Introduction
As the global COVID-19 pandemic gradually recedes, the worldwide tourism industry is making a comeback. The enchanting landscapes and diverse cultures of foreign lands have always been alluring. However, the various plug specifications and standards around the world can be perplexing. Different plug regulations exist within individual regions and even between countries.
Taking Europe as an example, the term "Euro-plug" we often hear isn't uniform. Although it mostly refers to type C, there are also type E, type F, and type G plugs, each suited for different countries and regions. The sheer number of standards across the world makes it challenging for hassle-free travel. Today, we'll focus on this topic and delve into knowledge about international standard plugs.
Background
One might wonder why a unified global plug standard isn't established. Such a standard would benefit travelers with cross-border needs and simplify the management of plug-in devices for different countries, reducing e-waste. The advantages are numerous.
However, the reality is that there are significant differences in power systems between countries. These differences directly lead to the adoption of standards and schemes that fit their own power systems for the configuration and design of electrical devices. In addition to power system disparities, an essential factor is the varying safety standards and certifications for electrical devices. This divergence contributes significantly to the myriad of charging equipment standards.
Differences in Power Systems
Currently, countries around the world commonly adhere to different voltage and frequency standards. By voltage distinction, there are two categories: low voltage, ranging from 100 to 130V, and high voltage, ranging from 220 to 240V.
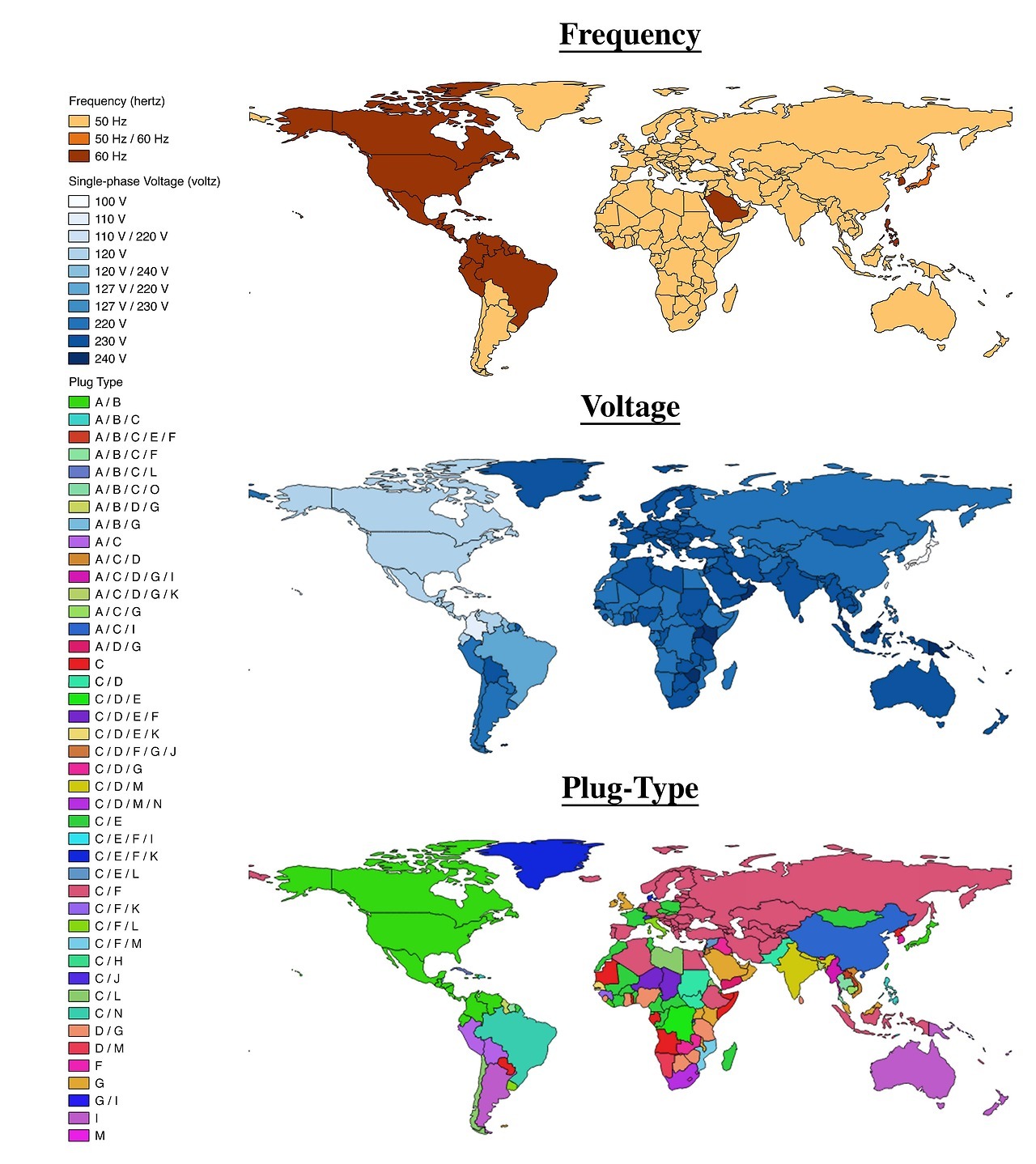
The graphic above summarizes the different power standards worldwide. In general, countries emphasizing energy efficiency tend to adopt high voltage and low frequency. For example, most European countries and China employ a voltage of 220-240 volts and a frequency of 50 hertz, while safety-focused countries like the United States and Canada use 110 volts and a frequency of 60 hertz. Such disparities can render electrical devices incompatible between countries, necessitating adapters or converters to adjust voltage and frequency.
