Introduction
With the widespread adoption of PD fast charging, more and more devices are equipped with USB-C ports, rendering some dedicated high-current DC power adapters obsolete. However, you can easily solve this issue by purchasing an adapter, eliminating the need to buy a new power adapter and minimizing environmental pollution.
Recently, ChargerLAB received a DC to USB-C power adapter from HP, which allows DC power adapters to support PD 3.0 fast charging output. In the following test, we will examine this adapter and evaluate its real-world performance.
Product Appearance
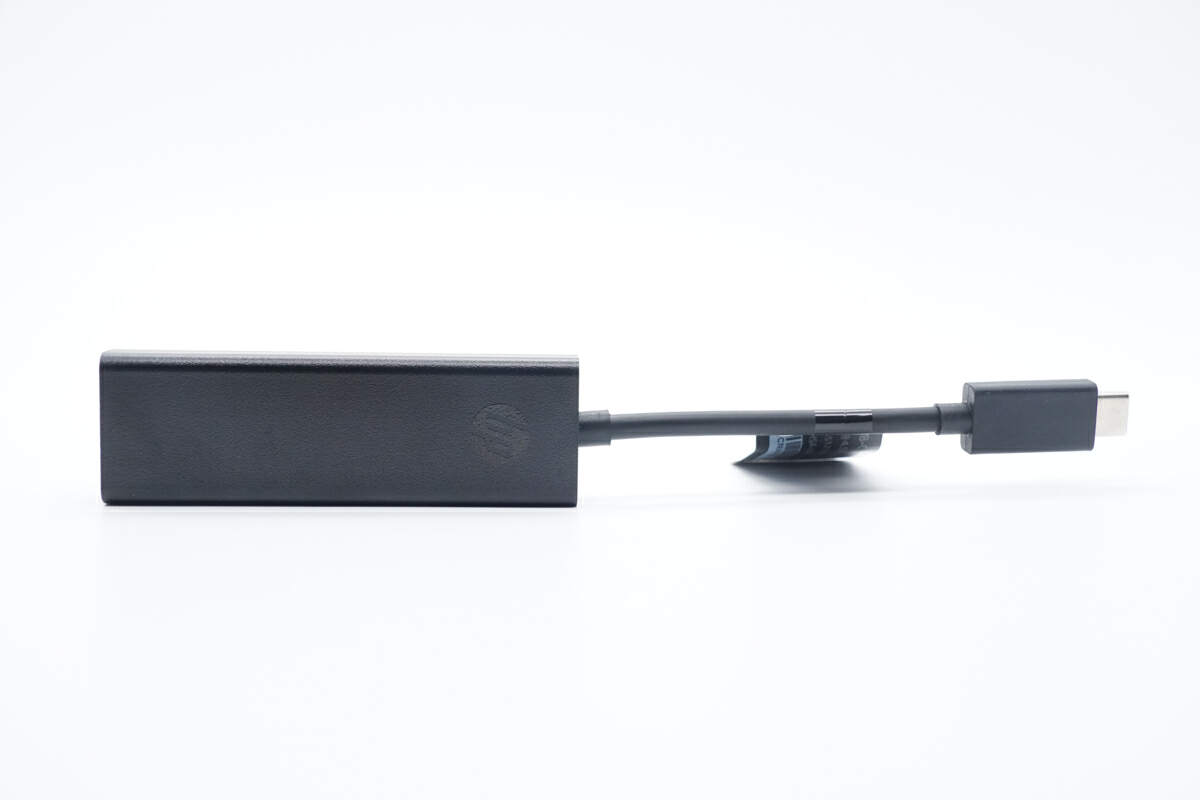

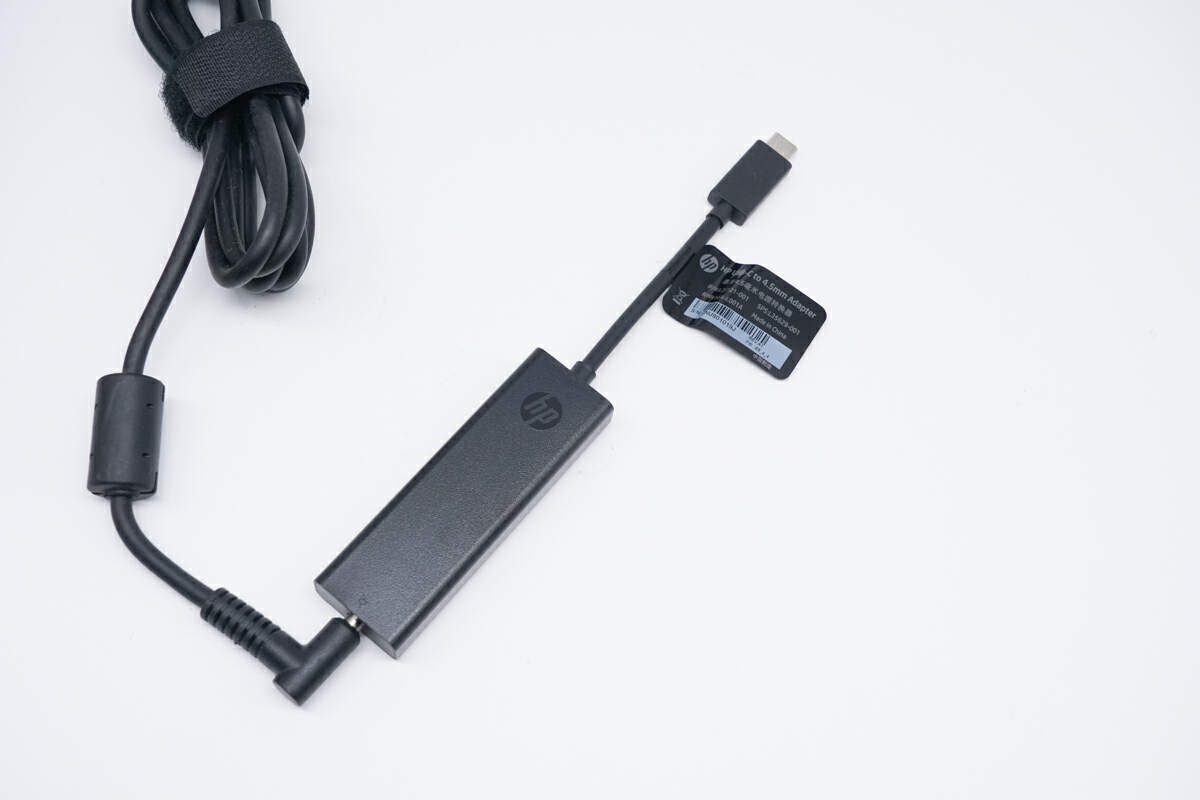
The HP 4.5mm DC to USB-C Power Adapter is made of fire retardant PC material, featuring a matte texture.
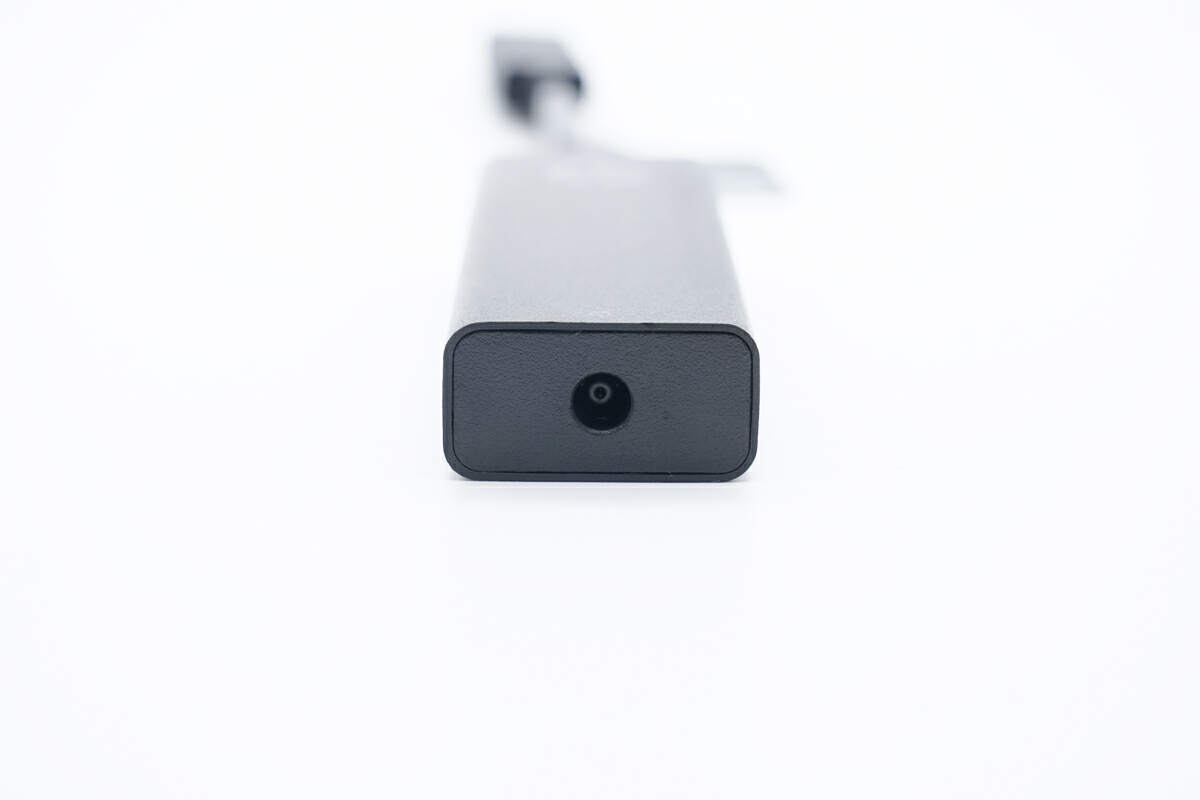

