Introduction
ChargerLAB this time got a 130W USB-C power adapter from ROG. The input end of this adapter uses a three-prong design and supports a wide input voltage of 100-240V. It also comes with a USB-C output cable. It has passed multiple safety certifications. Next, let's take it apart to see its internal components and structure.
Product Appearance
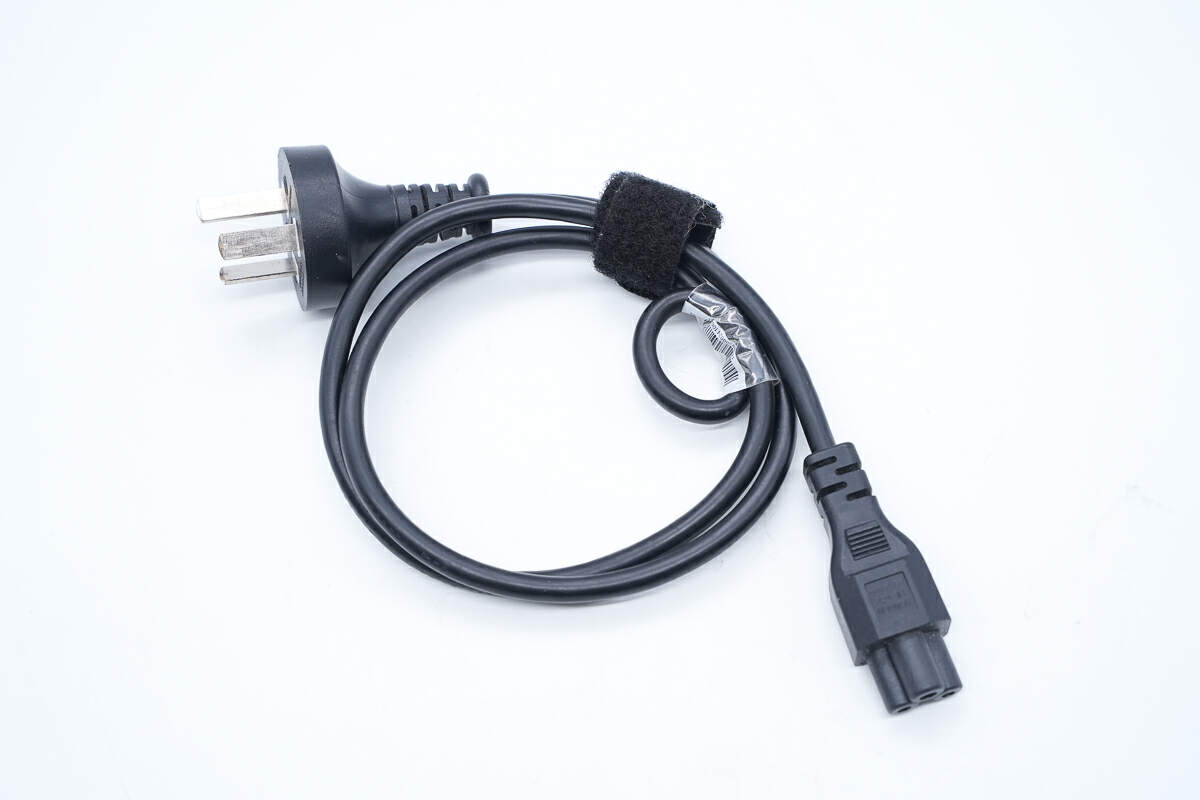

The power cord of the ASUS ROG 130W USB-C GaN Power Adapter is detachable, allowing users to replace different power cords for use in different countries and regions.
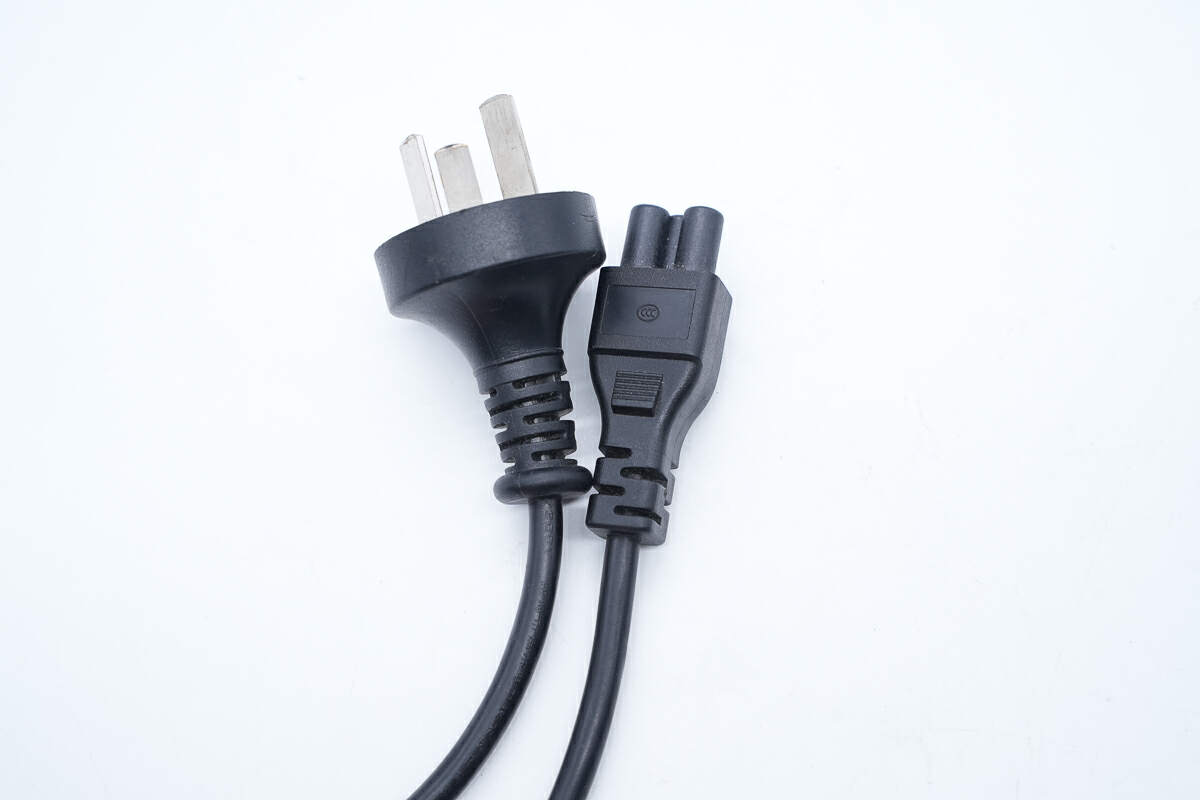

Both sides of the power cord adopt the three-prong design.
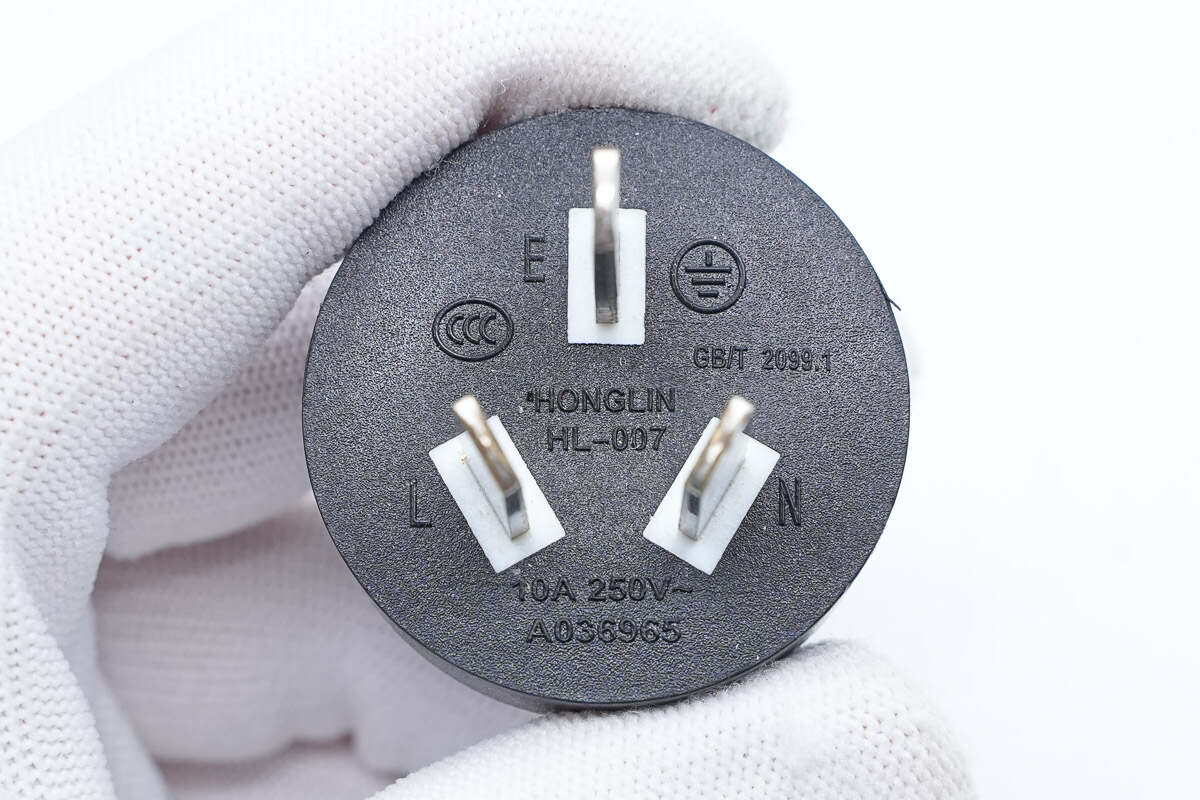

It can support input of 10A 250V~.
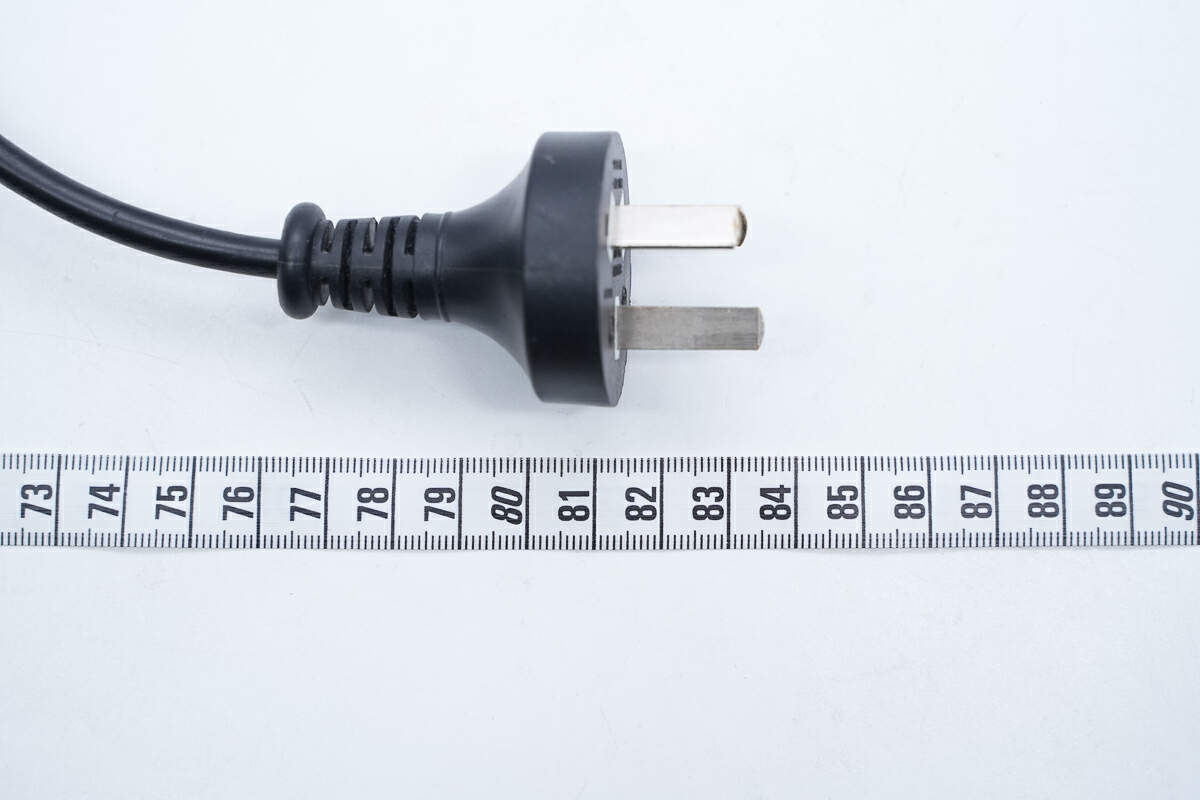

The total length of the power cord is about 83.5 cm (32.87 inches).
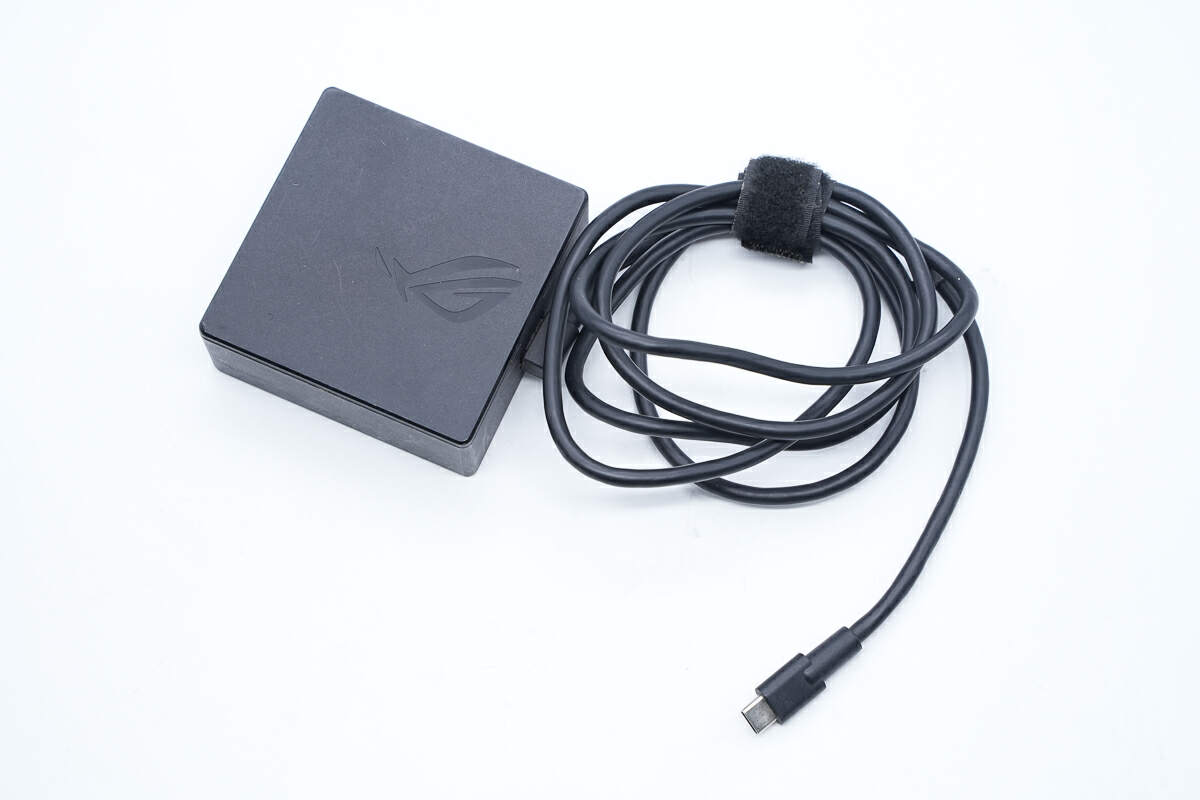

The power adapter is in the shape of a flat rectangle and comes with a USB-C output cable.
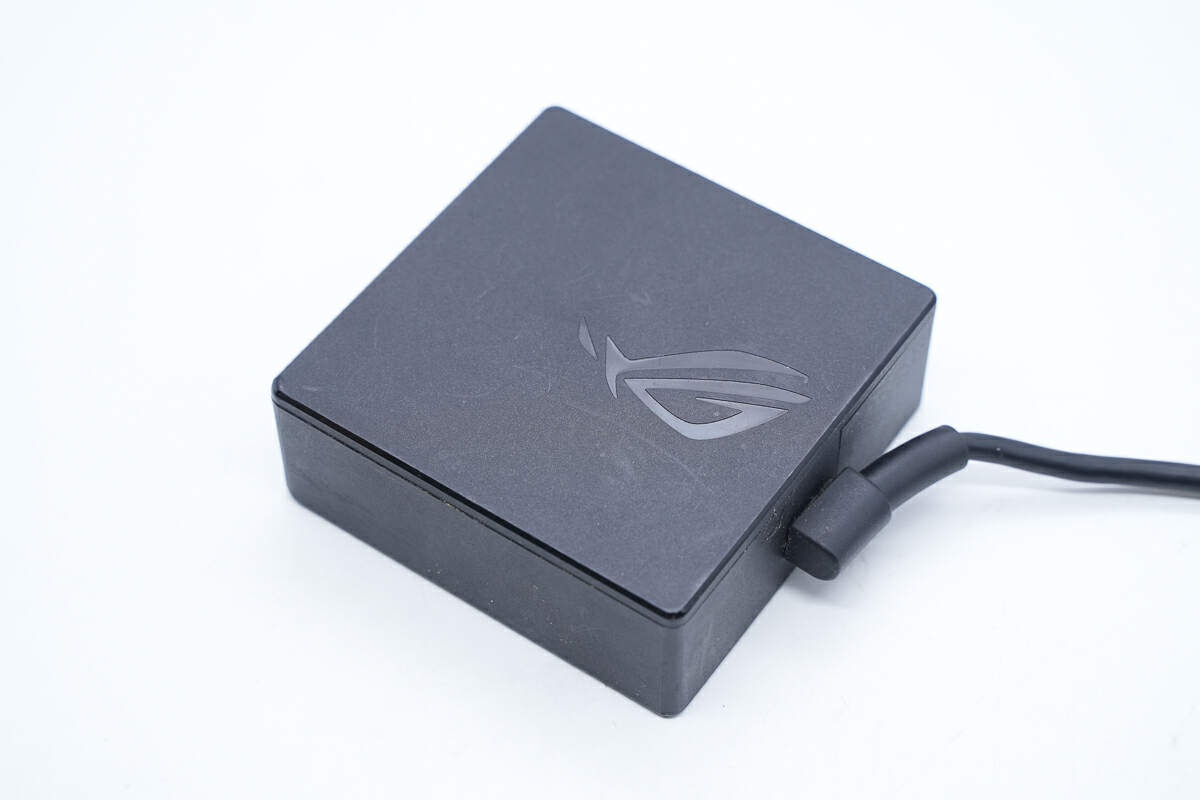

The black case is made of fire-retardant PC material, and the surface has a matte design.

There is a glossy ROG logo printed on the front.

There is a piece of anti-slip rubber pad on the bottom, and the specs info is printed on it. It has passed multiple safety certifications such as CCC, CE, GS, EAC, UKCA, UL, NOM, NYCE, etc., and can be used in most countries and regions.

