Introduction
With an increasing number of devices, including tablets, laptops, and computer motherboards, adopting USB-C physical ports, this type of port has proven to be more suitable for everyday users due to its physical compatibility for charging, transmission specifications, and portability. Additionally, many mainstream devices on the market with USB-C ports can support power delivery (PD) of 100W or even PD 3.1 at 140W, provided you use high-quality cables.
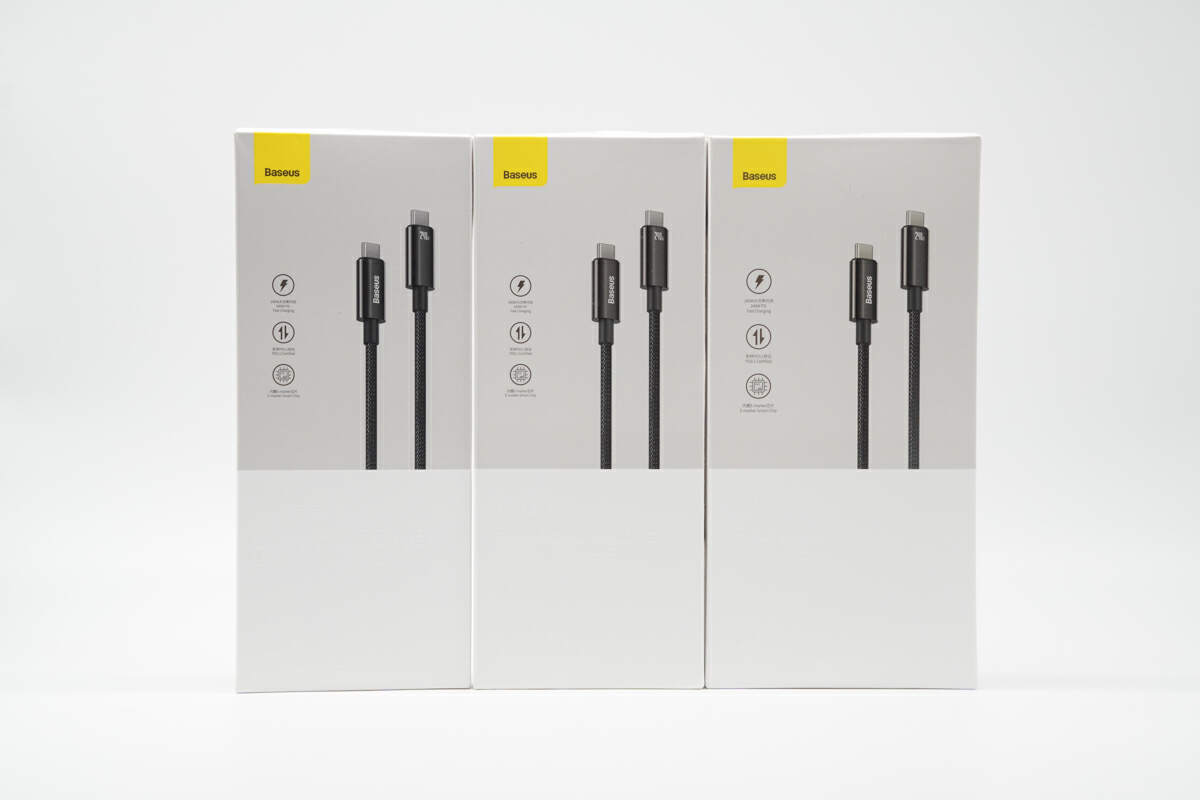

Today, ChargerLAB brings you three Baseus high-spec charging cables, boasting a nominal maximum power transfer capability of 240W, the name is Baseus 240W USB-C Fast Charging Cable. Moreover, the USB-C connectors are designed with full pins, potentially supporting additional features. While these three cable versions share identical specifications except for their length, this test will focus on the 1m version.
Product Introduction
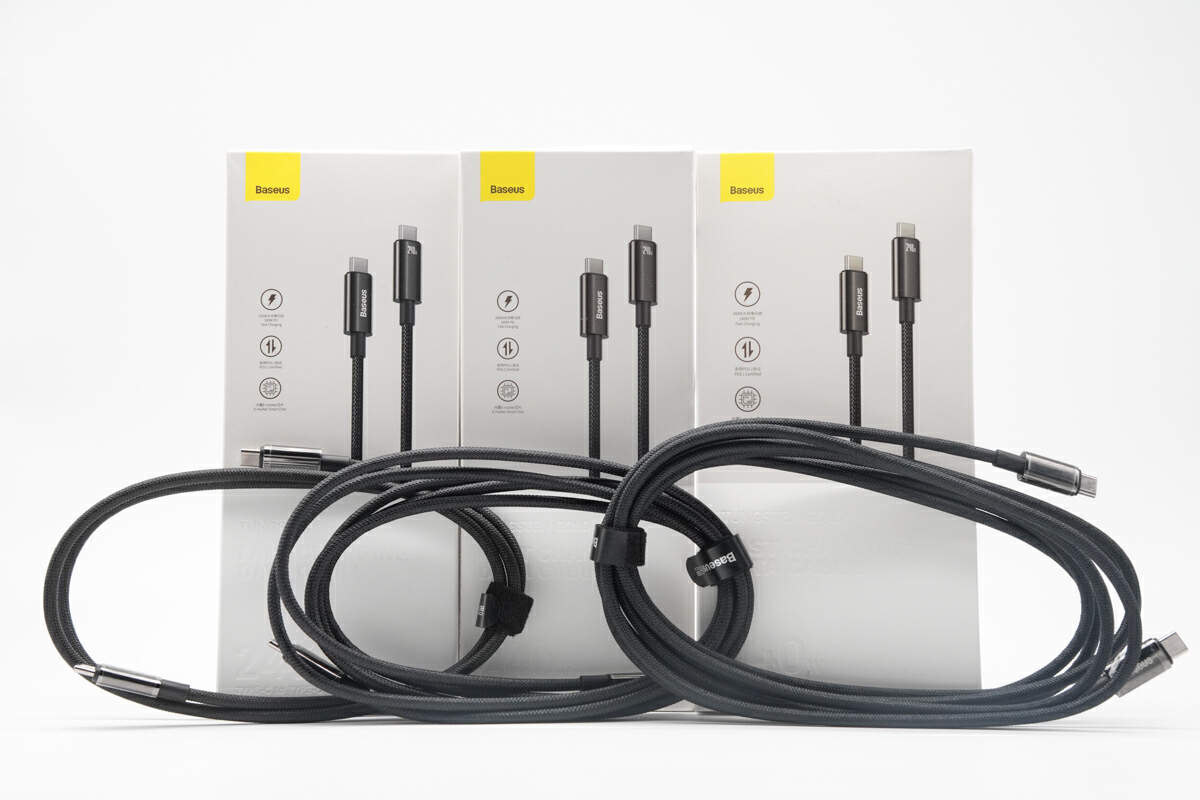

The product packaging maintains Baseus' classic design, featuring the three main selling points: 240W, PD3.1, and an embedded E-marker chip.

All the specs info are on the back. Model is CB000038. Its maximum charging power is 240W, and the transfer speed is 180Mbps.
