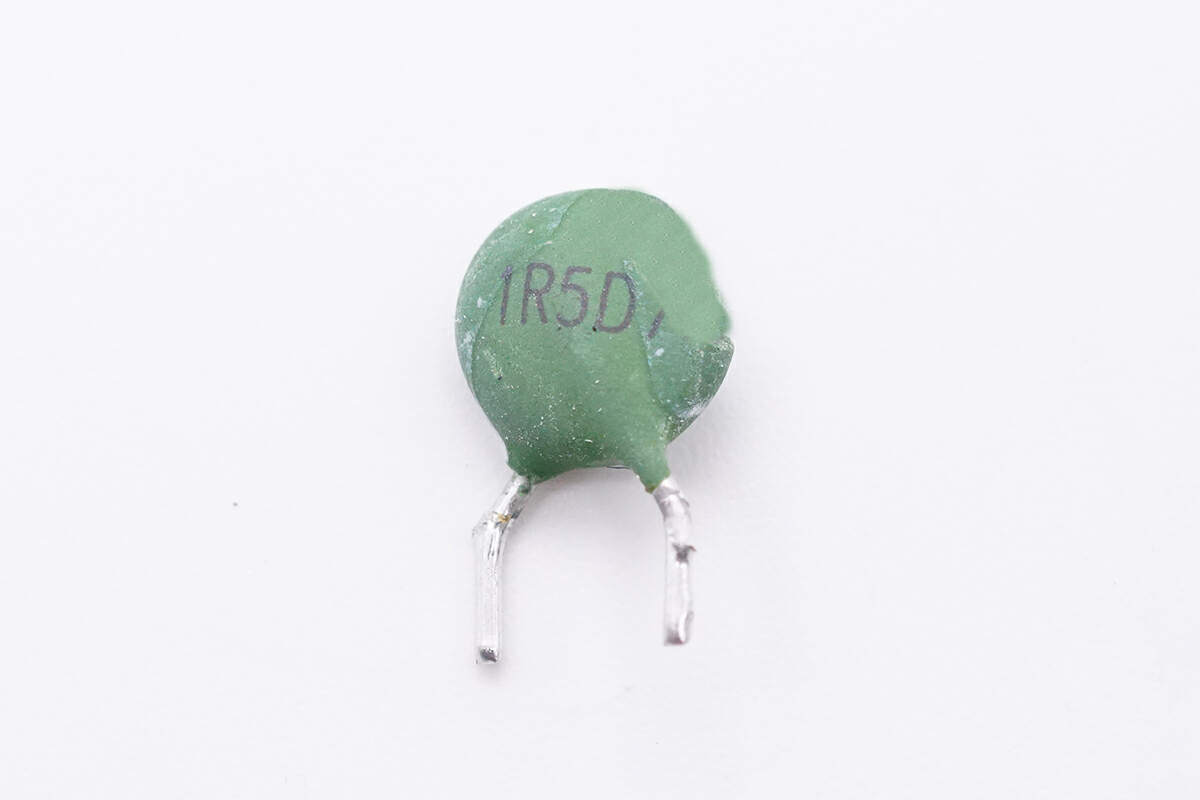

The green thermistor is used to suppress the surge current.
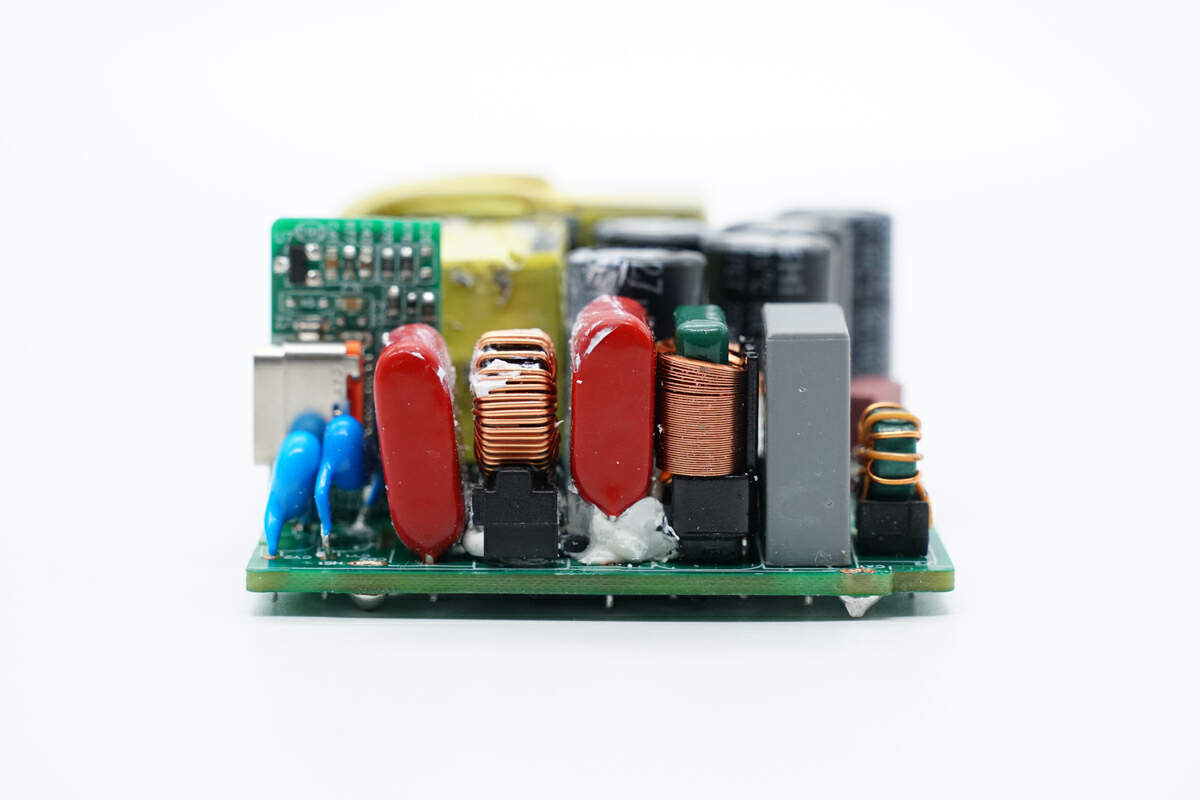

There are common mode choke, safety X2 capacitor, film filter capacitors, and blue Y capacitors on the side of the PCBA module.

The safety X2 capacitor is from SEC. 0.33μF.
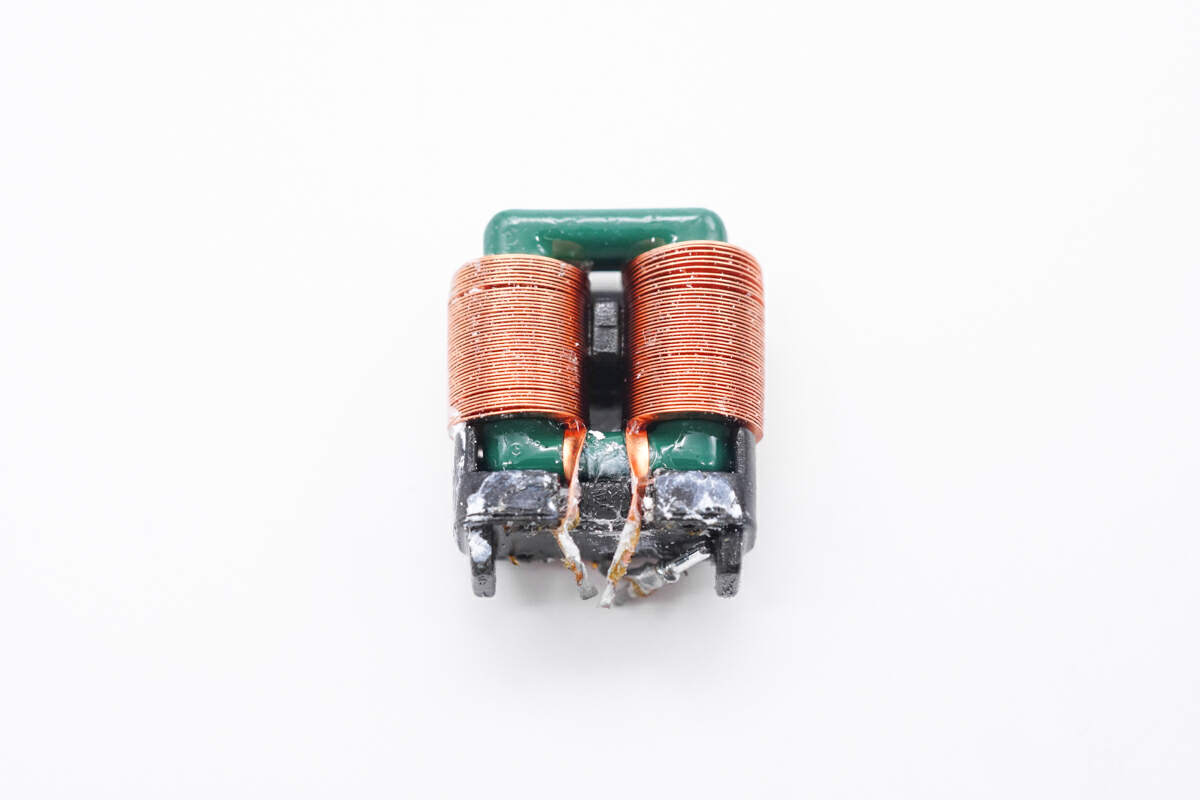

Another common mode choke is wound with flat copper wire, and insulated with a frame.
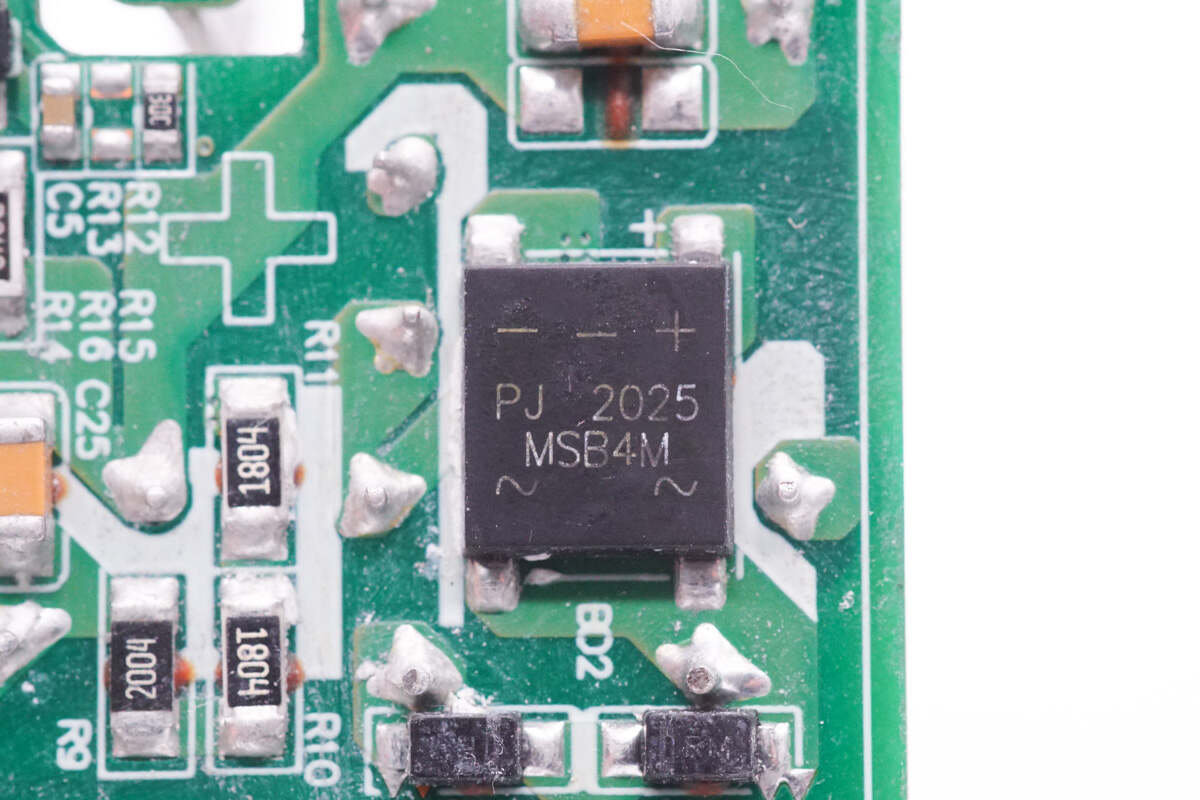