Model is ADP-130HB B. It can support input of 100-240V~50/60Hz 1.9A. The maximum output is 20V 6.5A, which is 130W. The manufacturer is Delta.
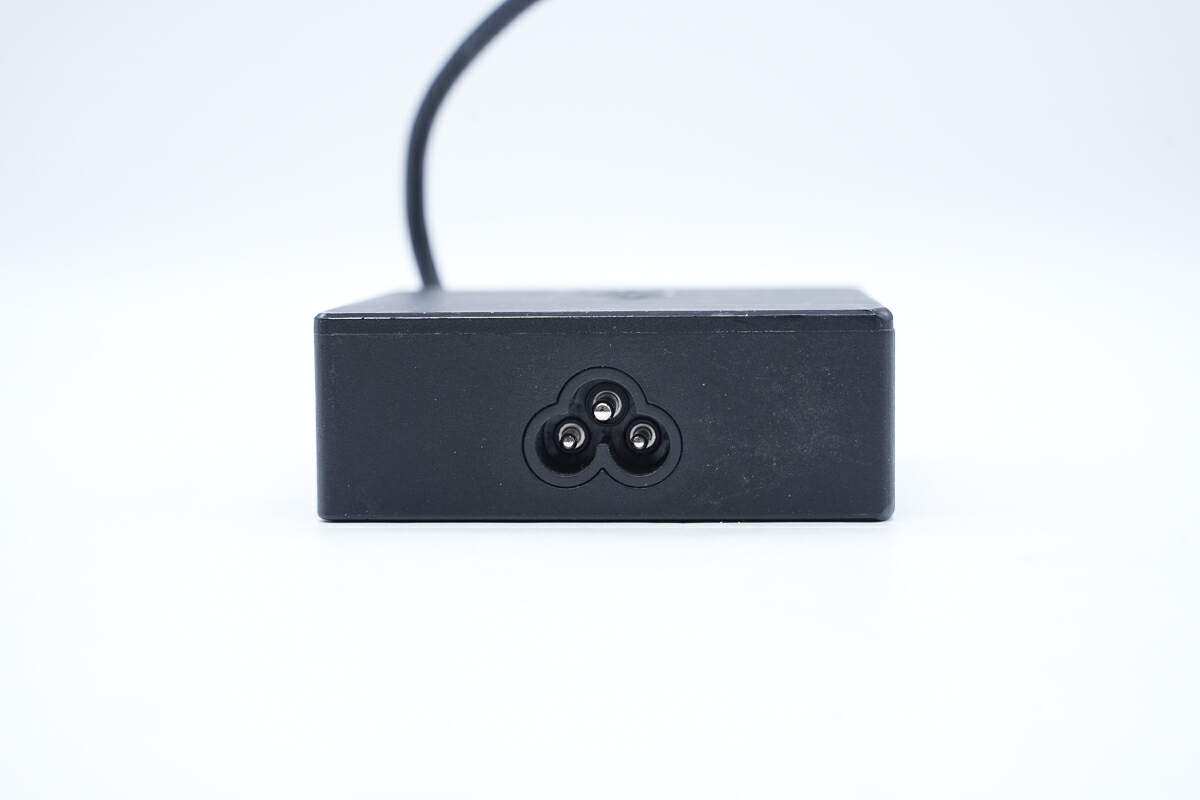

The input end has a three-prong slot.
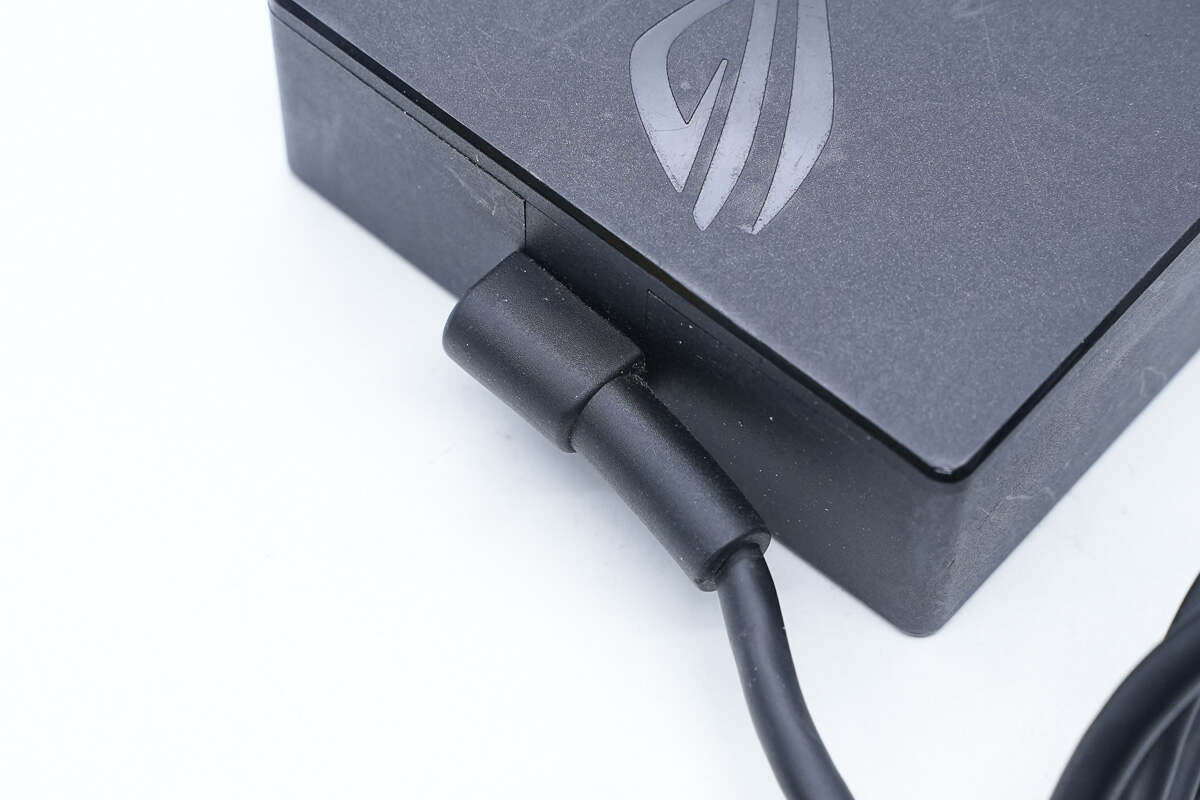

The connection between the output cable and the adapter adopts a bent design, which can save space and protect the cable.
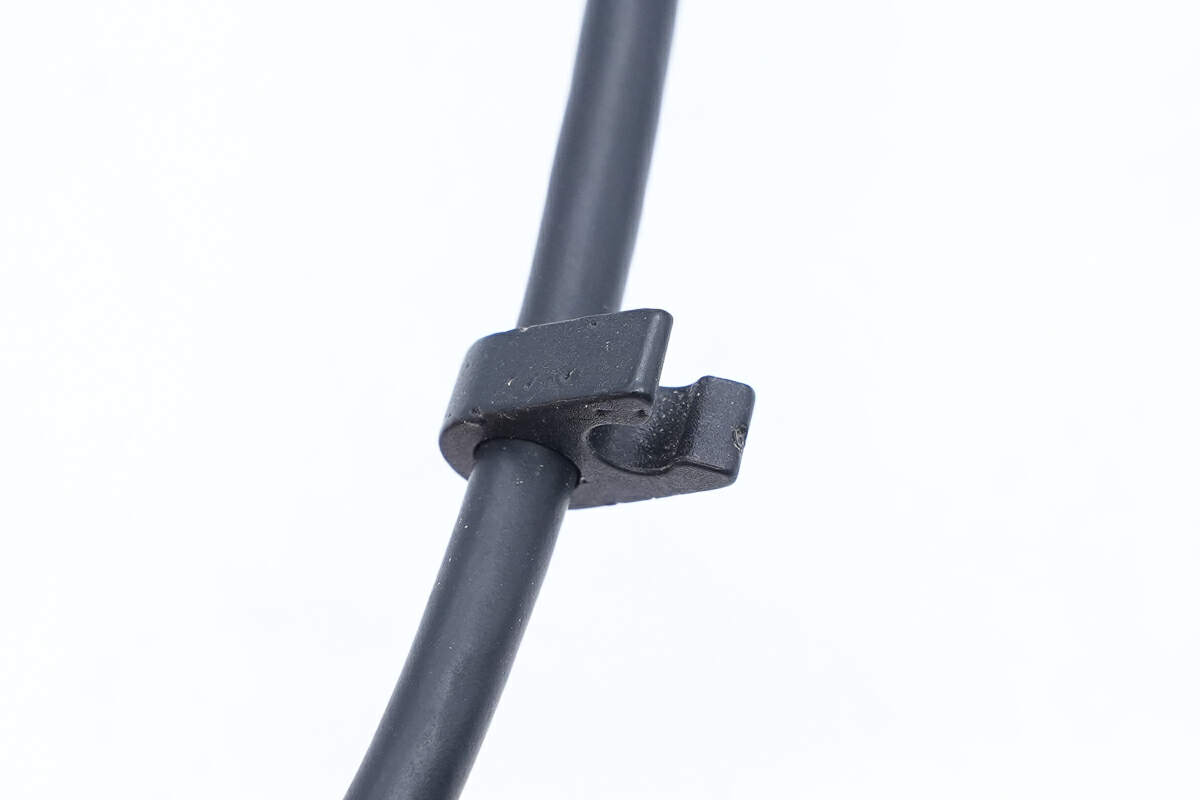

There is a cable clip on the output cable.
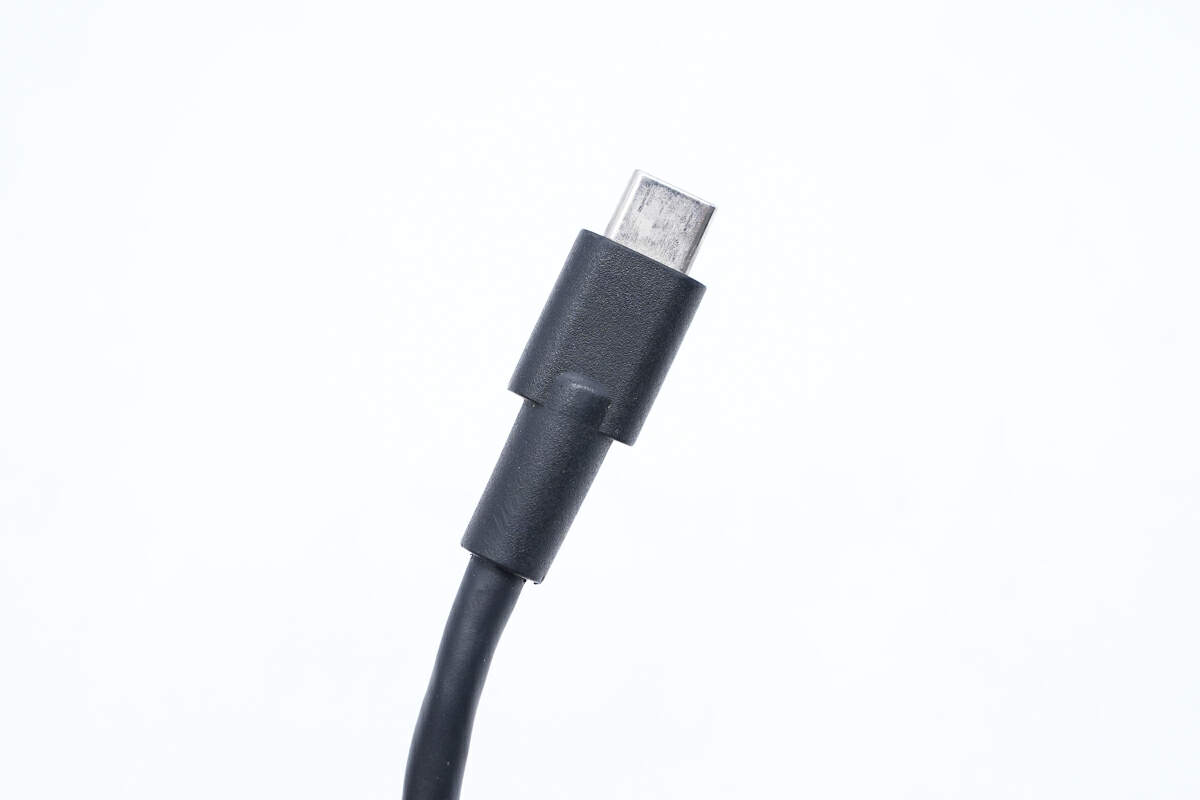

The USB-C connector adopts a thickened design.
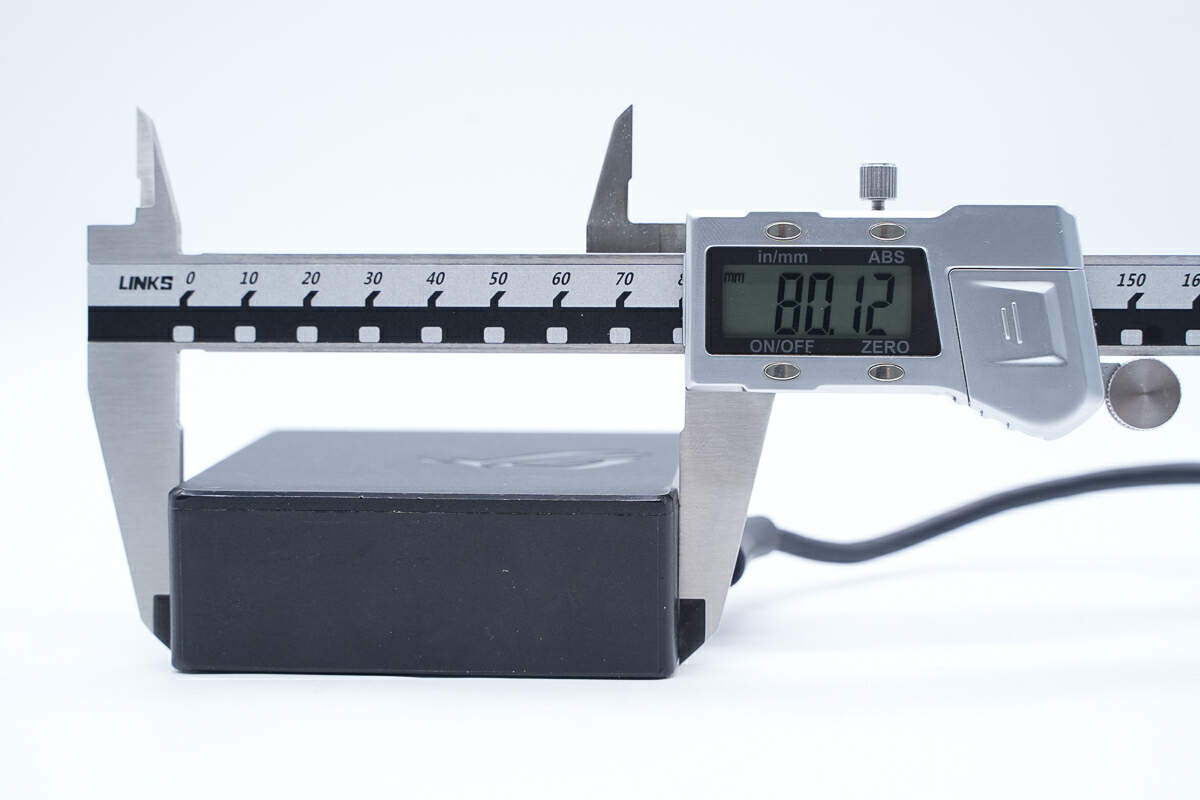

The length of the power adapter is about 80 mm (3.15 inches).
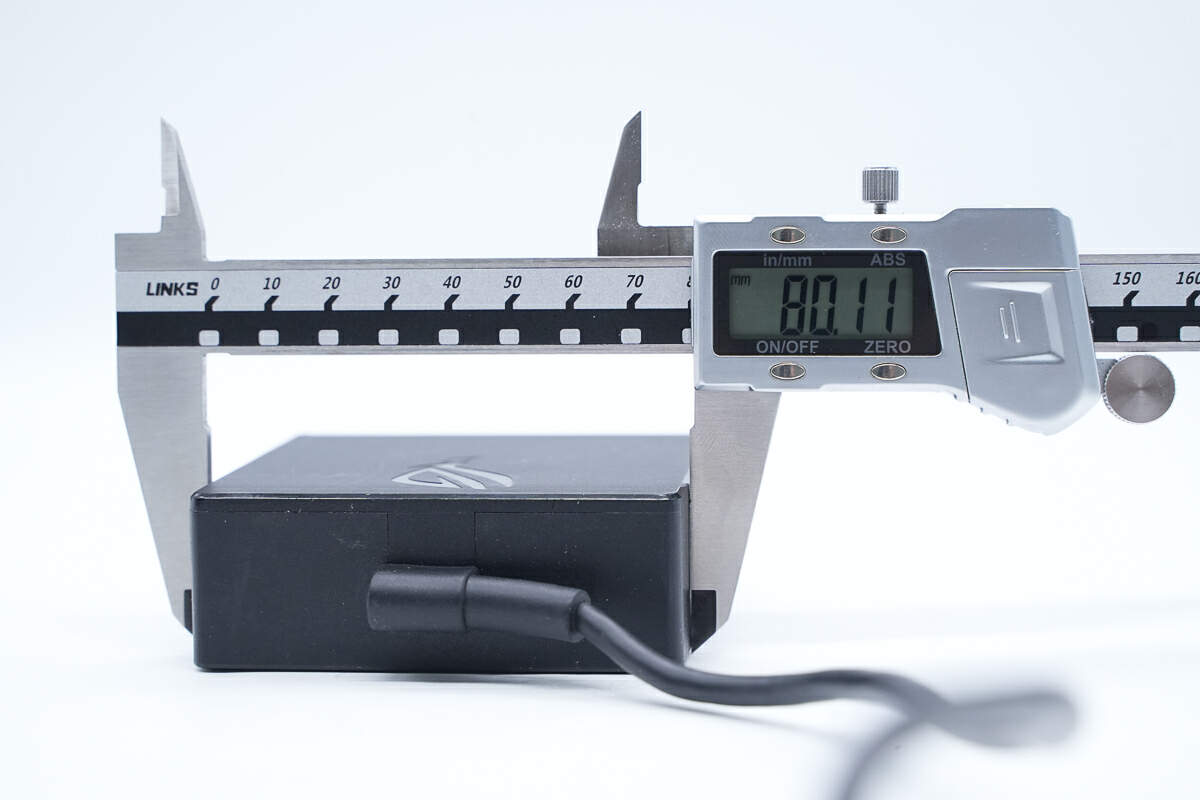

The width is also about 80 mm (3.15 inches).
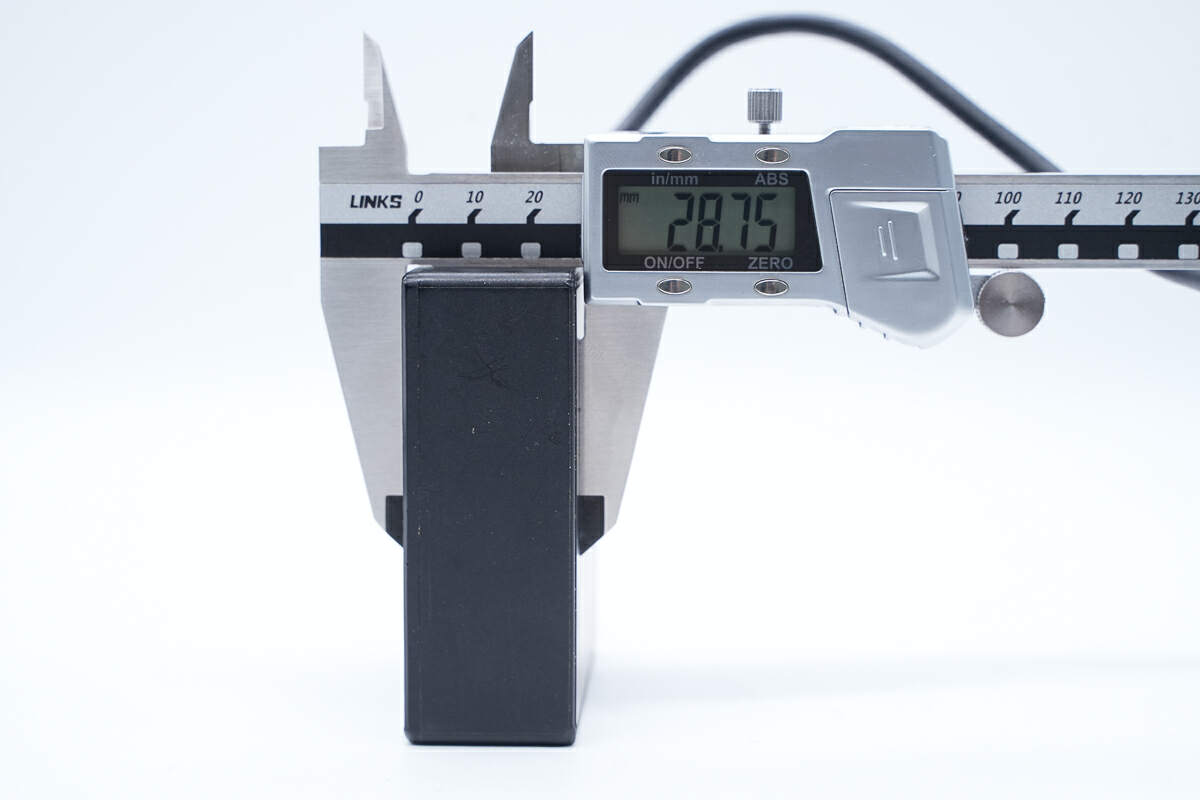

And the thickness is about 28.8 mm (1.13 inches).
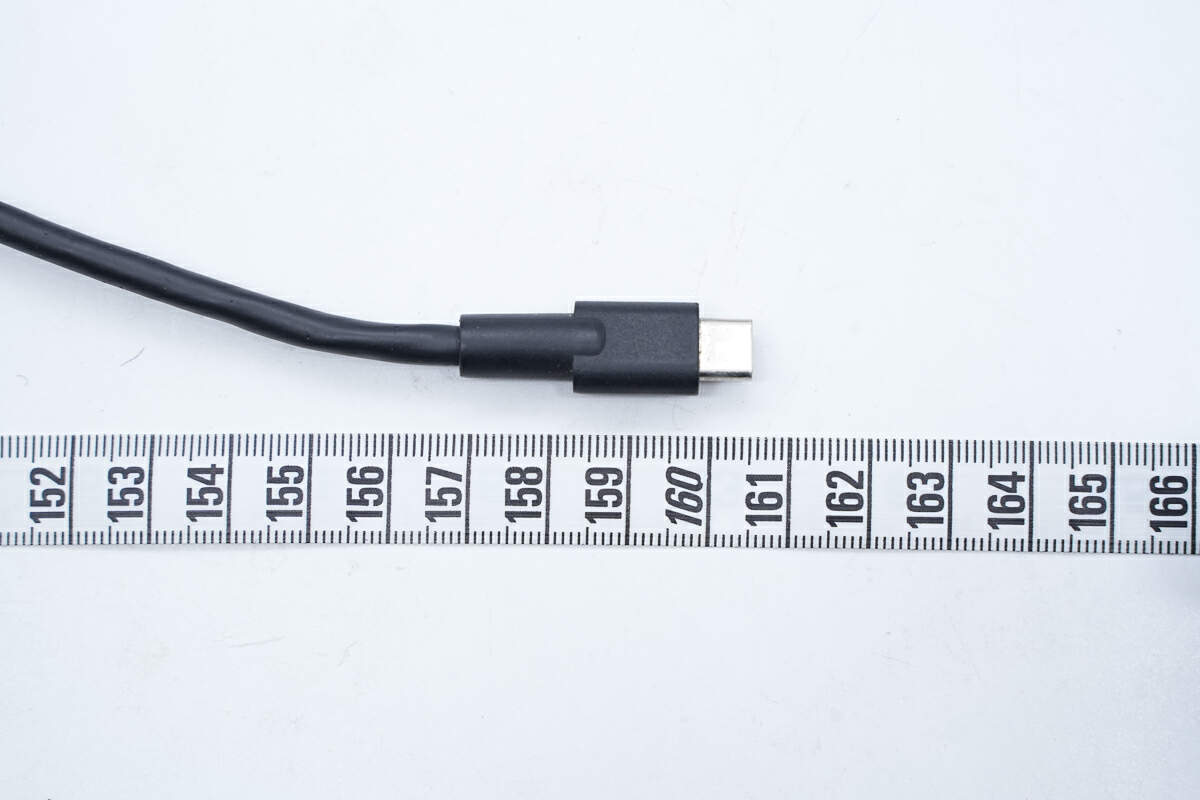

The length of the USB-C cable is about 160.5 cm (63.19 inches).