Differences in Safety Standards
Different countries have varying safety standards and certification requirements for electrical devices. For instance, Europe uses the CE mark as a safety certification, while the United States employs UL certification. These certification requirements cover the design, materials, manufacturing, and safety performance of electrical devices, ensuring compliance with local safety standards. Below are common international certification symbols:

Apart from this, symbols and warning signs used on electrical devices may also differ between countries. These indicators convey characteristics, safety precautions, and usage instructions for electrical devices. Therefore, understanding the meanings of these symbols and signs is crucial during international travel or when using appliances across different countries.
Common Standards
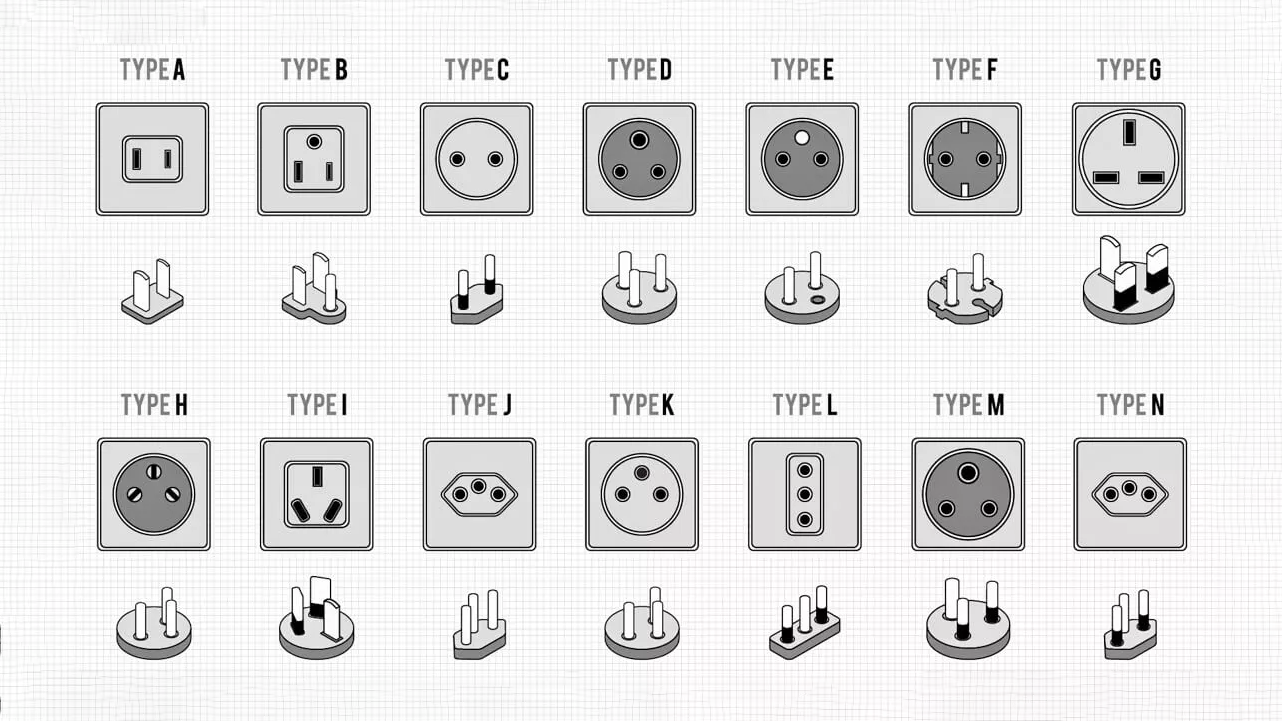
As mentioned earlier, there are various specifications for international standard plugs, categorized into two-pronged and three-pronged (with grounding) based on the grounding requirement. They can also be classified by the appearance of the prongs, such as flat, round, and hybrid types.
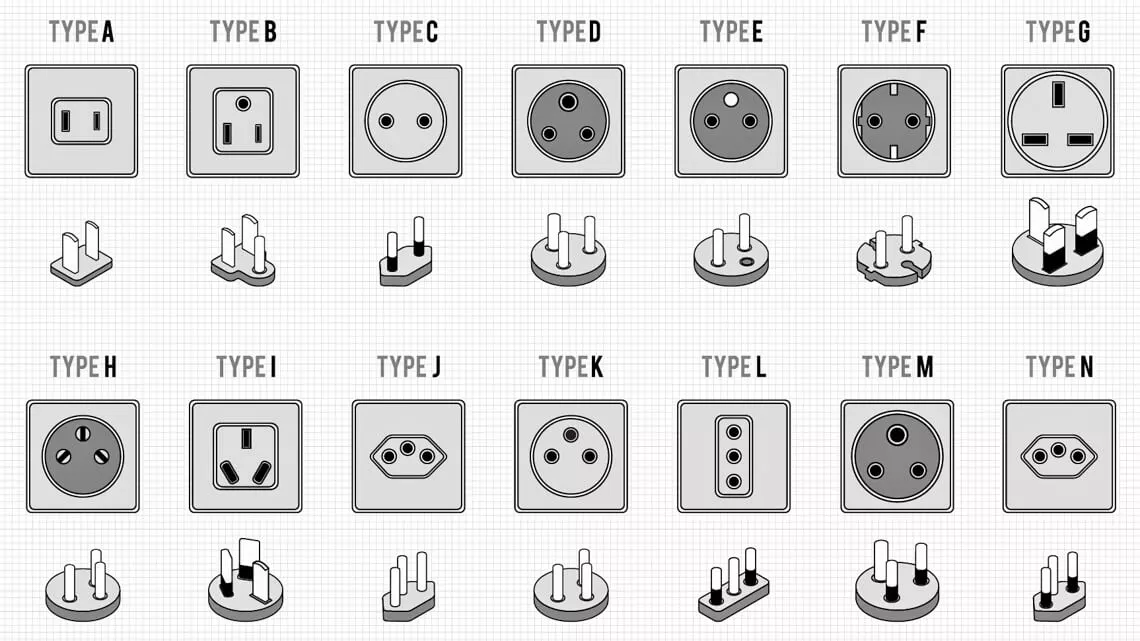
The common appearances of standard plugs worldwide are illustrated in the graphic above, showcasing significant design differences.