The input end consists of a DC jack.
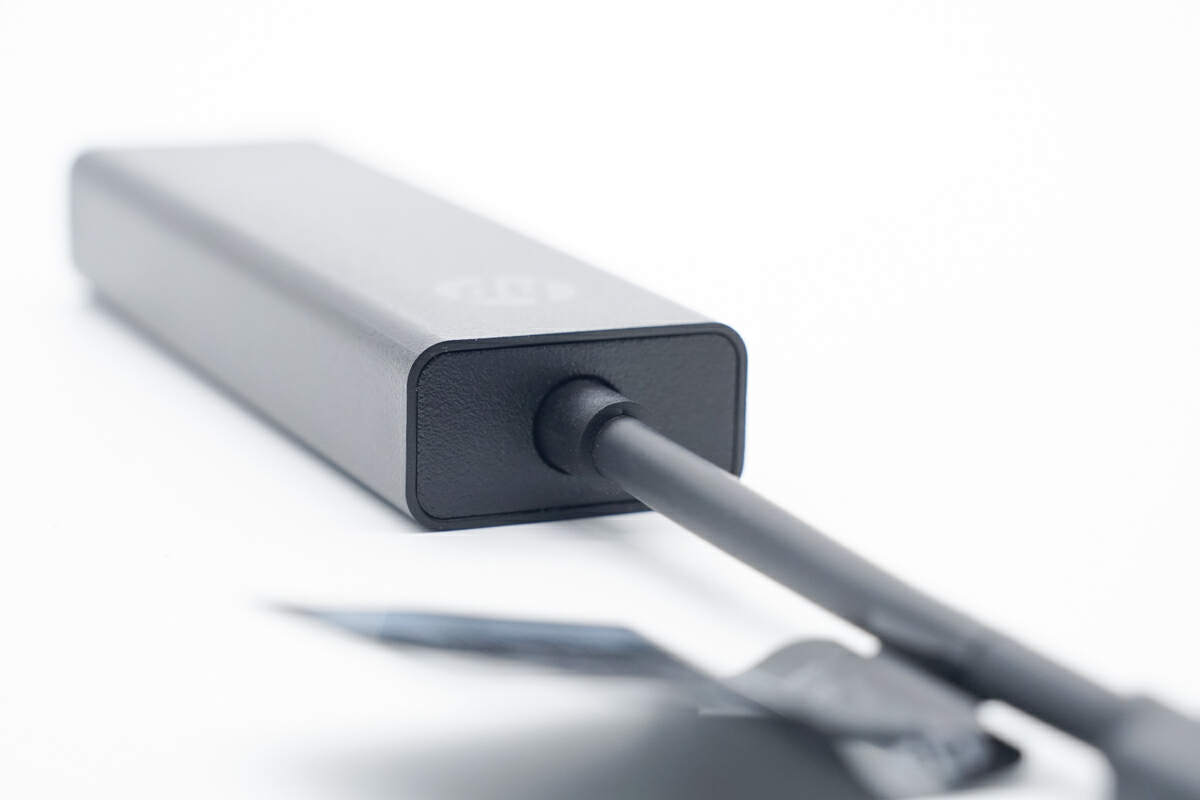

The joint between the cable and the power adapter has been reinforced.
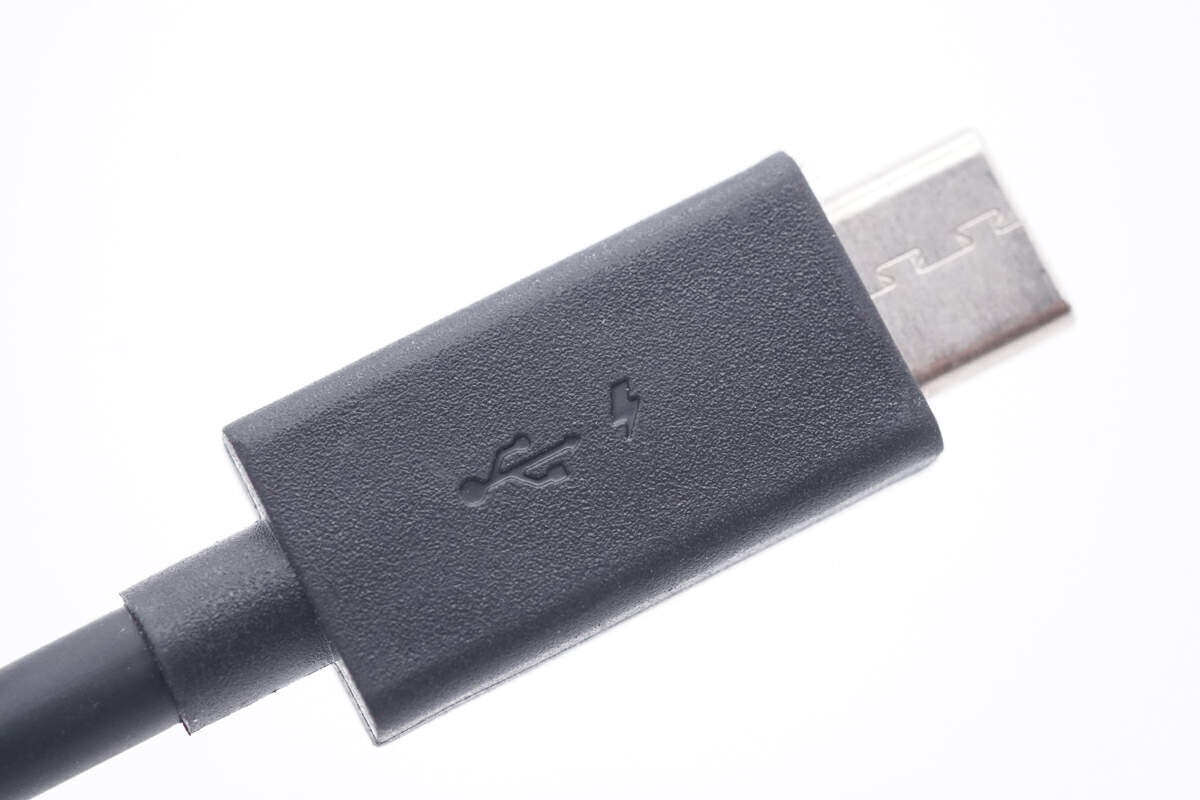