That's how big it is in the hand.
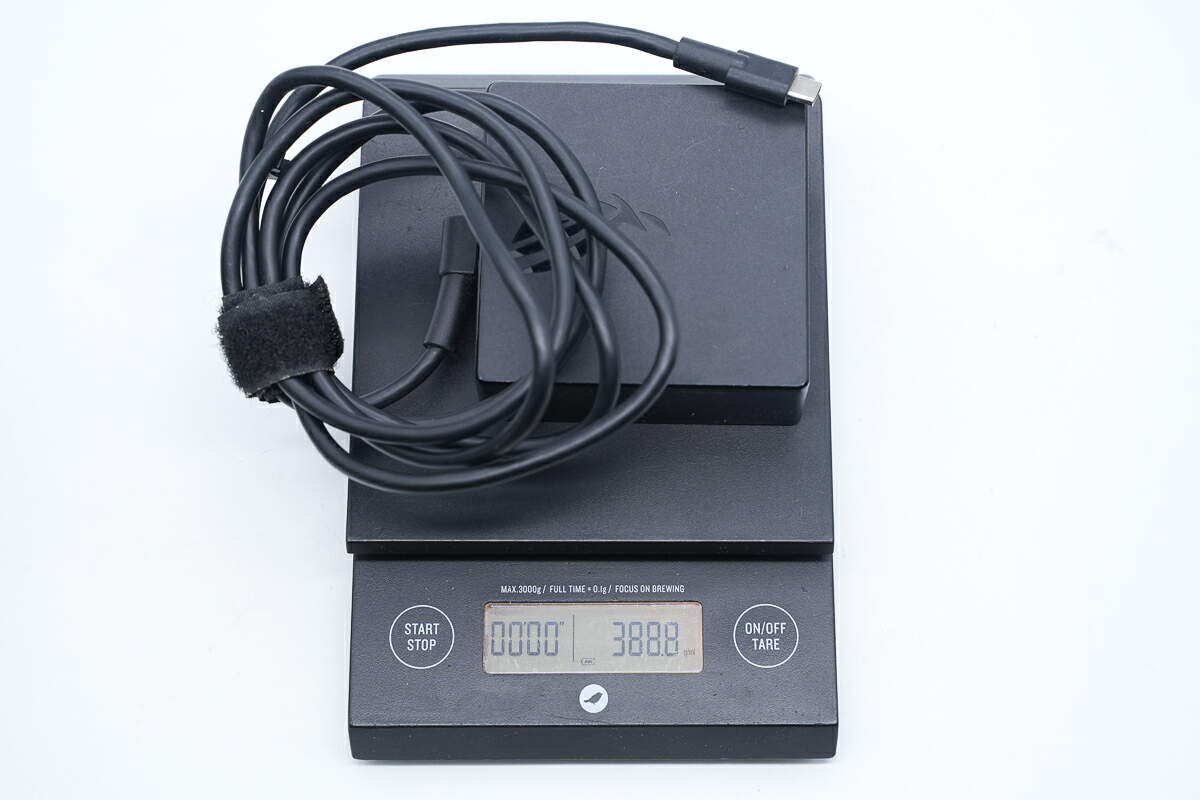

The weight is about 389 g (13.72 oz).
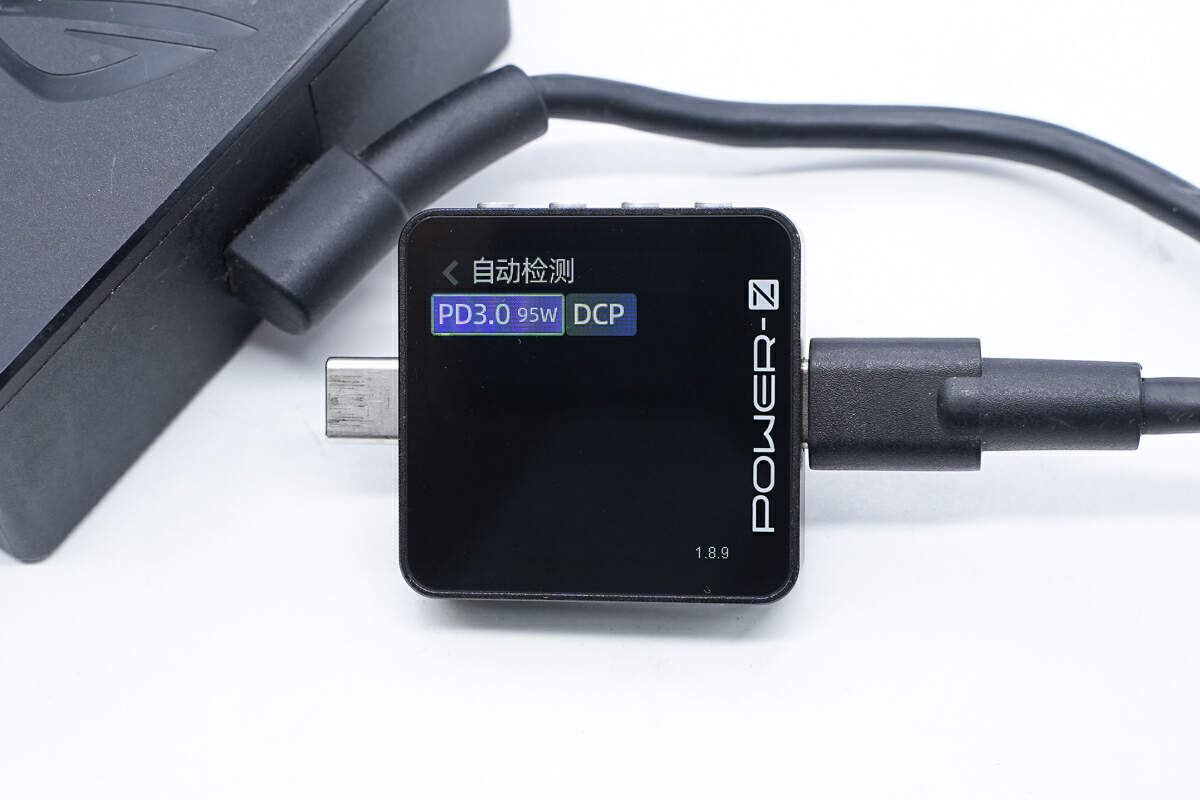

ChargerLAB POWER-Z KM003C shows the USB-C port can support PD3.0 and DCP charging protocols.
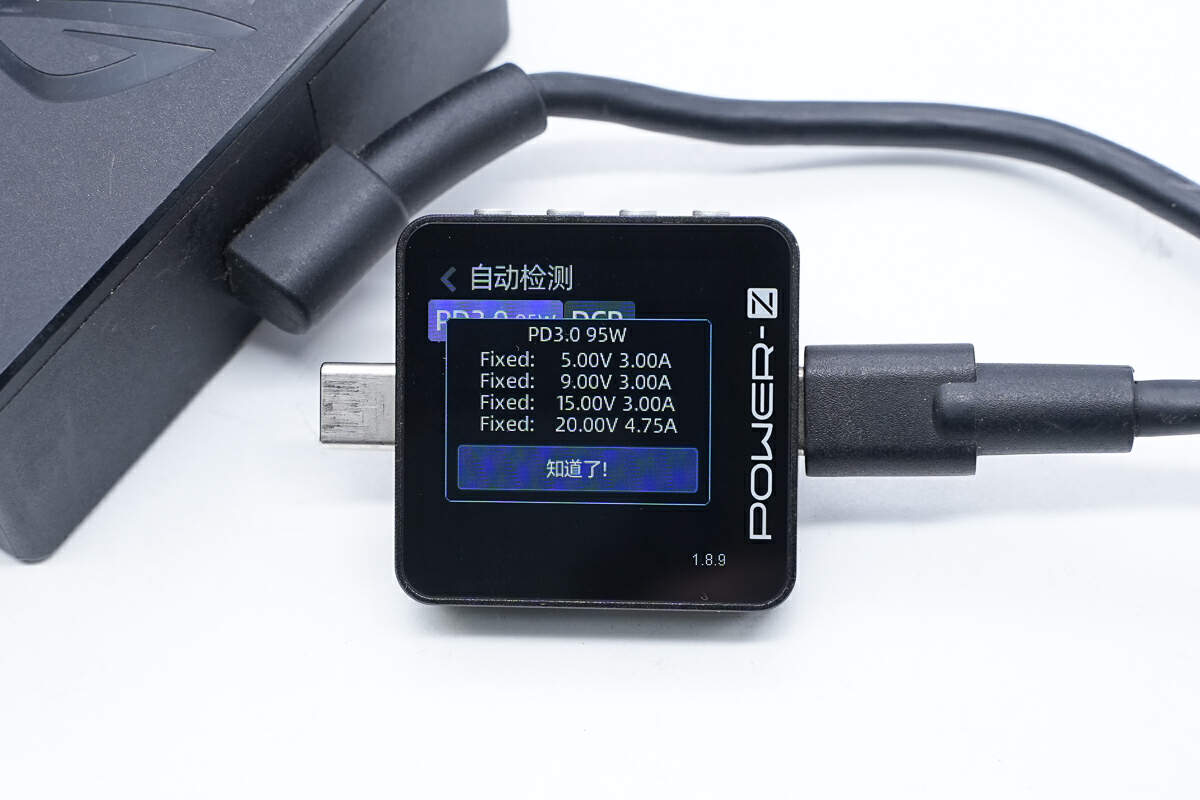

And it has four fixed PDOs of 5V3A, 9V3A, 15V3A, and 20V4.75A.
Teardown
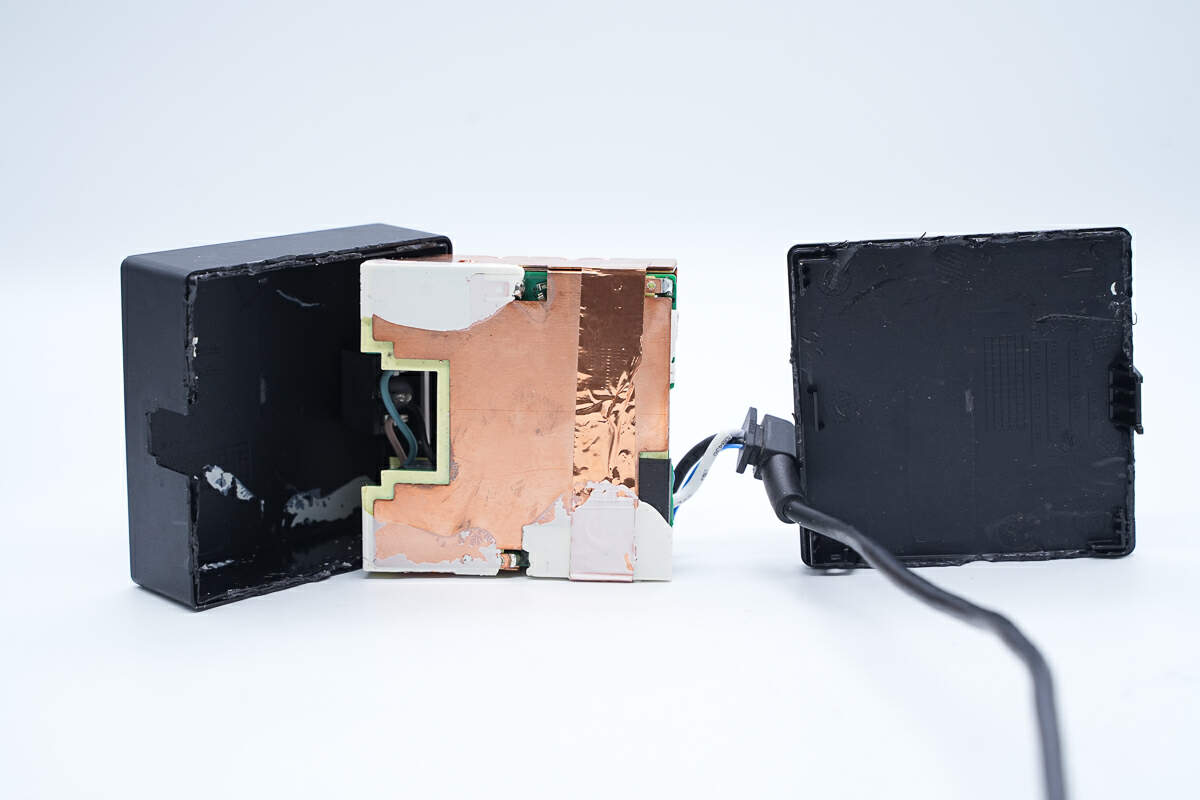
First, pry off the bottom shell along the gap, which uses an ultrasonic welding process.
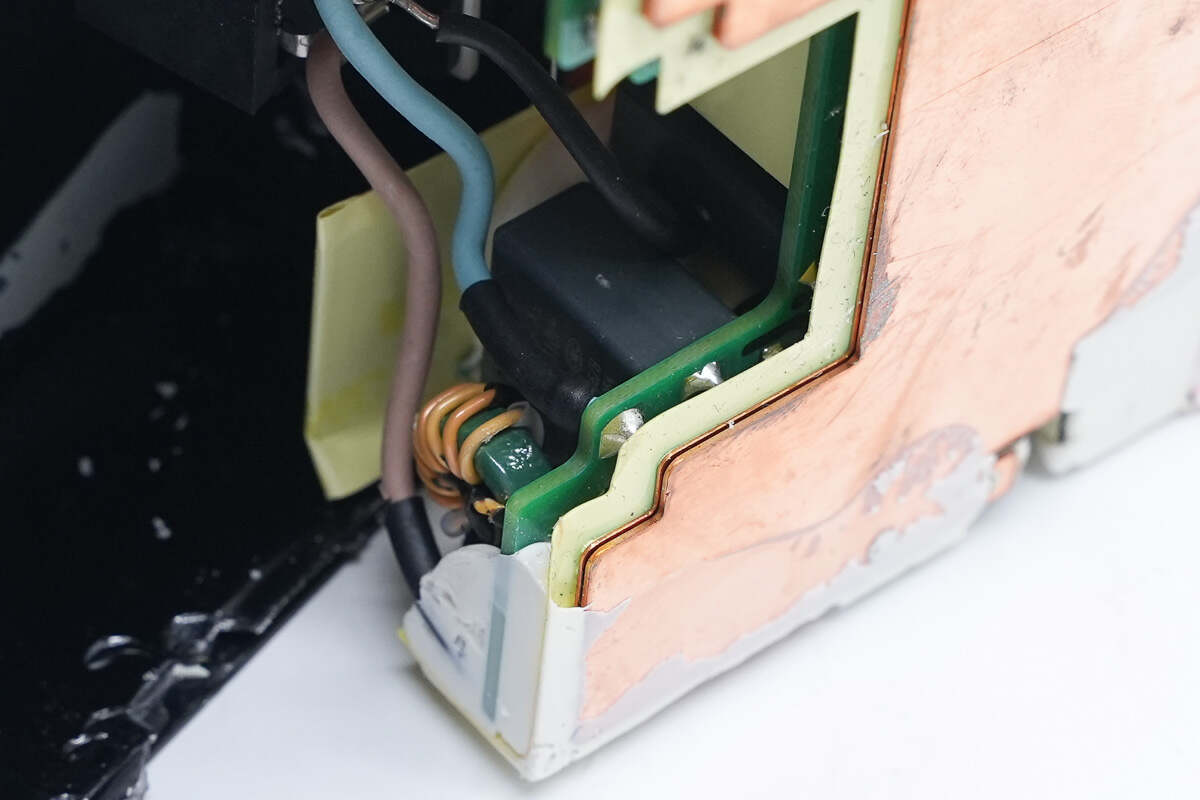
The input socket is connected to the PCBA module through wires and protected by rubber sleeves.
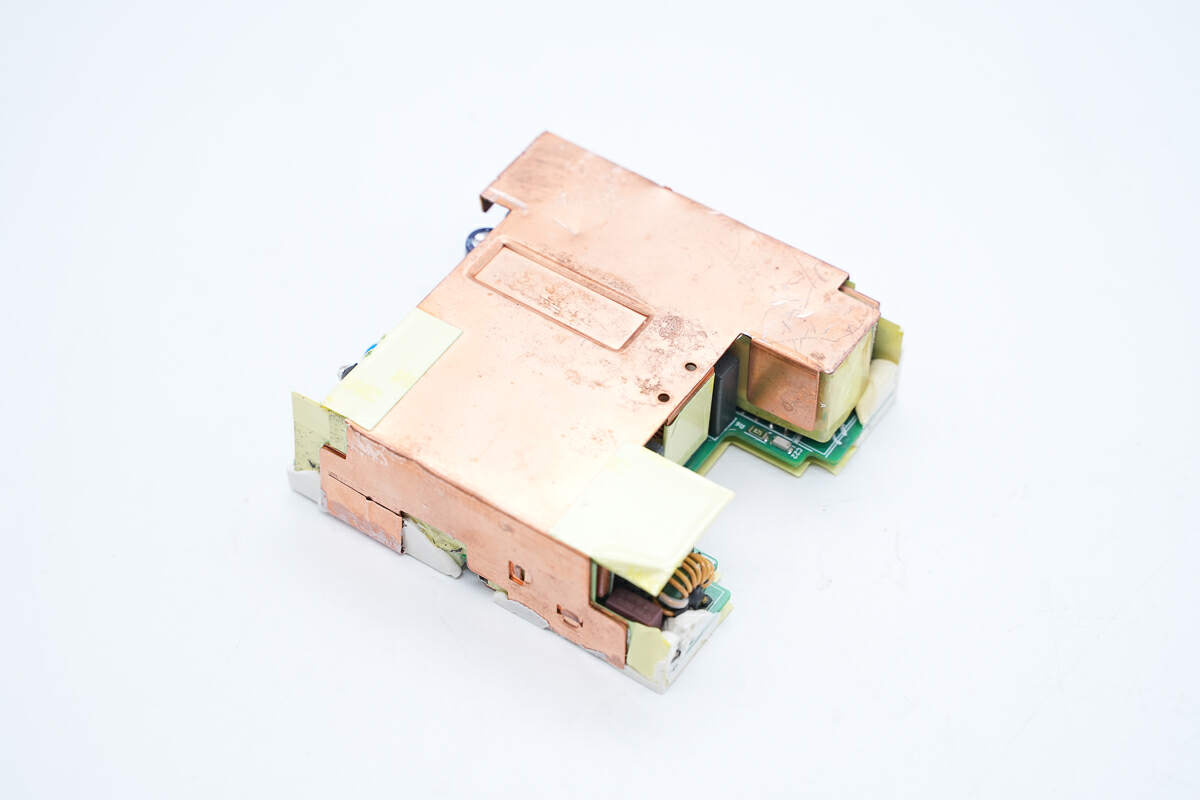

Take out the PCBA module. The entire module is covered with copper sheets for heat dissipation, and tape is pasted on the inside, and both ends for insulation.
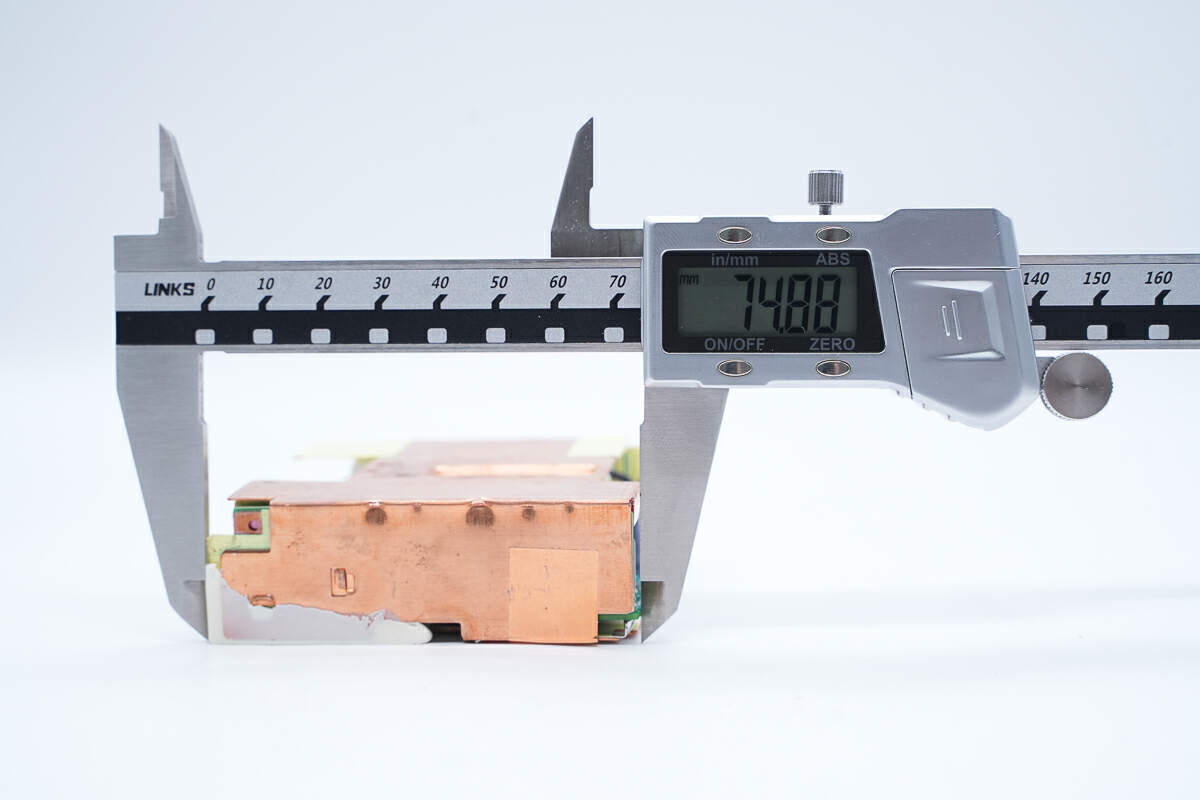