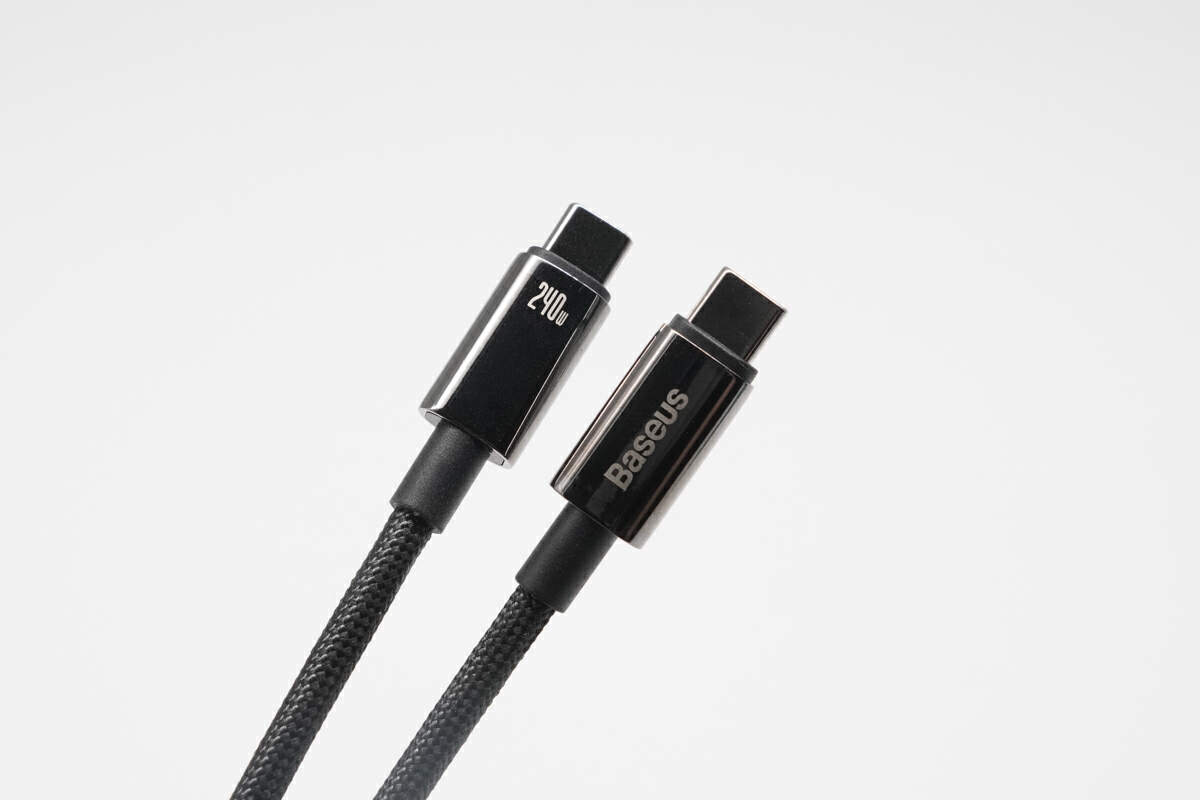

The USB-C connector's housing is made of zinc alloy, with "240W" and "Baseus" imprinted on it. Additionally, there's an extended protective sleeve at the connector-to-cable junction.
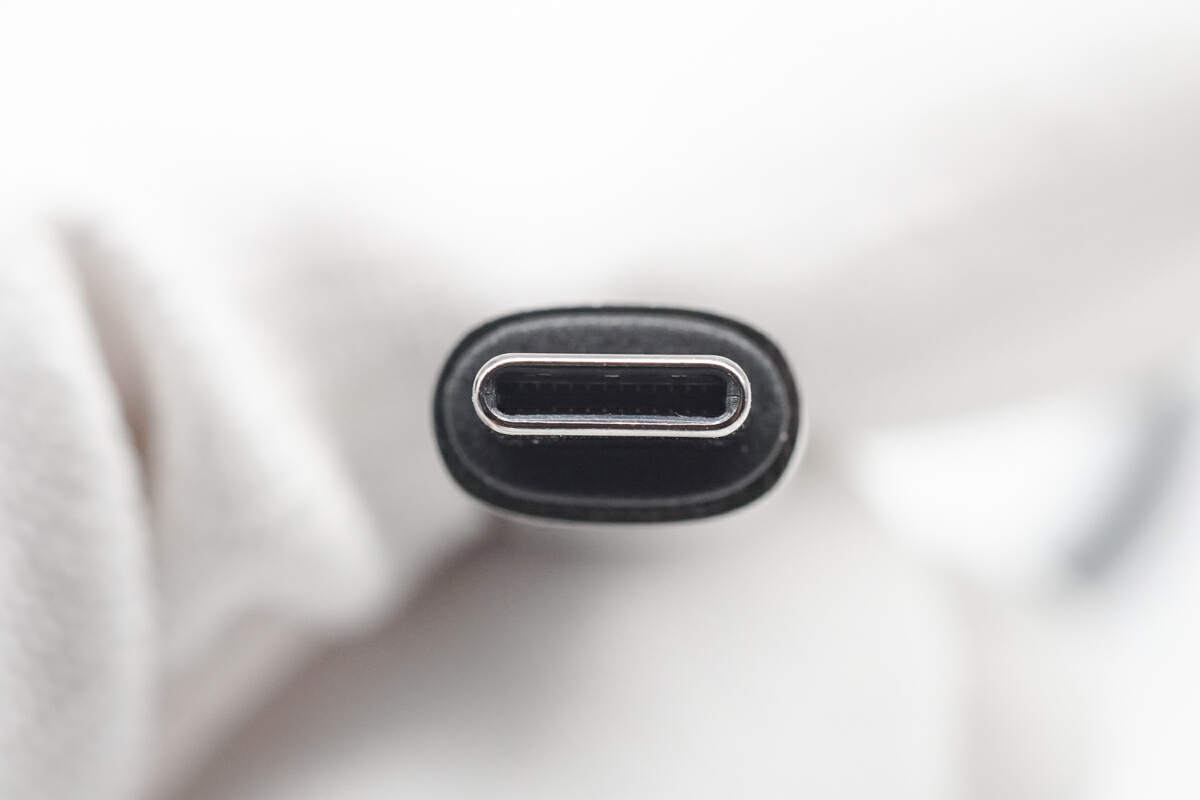

Upon close inspection of the connector's interior, it's evident that it features a full-pin design, and the specific supported functions will be tested later.

The braided cable body offers advantages like durability, resistance to tangling, and resistance to dirt, with no easily noticeable fraying.
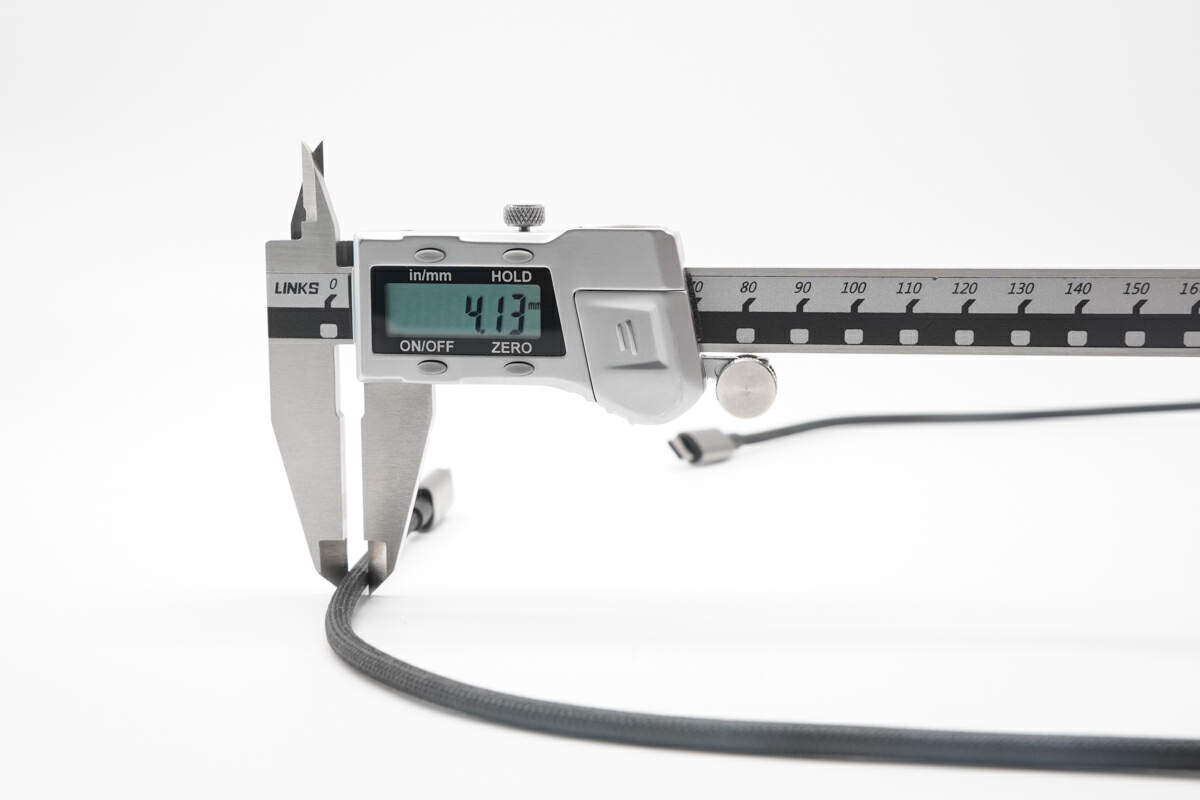

The cable diameter is about 4.1mm (0.16 inches).