And the USB-C connector is engraved with a small lighting icon.
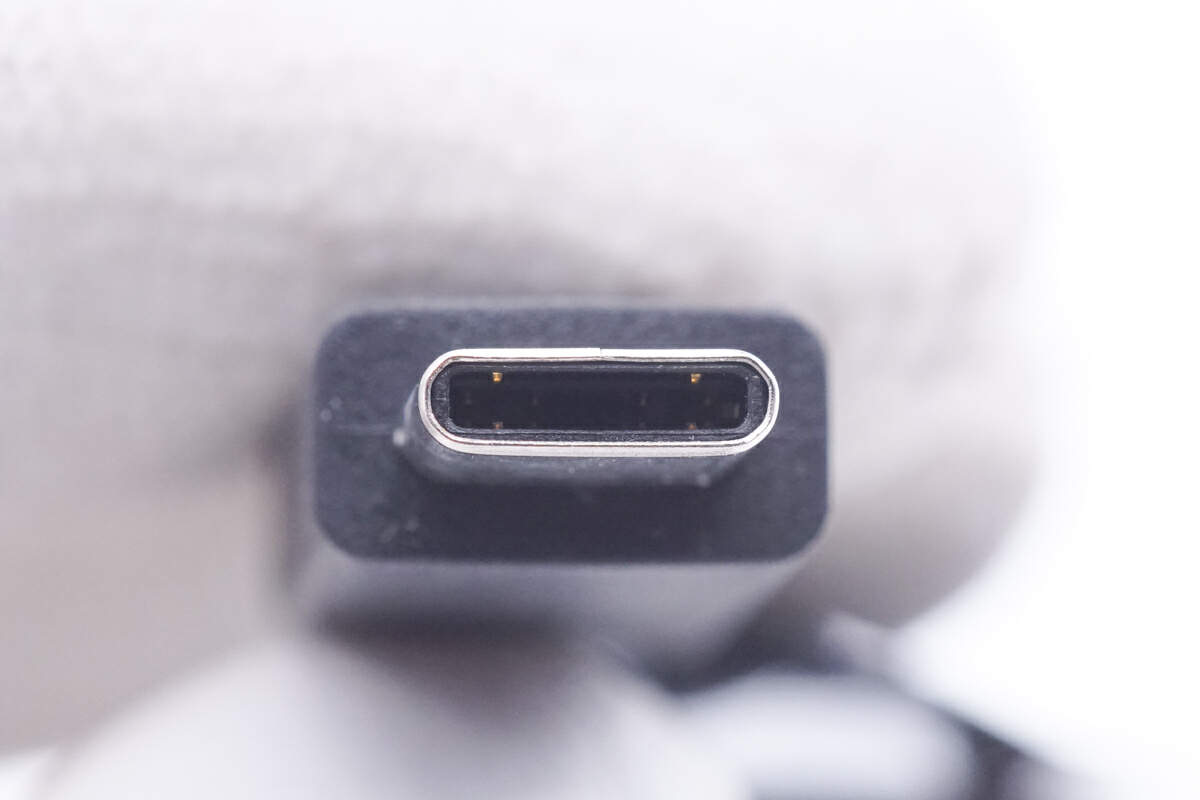

It adopts a special pin design.

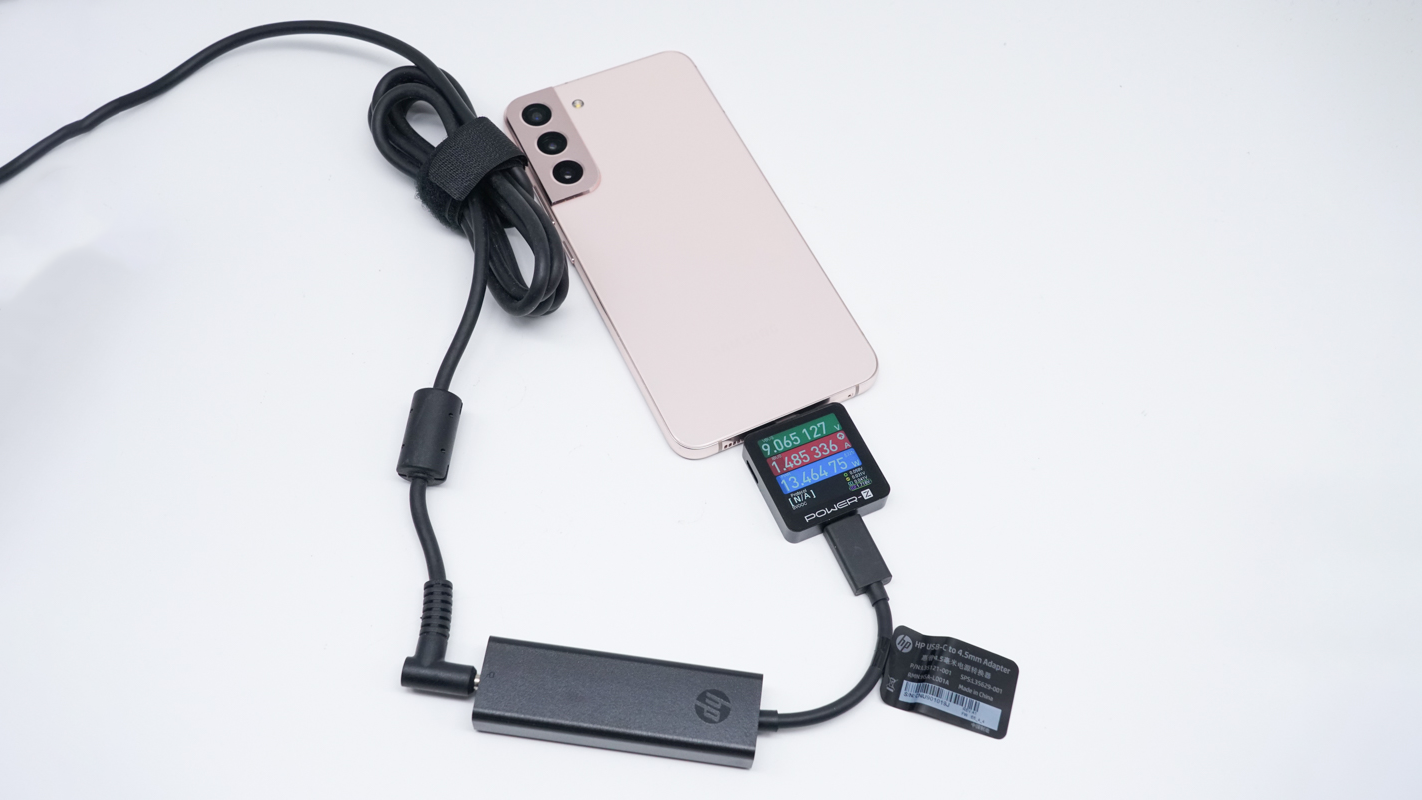
ChargerLAB POWER-Z KM003C indicates that it does not have an E-marker chip.

When connected to a hundred-watt level DC power adapter, it reads the fast charging protocols of the USB-C port, supporting DCP and PD 3.0 charging protocols.