The length of the PCBA module is 74.88 mm (2.95 inches).
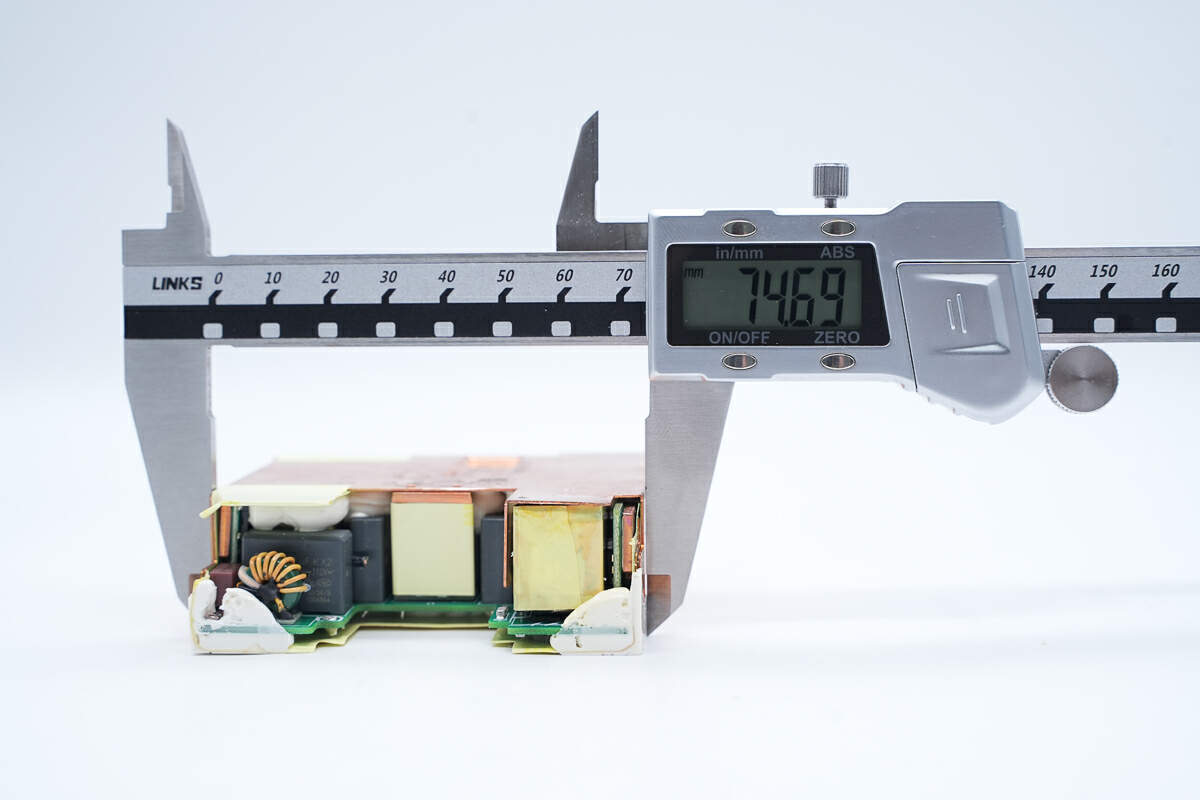
The width is 74.69 mm (2.94 inches).
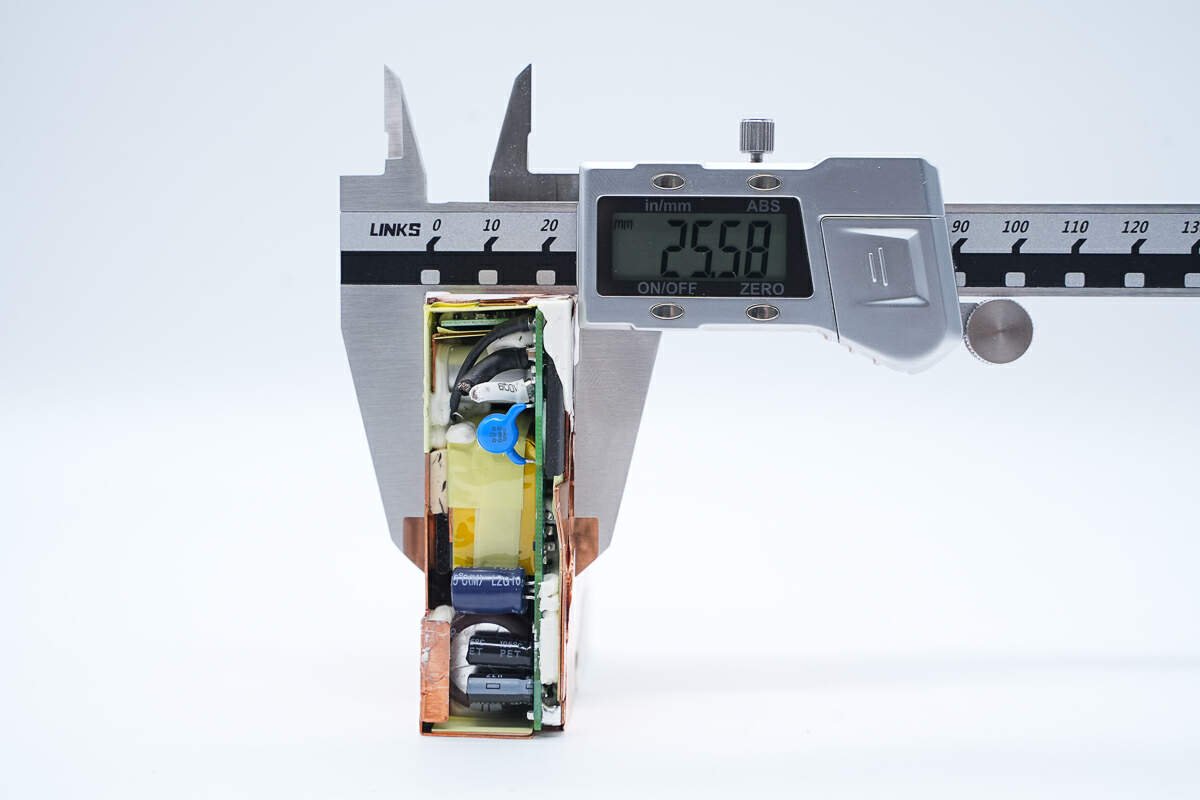
And the thickness is about 25.58 mm (1.0071 inches).
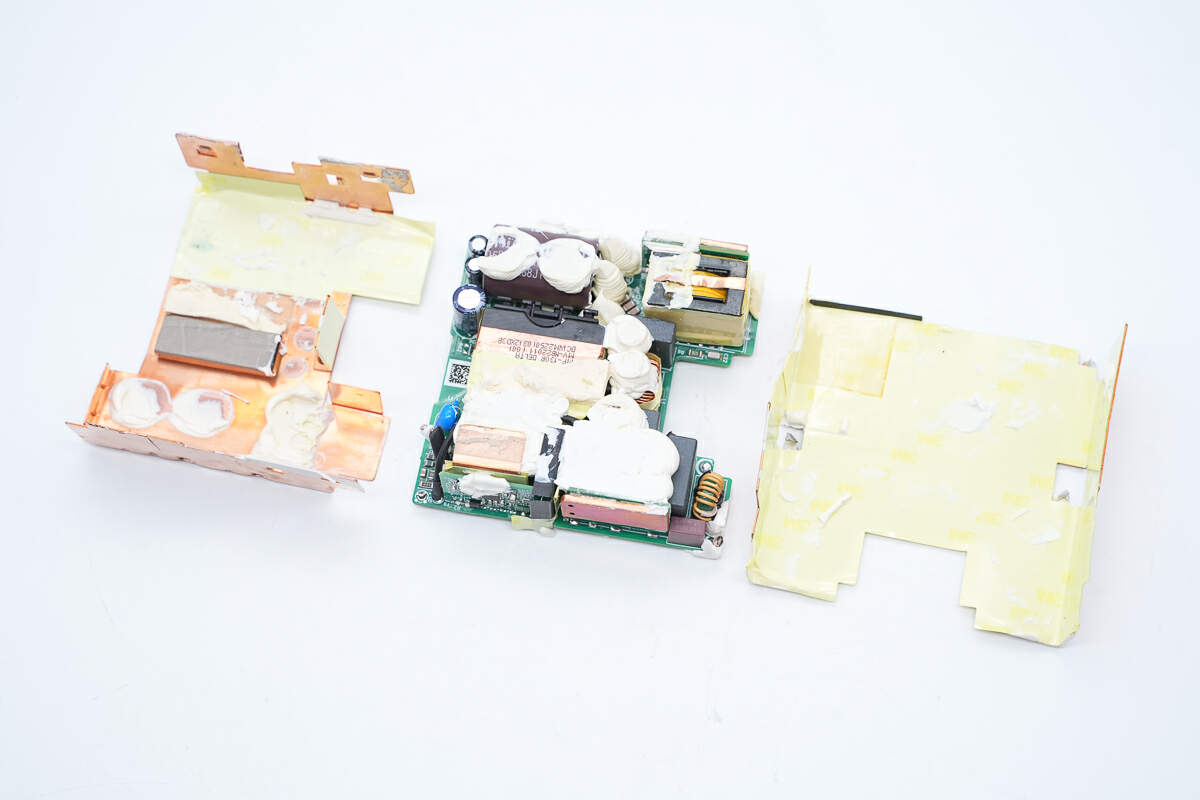
Remove the heat sink, and the conductive cloth is pasted on the corresponding position of the transformer.
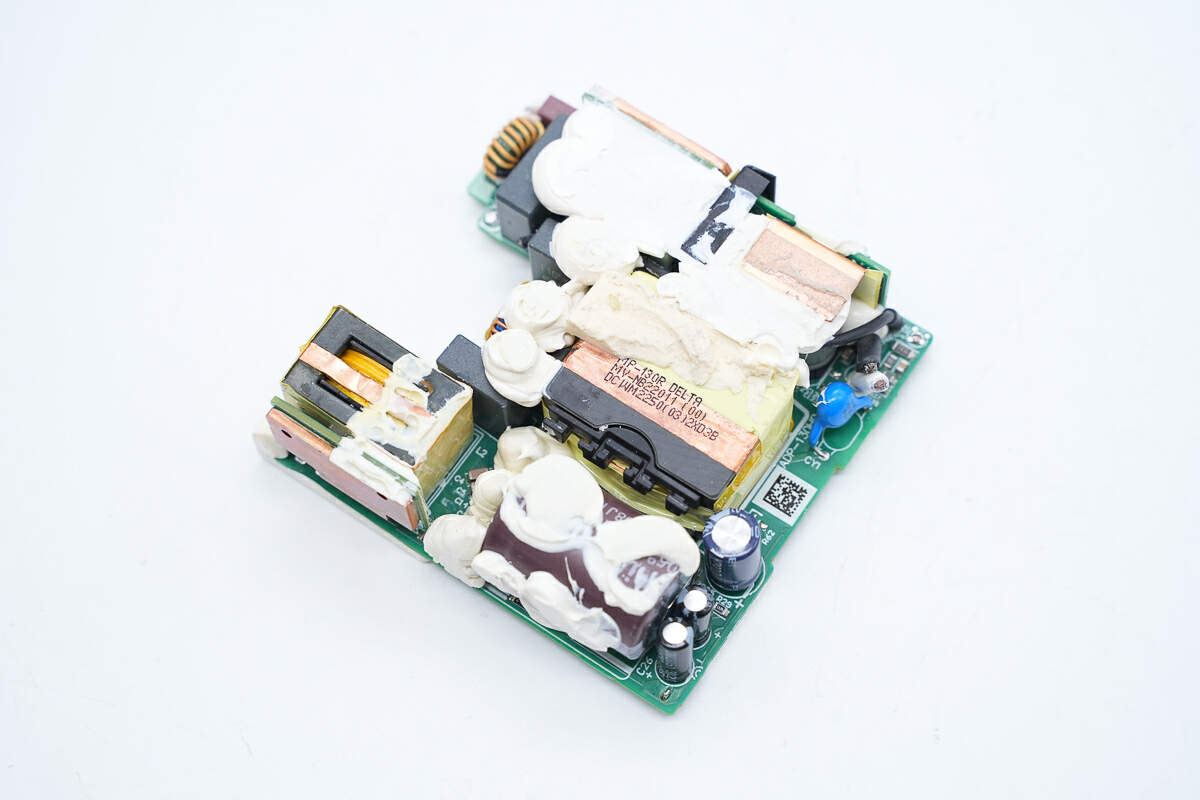

The components on the front of the PCBA module are filled with potting compound, and there are two small heat-dissipation copper sheets on both sides.
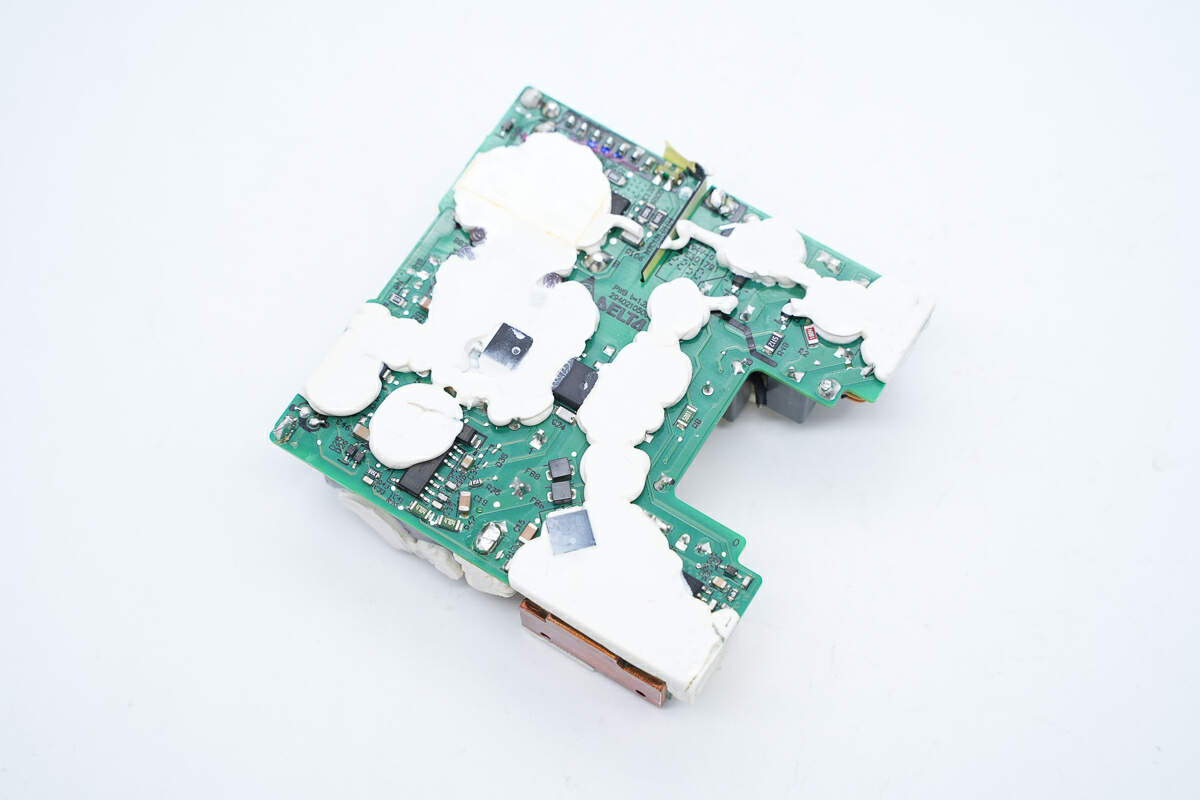

The main components on the back of the PCBA module also use the potting compound to help dissipate heat.
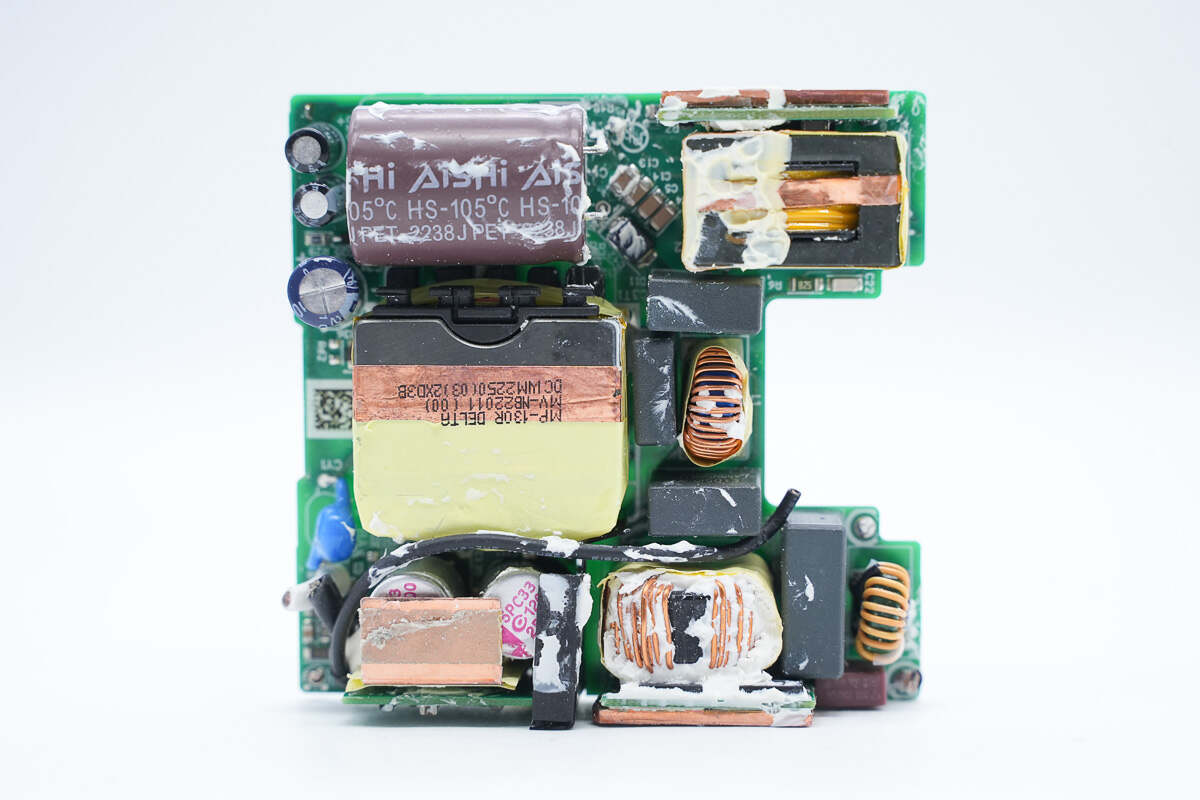
Clean up the potting compound. The time delay fuse, common mode choke, film capacitor, filter inductor, PFC boost inductor, electrolytic capacitor, transformer, and other components are on the front of the PCBA module.
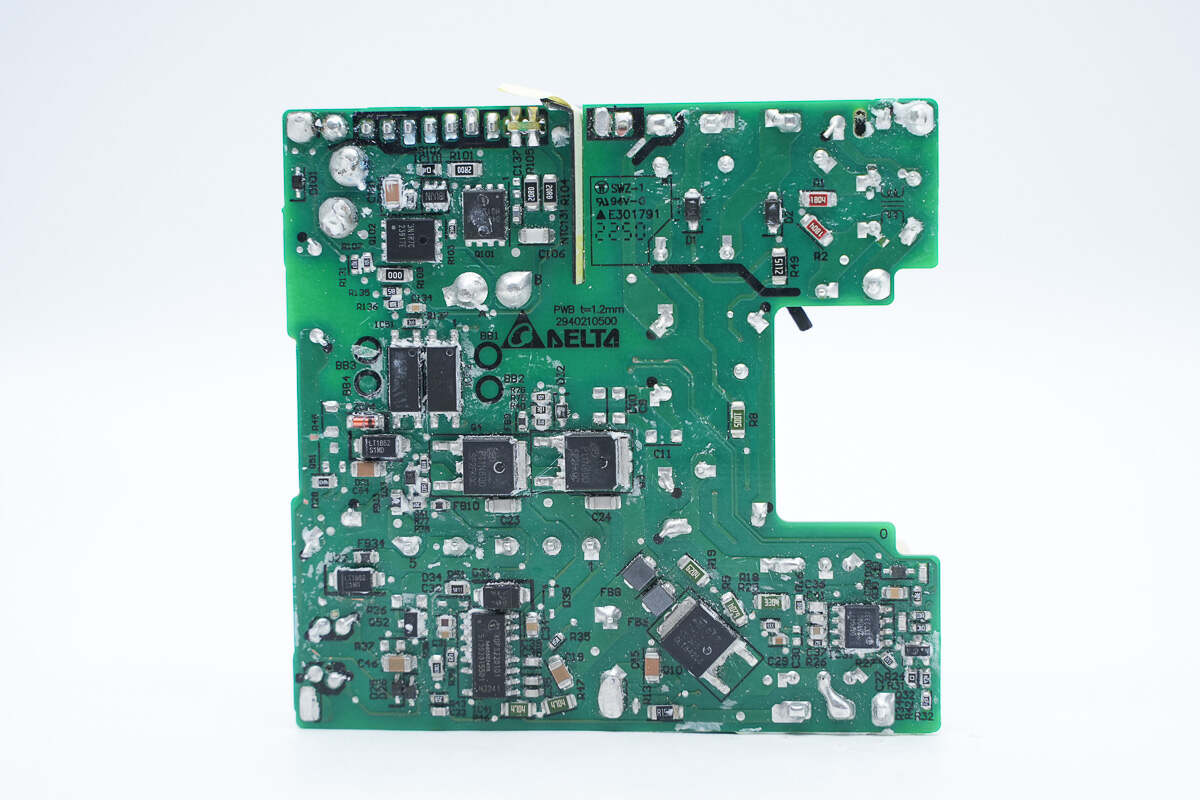
There is PFC controller, PFC rectifier, master control chip, HFB half-bridge MOSFET, optocoupler, synchronous rectifier controller, and synchronous rectifier on the back of the PCBA module.
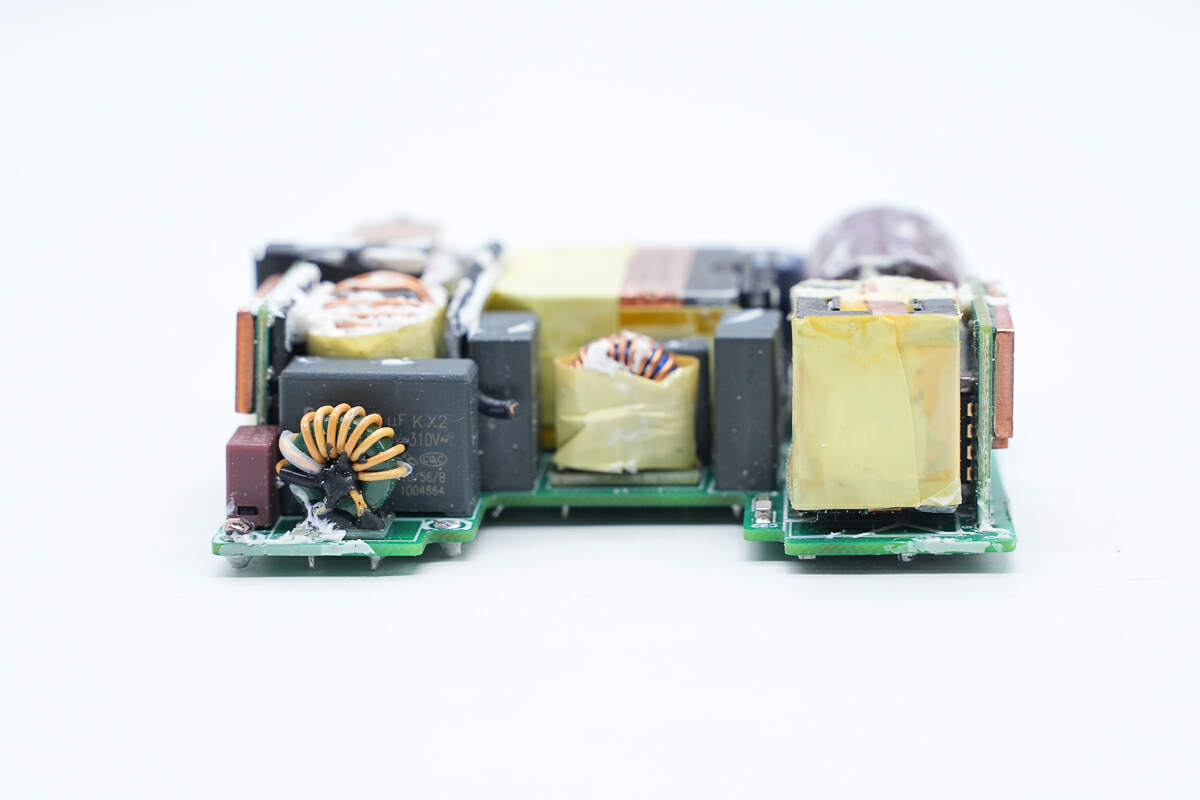