EU Standard
The European standard plugs refer to the types of plugs widely used in the European region. Below is an introduction to the main European standard plugs.

European standard two-prong plug type C: This is the most common plug type in Europe. It features two round prongs without grounding. Typically used for small electrical devices like phone chargers and small kitchen appliances. It's widespread in parts of Europe, Africa, and Asia, including countries like France, Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands.
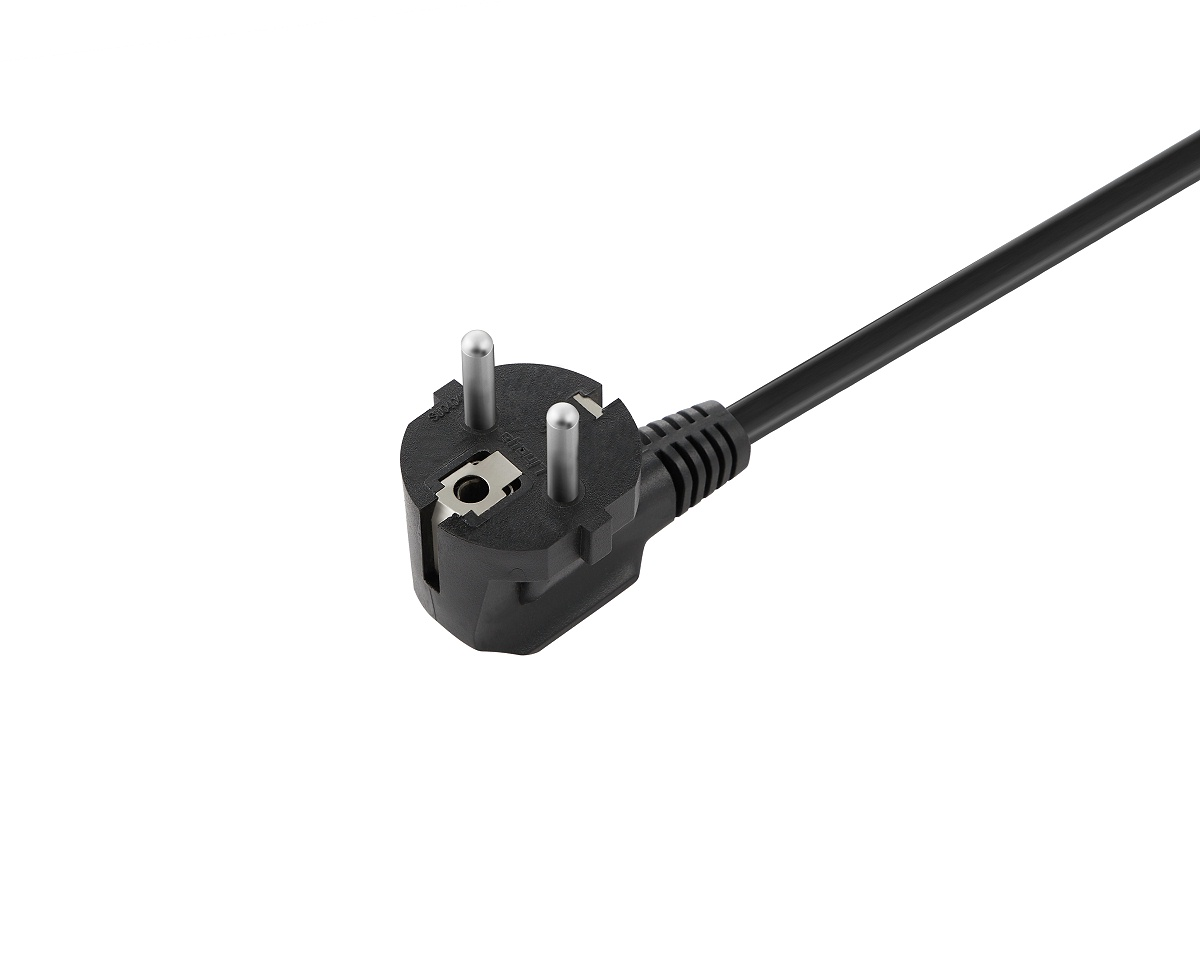

Type E: Widely used in France, it has two roundprongs and an additional grounding prong, with a slightly different shape compared to type C. Primarily used for large appliances like televisions and refrigerators. Apart from France, it's used in countries like Belgium and Monaco.