And it can support six fixed PDOs of 5V3A, 9V3A, 10V5A, 12V5A, 15V5A and 20V4.25A.
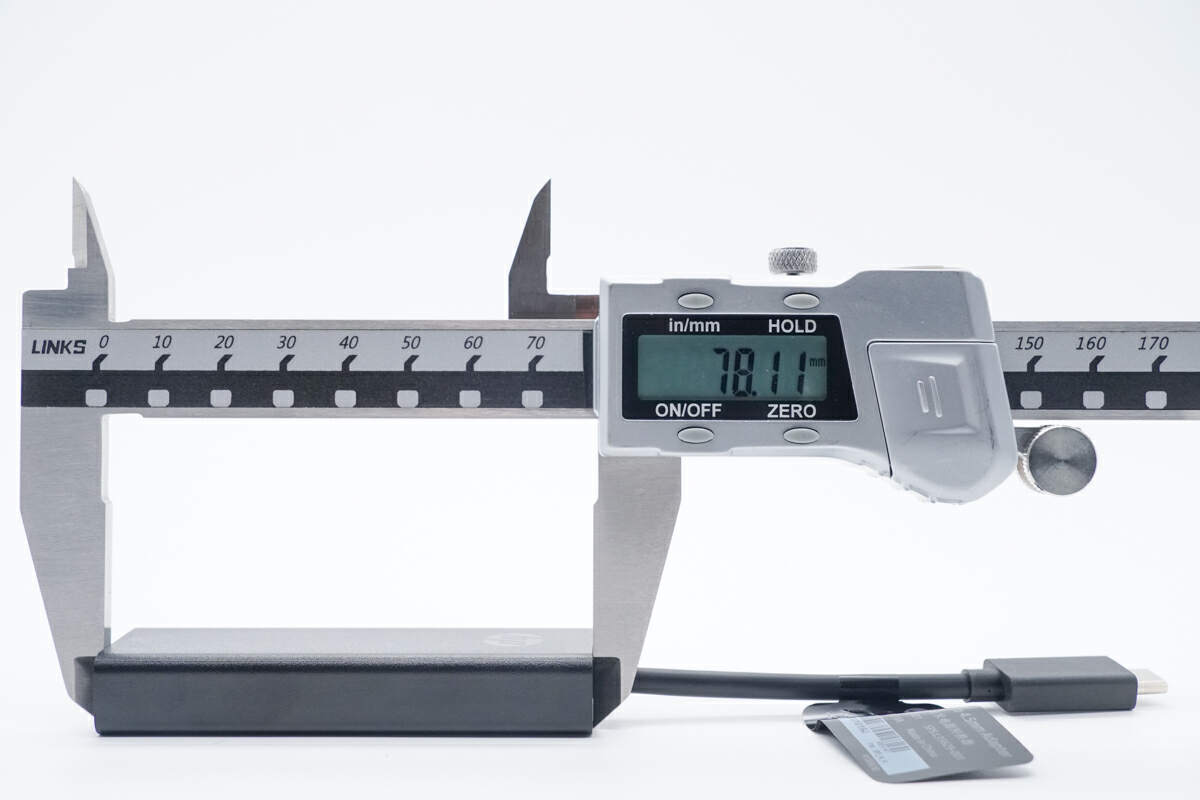

The length of this power adapter is about 78mm (3.07 inches).
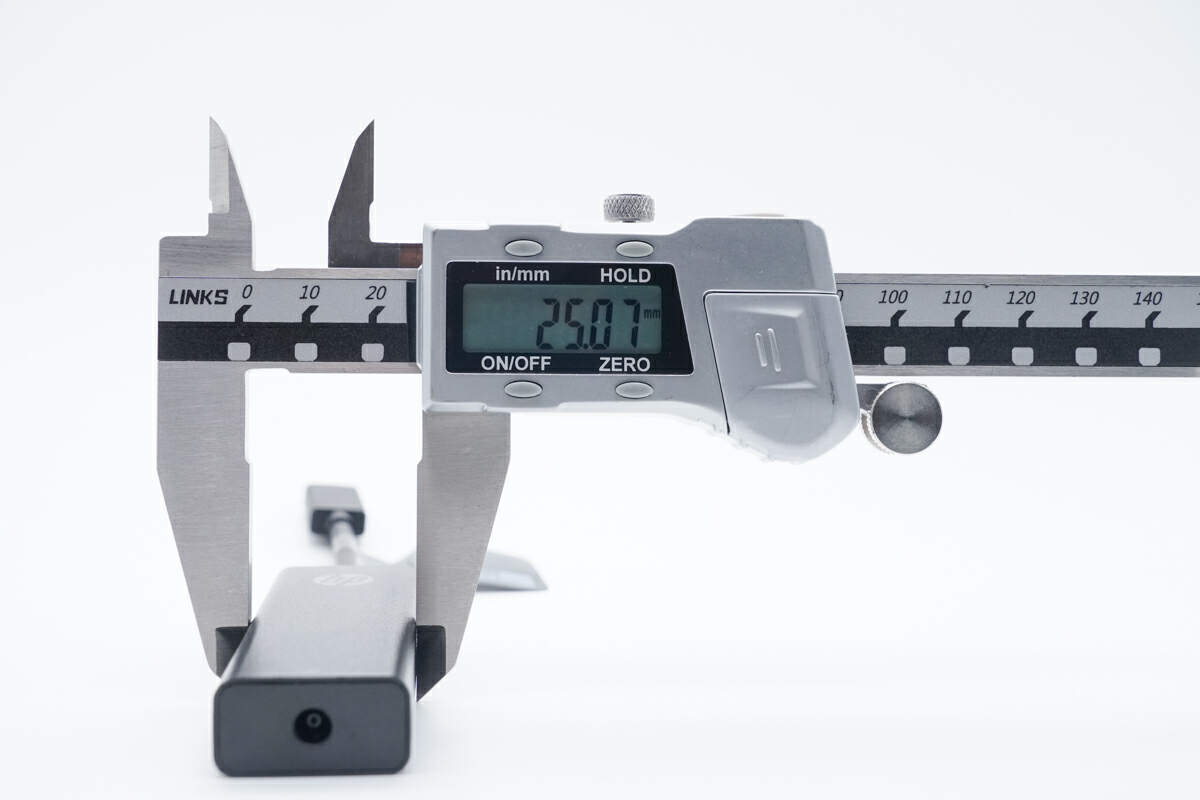

