On September 19, Huawei released the Mate 30 series smartphones in Munich, Germany including Mate30, Mate30 Pro, and Mate30 RS Porsche Design. All of them support 27W wireless charging and new generation of reverse wireless charging, and the company emphasizes that 27W is the power that being directly charged into the phone.
Released with the new Mate 30 series are two 27W wireless chargers for indoors and in-vehicle environments. So here is the teardown review of the Huawei 27W SuperCharge Wireless Charger (CP61).
I Unboxing
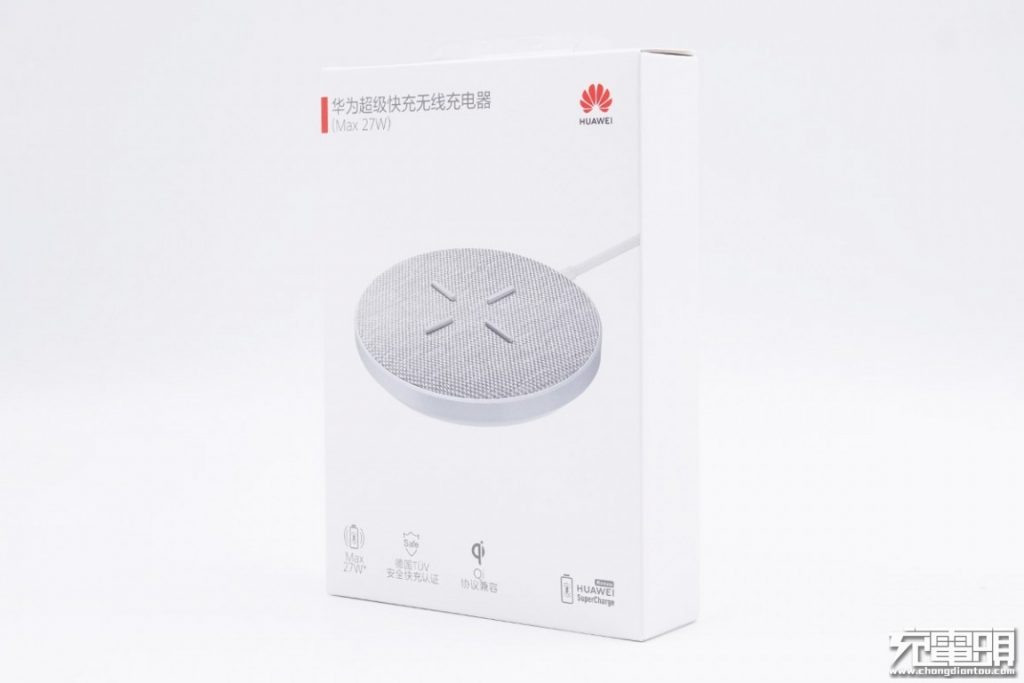

A clean white box. Main features: 27W maximum power, German TüV safety certification, and Qi compatibility.

Specifications on the back.Model: CP61Input port: USB Type-CInput: 5V-10V, 4A (Max)Output: 27W (Max)Wireless charging protocol: WPC Qi

An anti-counterfeit label and barcodes.

Open the package and slide out an inner box.