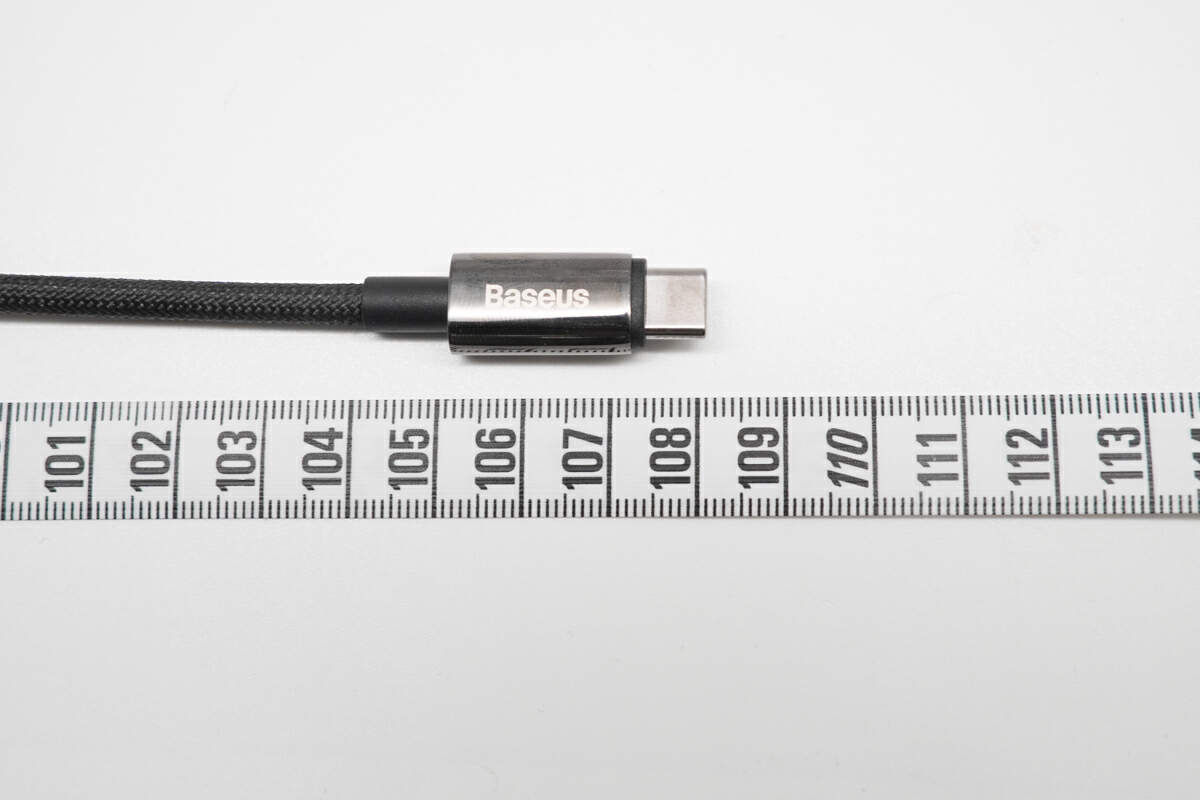

The length is approximately 108cm (3.54 ft).
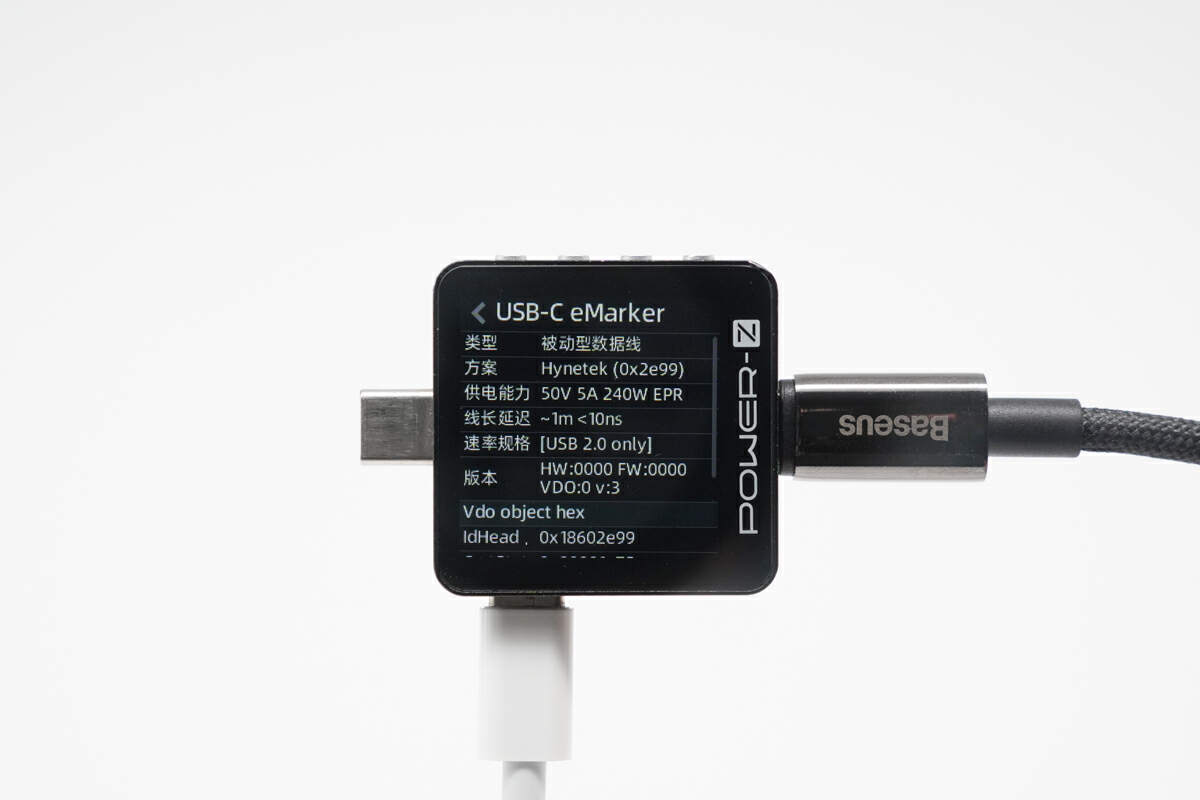

ChargerLAB POWER-Z KM003C shows it's indeed a USB 2.0 cable with an E-marker chip, and the power transmission is 50V5A 240W EPR.
Performance Test
Testing the cable involves evaluating its supported functions and internal quality. The former includes determining the types of fast charging it supports, and whether it can perform data transmission, and video transmission. The latter focuses on assessing the cable's internal quality.