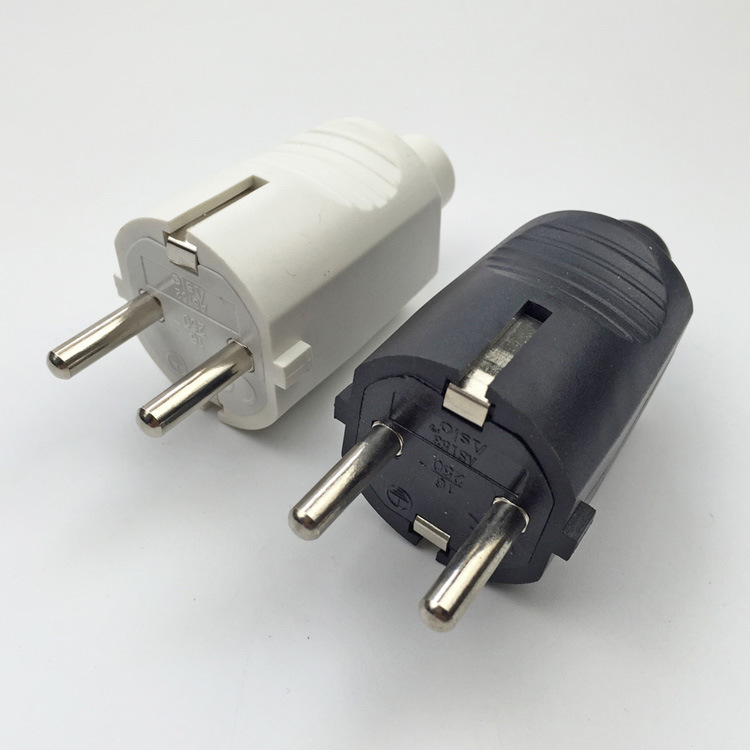

Type F: Commonly used in Germany, it also has two round prongs and a grounding prong, similar to the two-prong type in France (type E) but with minor differences. Type F plugs are also prevalent in countries like Austria, the Netherlands, and Indonesia.
US Standard
The United States and Canada use similar standard plugs collectively known as the US standard, which includes the following two types:
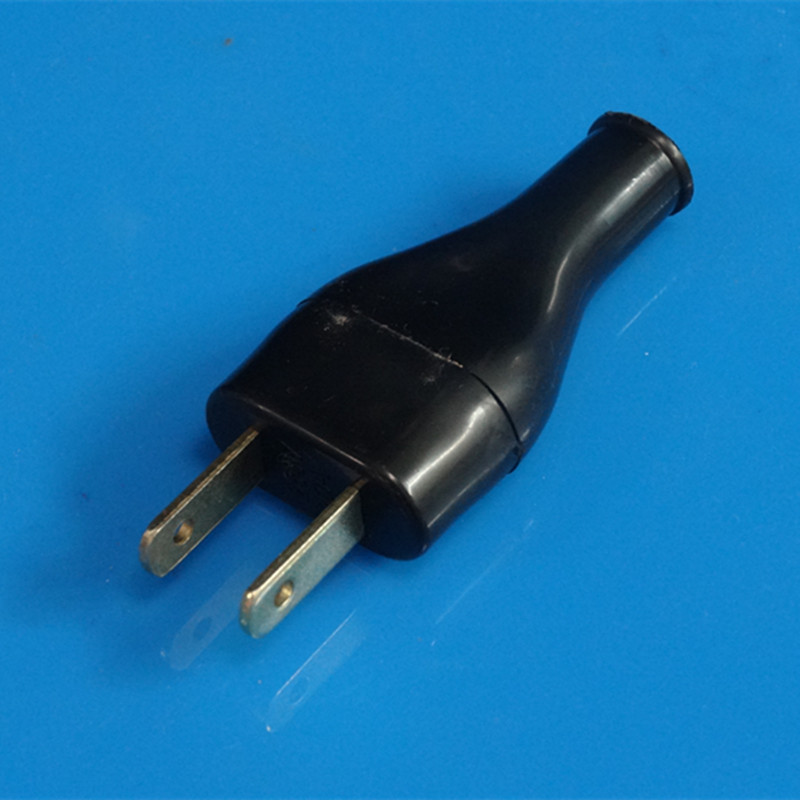

US standard two-prong plug type A: This is the most common plug type in the United States and Canada. It features two flat parallel prongs without grounding. It is commonly used for small electrical devices like phone chargers and small kitchen appliances. Widespread in the United States, Canada, Mexico, and some Central and South American countries.