Package contents: wireless charger, 5A USB-A to USB-C cable, user manual and warranty card.
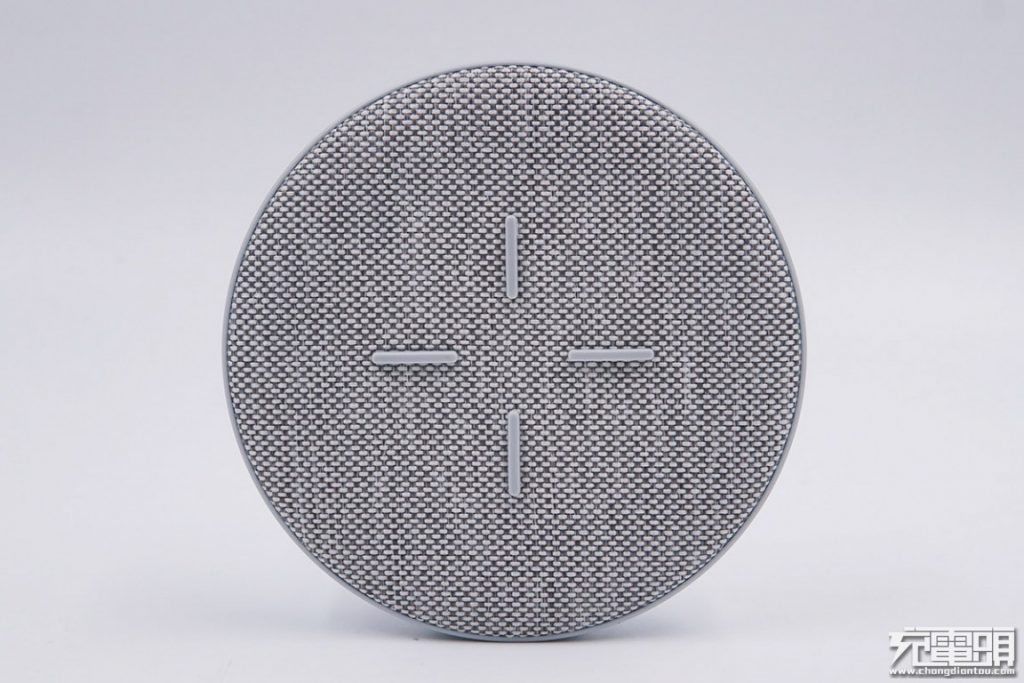

The wireless charging pad features a compact and minimalistic design with non-slip silicone pads on top. The surface is covered by a woven fabric for breathability
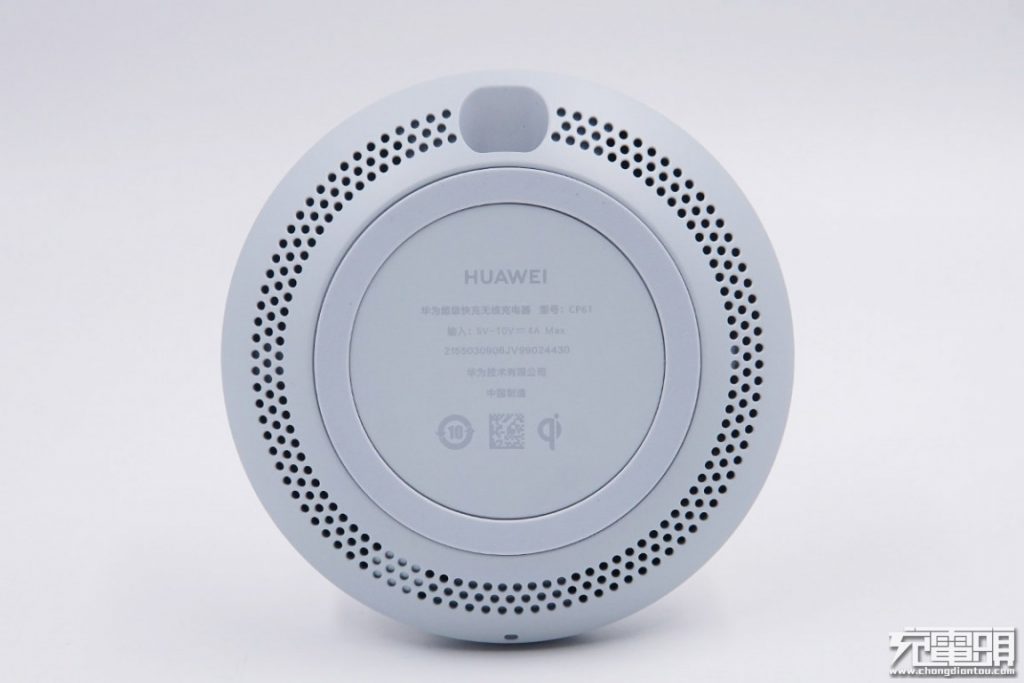