Charging Test
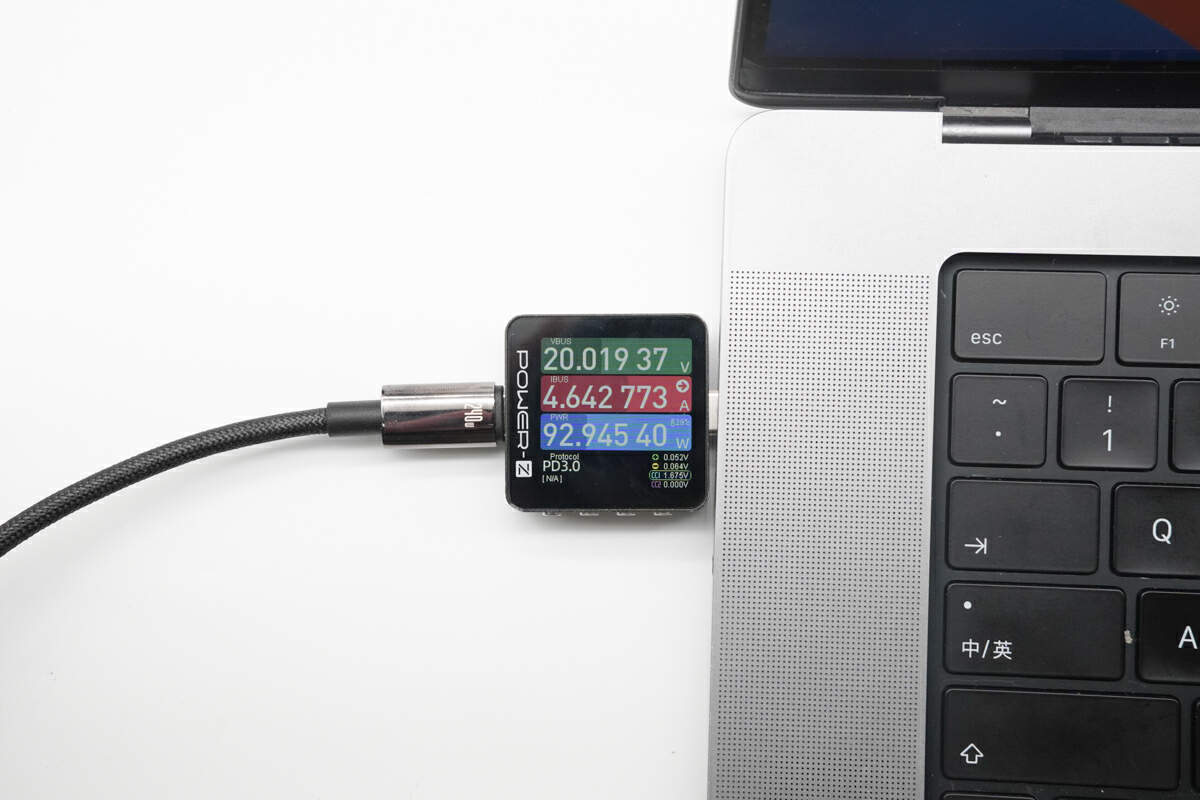

It can provide 93W to your 16-inch MacBook Pro M1 MAX 2021 when paired with the Apple 140W charger, which is the best you can get when using a USB-C cable.
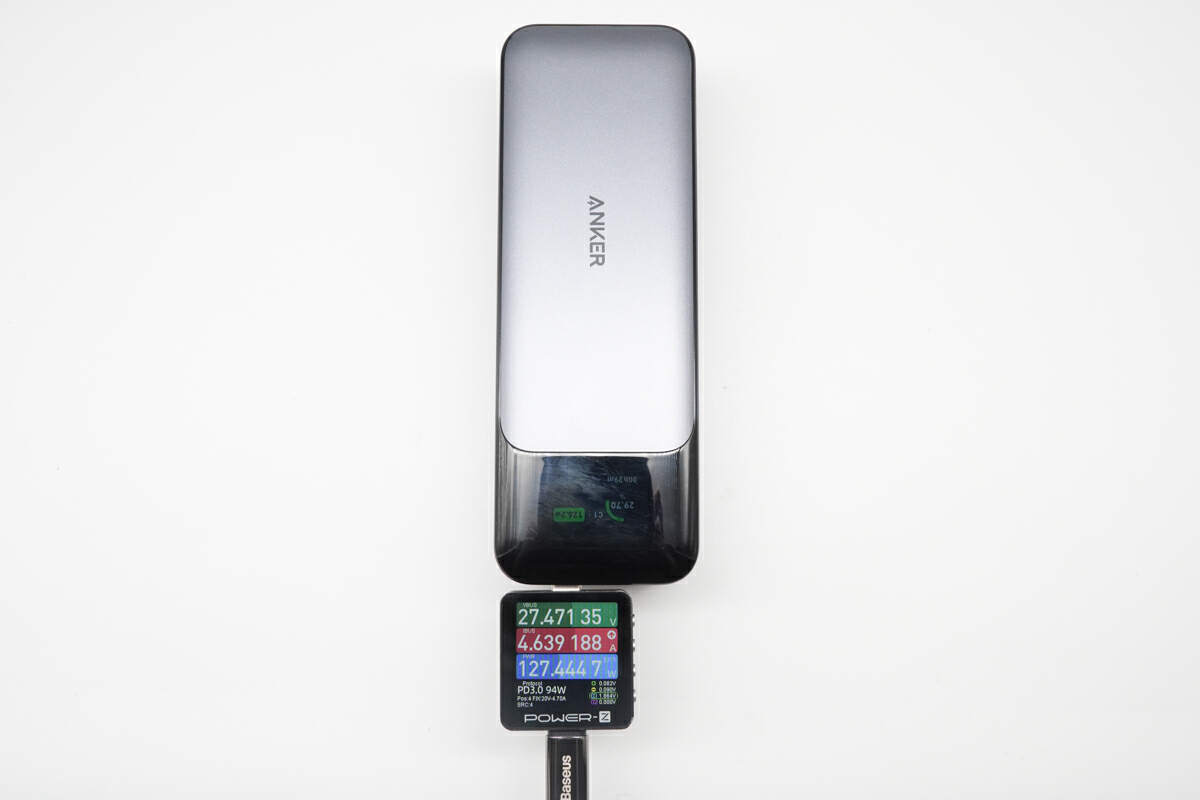

When charging the Anker 140W PD3.1 Power Bank, the power can be up to 127W, so it is confirmed that this cable can support PD 3.1 140W charging.

To further validate its power transfer capability, the cable's ends were connected to a power source and an electronic load. At this point, the power source showed a voltage of 28V and a current of 4.959A.

The load's power was measured at 27.090V 5.001A 135.468W, while the tKM003C displayed a power reading of 27.198V 4.999A 135.97W.