The width is about 25mm (0.98 inches).
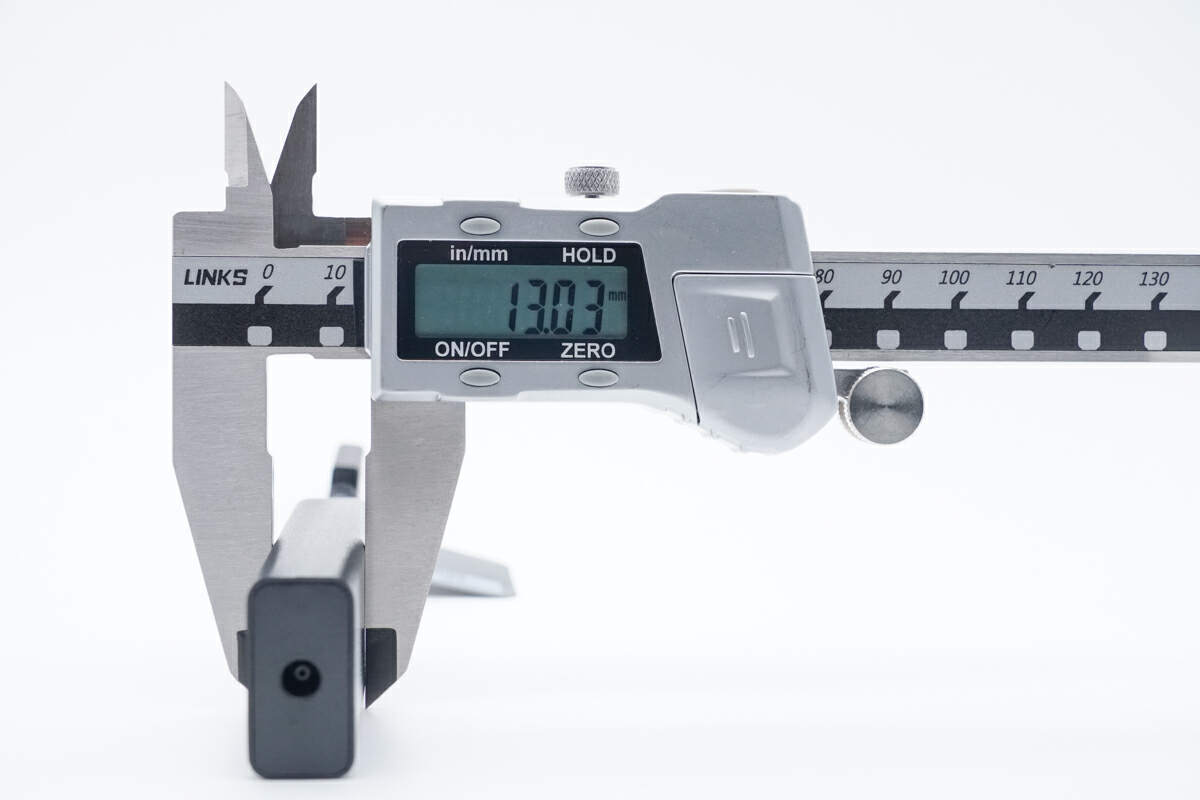

The thickness is about 13mm (0.51 inches).
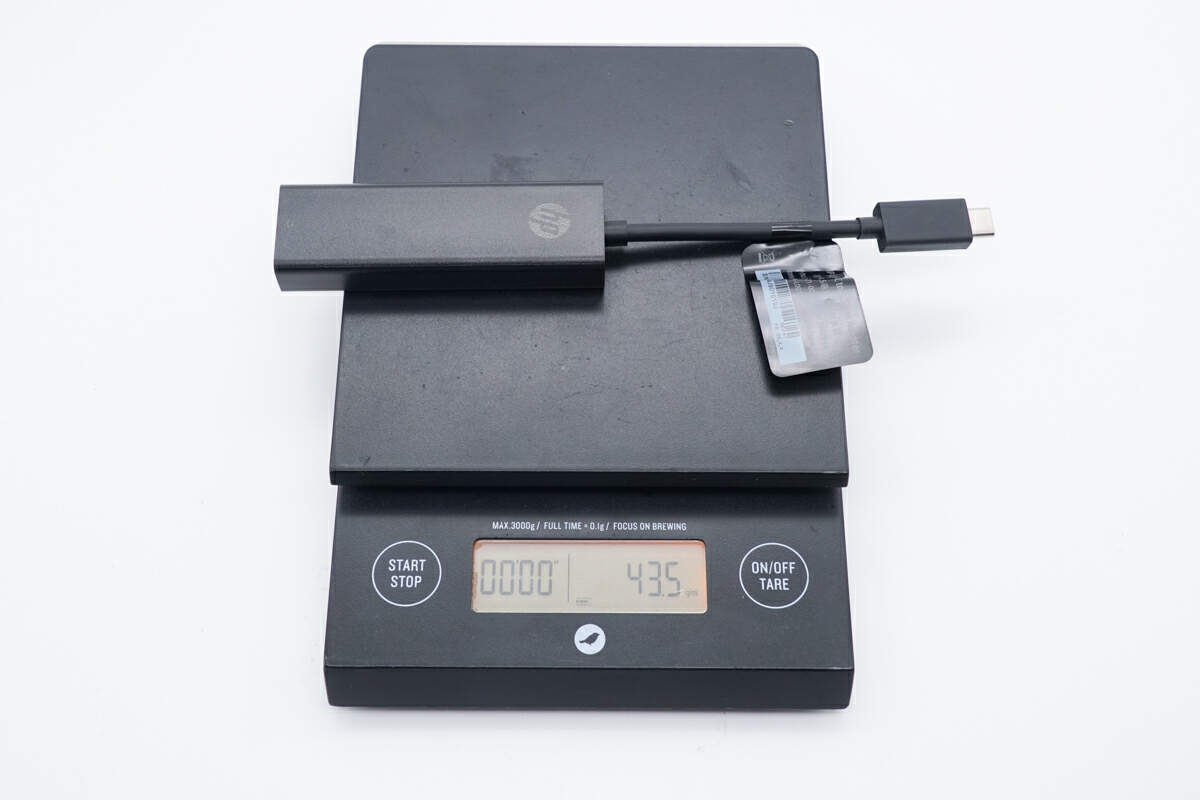

And the weight is about 44g (1.55 oz)

This is how it looks like on my hand.
Charging Test

Next, we conducted a test using a random DC power adapter in conjunction with the HP 4.5mm DC to USB-C Power Adapter, which supports 20V5A DC input.
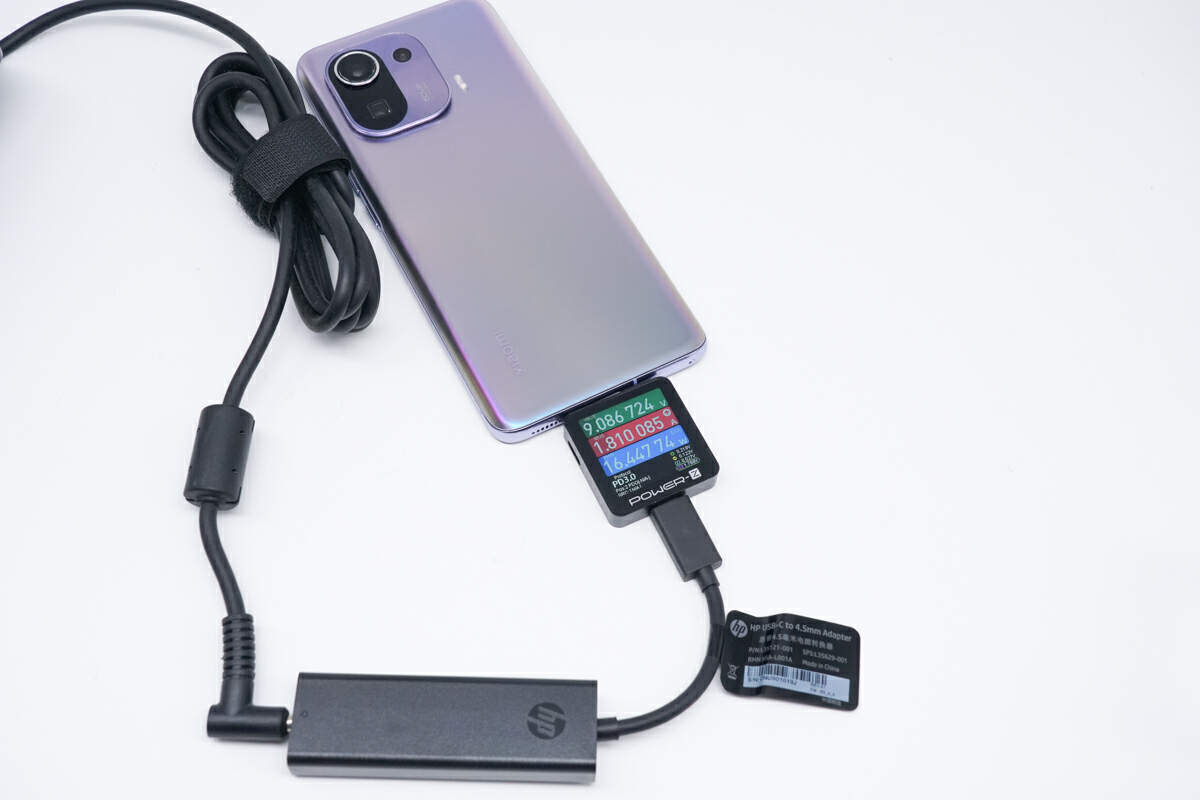