The bridge rectifier is from PANJIT. Model is MSB4M. 1000V 4A.
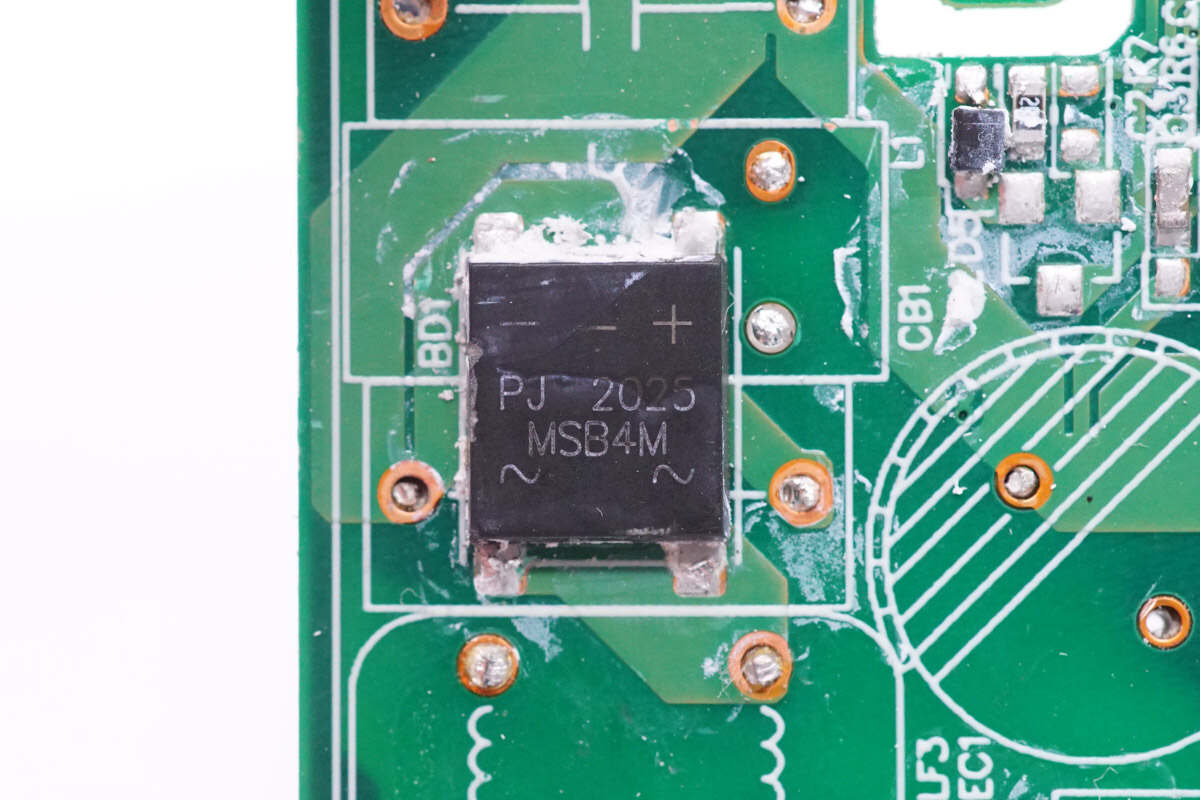
The other bridge rectifier is the same as the previous one. The two bridge rectifiers can share the heat equally.
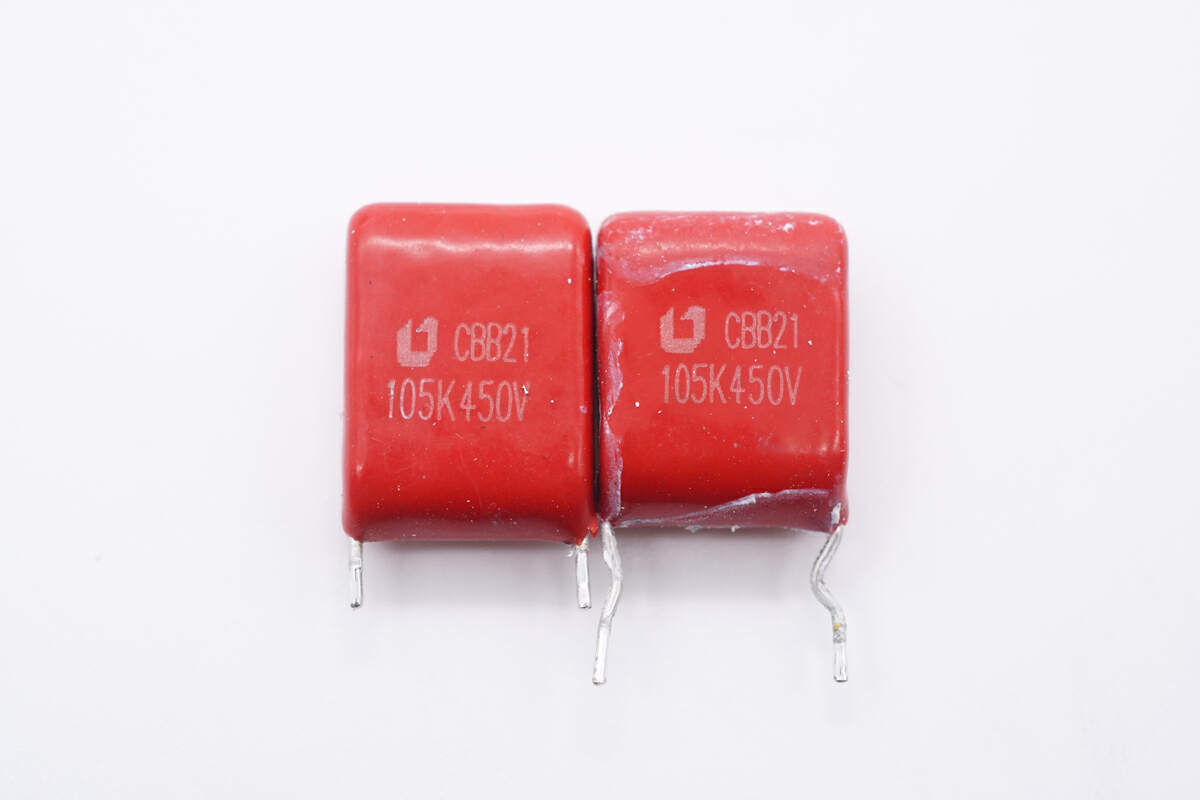

There are two film filter capacitors. 1μF 450V.
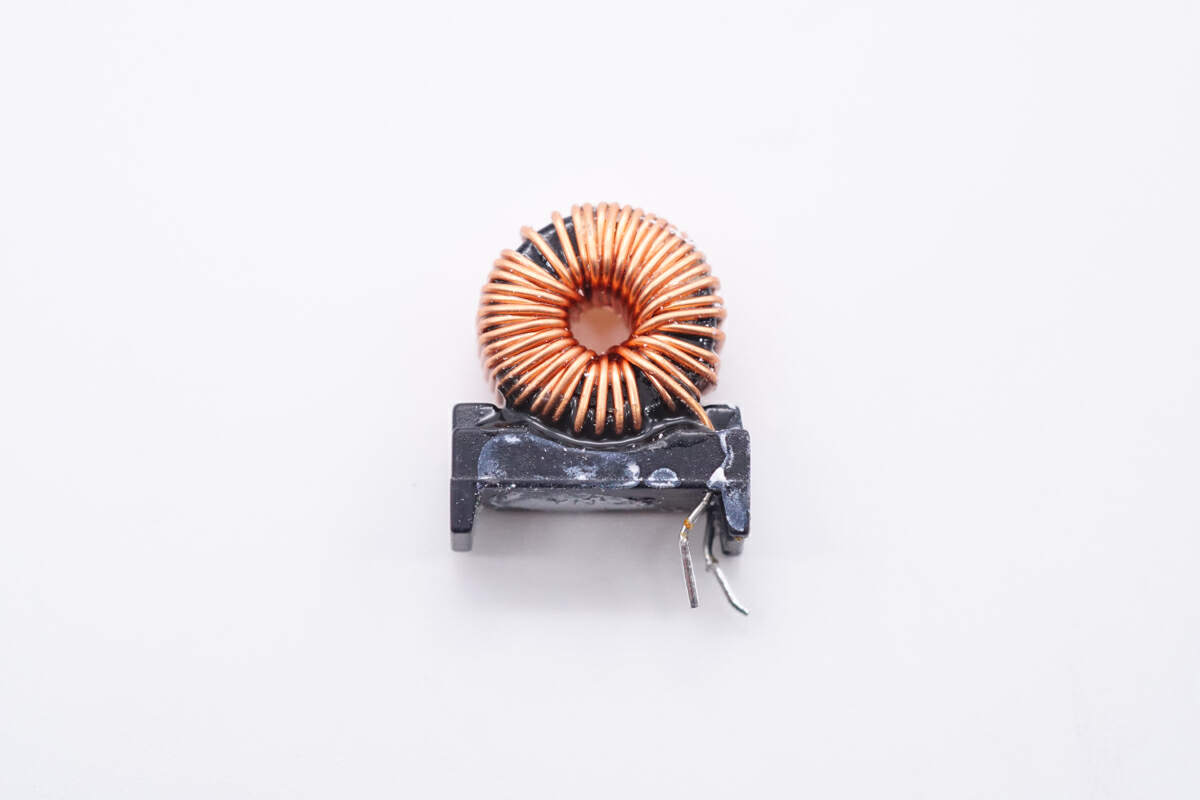