Data Transmission
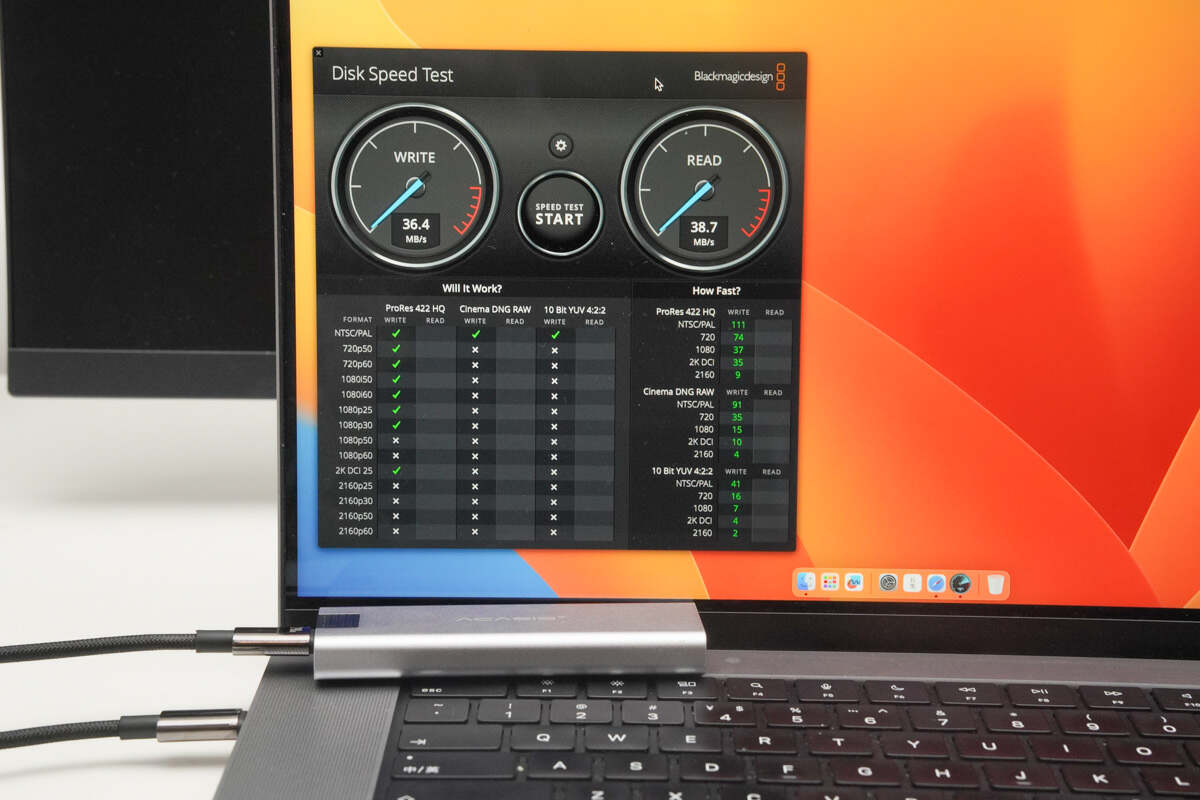
In macOS, using the Disk Speed Test, the cable achieved a read speed of up to 38.7MB/s and a write speed of up to 36.4MB/s.
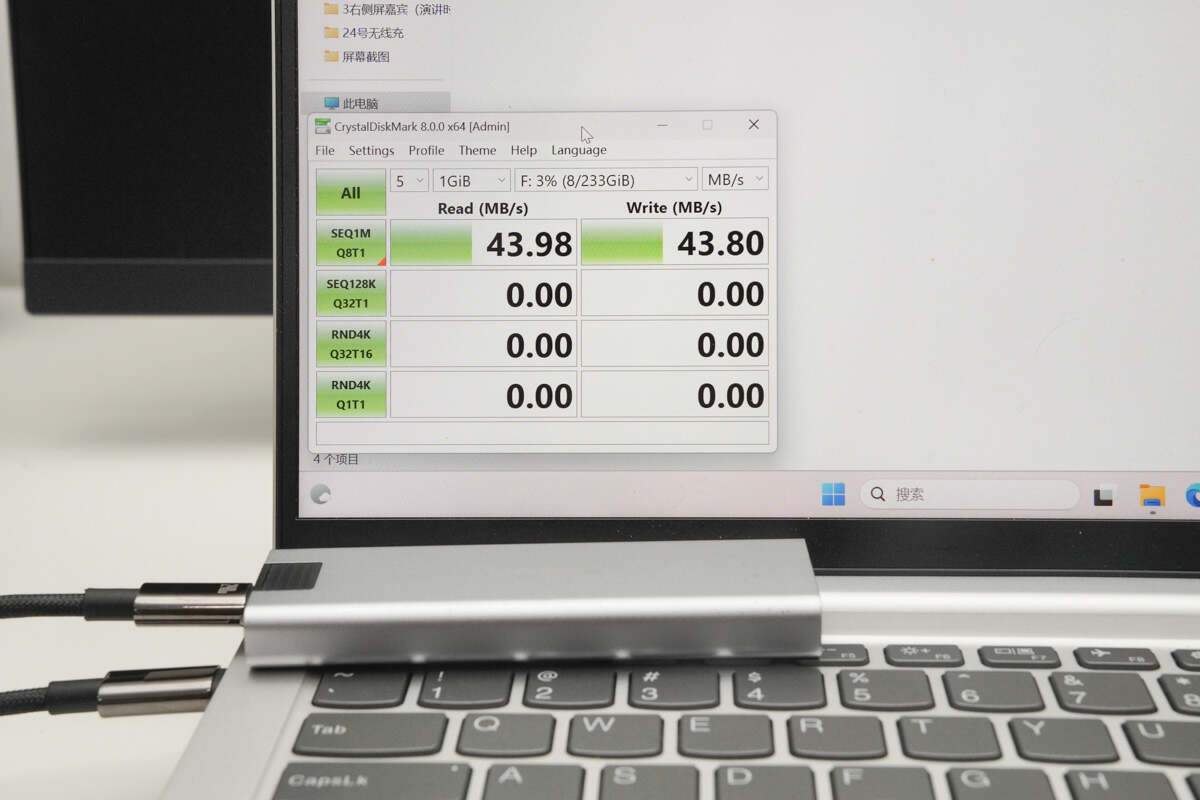
When switched to the Windows operating system, both read and write speeds improved, reaching 43.98MB/s and 43.8MB/s, respectively.
Due to differences in algorithms between macOS and Windows systems, macOS tends to have slightly slower read/write speeds. However, overall, the transmission rate aligns with the claims.
Video Transmission
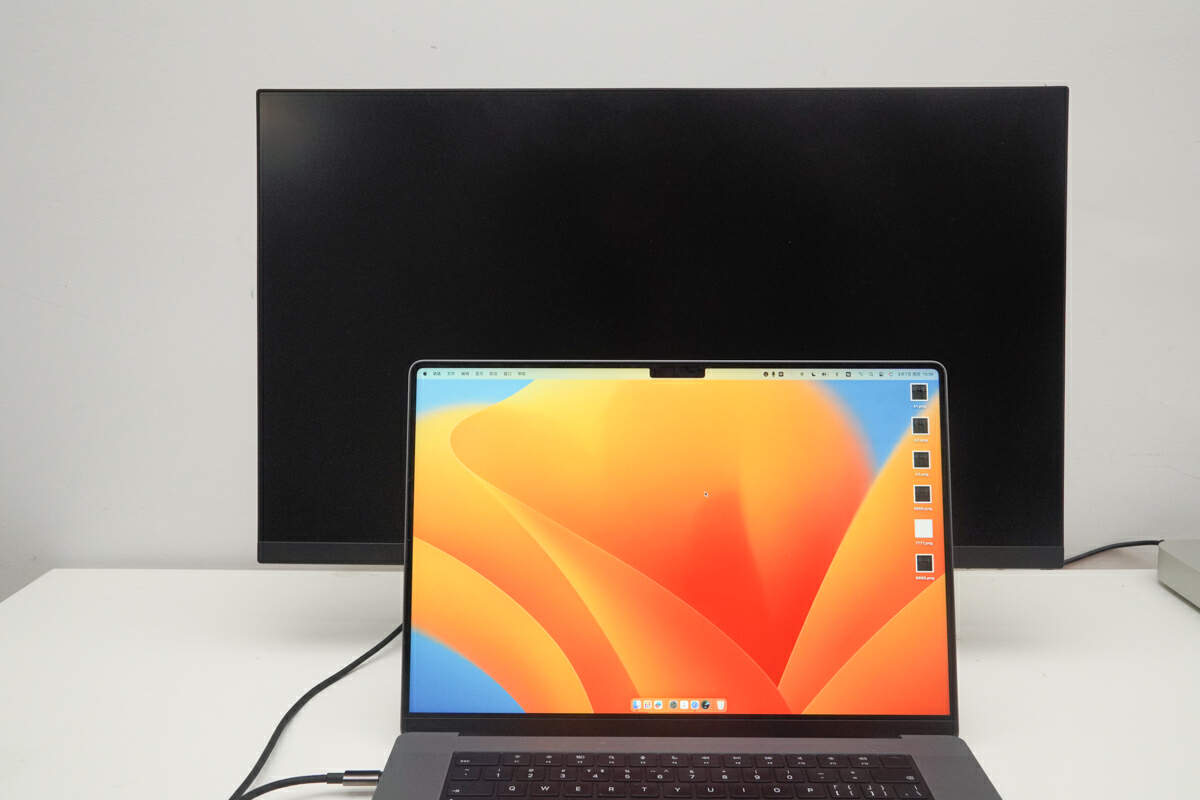

When we try to use this cable to project the 16-inch MacBook Pro 2021 screen onto a monitor, it shows no signal input.