Specifications on the bottom, and there is a ring-shaped non-slip silicone pad.
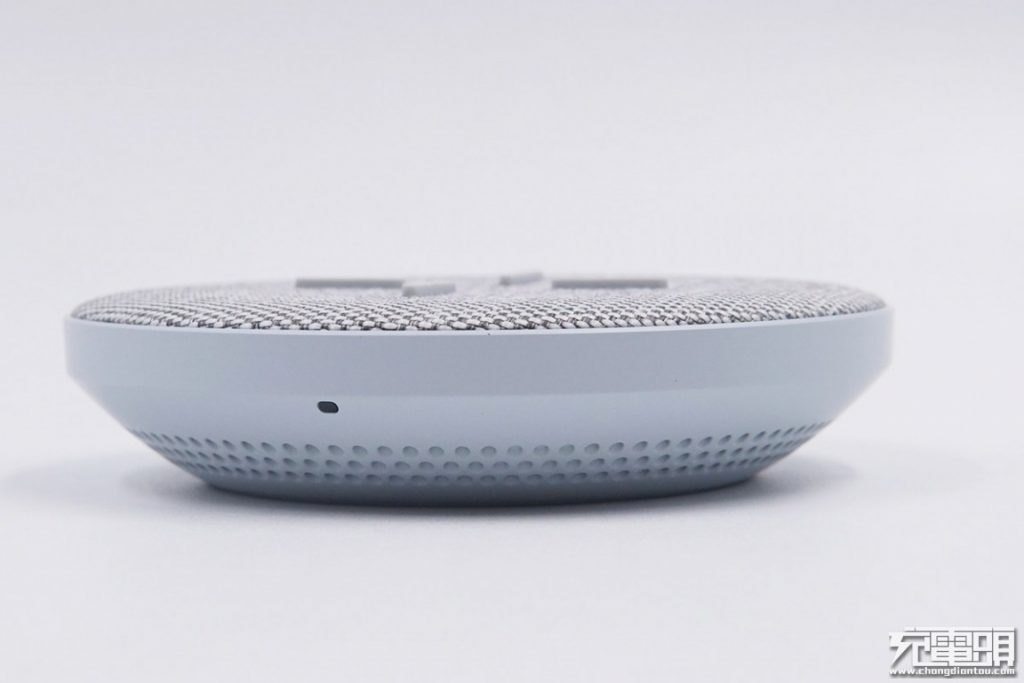

The overall shape is like a bowl, with vent holes around the lower part. The product adopts an independent C-shaped three-dimensional airflow design, bringing stronger heat dissipation capability, and the company claims that the heat dissipation capability is increased by 30%. It also has a smart silent fan built-in, which will switch to silent mode at night.

An LED indicator.

The USB-C input port.

The port is recessed for a cleaner look.
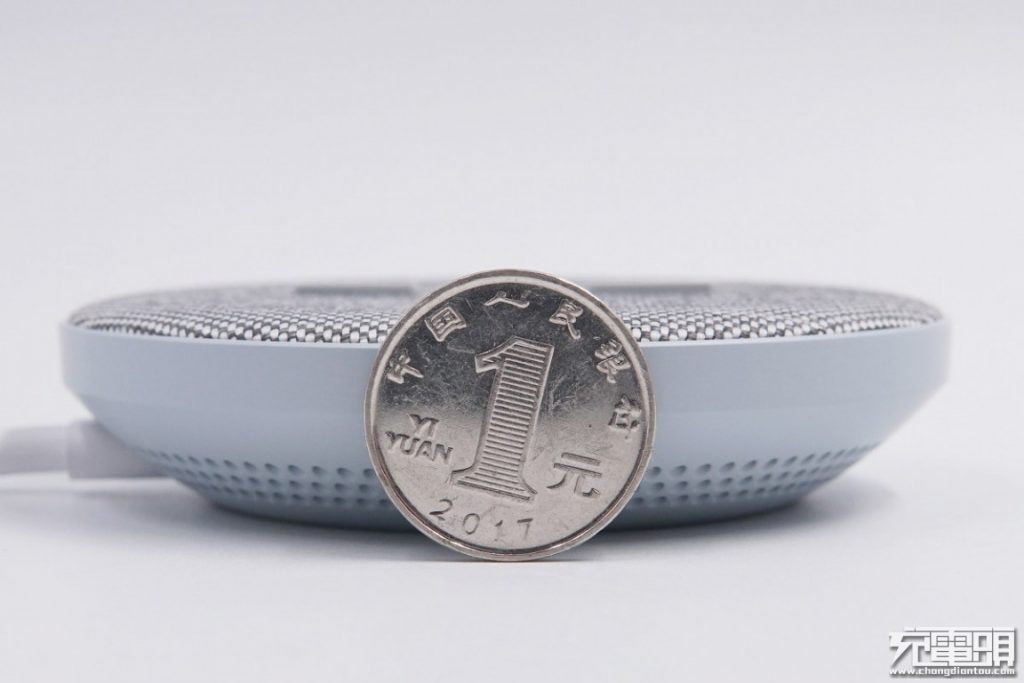