The filter inductor is wounded with magnetic ring and insulated by a black frame.
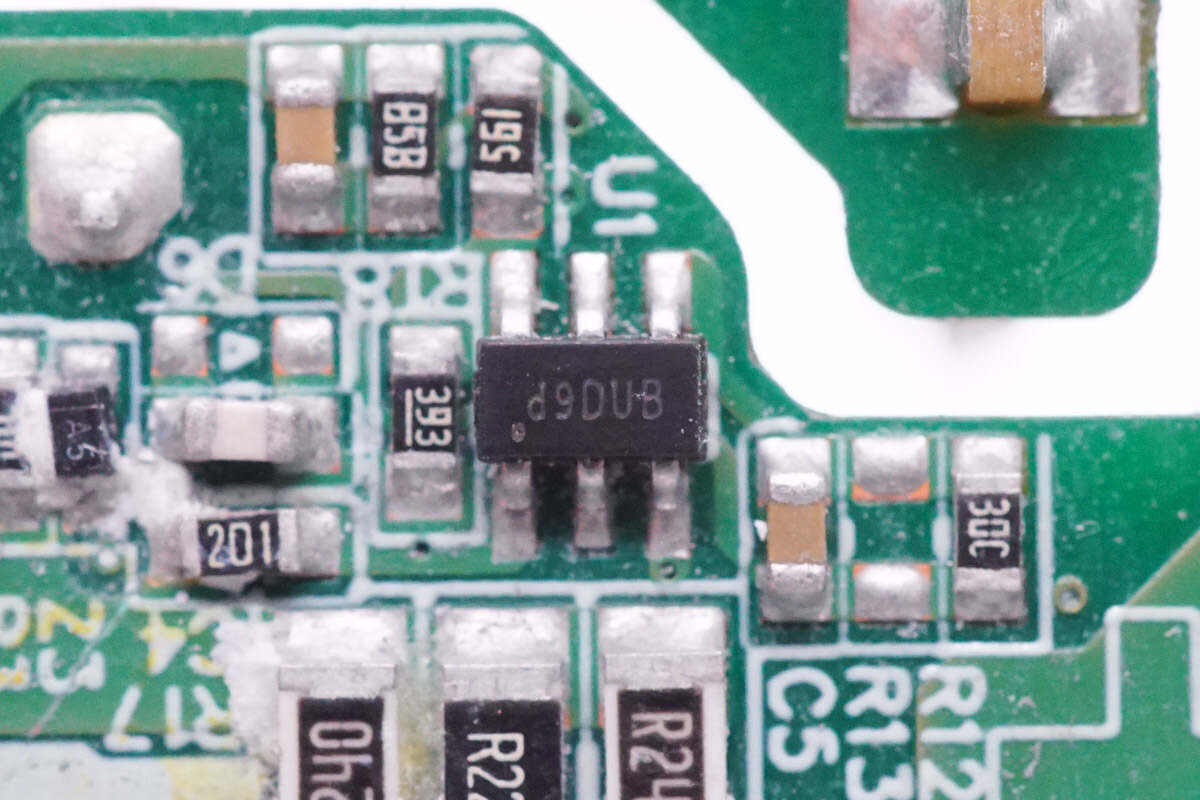
The PFC controller is from Silergy. It integrates the boost converter for high efficiency. Model is SY5072B.
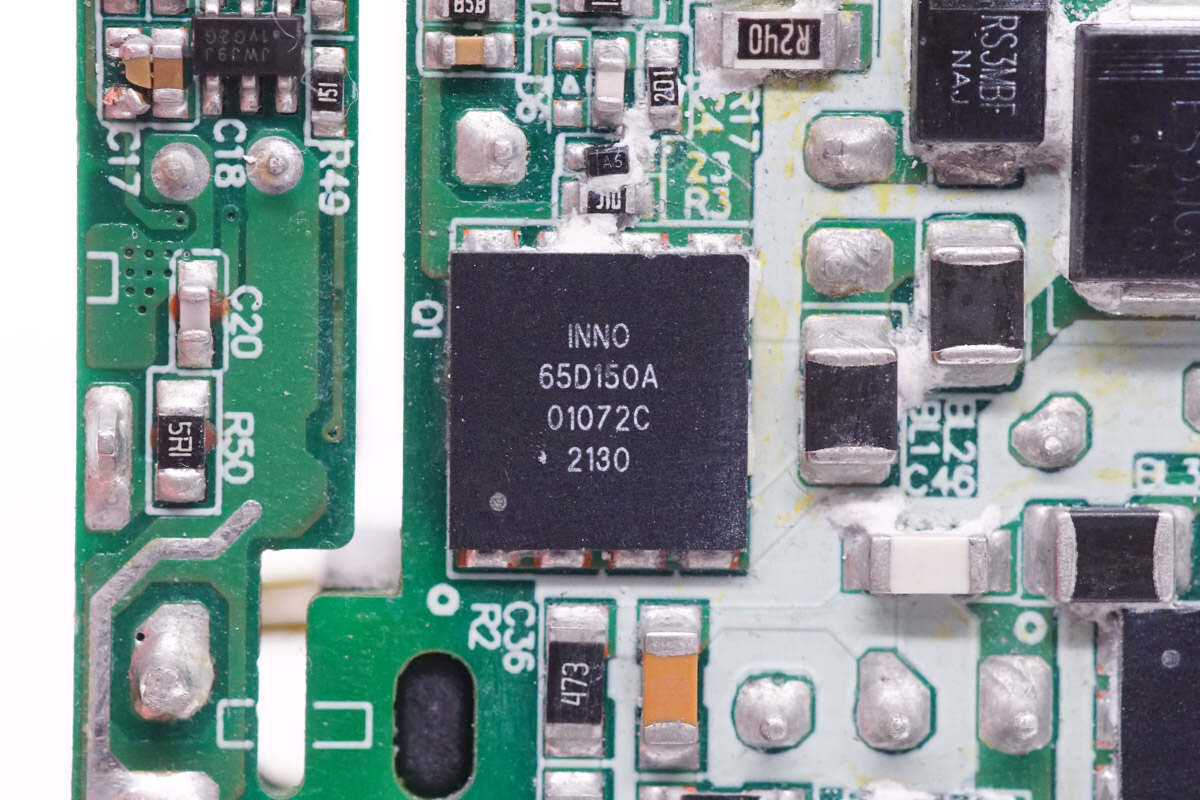
The PFC boost MOSFET is from Innoscience and adopts DFN8 x 8 package. It supports high switching frequency and has the low gate charge and output charge. Model is INN650D150A. 650V 150mΩ.

The PFC boost inductor is wound with ATQ17 magnetic core. 180W.
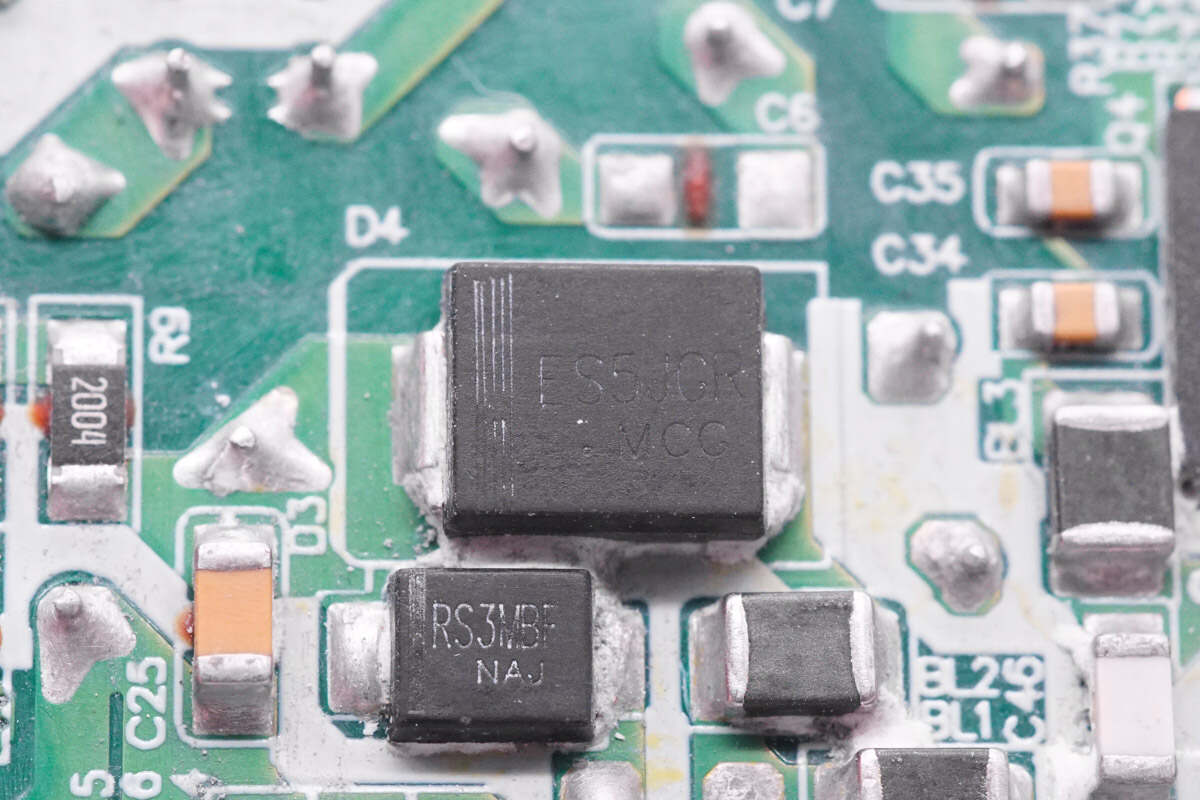
The PFC rectifier is from Pingwei. Model is ES5JGR. 5A 600V.
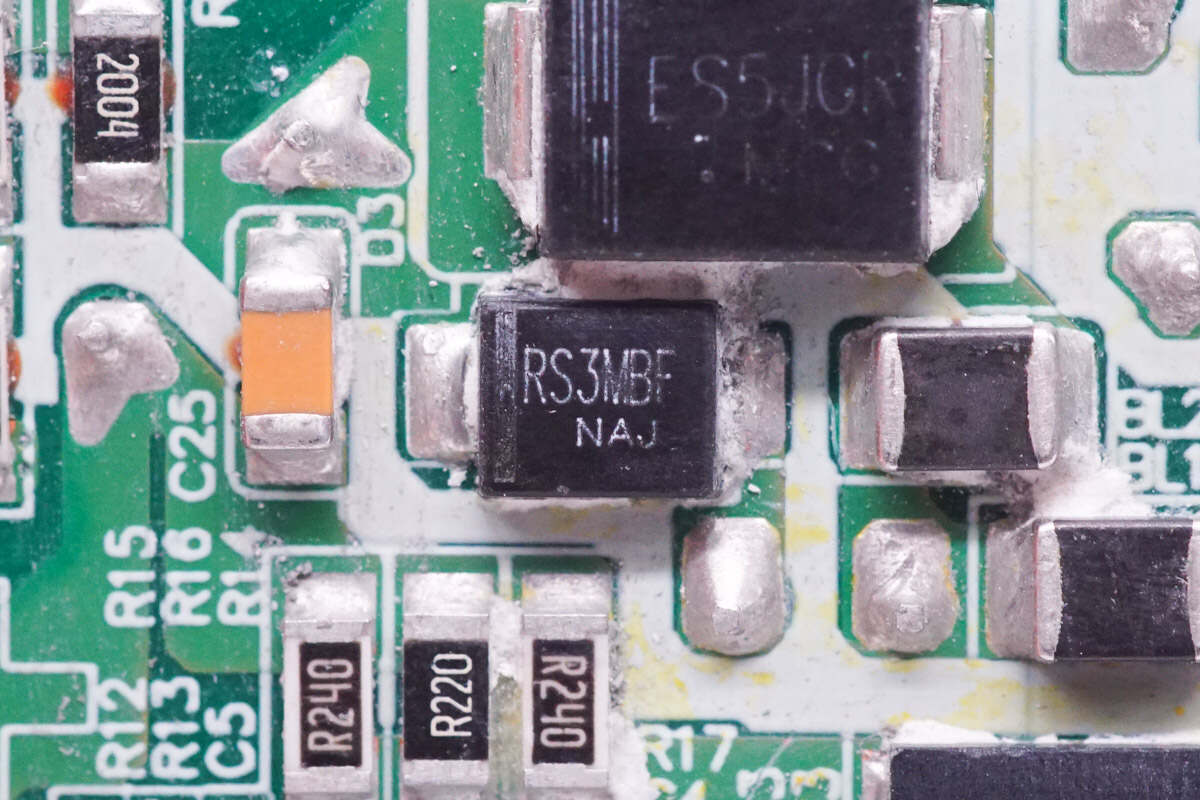
The diode is marked with RS3MBF.
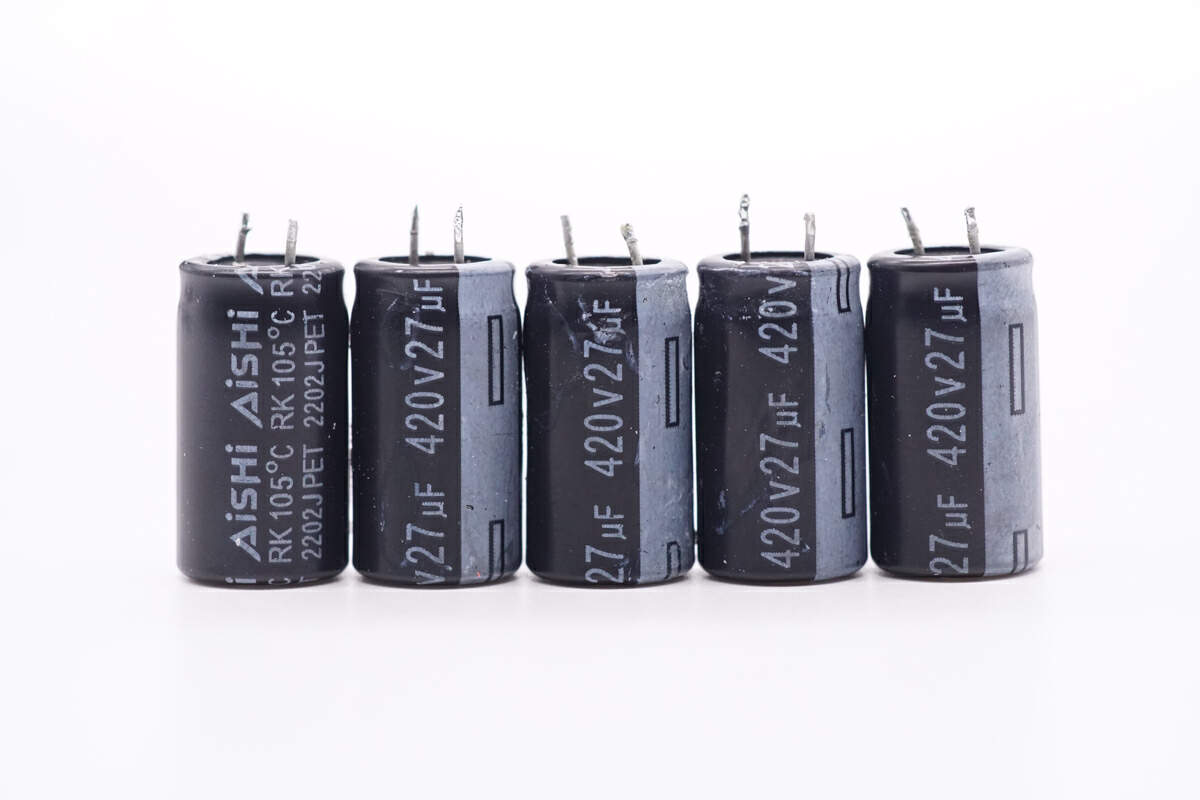