Voltage Drop Test
Voltage drop is an important factor in measuring the quality of the cable. During daily use, when the charger outputs the voltage and current to one end of the cable, it passes through the cable to the other end, which creates the voltage drop.
In this part, due to the differences in length, there were variations in the data obtained for the three cable specifications, as shown below:
1m
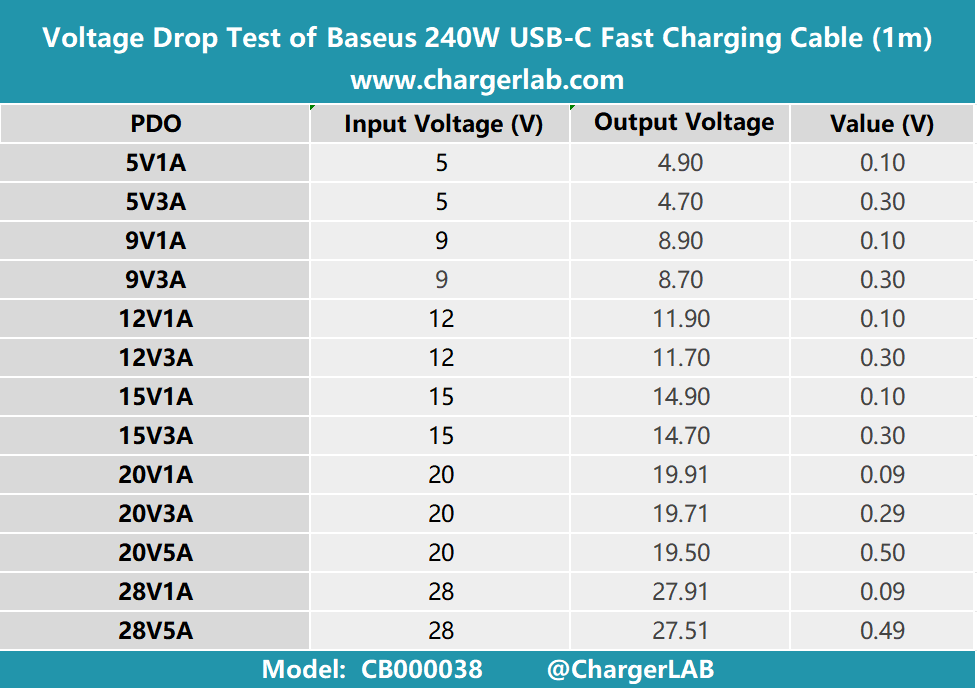
Firstly, we have 1m. Connect the cable to the power supply and the electrical load, respectively. And we will test the voltage drop value under different voltage and current. Here is the result.
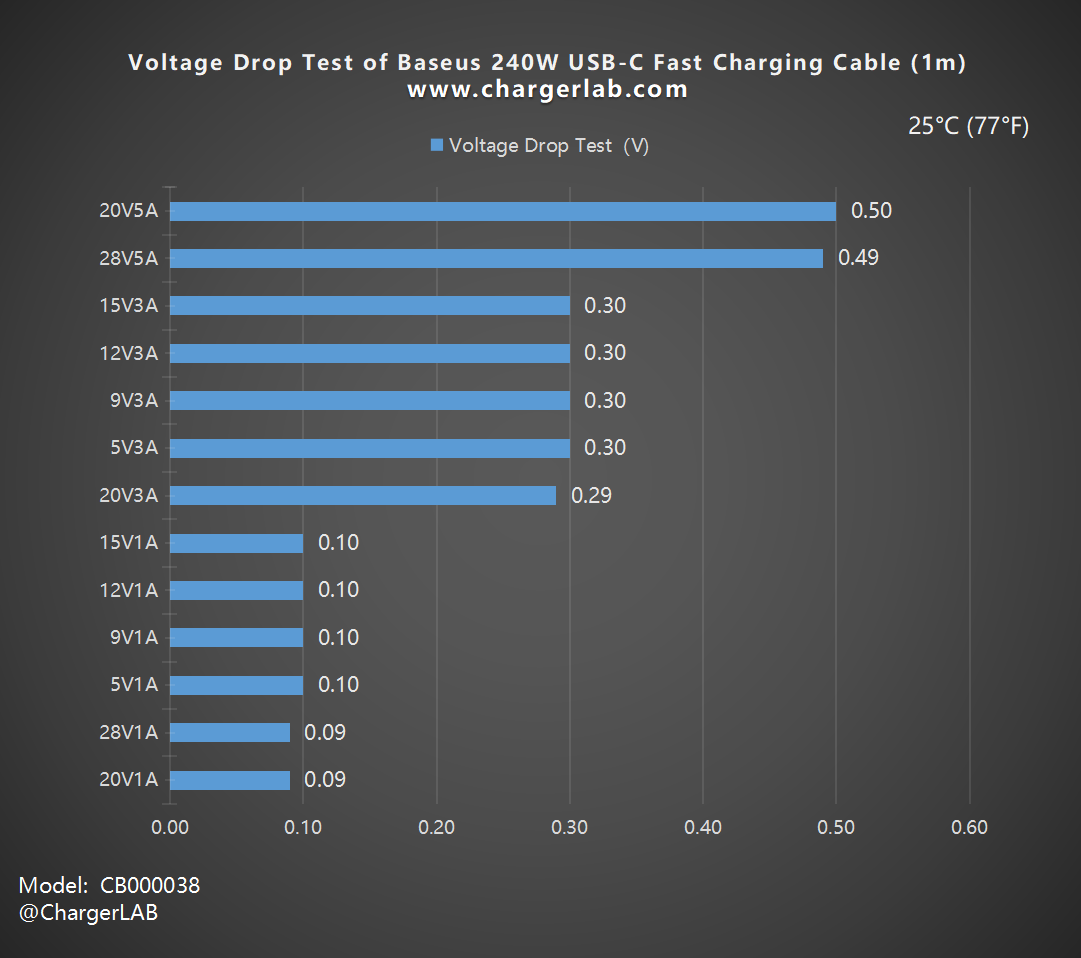
From the bar chart, we can see that the voltage drop falls into three categories: 0.10, 0.30, and 0.50. In the context of USB-C cables, this performance level is considered normal.