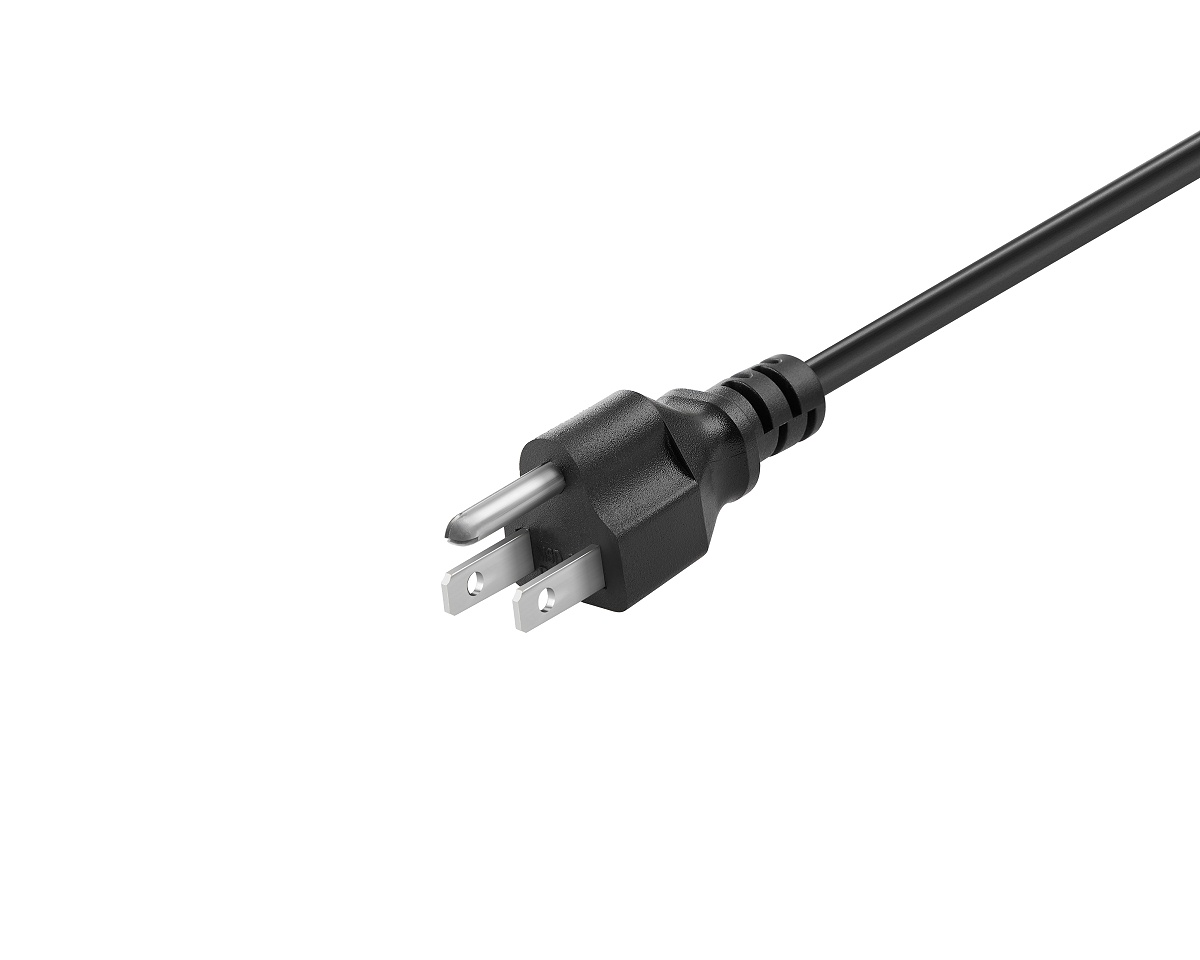

Type B: With two flat prongs and an additional grounding round prong, type B is used for larger appliances like televisions and refrigerators, providing secure connections for devices requiring grounding protection. Found in the United States, Canada, and other regions, it caters to the safety needs of appliances.
UK Standard
The UK standard three-prong plug type G: Common in the UK and several other countries, it features three rectangular prongs, two of which are of equal height, while the third is slightly shorter and used for grounding.
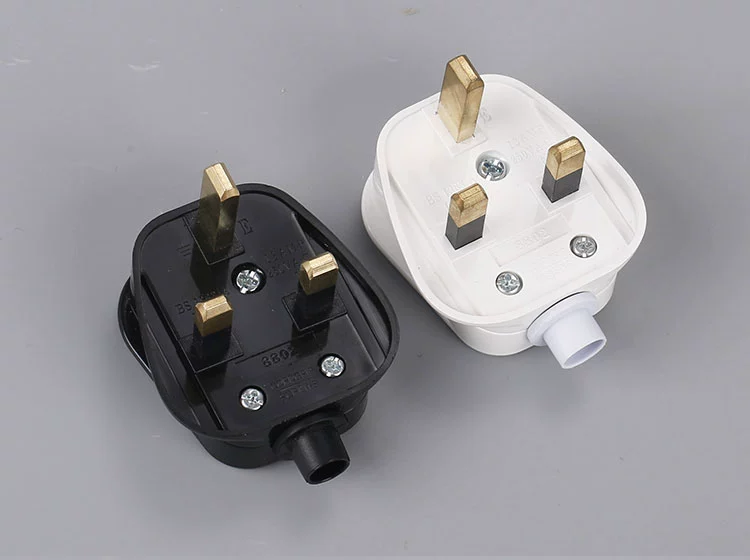

Type G plugs include a grounding function, providing a safer power connection. These plugs are used for larger appliances and critical household items like televisions, computers, and refrigerators.
Due to well-known reasons, type G plugs are widely used in the UK, its territories, and related countries. Apart from the UK mainland, they're also used in countries and regions like Malaysia, Singapore, Hong Kong, Ireland, Cyprus, and Malta.
AU Standard
Similar to many other countries, Australia's standard plugs come in both two-pronged and three-pronged varieties.