Charging the Xiaomi 11, which supports a maximum charging power of 55W, resulted in a power output of 9.09V 1.81A 16.45W. At first glance, its compatibility may seem mediocre, but considering that third-party chargers generally provide power levels of around 18W for the Xiaomi 11, it is reasonable.
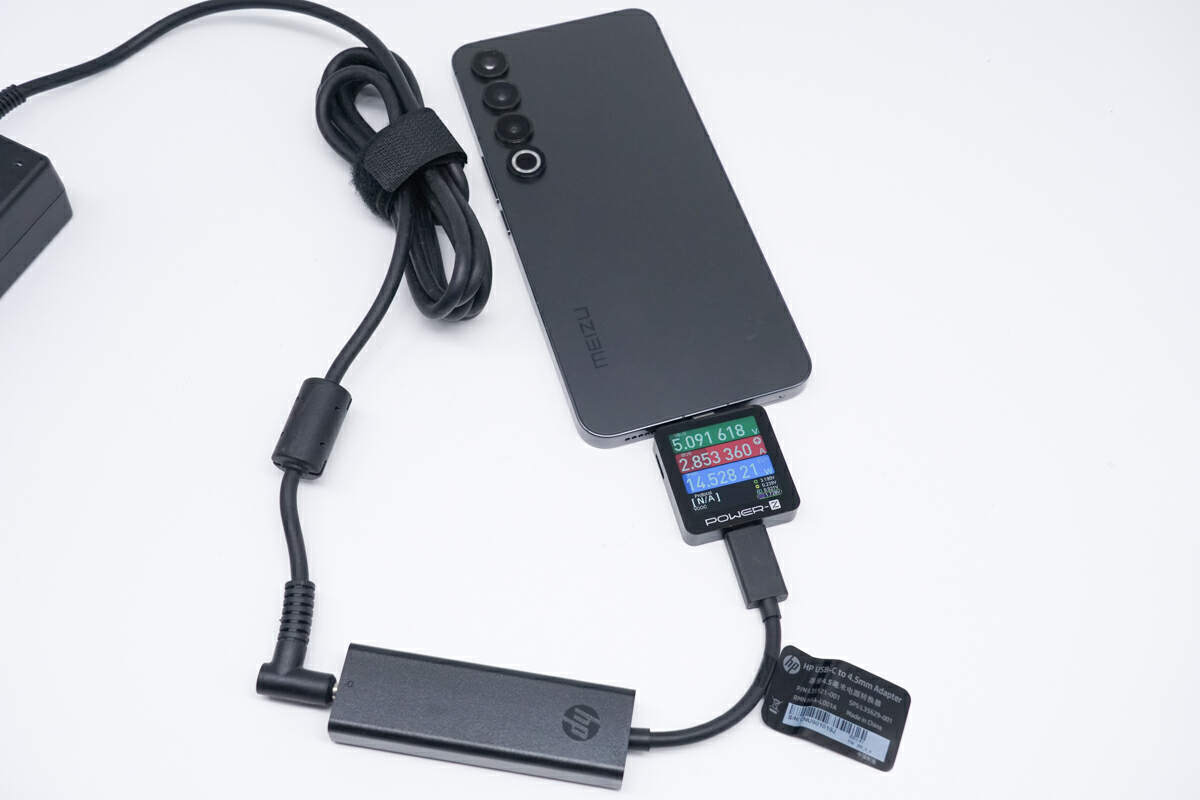

Switching to the more compatible Meizu 20 Pro, the power output is only 5.09V 2.85A 14.53W, which is somewhat disappointing.
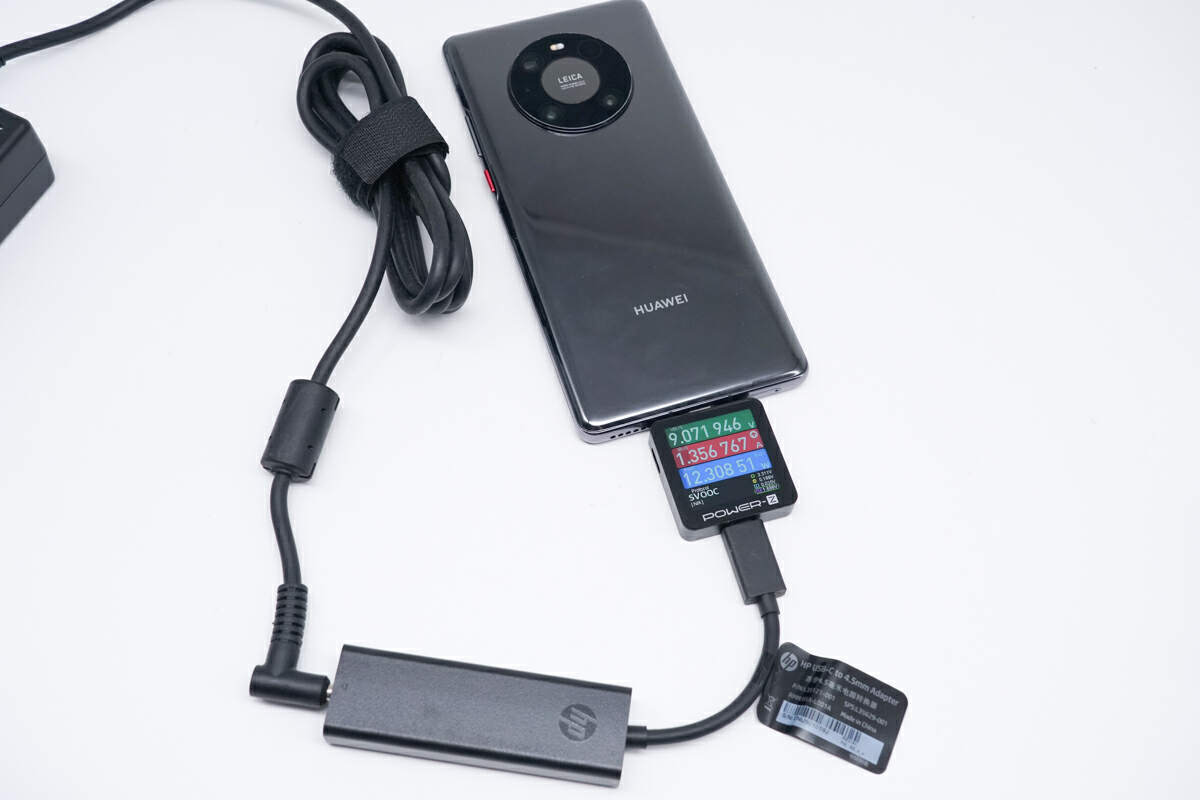

Next is the Huawei Mate40 Pro, with charging power reduced to 9.07V 1.36A 12.31W.
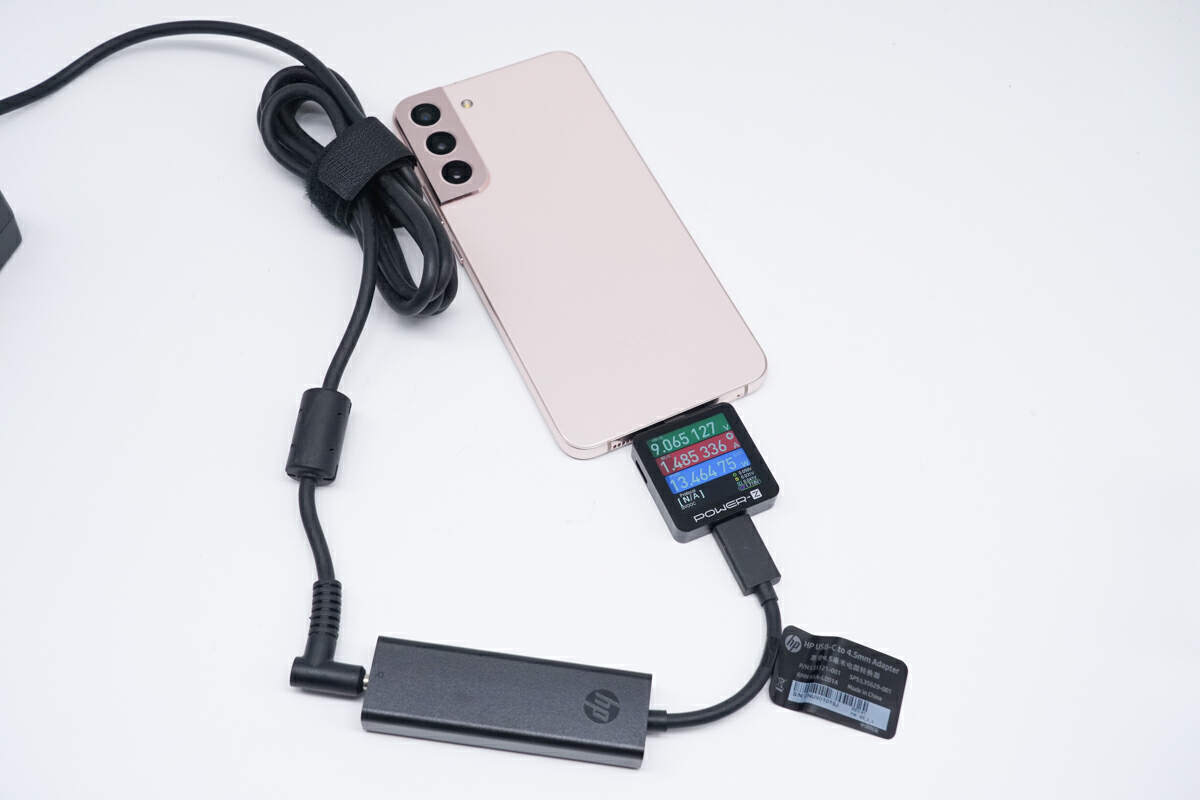