These electrolytic capacitors for input filtering are from AiSHi RK series and they are connected in in parallel. 420V 27μF for each. The total capacity is 135μF.
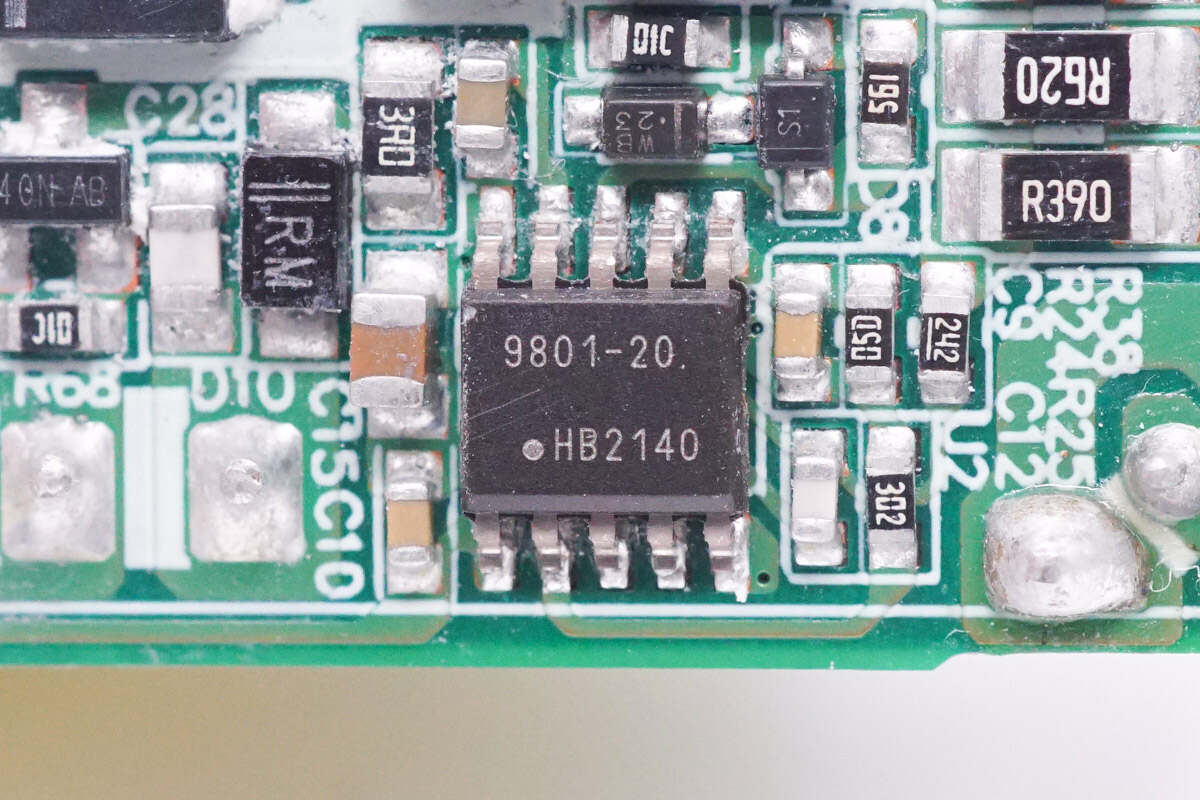
The PWM controller is from Dialog. It is a digital flyback controller that supports zero-voltage switching and adaptive multi-mode control operation. Model is iW9801.
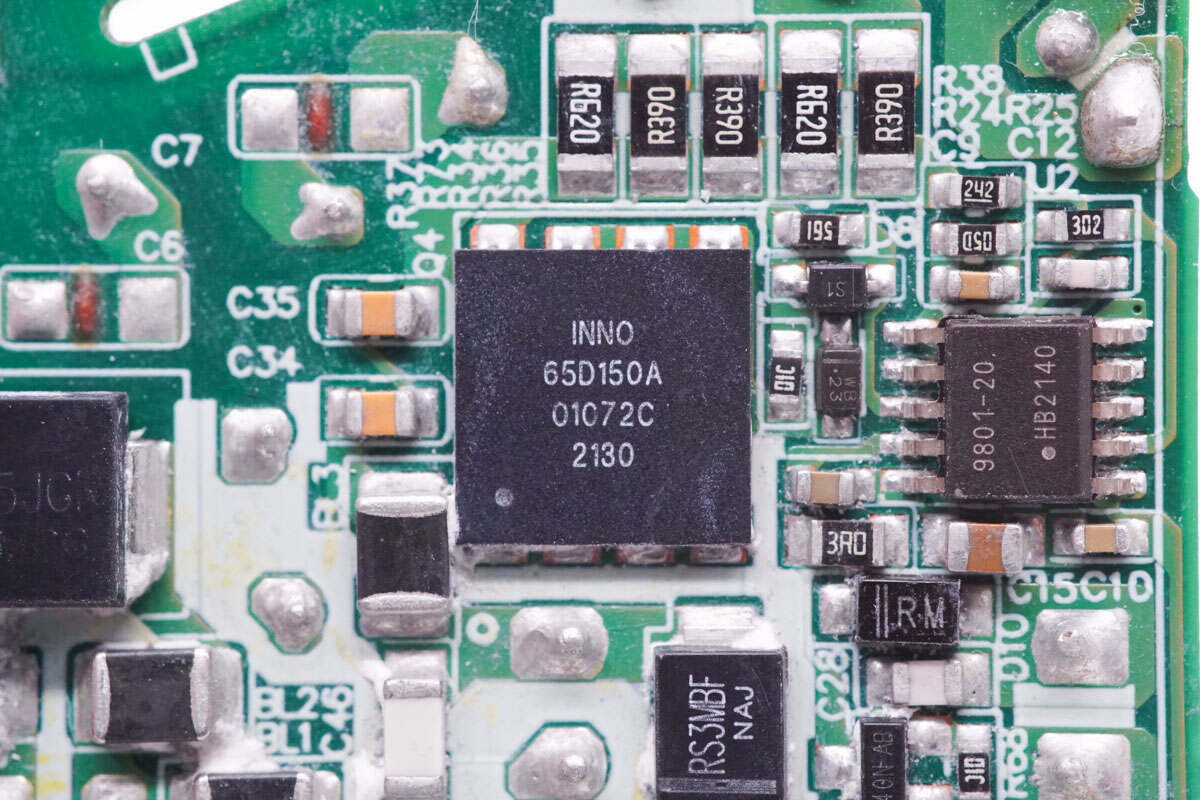
This MOSFET is from Innoscience. Model is INN650D150A.
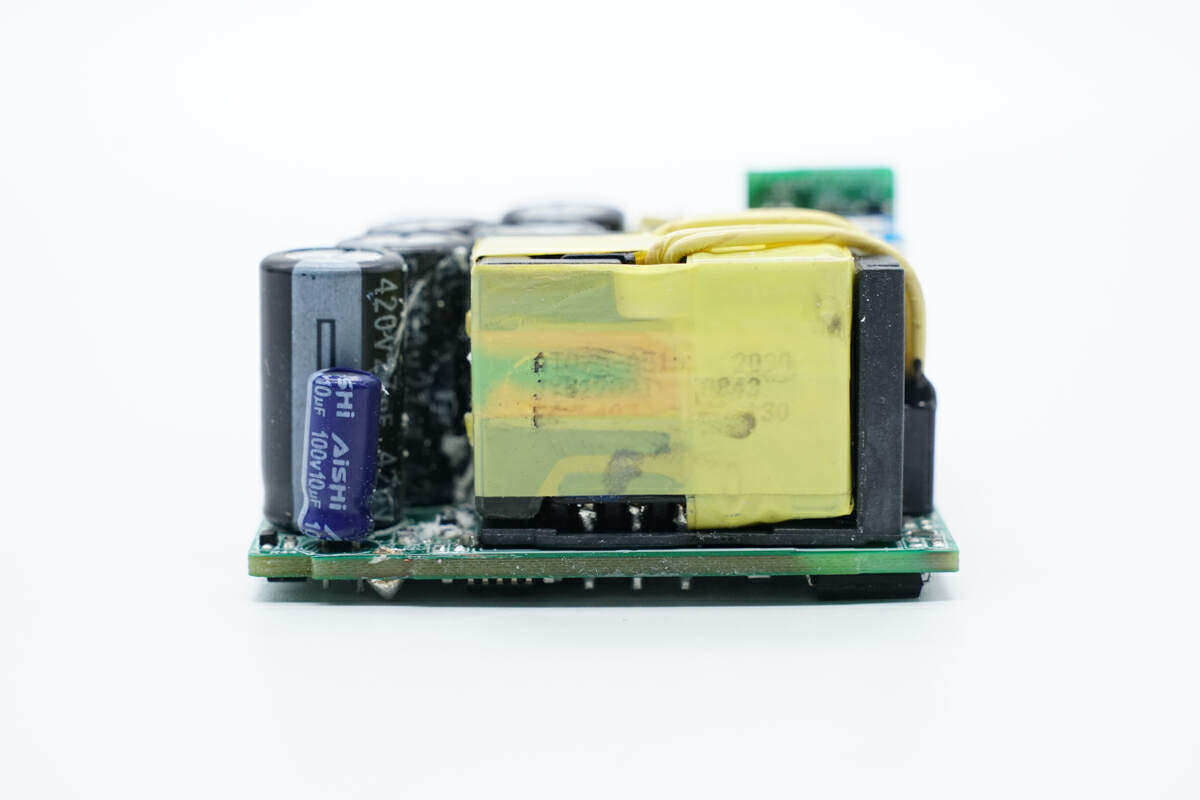