On the left side of the input end, there is a time delay fuse, common mode choke, and safety X capacitor, and the filter inductor in the middle is wrapped with tape for insulation.
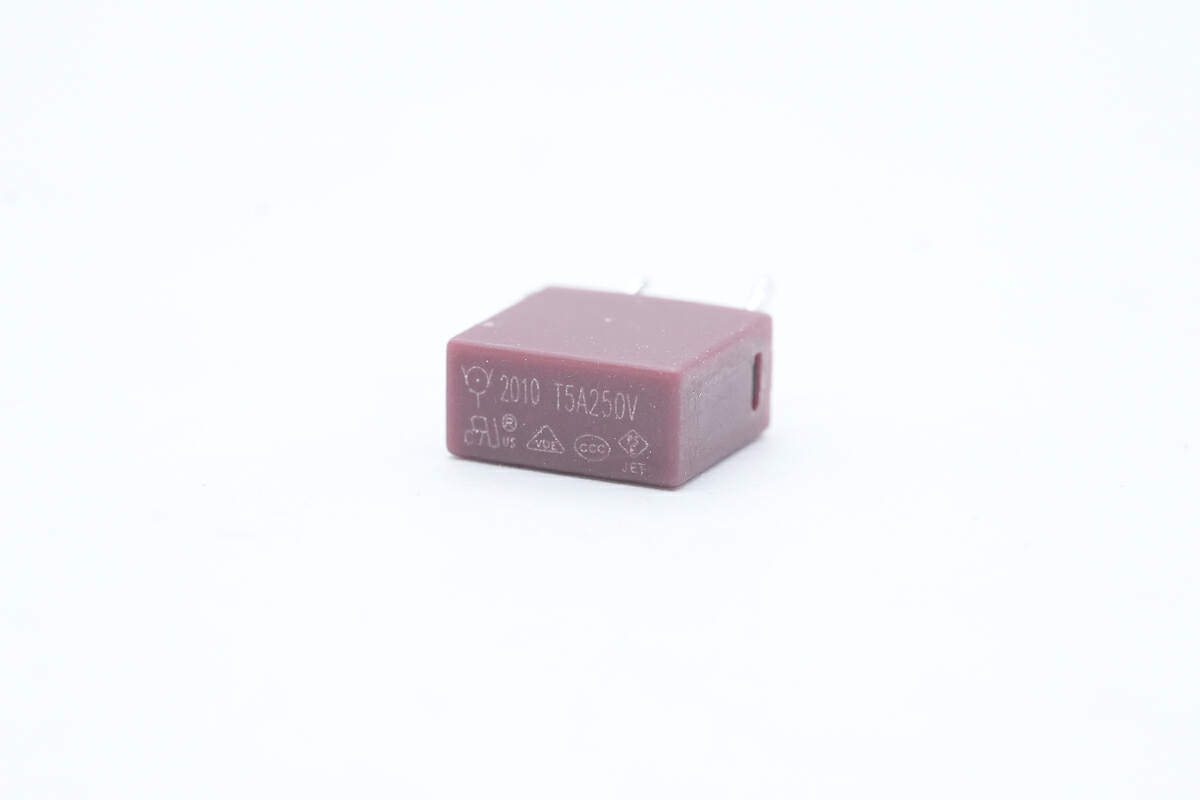

The time delay fuse is from WalterFuse. 5A 250V.
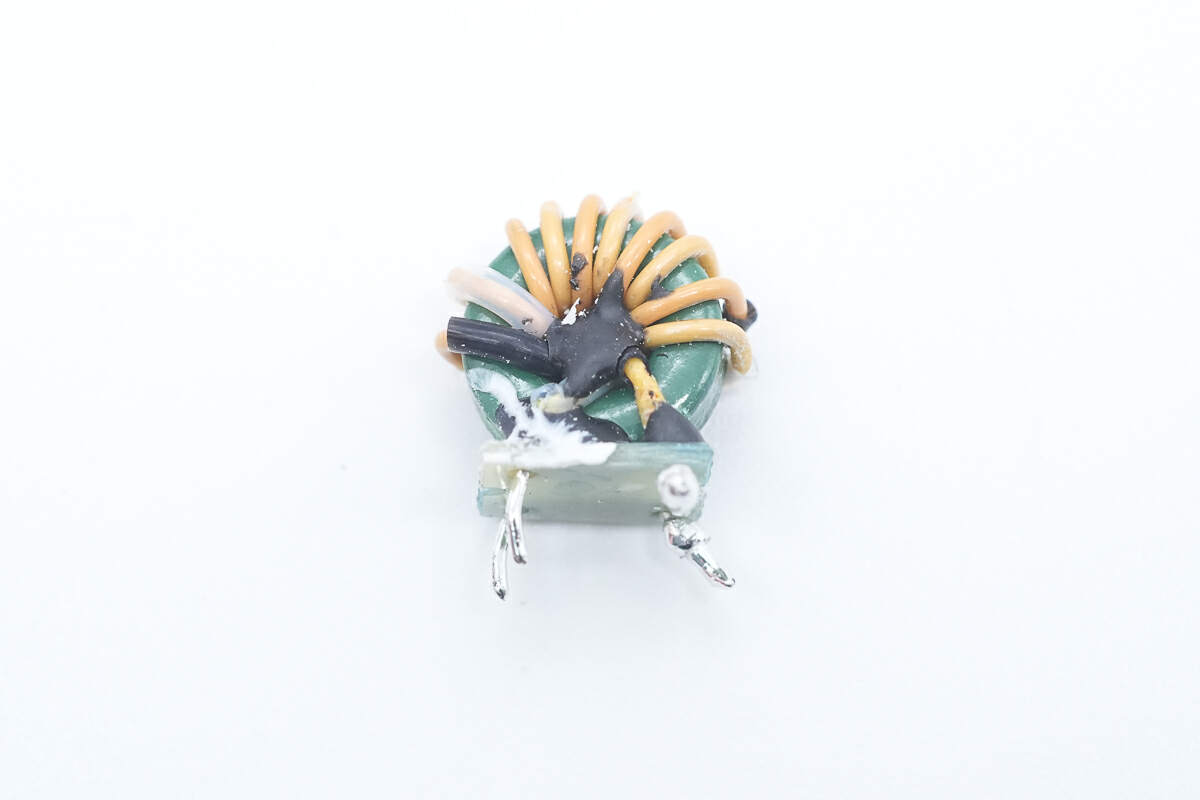

There is the common mode choke.

The safety X2 capacitor is from SCC. 0.47μF.
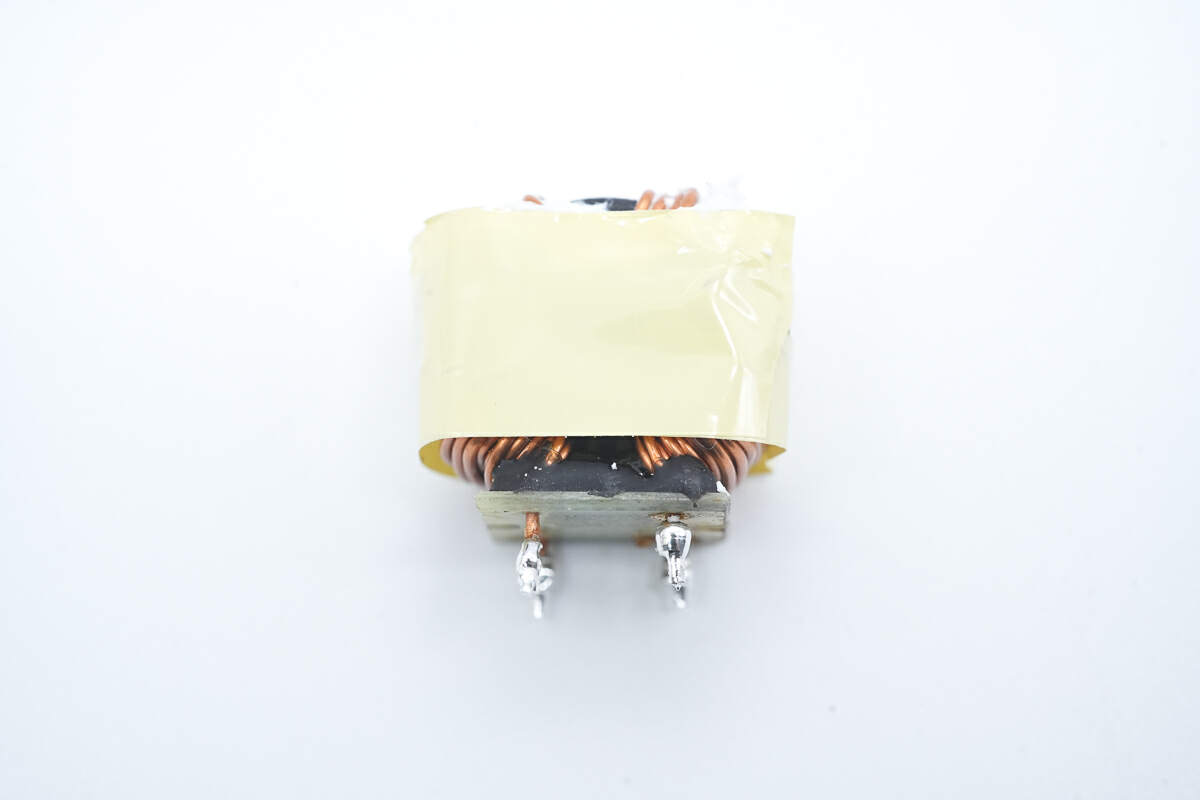

The common mode choke is insulated by tape.
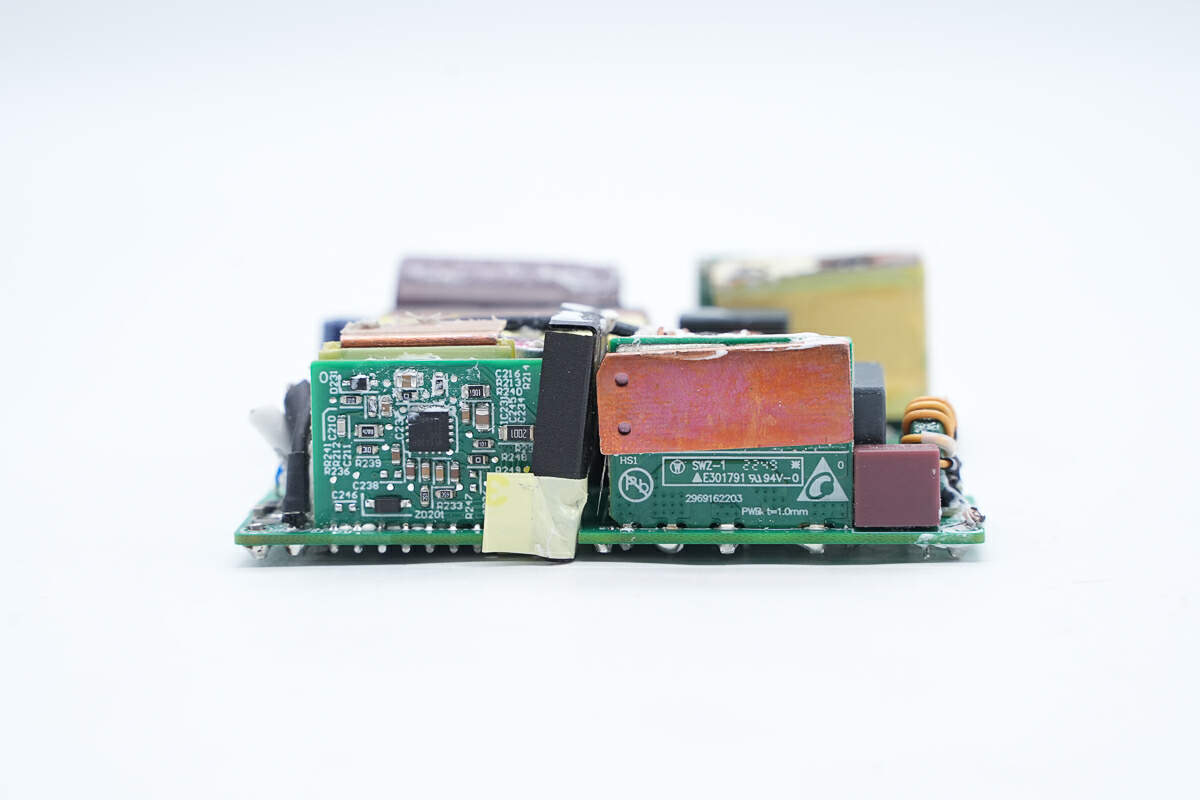

There is a mylar sheet between the PCB of the bridge rectifier and the PCB of the output protocol for isolation protection.
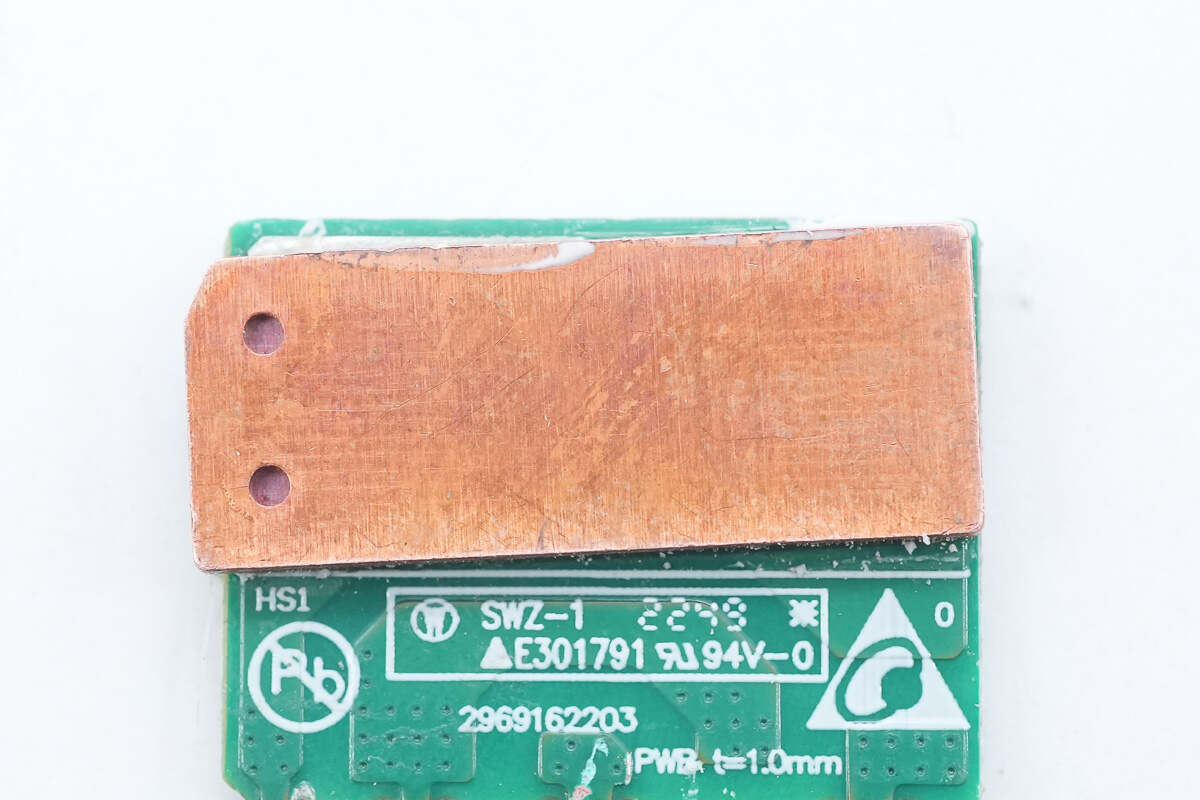

Remove the PCB of the bridge rectifier, and there is a copper heat sink on the back.
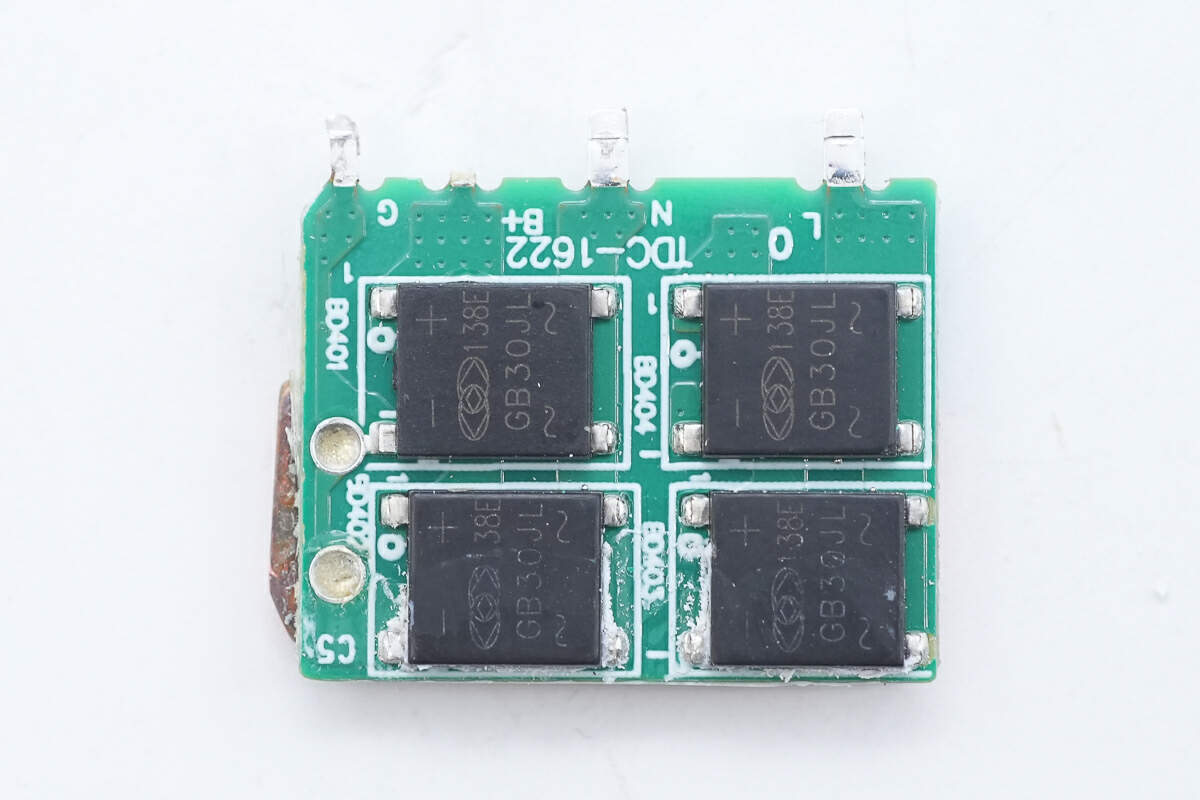
There are four bridge rectifiers on the front. The models are all GB30JL.