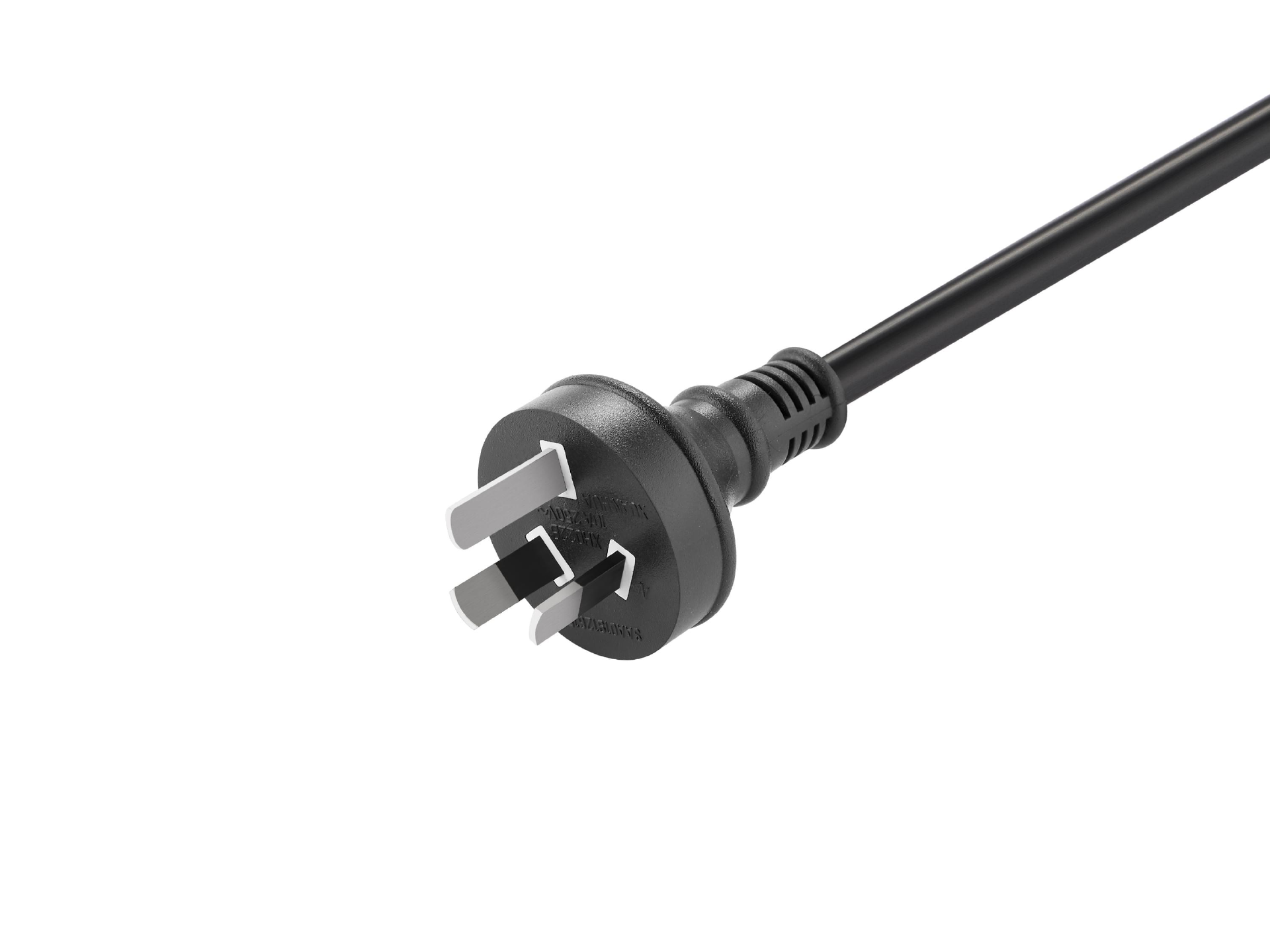

Australian standard three-prong plug type I: Commonly used in Australia and New Zealand, it features three flat prongs, two of equal height and the third slightly shorter, used for grounding to ensure a safer power connection. This plug type is typically utilized for large appliances and household items such as televisions, computers, and refrigerators.

Australian standard two-prong plug: Part of Australia's AS/NZS 3112 standard and a type I plug, the only difference from the three-prong version is the absence of the grounding prong. It is commonly used for small electrical devices like phone chargers and electronics. Both these plug types are extensively used in Australia, New Zealand, and their territories.
Others
In addition to the commonly used national standard plugs mentioned above, there are distinctive plugs in other countries.

For example, Italy and Chile adopt the three-prong round plug type L. Apart from these, there are many other countries with unique plug types not listed here.
Adapters and Converters
In the landscape of diverse global plug standards, plug adapters/converters come as essential tools for international travel. They bridge the gap between different countries' plug standards and voltage specifications.
Plug Adapter
A plug adapter is a simple electrical accessory used to convert your device's plug into one that fits the socket standard of your destination country. It doesn't alter voltage; its purpose is to address the mismatch in plug shapes.