There are filter capacitors and a transformer on the side of the PCBA module.
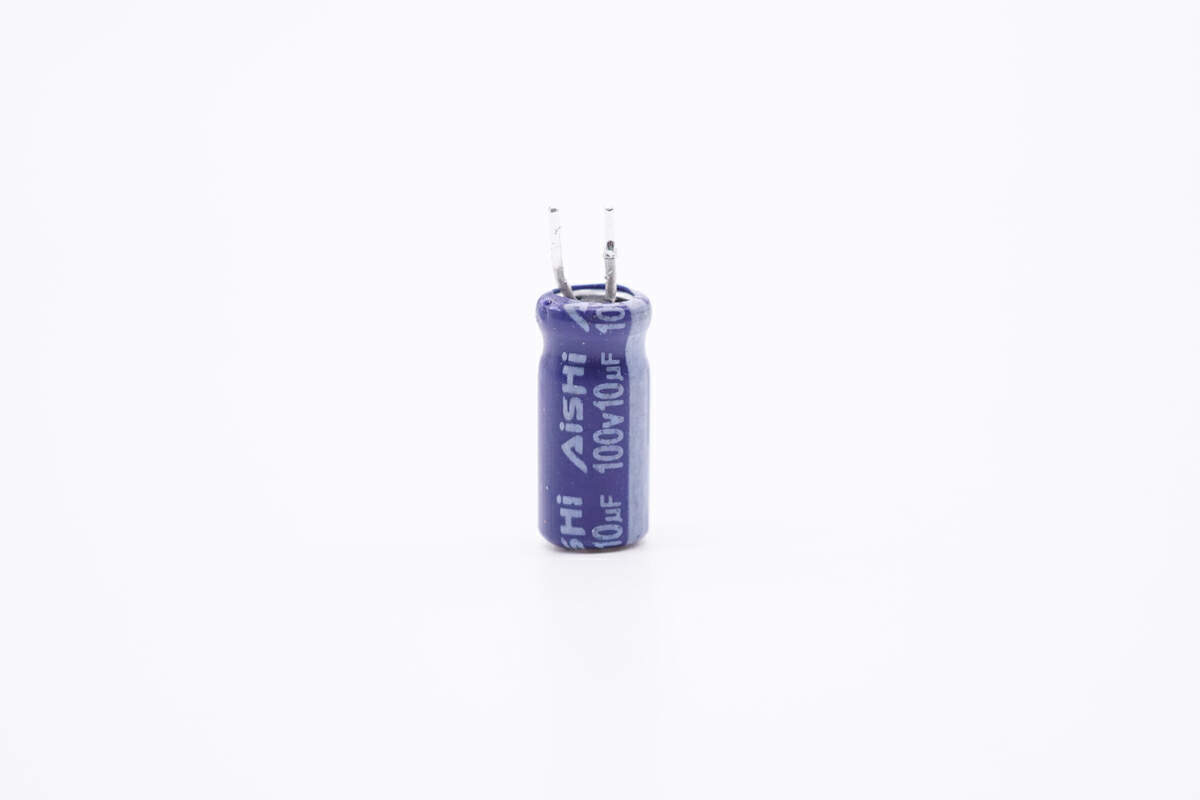

This is the filter capacitor that powers the master control chip. 100V 10μF.
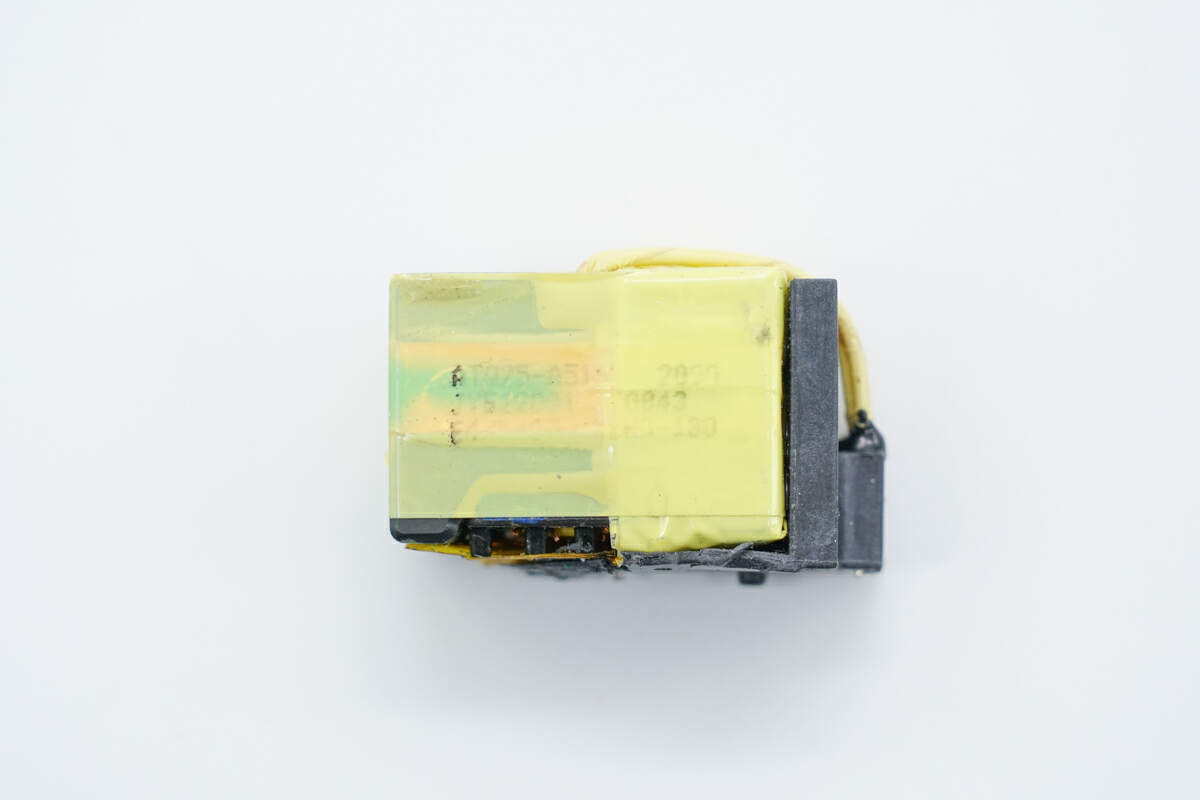

The transformer adopts ATQ25 magnetic core.
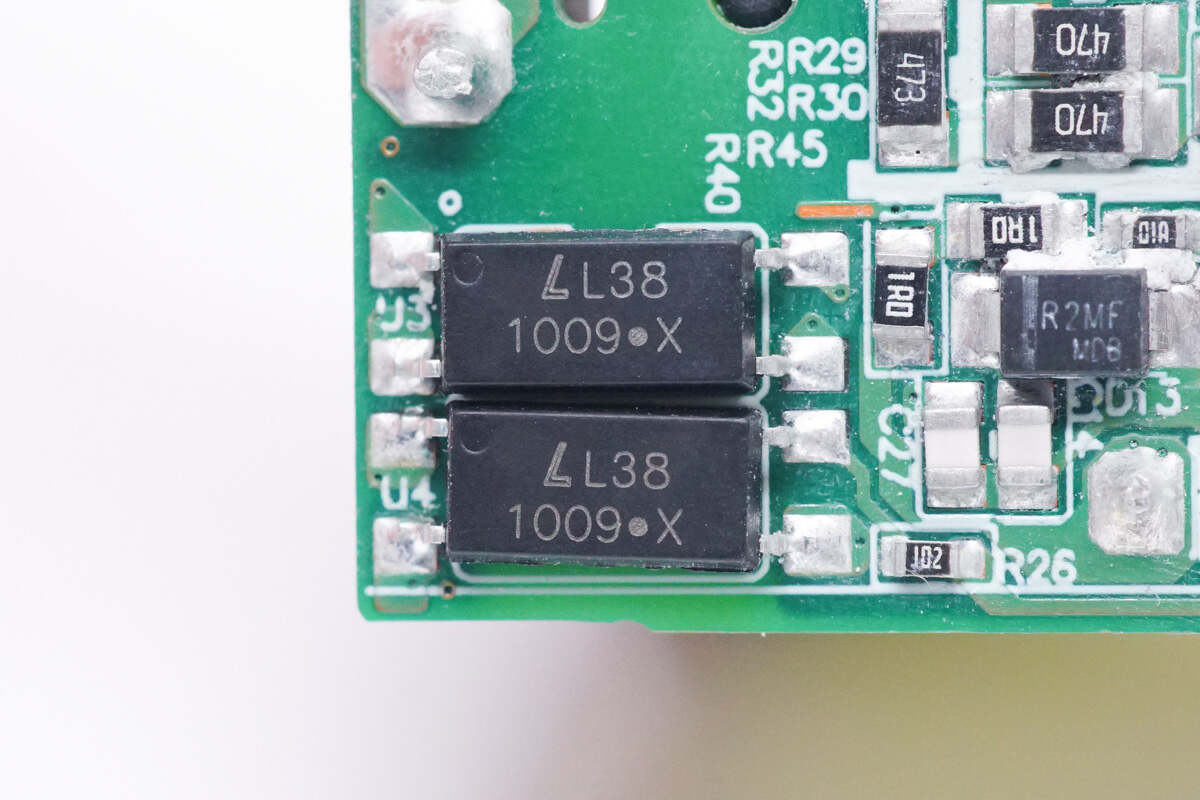
These two optocouplers are used for PFC control and output voltage feedback respectively.
The output side has a synchronous rectifier, two solid capacitors, a PCB of USB-C socket, and two blue Y capacitors.
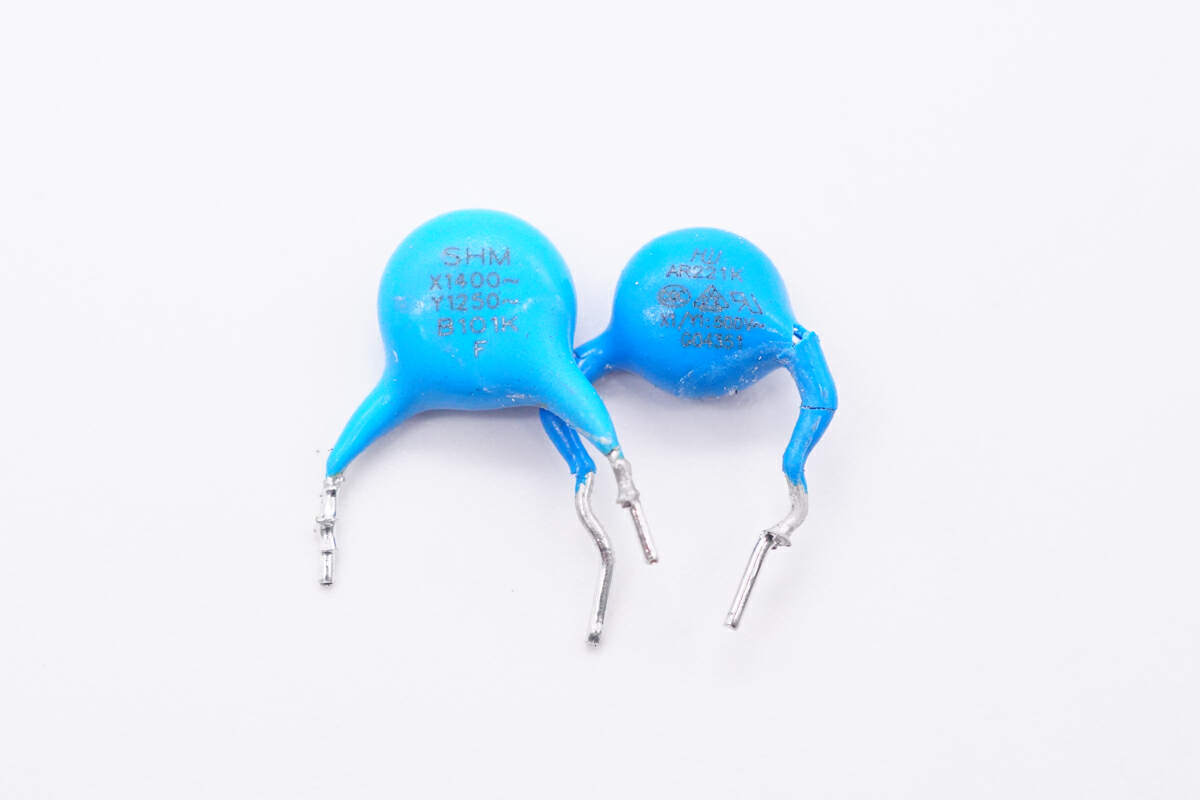