These are two film capacitors. 1μF 450V.
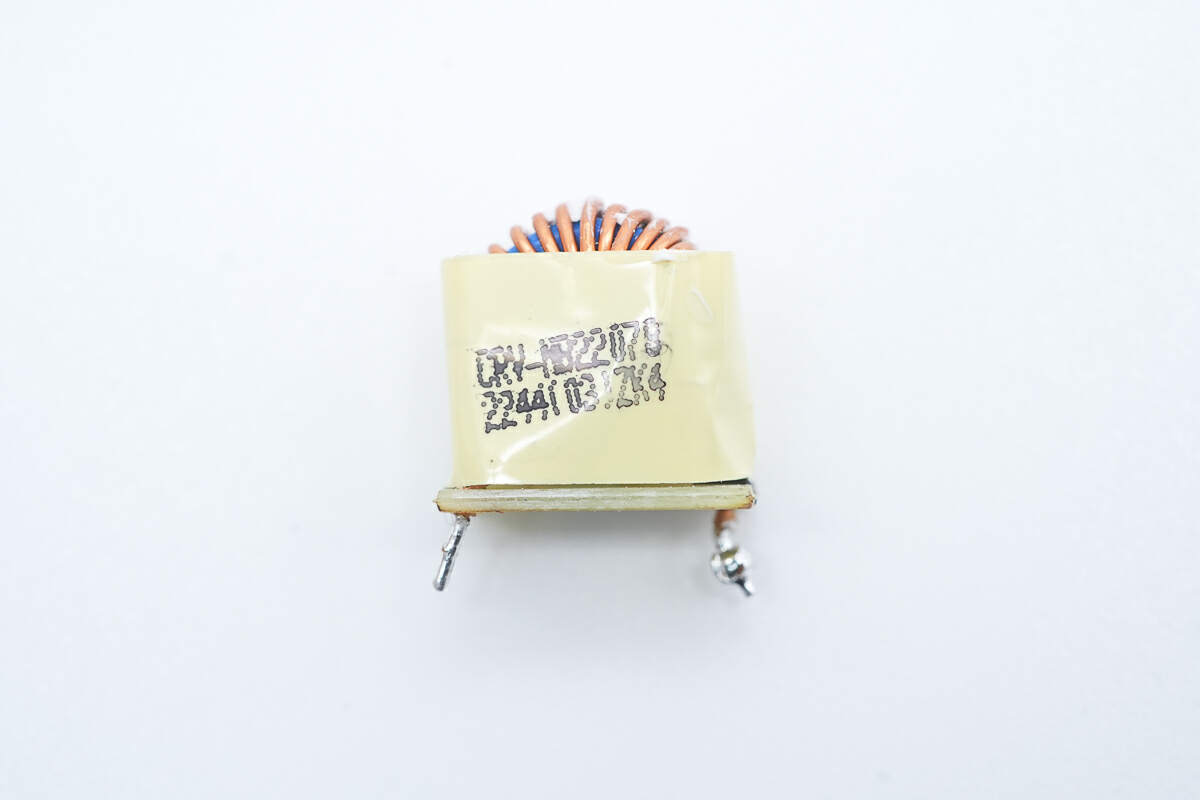

The filter inductor is insulated by tape.
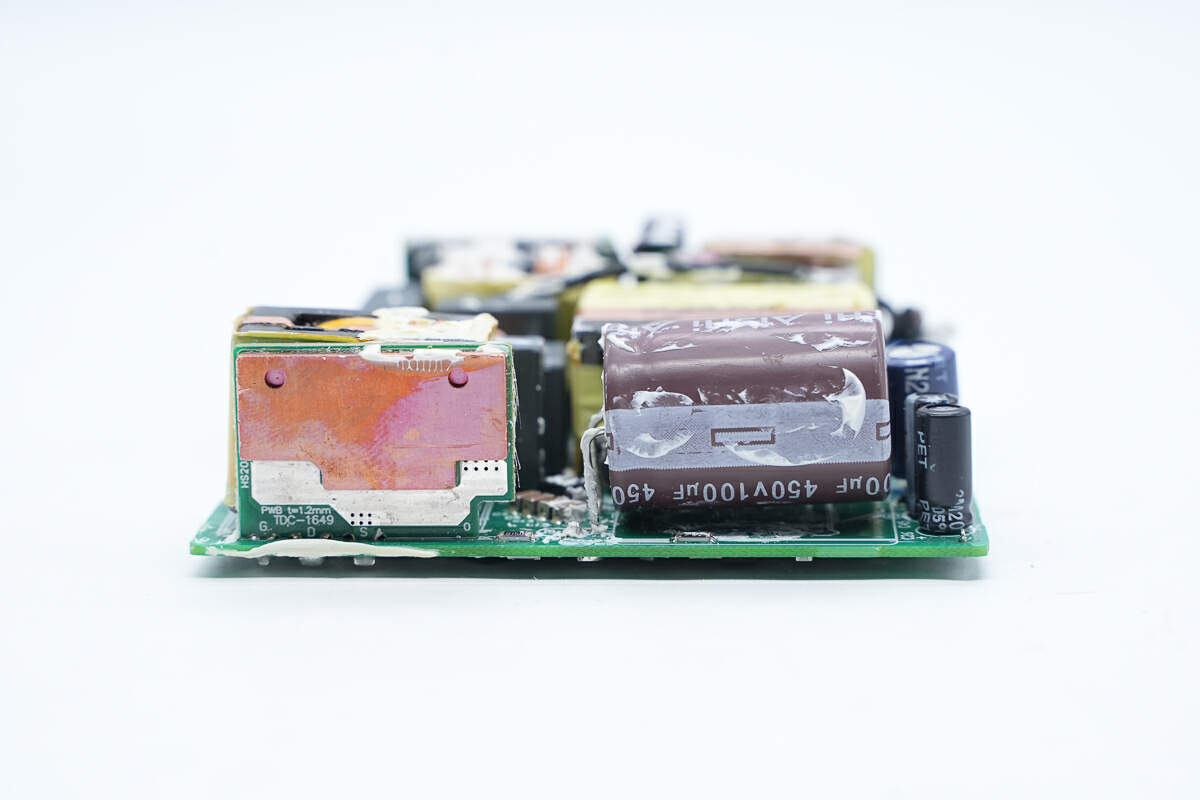
There is a PCB of the PFC boost circuit next to the PFC boost inductor and an electrolytic capacitor on the right.
There is a copper heat sink on the back.
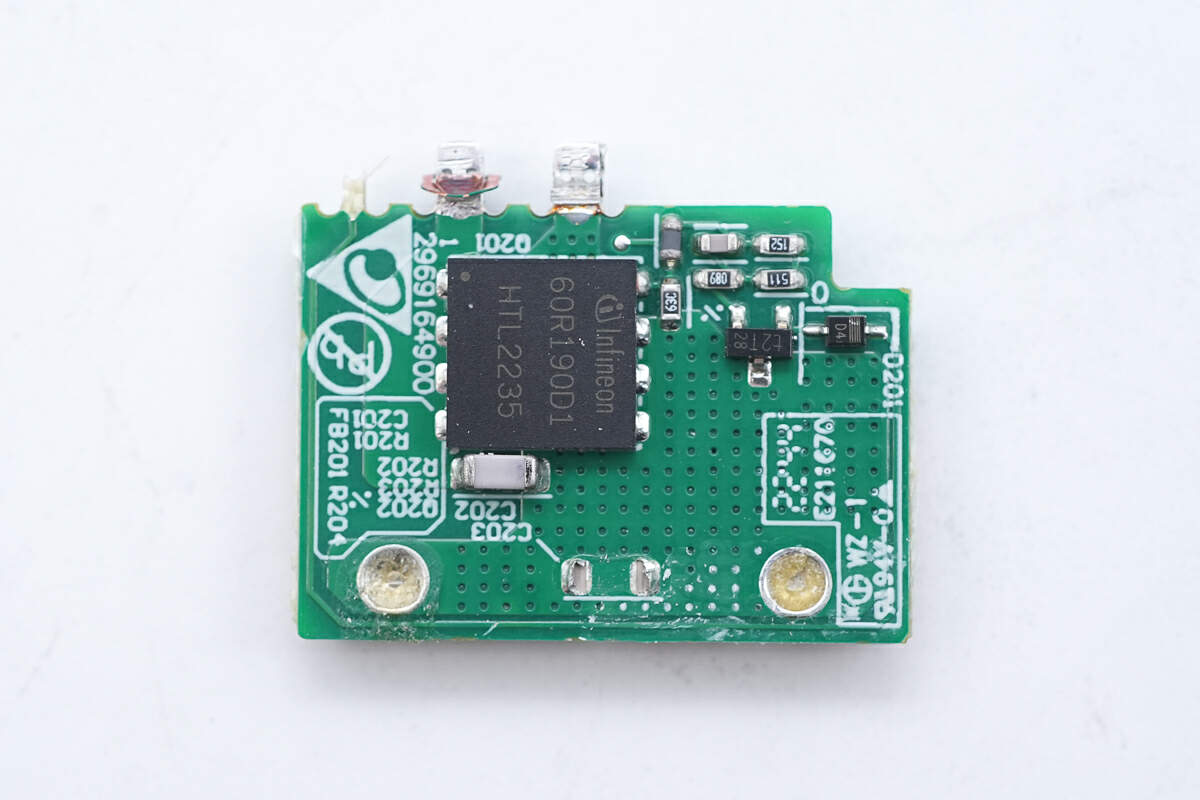

There is a PFC MOSFET on the front.
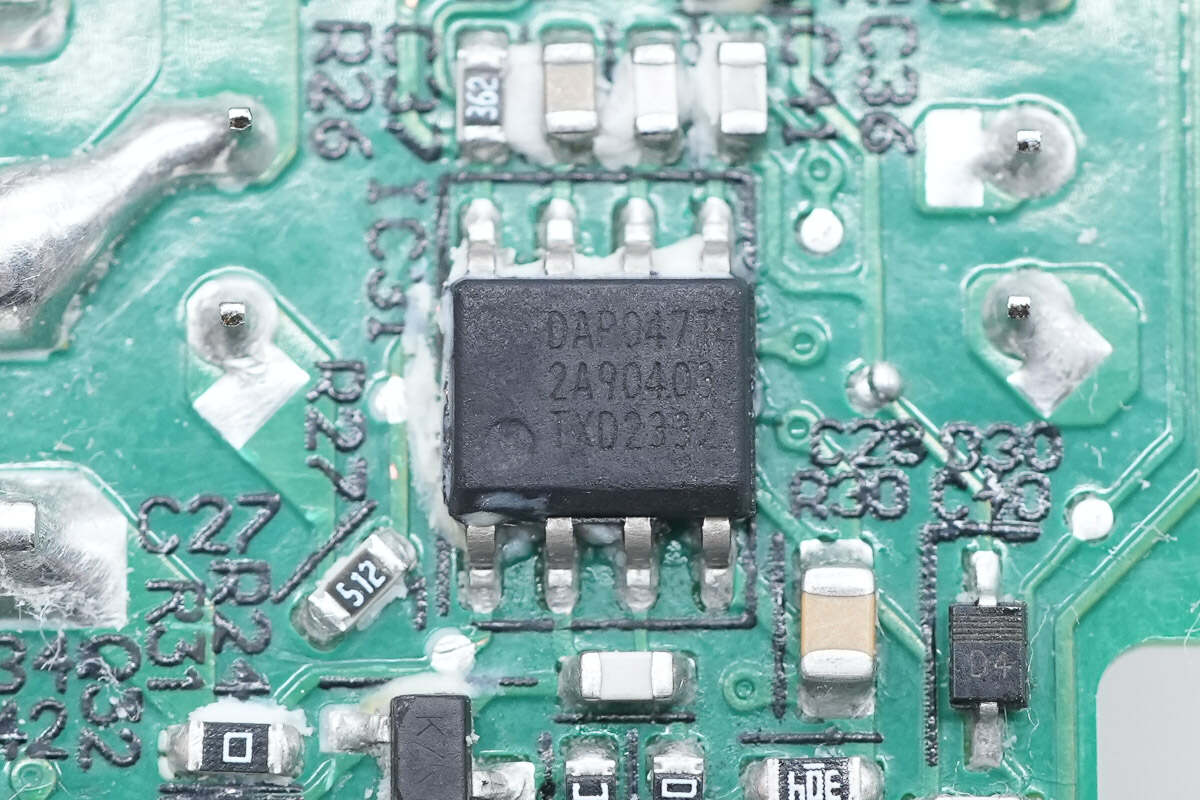
The PFC controller marked with DAP047T is from Delta.

The PFC MOSFET is from Infineon and adopts PG-LSON-8-1 package. The withstand voltage is 600V, and the resistance is 140mΩ. Model is IGLD60R190D1.

Here is the PFC boost inductor.
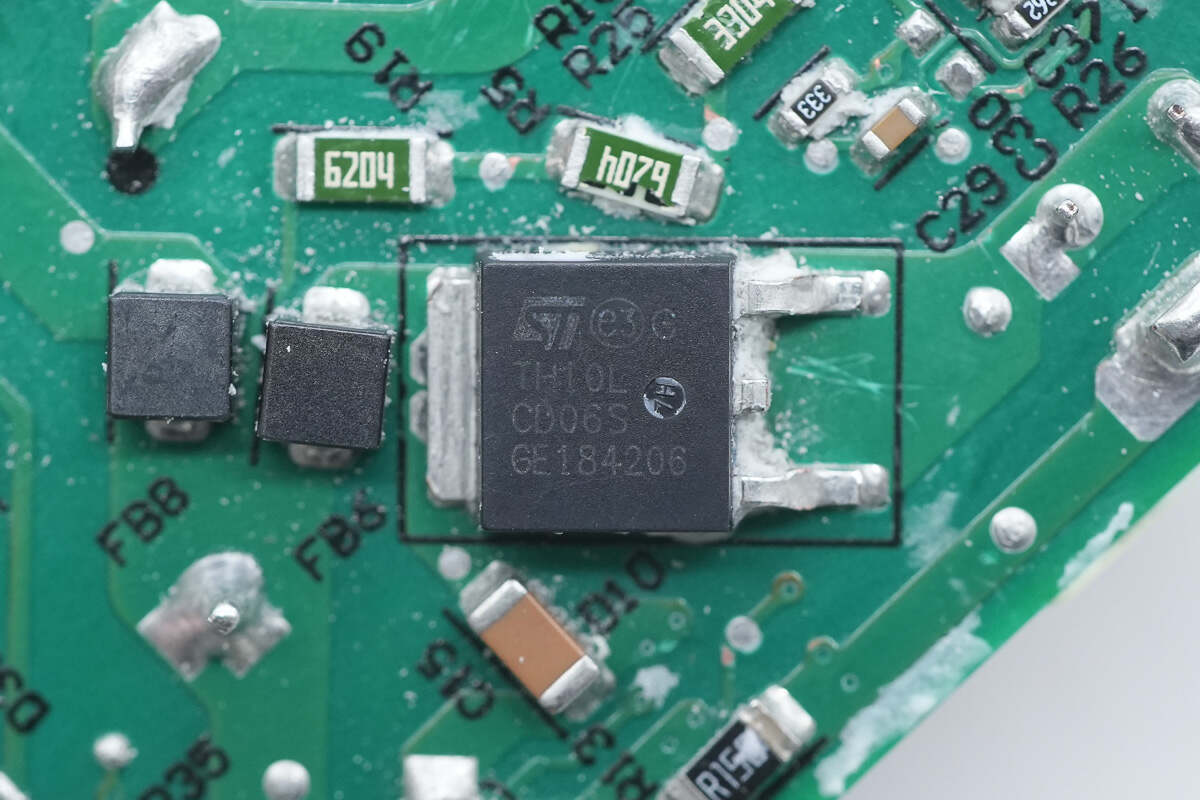
The PFC rectifier is from ST and adopts DPAK package. Model is STTH10LCD06S. 10A 600V.
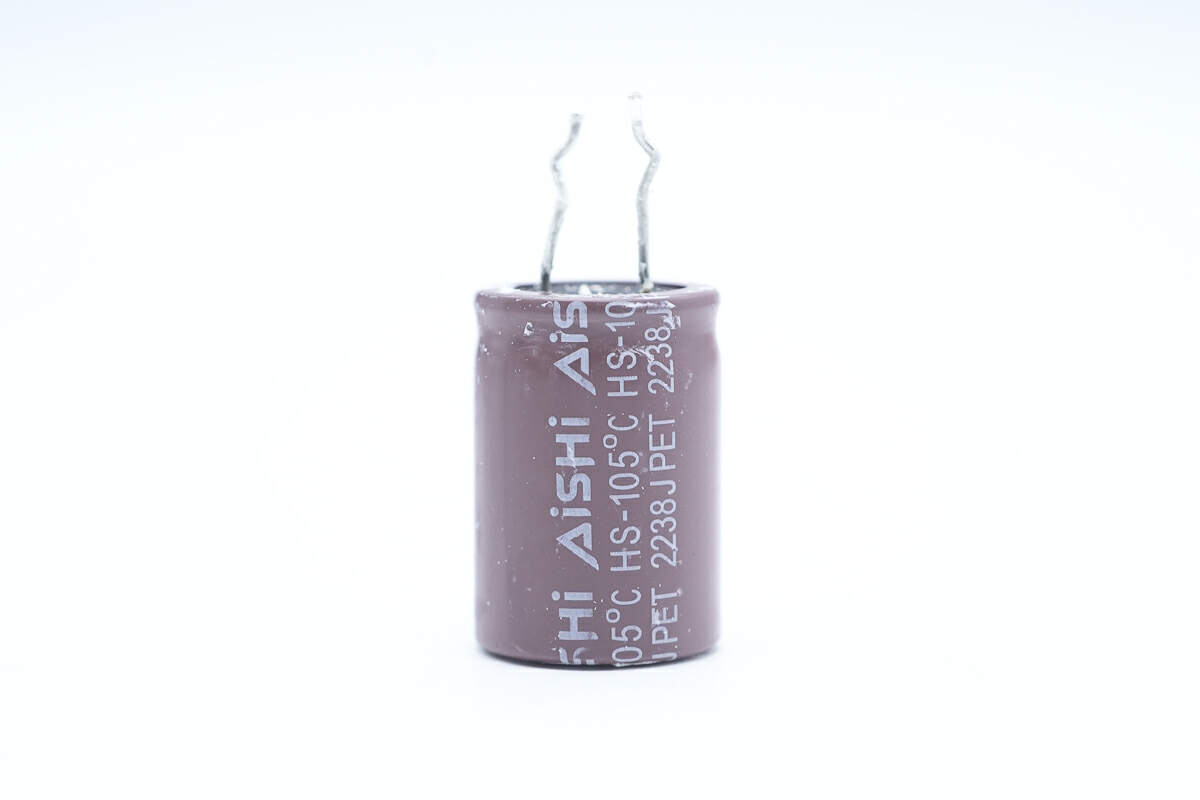