2m
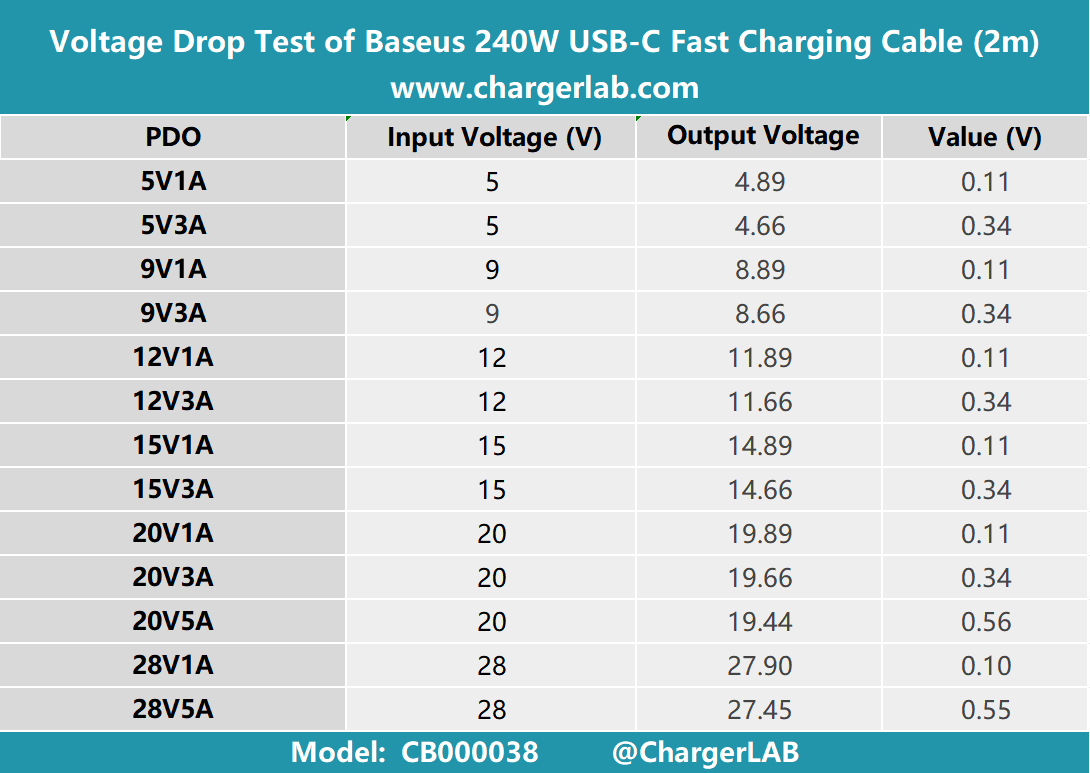
Moving on to the 2m cable, there doesn't seem to be any noticeable difference compared to the 1m version.
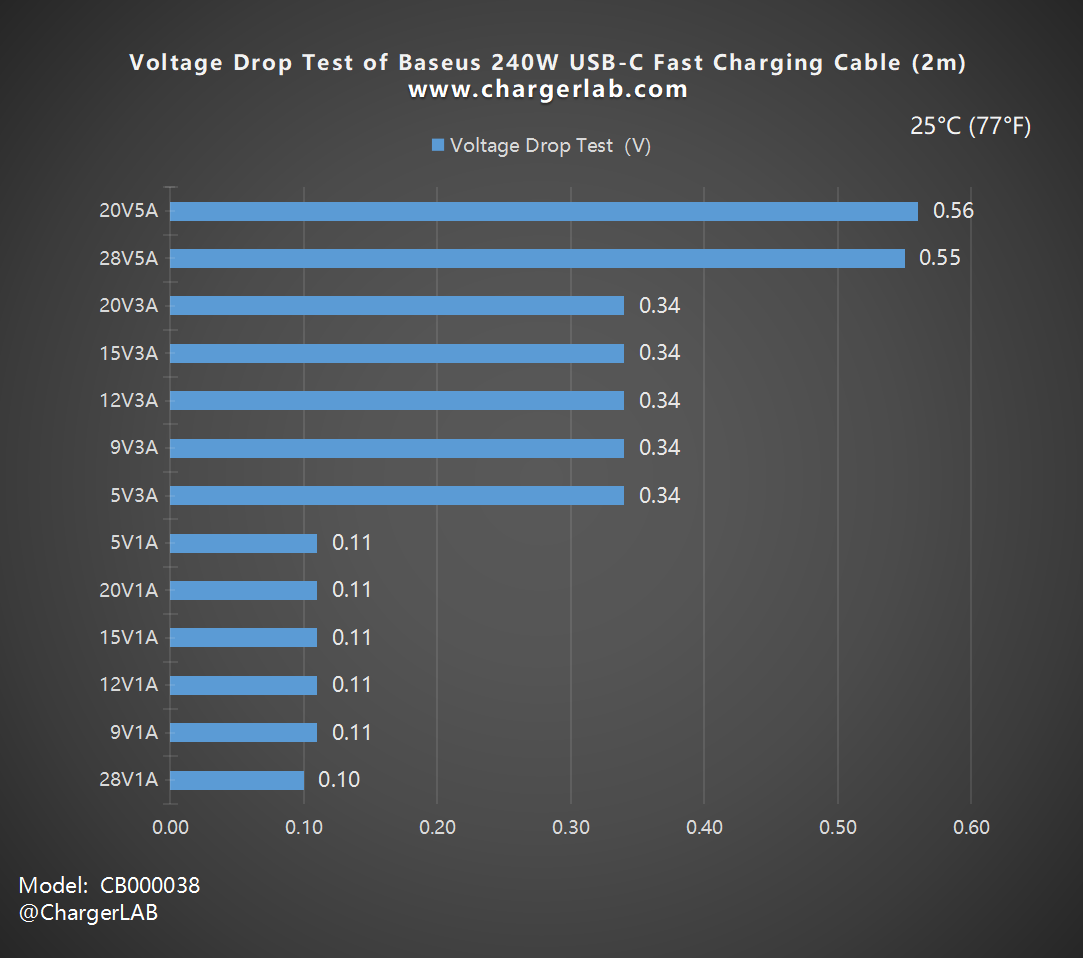
To get a clearer picture, we plotted a bar chart, which shows an increase in all three categories, which are 0.11, 0.34, and 0.55, respectively.
3m
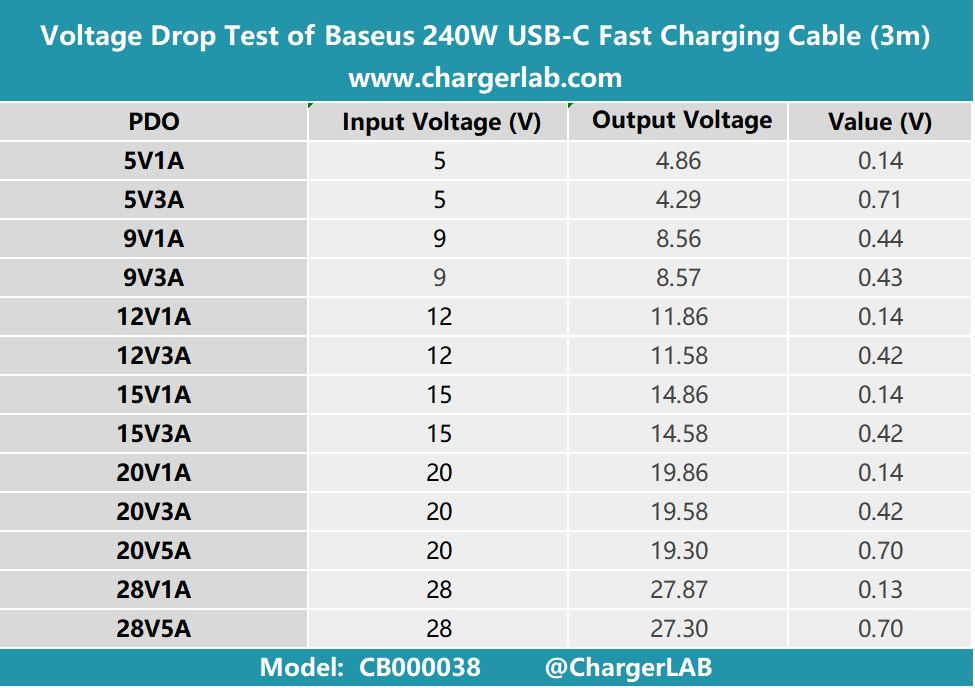
Lastly, we have the 3m version.