There are two blue Y capacitors.
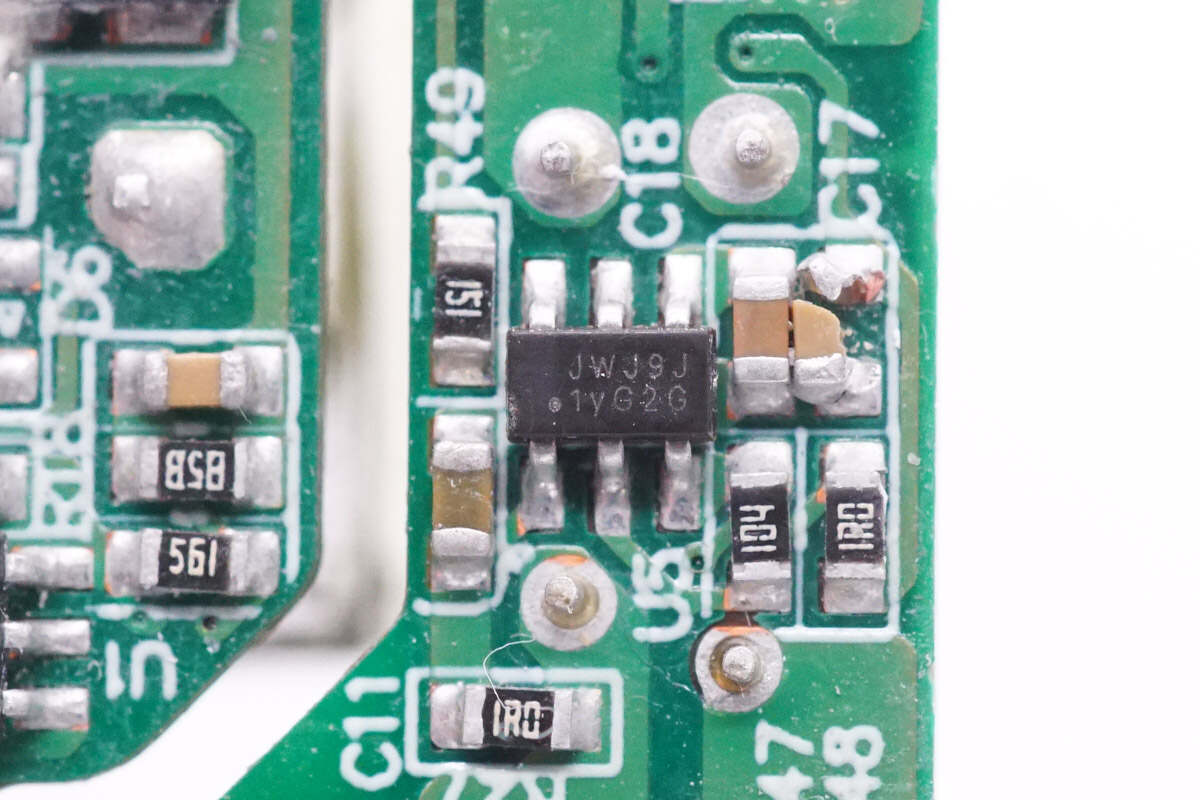
The synchronous rectifier controller marked with JWJ9J is from JOULWATT. It supports modes of DCM, CCM, QR, and ACF. Model is JW7726B.
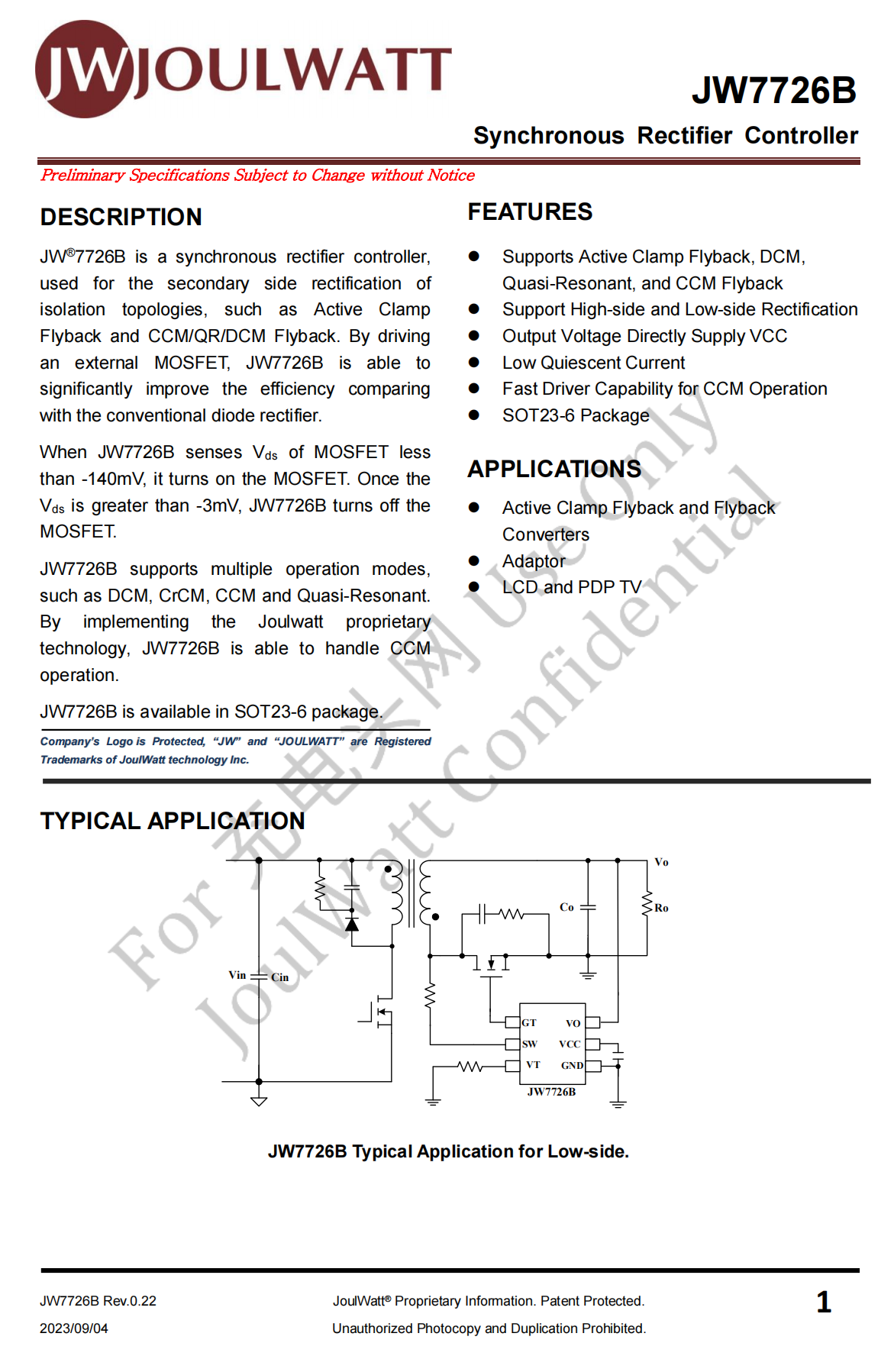
There is all the information about the JOULWATT JW7726B.
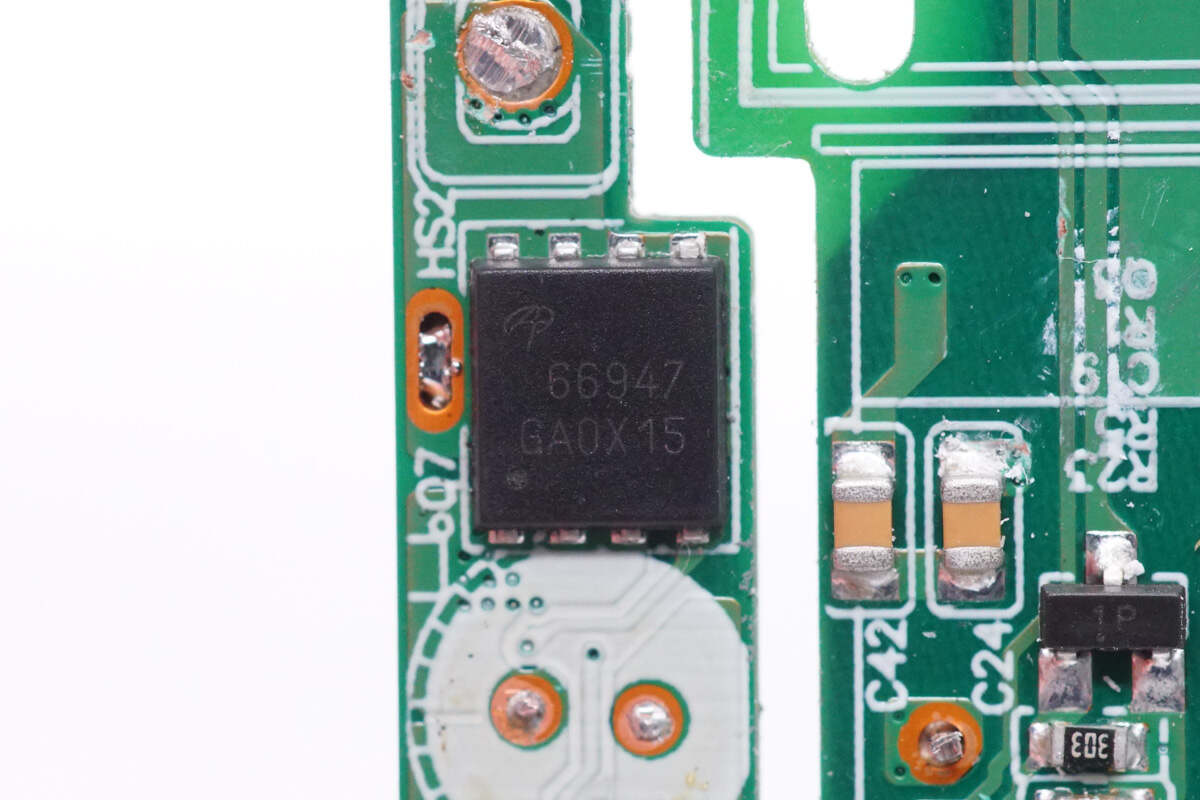

The synchronous rectifier is from AOS and adopts DFN5 x 6 package. Model is AONS66947. 100V 2.9mΩ.
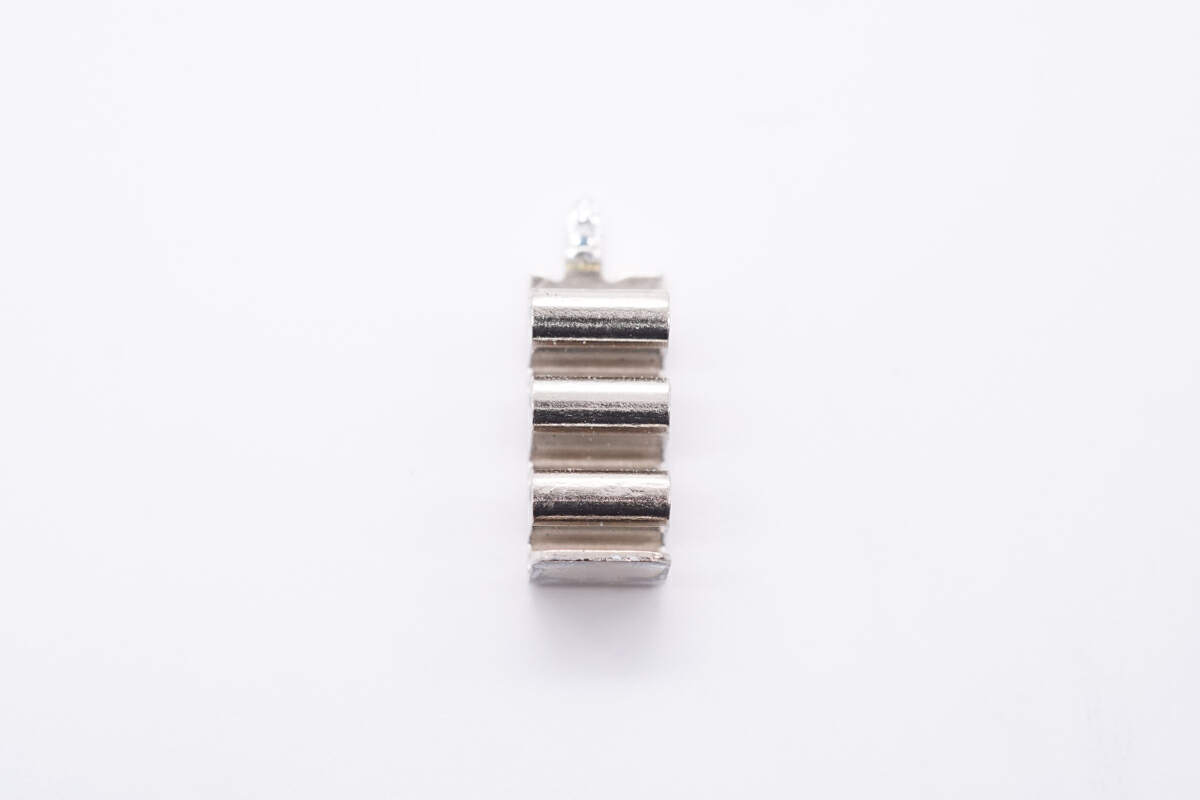