The electrolytic capacitor is from AiSHi. 450V 100μF.
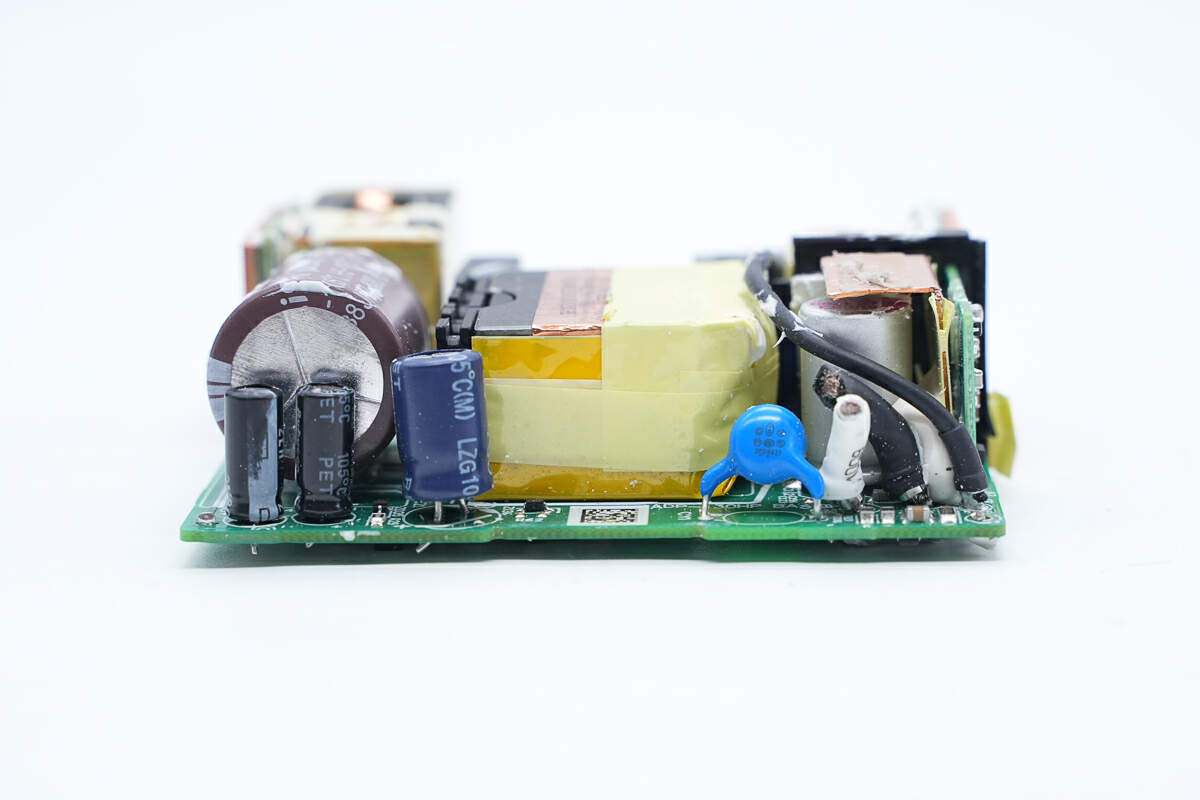
On the left side of the output end, there are capacitors that power the master control chip, in the middle is the transformer, and on the right side is the Y capacitor and the solid capacitor for output filtering.
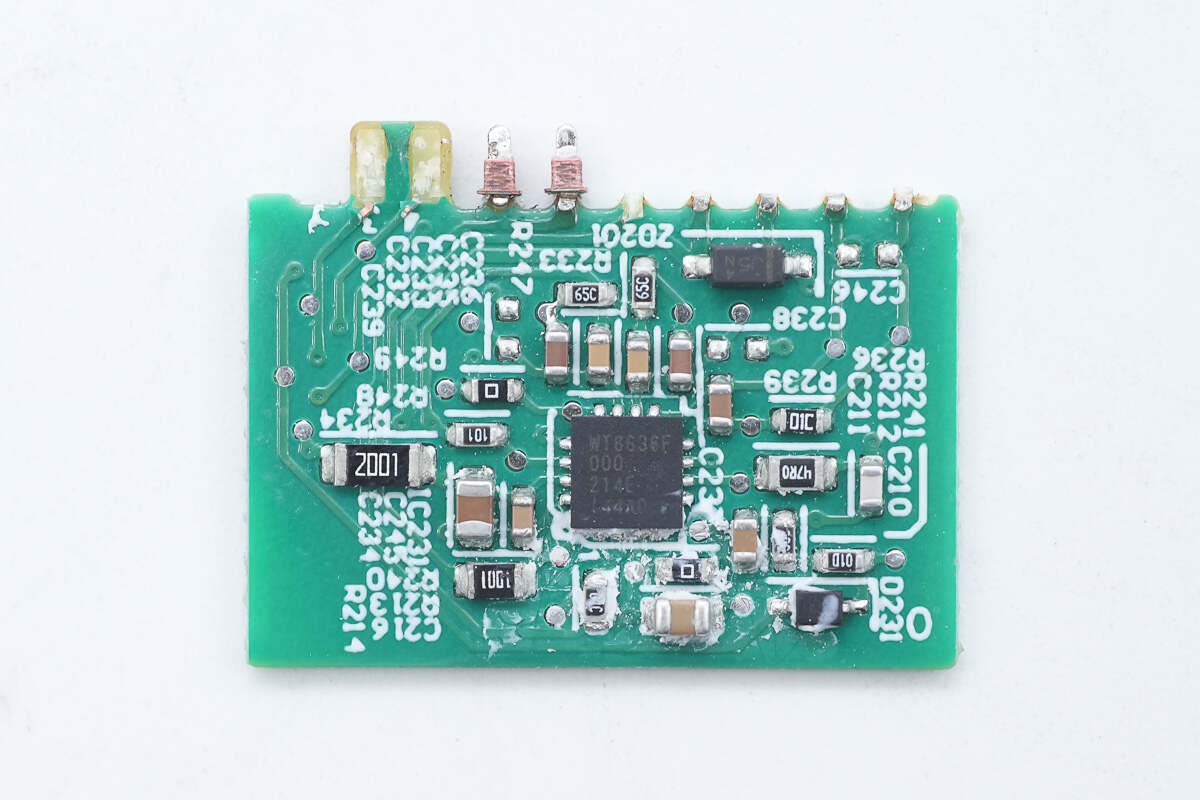
Remove the output PCB, and there is a protocol chip.
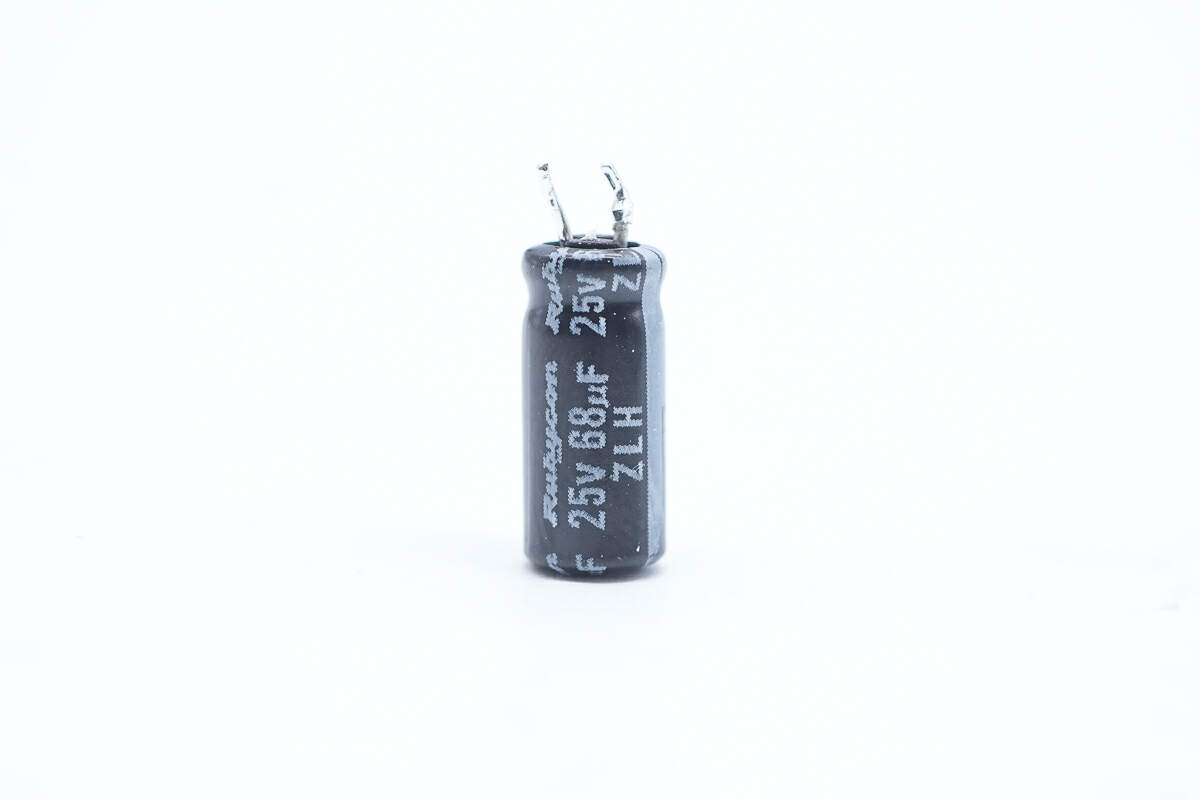

The capacitors that power the master control chip are from Rubycon. 25V 68μF.
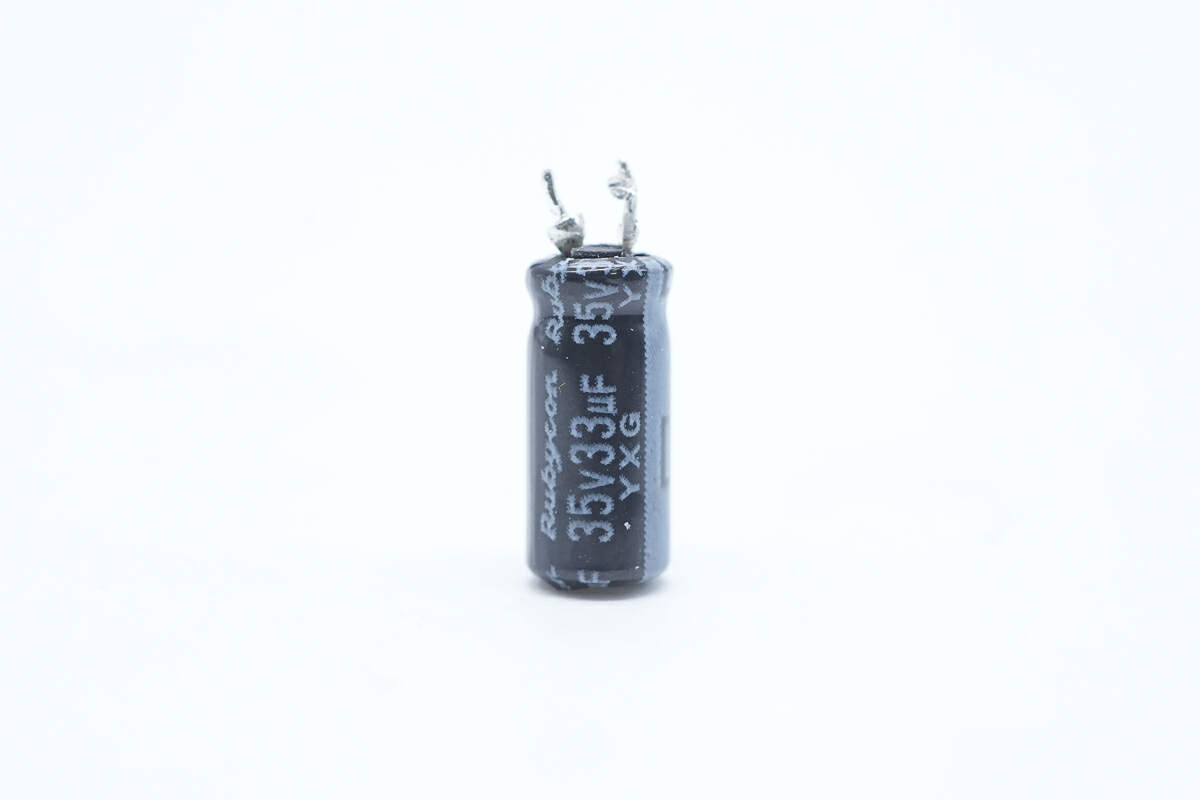

The other one is also from Rubycon. 35V 33μF.
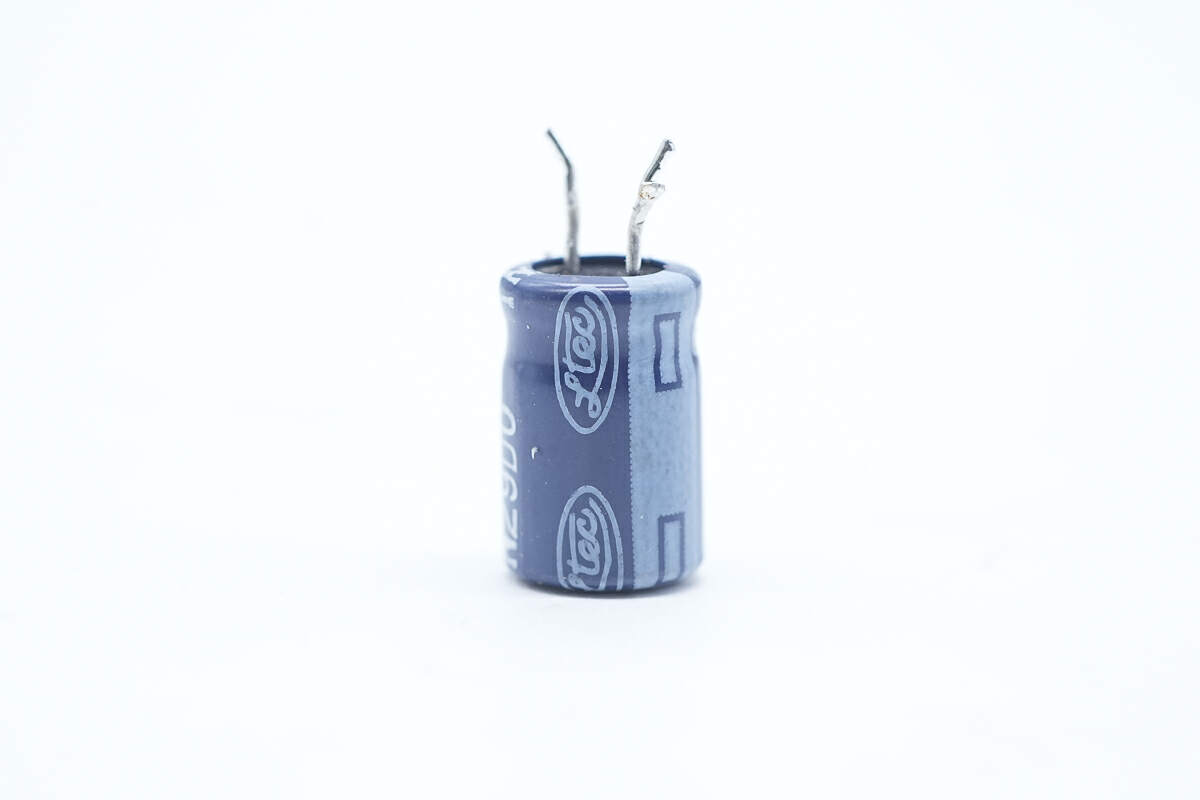

Another one is from LTEC. 100V 22μF.
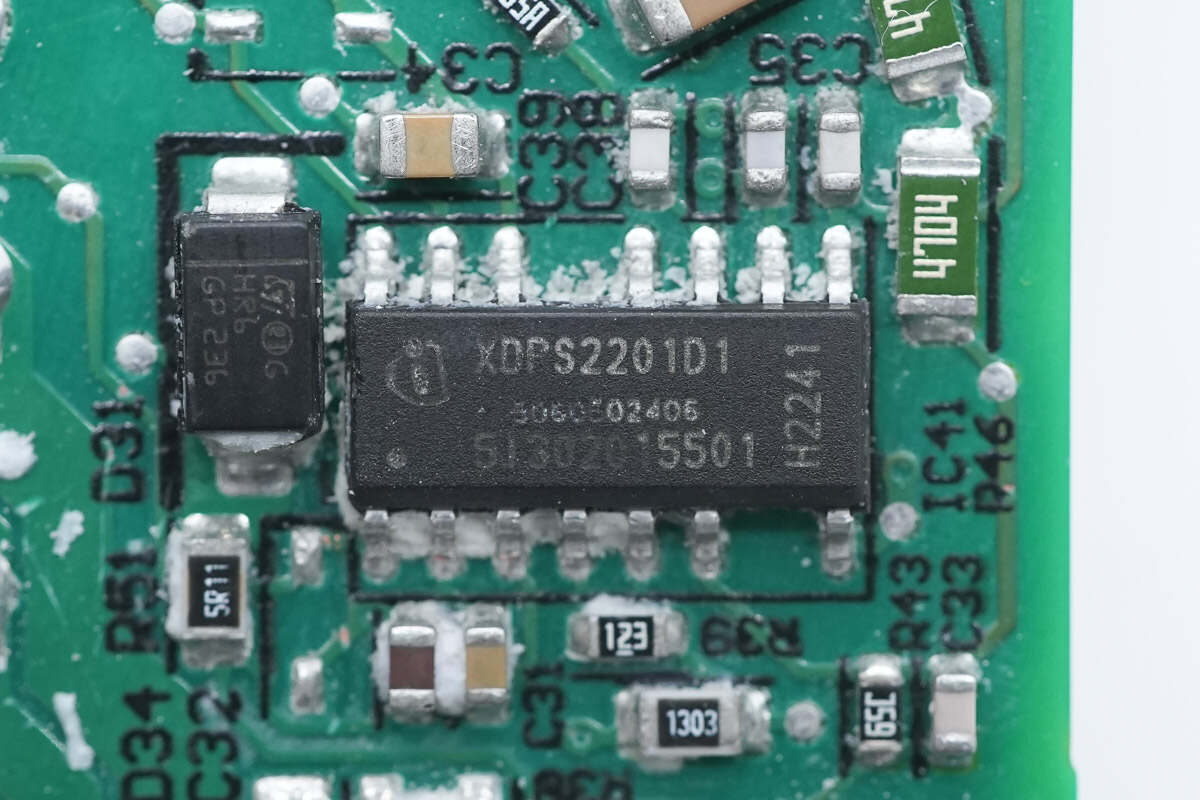
The master control chip is from Infineon and adopts PG-DSO-14 package. It is a digital hybrid flyback controller with an integrated 600V high-voltage startup circuit and high- and low-side MOS drivers. It supports primary side overvoltage protection, and standby power consumption is less than 75mW. Model is XPDS2201.
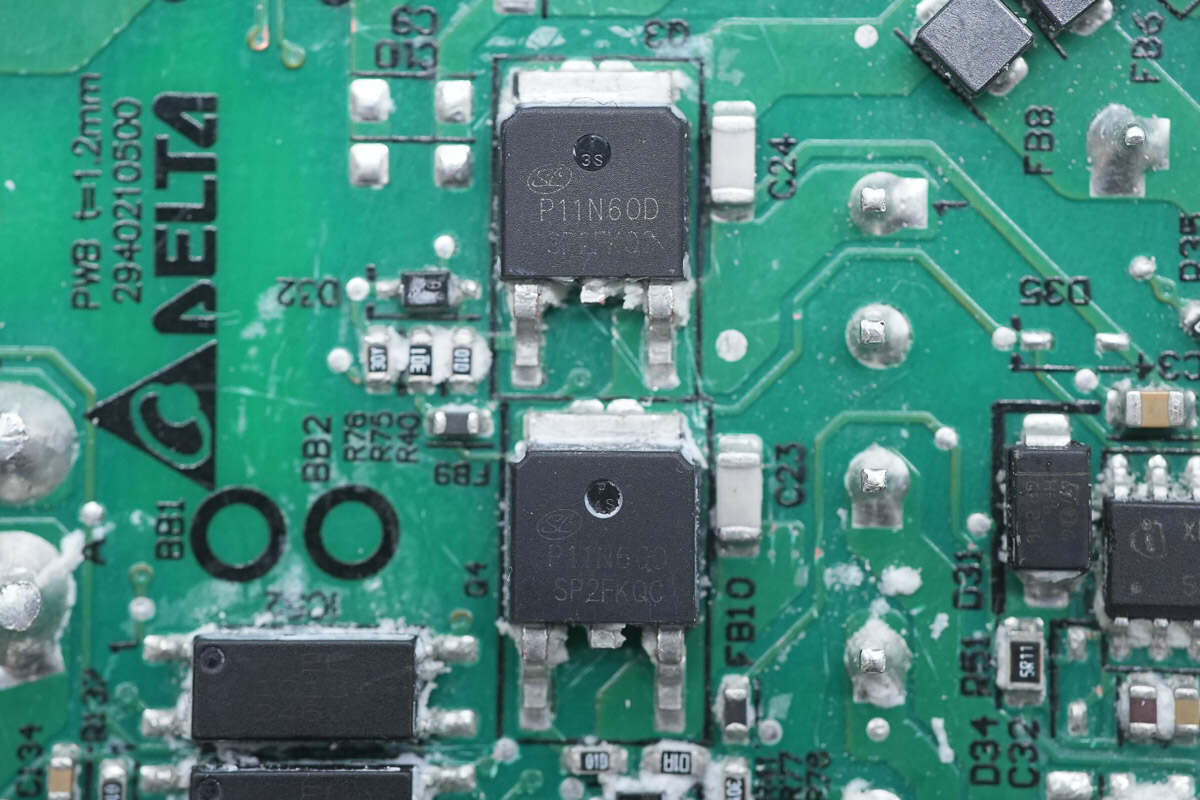
The HFB half-bridge MOSFET is from Silan and adopts TO-252 package. Model is SVSP11N60DD2TR. 600V 300mΩ.

Here is the resonant capacitor. 0.47μF 450V.
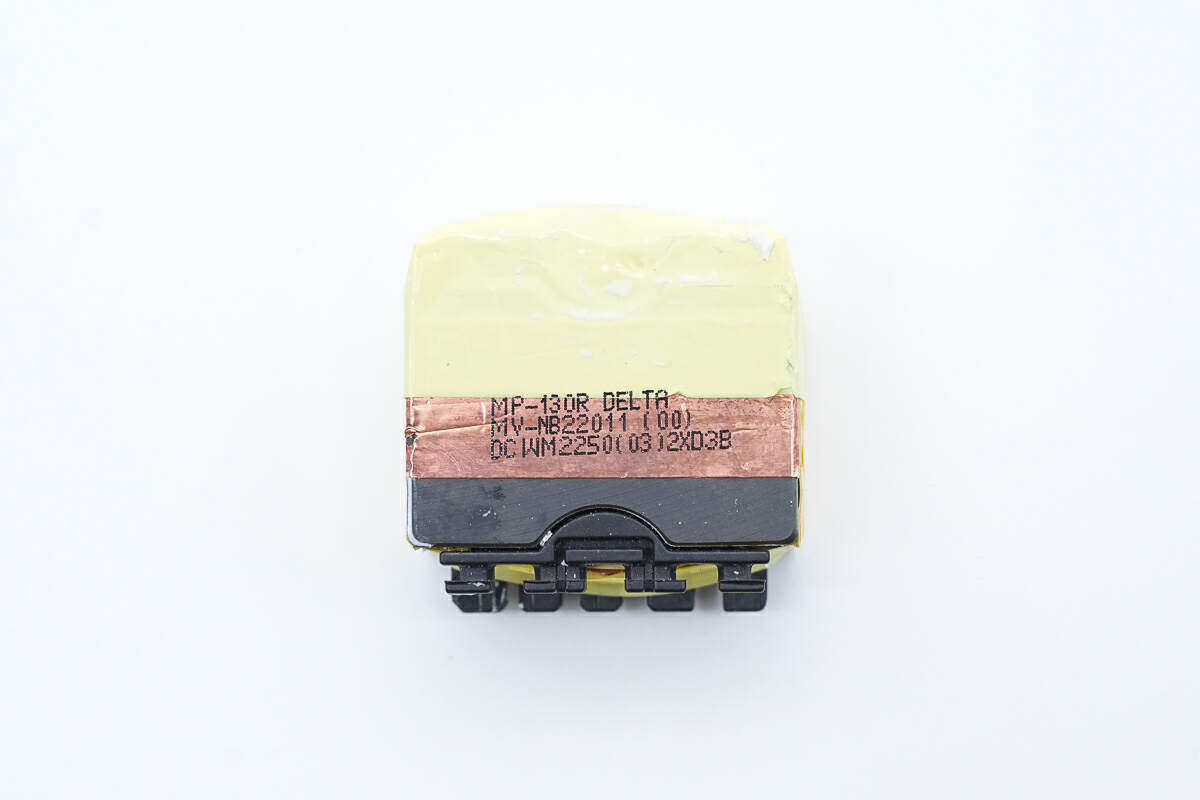