Lastly, for the Samsung Galaxy S22+, the charging power is 9.07V 1.49A 13.46W. As we can see, for mainstream smartphones in the market, the charging power is around 18W, which is sufficient.
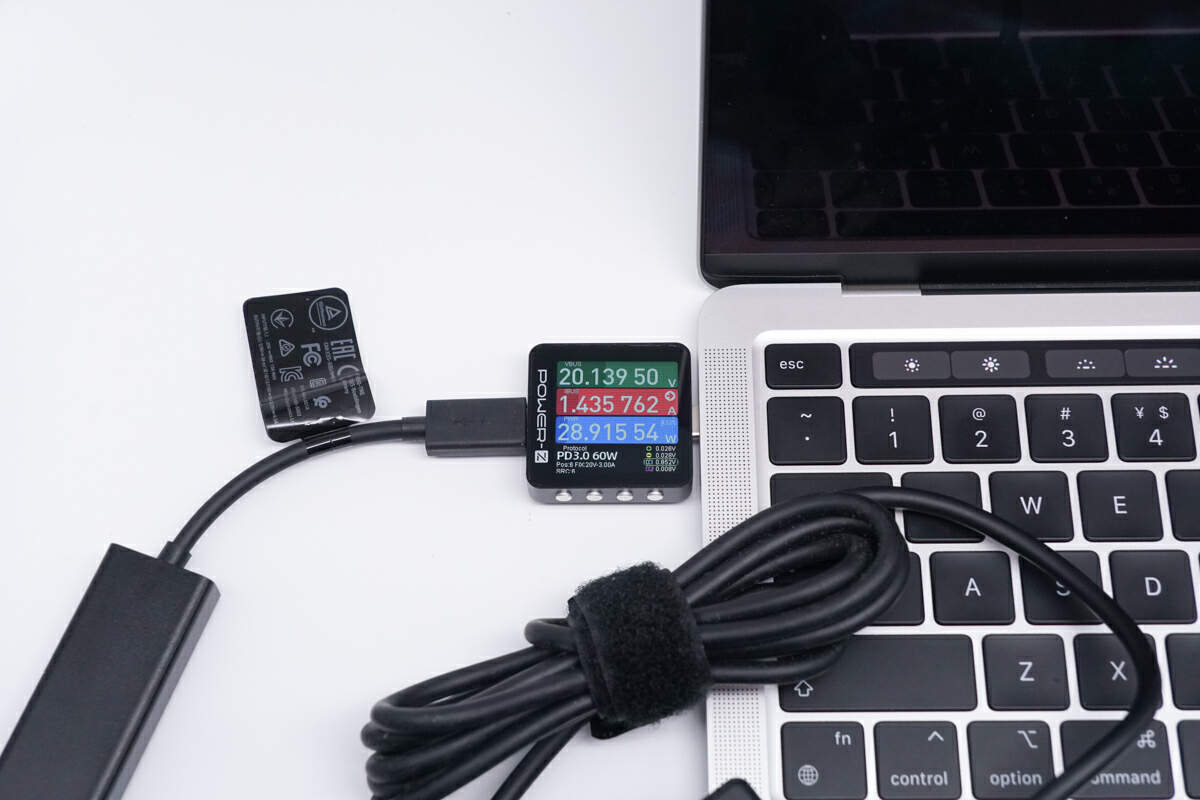

Moving on to laptops, it can provide 20.14V 1.44A 28.92W for the MacBook Pro M2 2022.
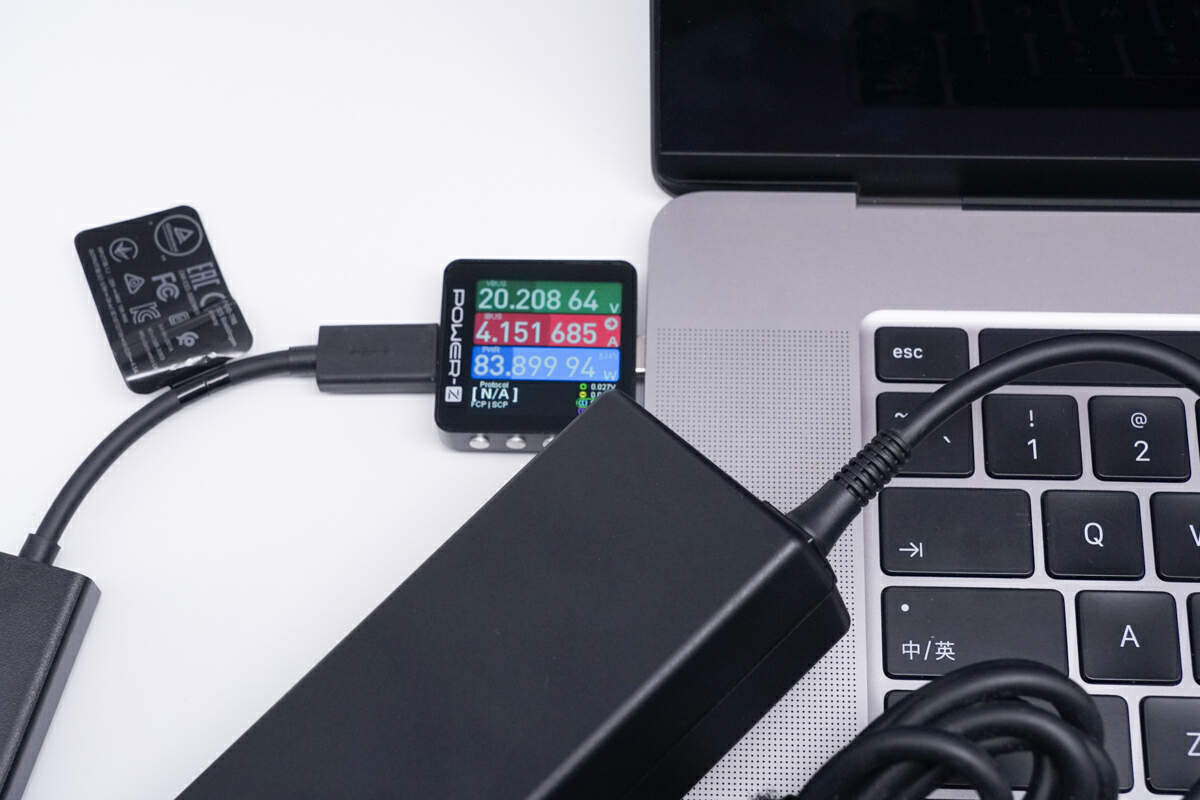