This is the heat sink for the synchronous rectifier.
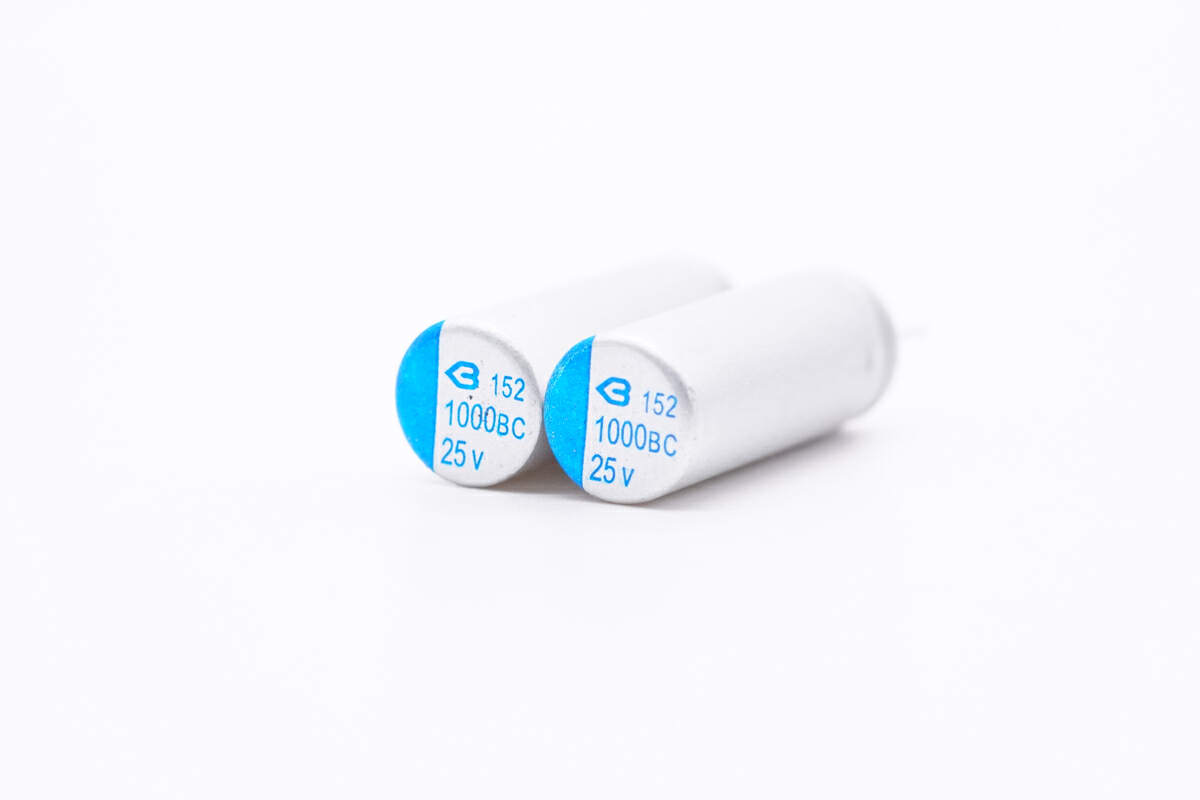

These two solid capacitors are from BERYL. 1000μF 25V, respectively.
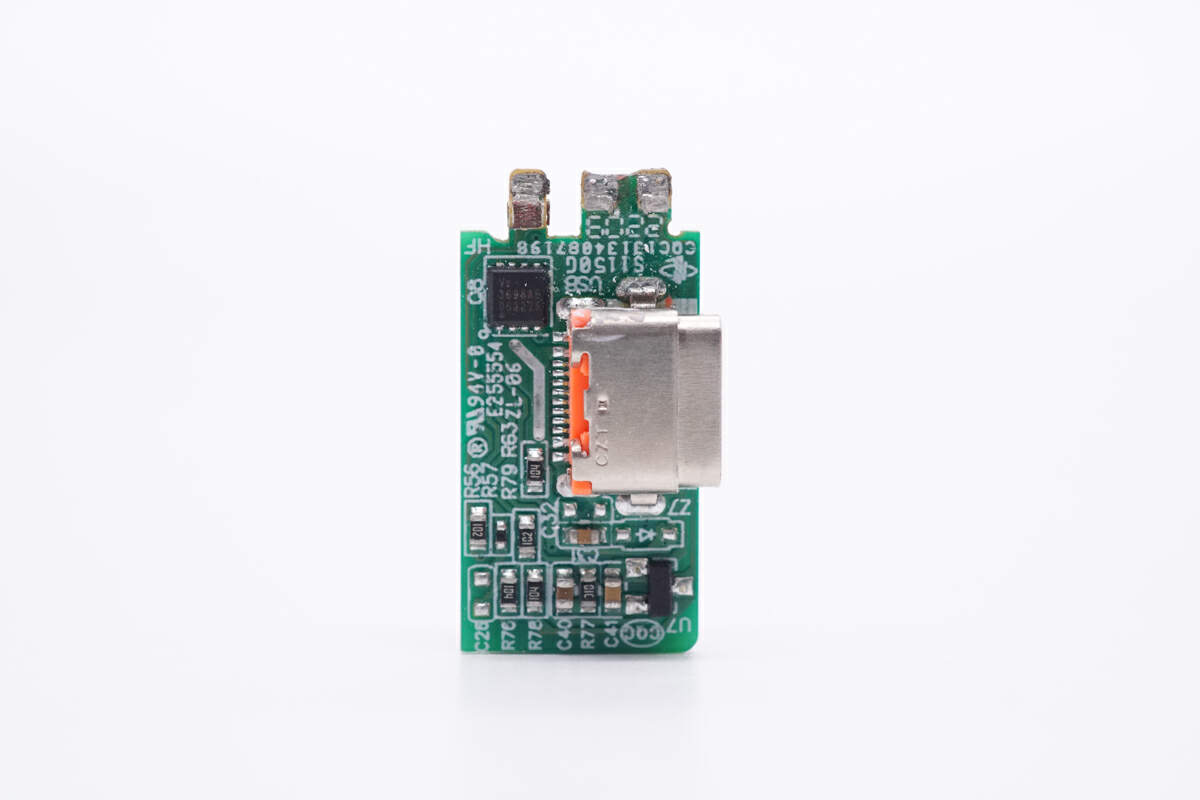

There is a VBUS MOSFET on the front of the PCB of the USB-C socket.
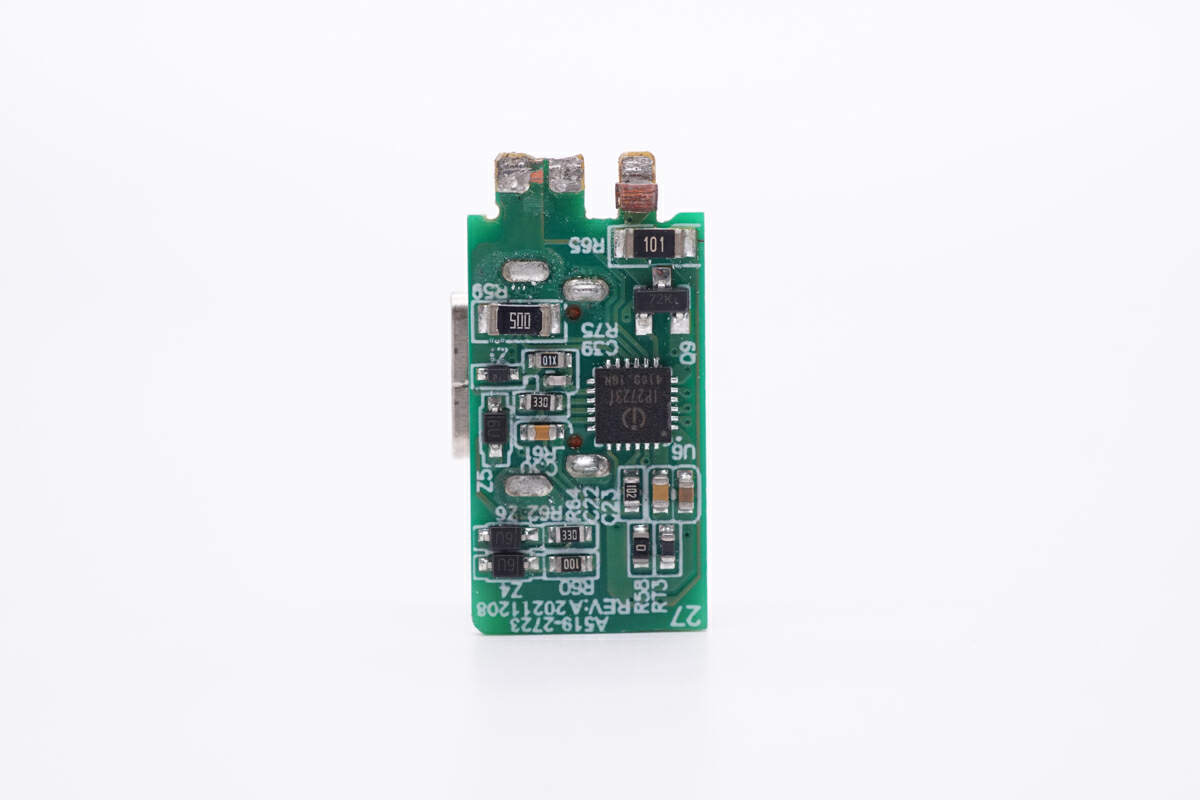

The protocol chip, current sampling resistor, TVS diode, and thermistor are on the back.
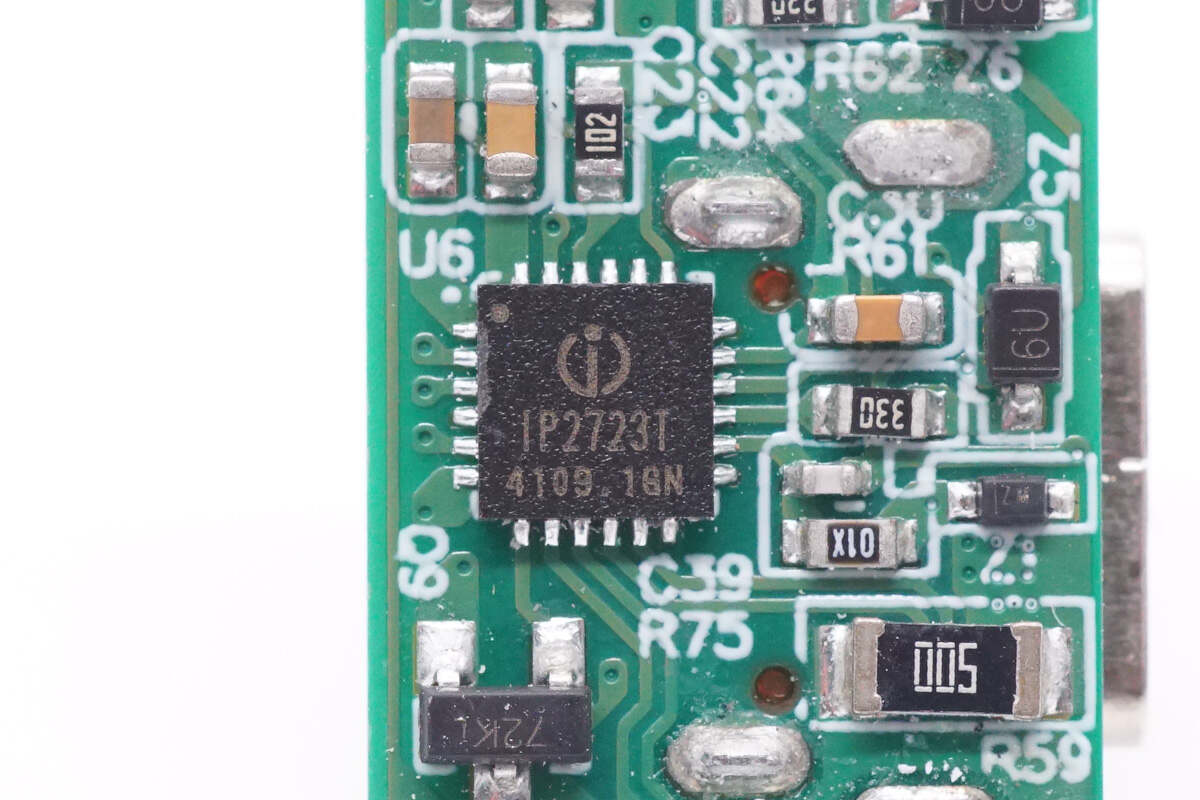
The protocol chip is from Injoinic. It supports a variety of fast charging protocols, including DFP, PD2.0/3.0, PPS, QC4, QC4+, QC3.0/2.0, FCP, SCP, AFC, MTK PE+ 2.0/1.1, Apple 2.4A, and SAM 2A. Model is IP2723T.