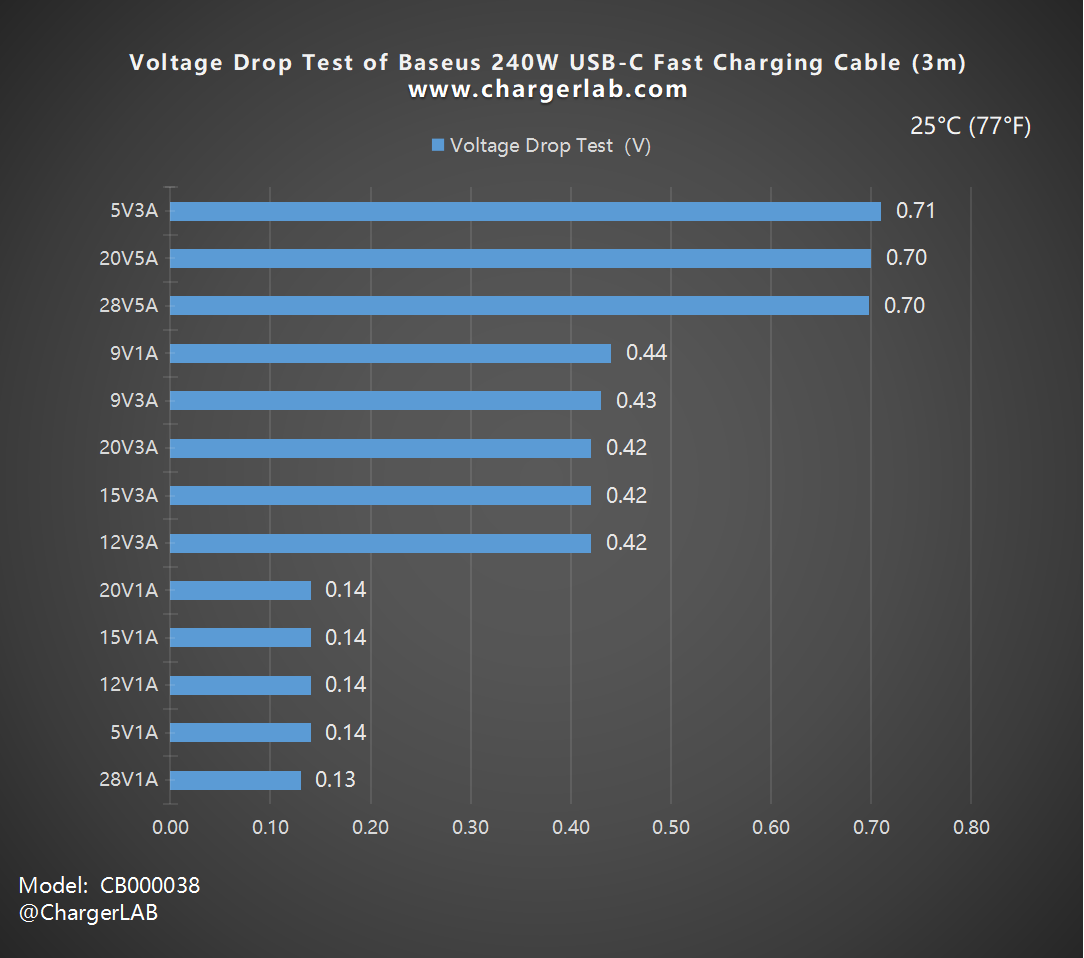
Once again, we created a bar chart, and it's evident that the difference in voltage drop between the 3m and 2m cables is greater than the difference between the 2m and 1m cables, indicating that as the length increases, the rate of voltage drop growth becomes increasingly significant.
Full Charging Test
Next, we fully charged an Anker 737 power bank using this cable. Throughout the test, both the cable and the power bank were kept inside a constant-temperature chamber at 25°C. The test results are as follows:
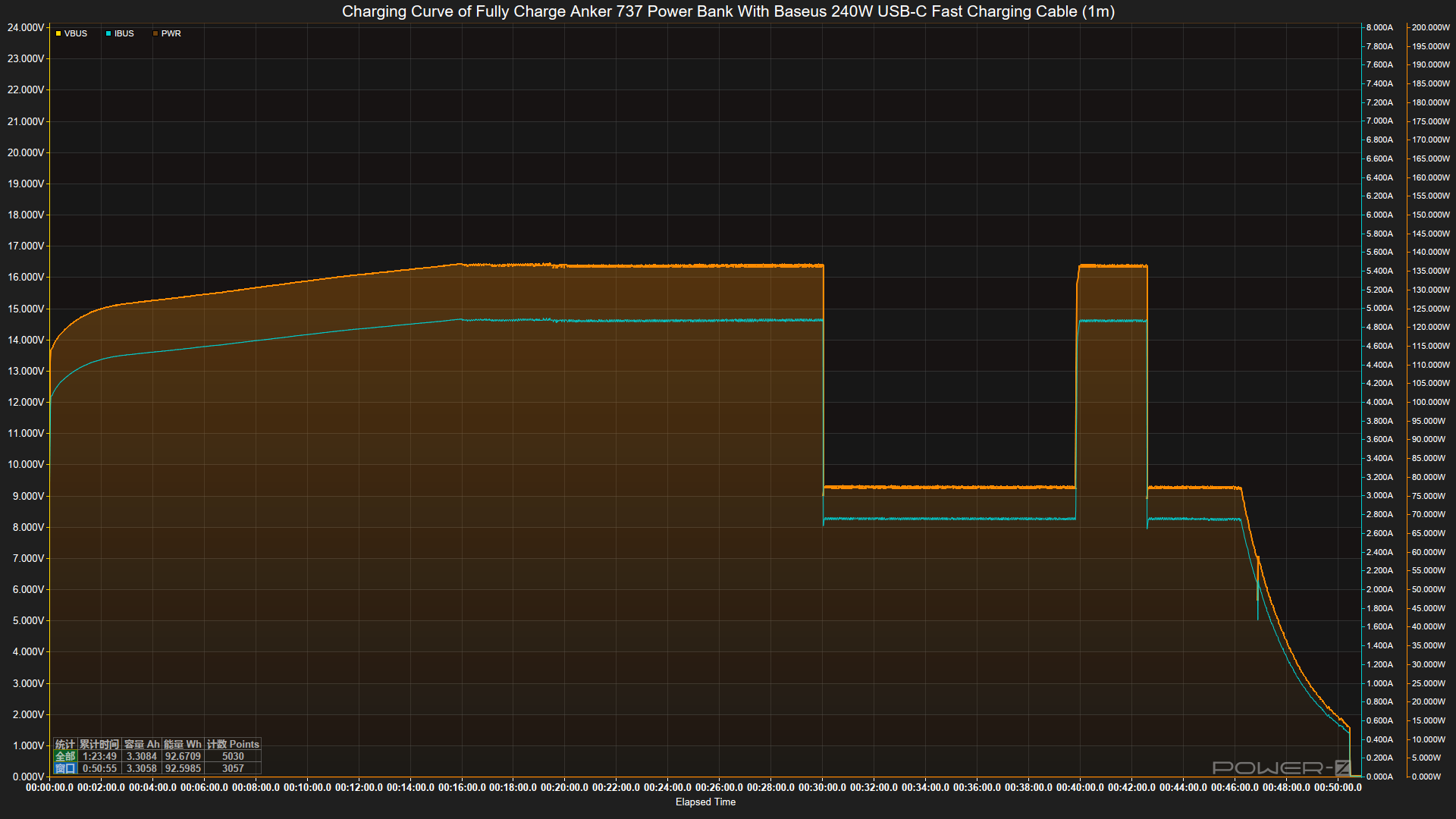
The maximum output power reached 136W, which aligns with the performance of PD 3.1 charging. The entire charging process took 51 minutes.
Summary of ChargerLAB
In terms of performance, the Baseus 240W USB-C Fast Charging Cable can support PD 3.1 140W charging, and the data transfer rate was measured to be USB 2.0. Additionally, it does not support video transmission. In the voltage drop test, the overall differences were relatively consistent, and the output remained stable. Overall, its performance is quite good, and the three different cable lengths can meet the needs of various users in different scenarios.
Related Articles:
1. Teardown of Apple Thunderbolt 4 Pro Cable (1.8 m)
2. Review of HP Thunderbolt 4 Cable
3. Review of LG 240W USB4 Cable with Full Pin Design