Here is the transformer.
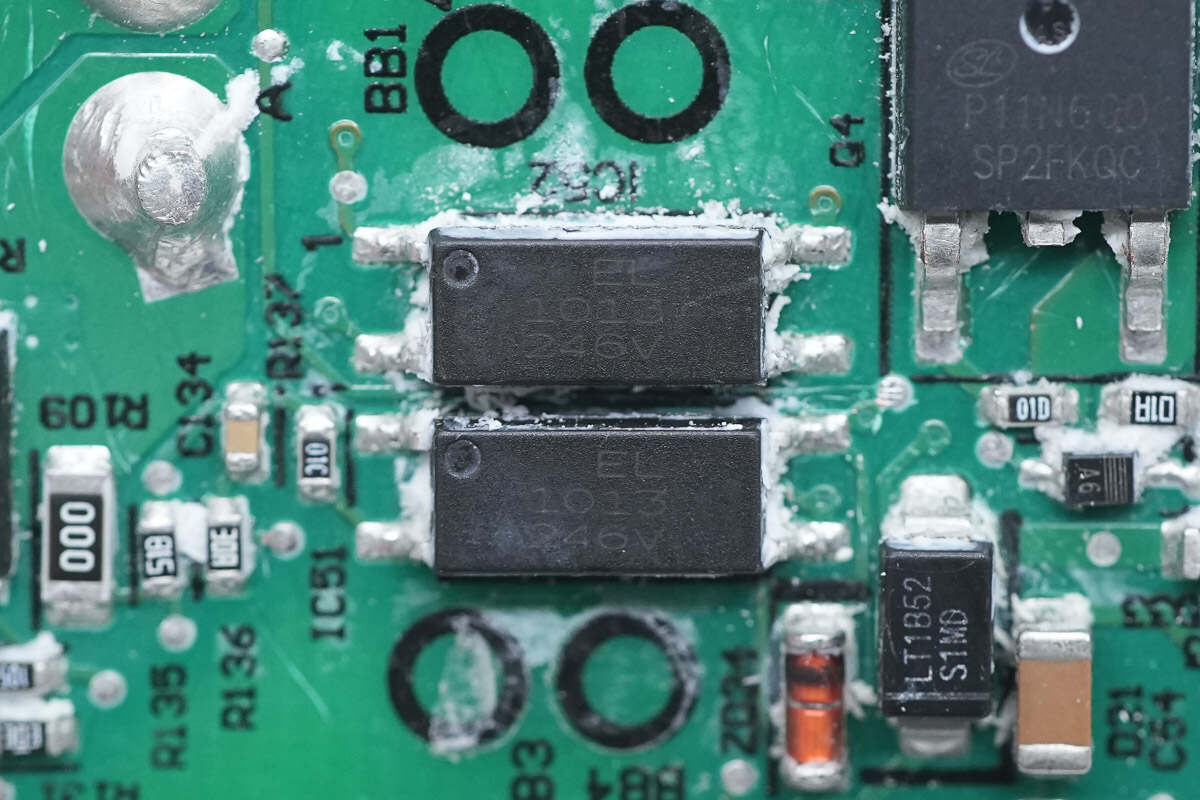
These two optocouplers for output voltage feedback and protection are from Everlight. Model is EL 1013.
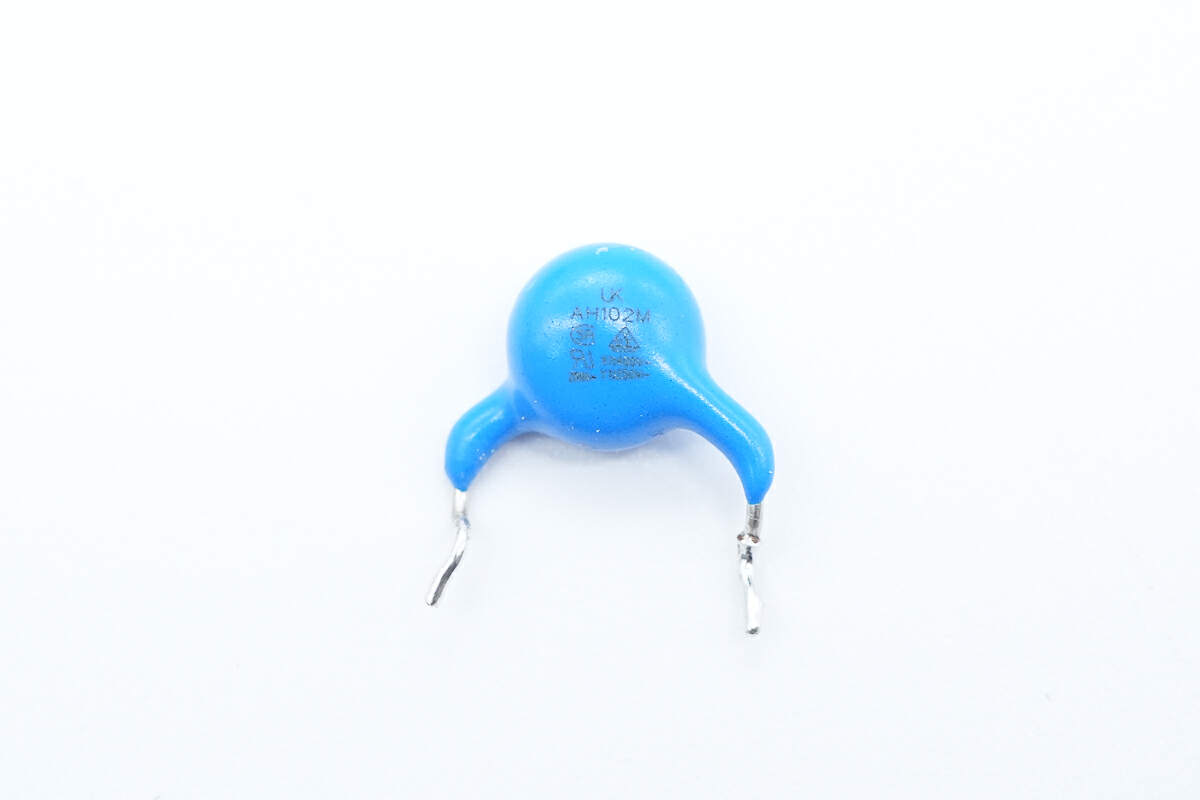

This is the blue Y capacitor.

The synchronous rectifier controller marked with IBUJN is from MPS and adopts TSOT23-6 package. It supports DCM, CCM, QR, and ZVS operating modes, as well as ACF active clamp flyback and HFB hybrid flyback, with an operating frequency of up to 1MHz. It supports both high-side and low-side applications. Model is MP6951.
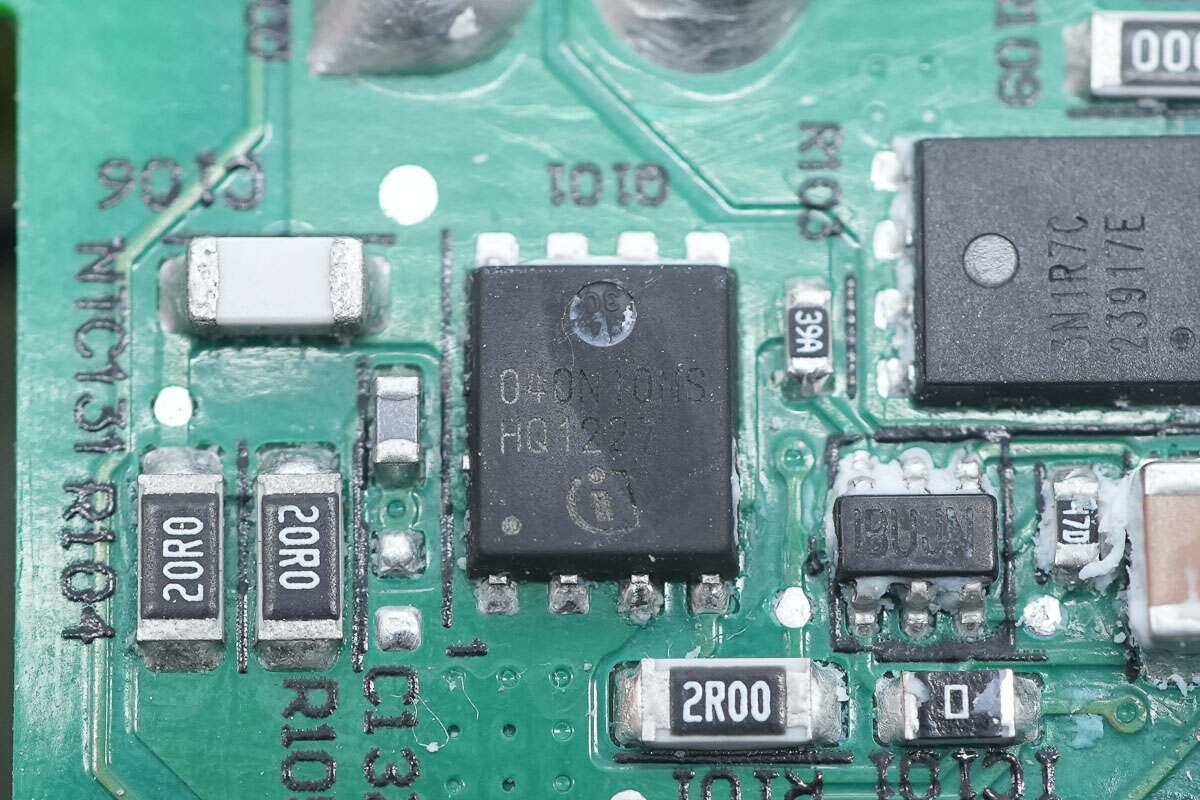
The synchronous rectifier is from Infineon and adopts PG-TDSON-8 package. Model is BSC040N10NS. 100V 4mΩ.
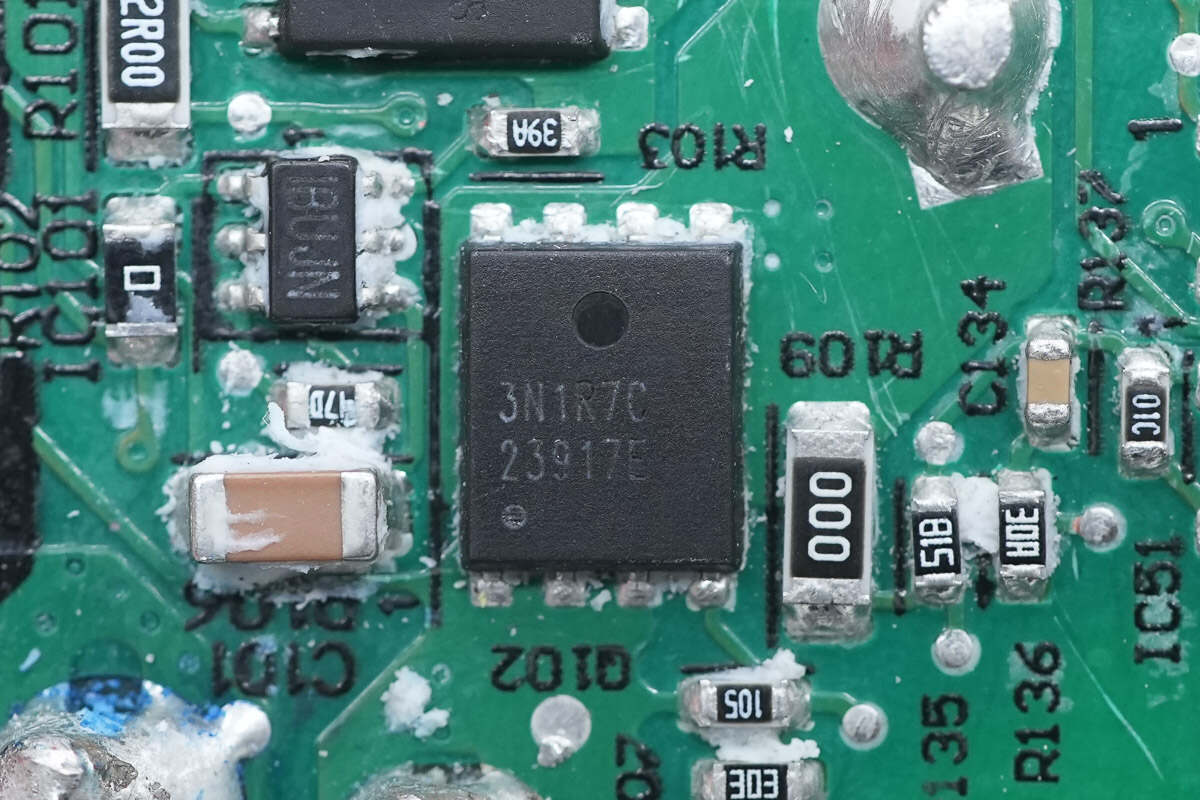
This MOSFET is marked with 3N1R7C.

These two solid capacitors for output filtering are from APAQ. 25V 1200μF.
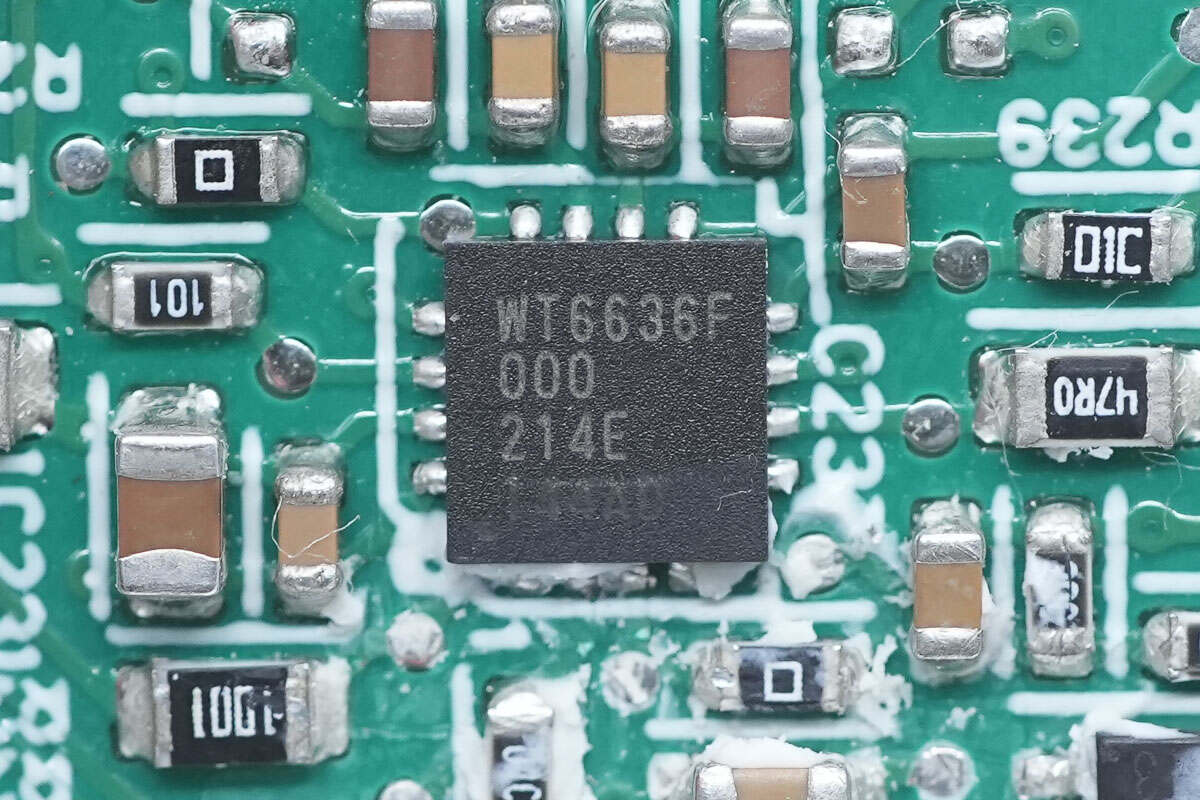
The protocol chip is from Weltrend. It has passed the USB-IF Association USB PD3.0 (PPS) certification and Qualcomm QC4+ certification. It supports USB PD3.0 and PPS, supports wire loss compensation, and supports multiple protection functions. It integrates 10-bit ADC for voltage and current detection, a built-in 8051 core microcontroller, and a built-in discharge MOSFET. Model is WT6636F.
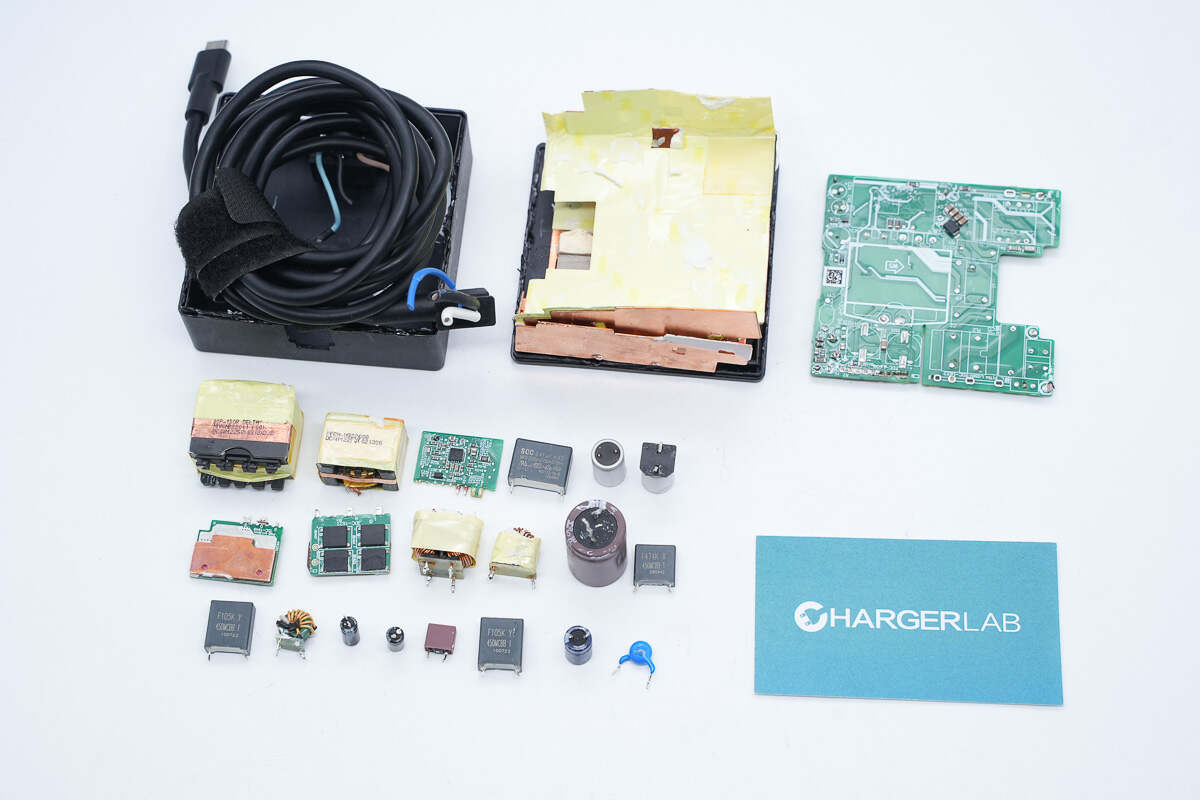

Well, those are all components of the ASUS ROG 130W USB-C GaN Power Adapter.
Summary of ChargerLAB
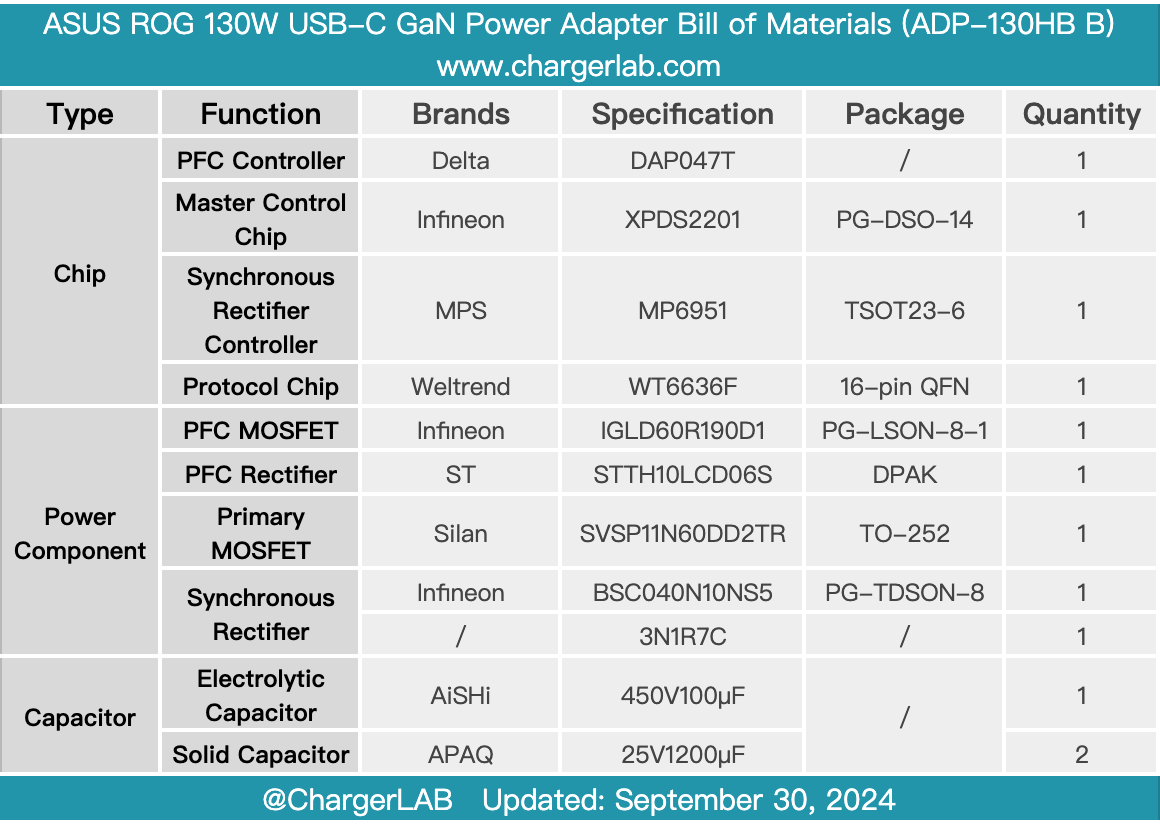
Here is the component list of the ASUS ROG 130W USB-C GaN Power Adapter.
The ASUS ROG 130W USB-C GaN Power Adapter features a black matte shell with a glossy ROG logo and comes with a 1.6-meter-long USB-C output cable. It adopts a detachable power cord design, and the power cord can be replaced with different lengths according to the usage scenario, making it convenient to use. The maximum power of 130W meets the power supply needs of laptops.
After taking it apart, we found the PCBA module is made up of multiple small PCBs, each with a copper heat sink. The components are reinforced with potting compound. The overall materials are luxurious, and the workmanship is solid and reliable.
Related Articles:
1. ASUS Launches ROG 140W USB-C GaN Charger for Multi-Device Fast Charging
2. Enhanced Gameplay: ROG Ally's Monitor Compatibility Explored
3. Charging Review of ASUS ROG Ally Handheld Gaming Console