There is all the information of the Injoinic IP2723T.
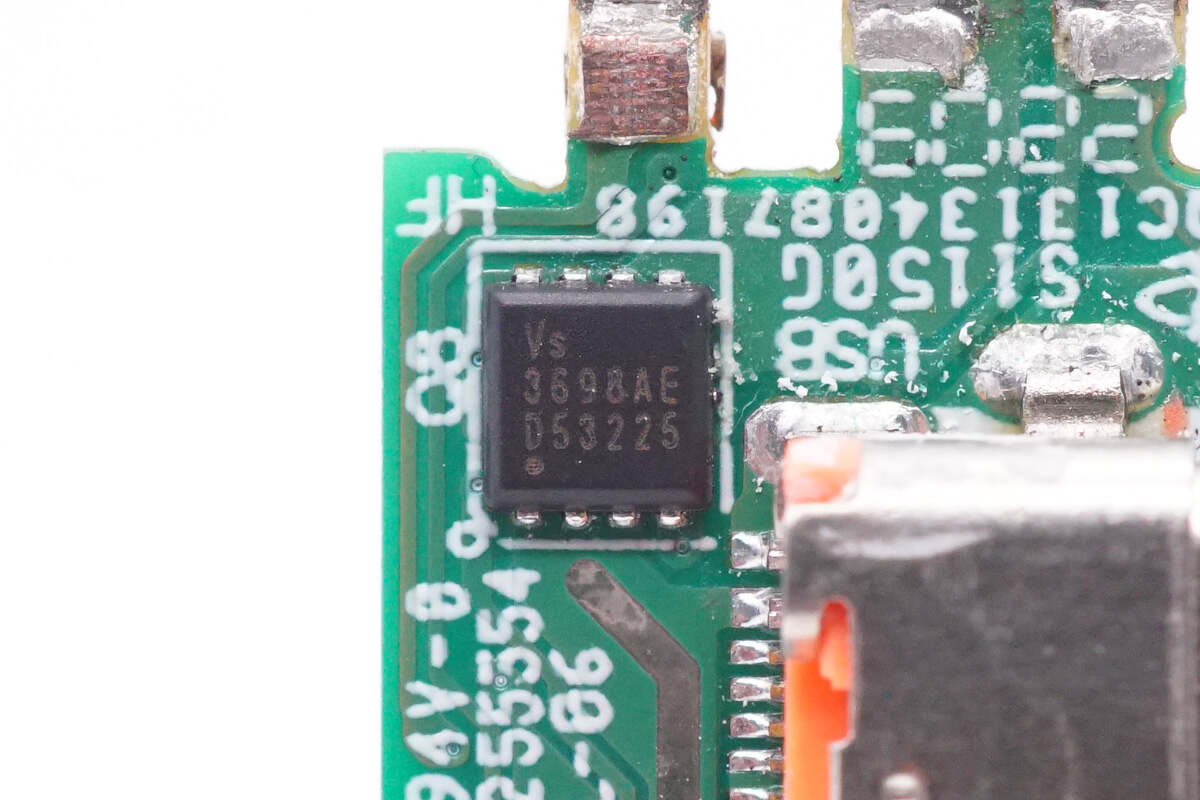
The VBUS MOSFET for output is from VGSEMI and adopts PDFN3333 package. Model is VS3698AE. 30V 3mΩ.
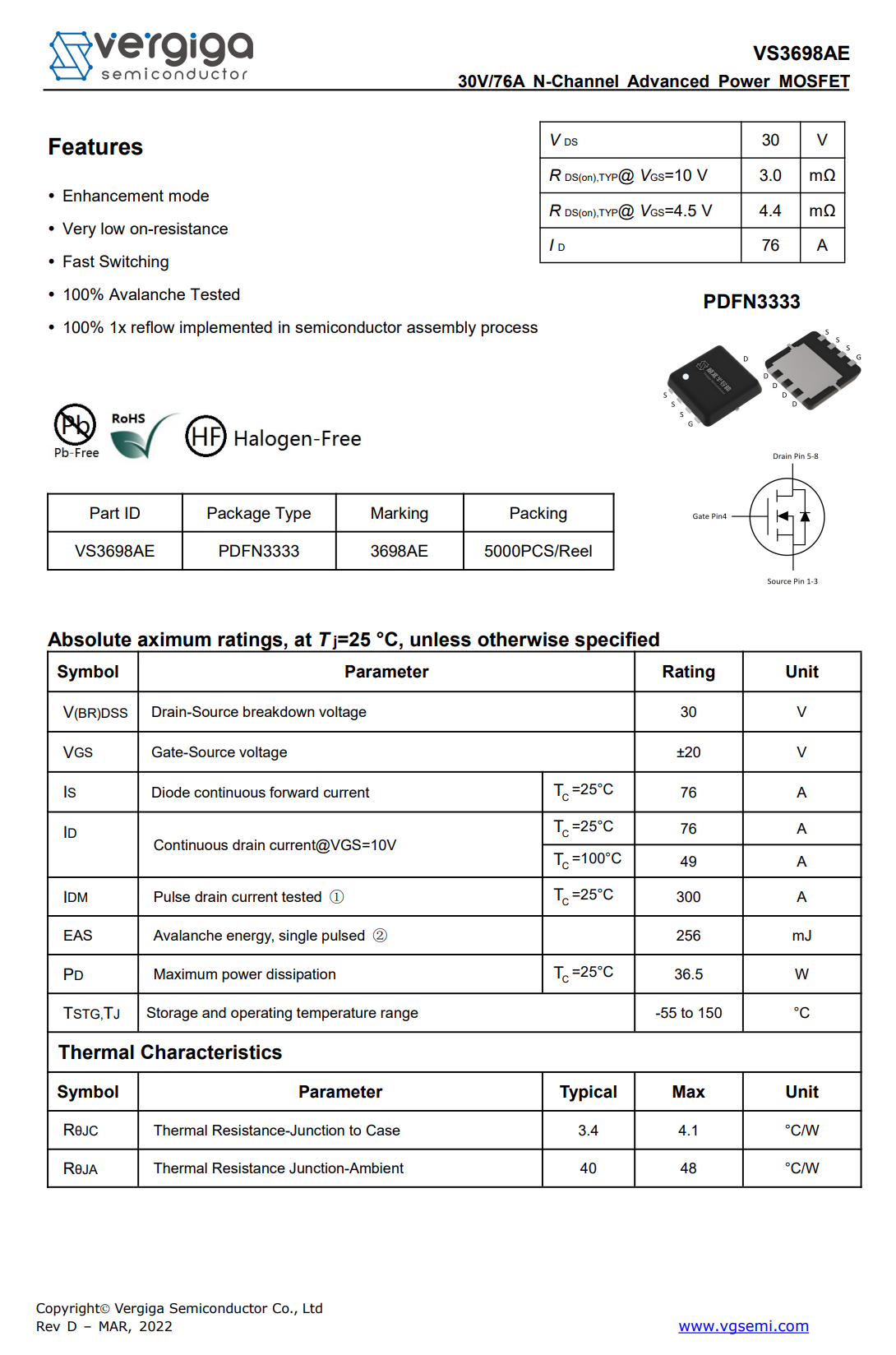
There is all the information about the VGSEMI VS3698AE.
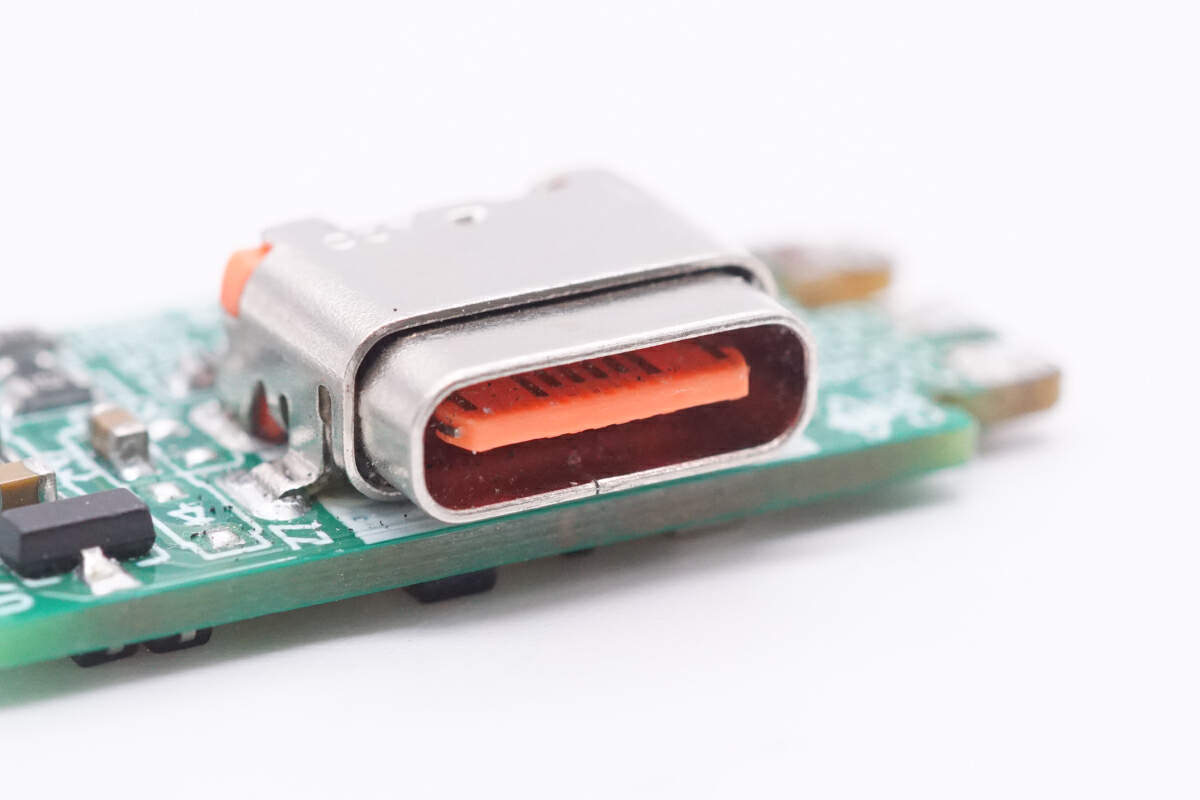
There is the orange USB-C socket.

Well, those are all components of the Infinix 180W USB-C GaN charger.
Summary of ChargerLAB
It adopts a one-piece white case and European pins. The maximum output power is 20V9A 180W. It can also support fast charging of 100W PD and 3.3-21V5A PPS. It has good fast charging compatibility for Android phones and laptops.
After taking it apart, we found it adopts a PFC circuit and flyback topology. It uses a PFC controller and a ZVS flyback controller, paired with two GaN FETs. The charger has copper heat sinks to dissipate heat for the PFC boost inductor and GaN FETs. The internal components are fixed with glue, and the workmanship is solid.
Related Articles:
1. PD3.1 | Teardown of Kovol 140W GaN Charger
2. Teardown of MOVESPEED 140W PD3.1 4-in-1 Charger (YSFCG107-140Y)
3. Teardown of LDNIO 140W GaN 6-in-1 Desktop Charger (A6140C)