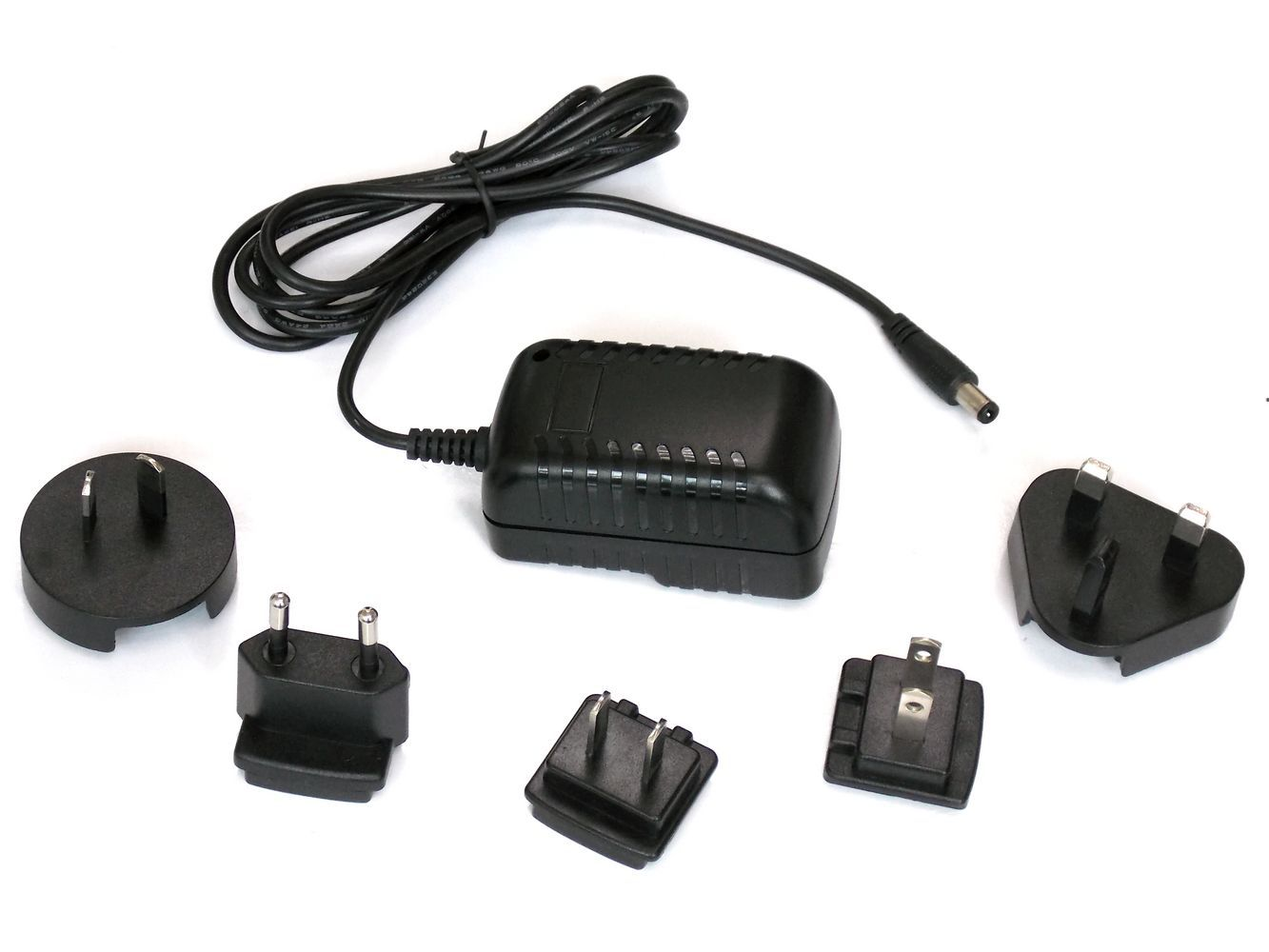

For example, if your device has a US type A plug, but you're traveling in Europe, you can use a plug adapter to convert the type A plug to type C, allowing your device to fit into the local socket and function normally.
Voltage Converter
A voltage converter not only adapts plugs but also adjusts the voltage of your electrical devices. This is particularly useful when there are different voltage standards in various countries.
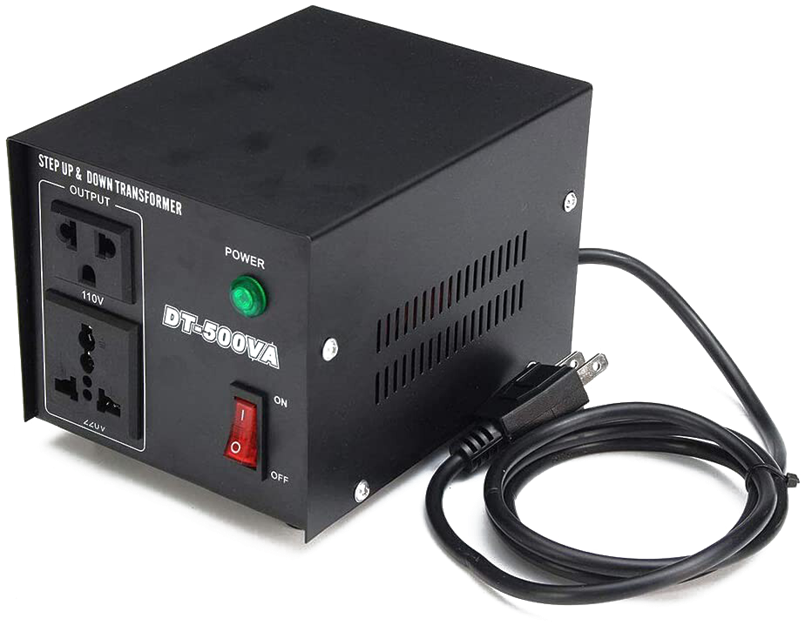

For instance, the standard voltage in the US is 110 volts, while in Europe, it's 220-240 volts. If you're taking devices from the US to Europe, a plug adapter can solve the socket mismatch, but the voltage difference might damage your devices or prevent them from working correctly. In such cases, a voltage converter is needed to adjust your device's voltage from 110 volts to 220-240 volts, aligning with the target country's voltage standard.
Standardization Efforts
Given the current situation, plug standardization is an important developmental trend to address the differences in power plugs across countries and regions. International organizations have been working diligently to push for the establishment of unified standards. Furthermore, emerging technologies and innovations are also propelling the development of plug standardization.
Organizations
Organizations dedicated to promoting plug standardization include the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).