When charging the 16-inch MacBook Pro 2019, it reached an impressive power output of 20.21V 4.15A 83.9W, which is excellent.
Temperature Test
Heat generation is another important aspect to consider. Let's evaluate how it handles temperature during charging. The test was conducted in a constant temperature chamber at 25°C (77℉).
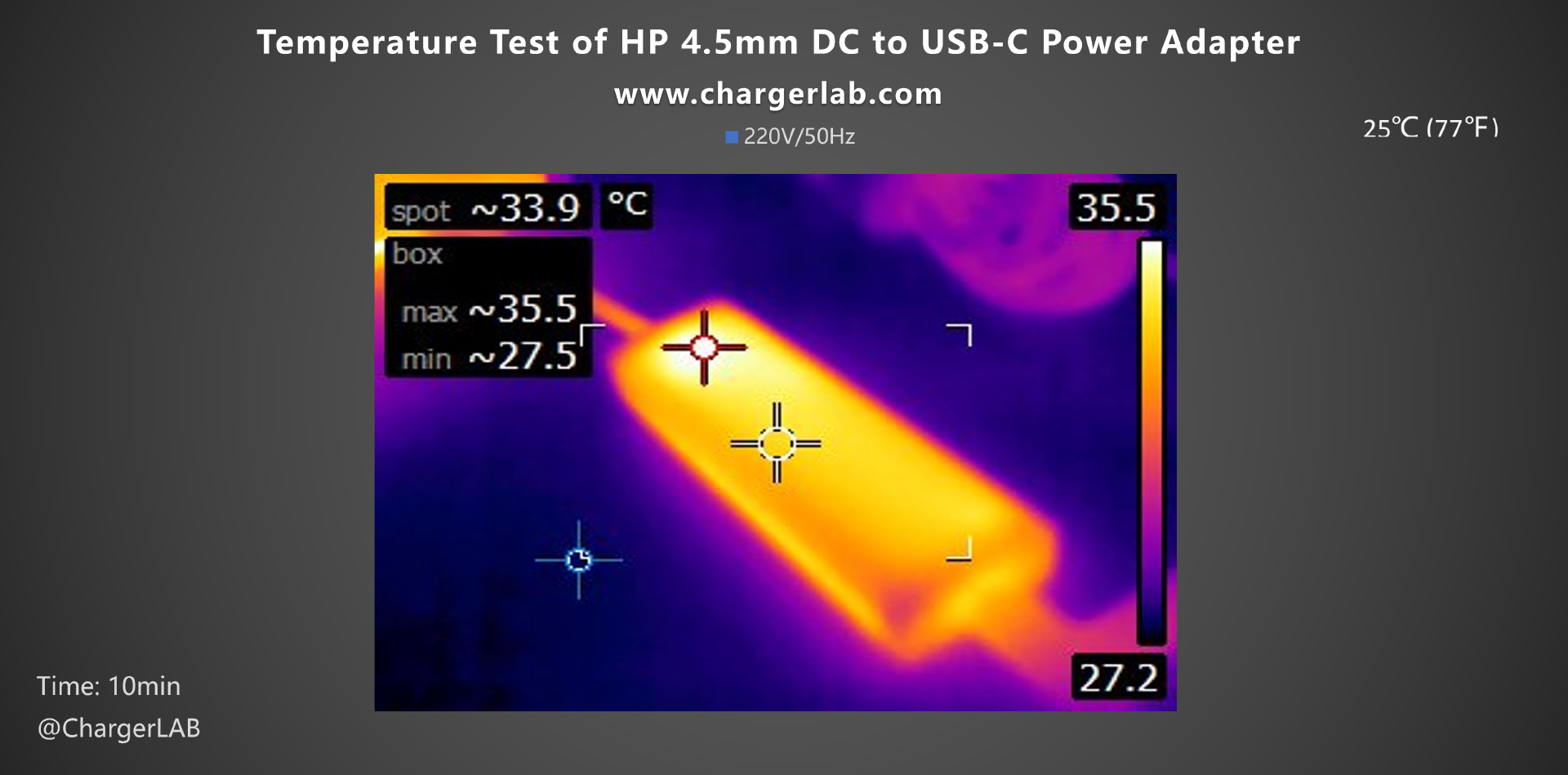
After 10 minutes of charging, a thermal imager captured the front of the adapter, with the highest temperature recorded at 35.5°C
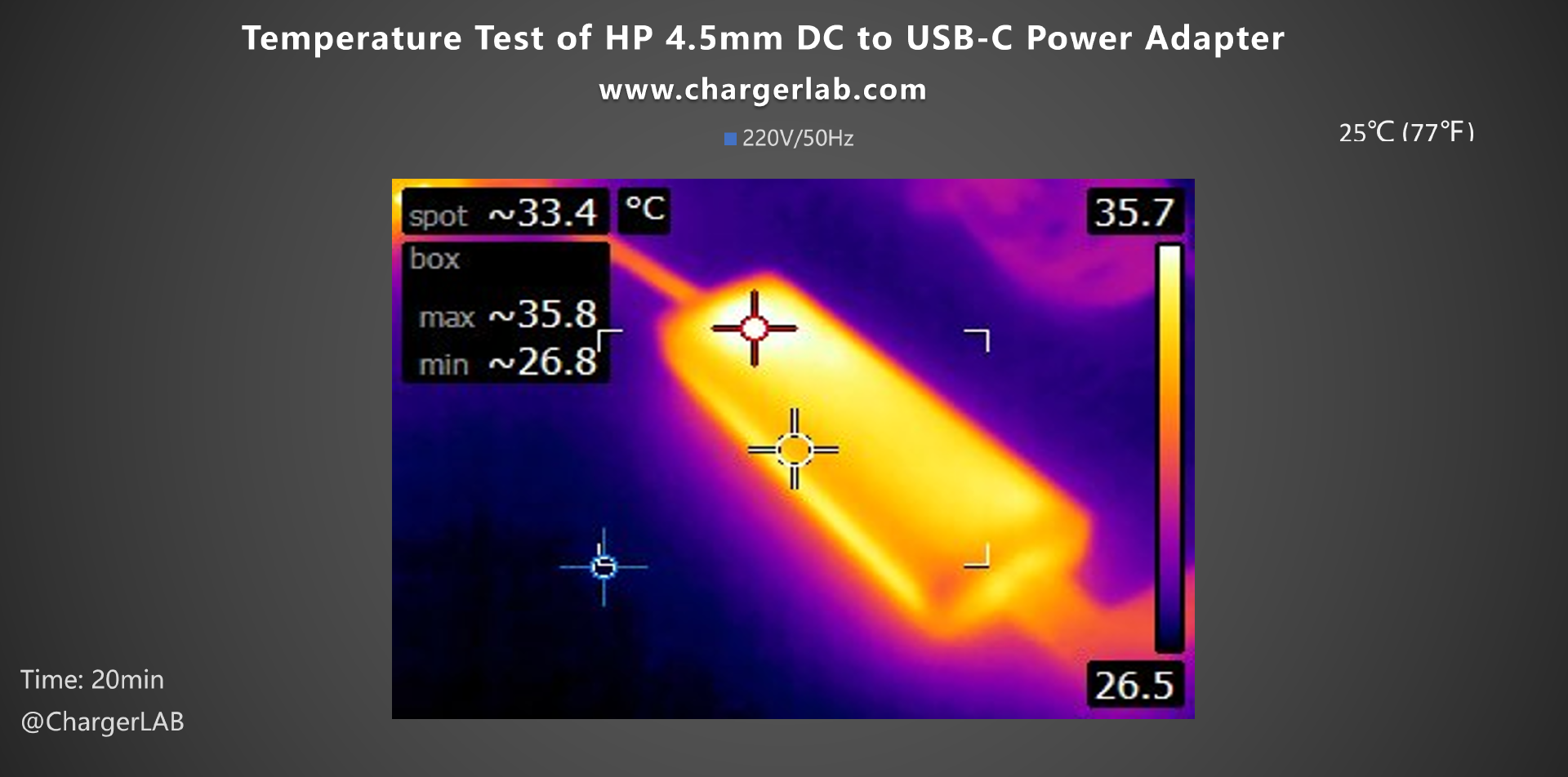
After 20 minutes, the highest temperature on the front reached 35.8°C. It can be observed that the temperature of the adapter remained around 35°C at both selected time points, showing no significant temperature rise and feeling warm to the touch.
Summary of ChargerLAB
In conclusion, the HP 4.5mm DC to USB-C Power Adapter offers several notable advantages, such as its ability to minimize environmental pollution and its impressive power output when charging certain models. The device also demonstrates good temperature control, ensuring safe and efficient charging. However, it is worth mentioning that the adapter supports limited charging protocols and may have average compatibility when charging smartphones. Nonetheless, it is important to note that this product is primarily designed for laptops, and these limitations do not significantly detract from its overall functionality. It is a practical solution that caters to its intended purpose.
Related Articles:
1. Teardown of Apple Thunderbolt 4 Pro Cable (1.8 m)
2. Review of HP Thunderbolt 4 Cable
3. Teardown of 240W "DIY" Thunderbolt 4 USB-C Cable