ISO and IEC are two international standardization organizations committed to creating international standards, including those for electrical plugs. Through the collaboration of these organizations, it's hopeful that different countries and regions will develop consistent plug standards, promoting interoperability and safety of global electrical devices.
Additionally, many regions have established regional standardization organizations, such as the European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). These organizations assist in formulating regional electrical plug standards to meet local needs and requirements.
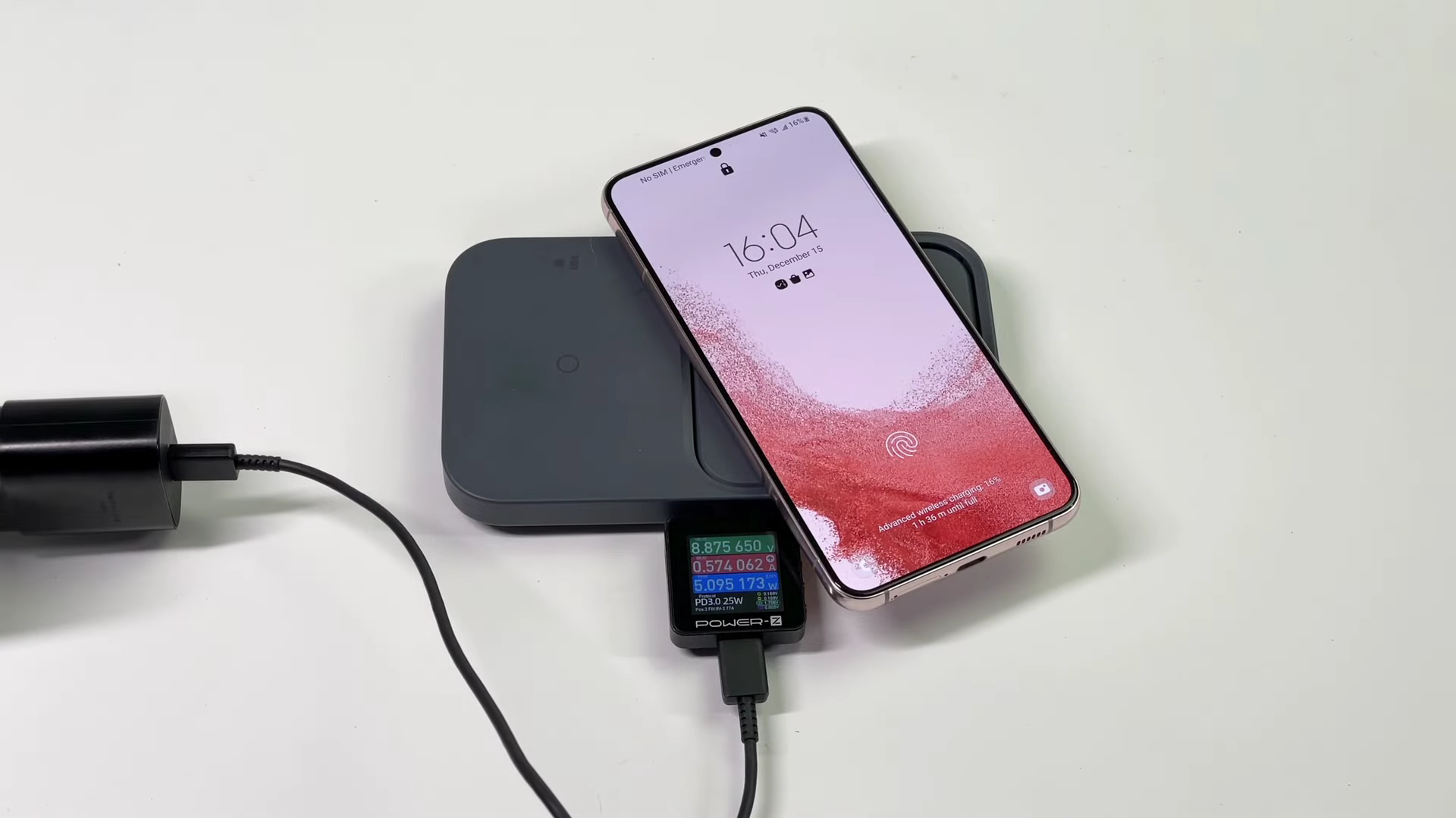
Wireless Charging Technology
Innovations in power transmission technology can also significantly impact the standardization of international plugs, even triggering revolutionary technological changes.

The advancement of wireless charging technology could lead to changes in plug standards, potentially introducing more standards based on wireless charging. This would allow devices to be charged without the need for physical plugs and sockets. As a result, traditional plugs and sockets might become obsolete in scenarios involving wireless charging.
Summary of ChargerLAB
In general, given the current differences in power systems and safety standards among countries, the trend of each country maintaining its own plug specifications is unlikely to change significantly in the short term. Travelers with international travel needs should still understand the local electrical equipment standards to avoid unnecessary hassles.
However, the good news is that the market for multi-country power adapters and converters is rapidly evolving. Not only are there abundant options, but their performance is also becoming more robust, and compatibility with various international standards is increasing. This is of paramount importance for lightening the load of international travelers.
Furthermore, international efforts to unify plug standards are gaining momentum, and the emergence of new technologies is driving standardization toward unity. Some regions, like the European Union, are already leading the way in plug standardization. Presently, type C plugs are widely used in EU countries.
Related Articles:
1. What is USB-C? All you need to know! - ChargerLAB Explained
2. What's USB Type-B Connector? | Introduction and Explained
3. What's Difference Between 5A Cable and 3A Cable