Is has a diameter of 90mm, and a height of 20.85mm.

According to Huawei, compared with the previous generation Huawei 15W wireless charger, this new generation 27W wireless charger has a power increase of 80%.
Our testbed: Huawei's 40W SCP charger (the Huawei Mate 30 series in-box charger) is used as an input source, which is monitored by ChargerLAB POWER-Z KT001. The Huawei 5A cable is used as the power cable to connect Huawei 27W wireless charger.
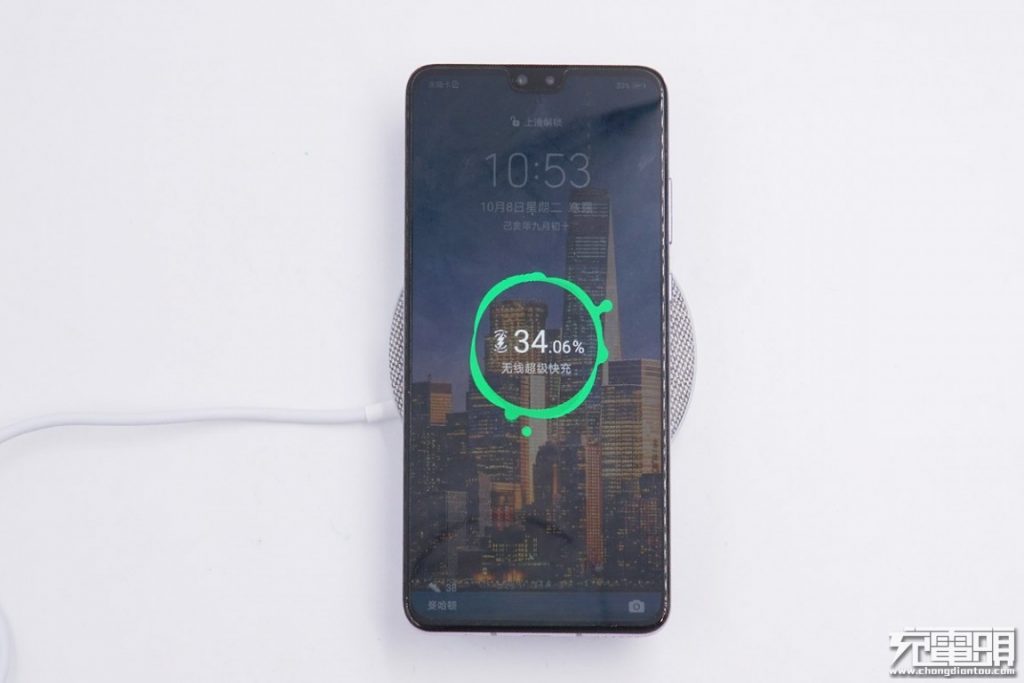

After the Huawei Mate30 is placed on the wireless charger, the display shows the “Wireless Super Fast Charge” is on.
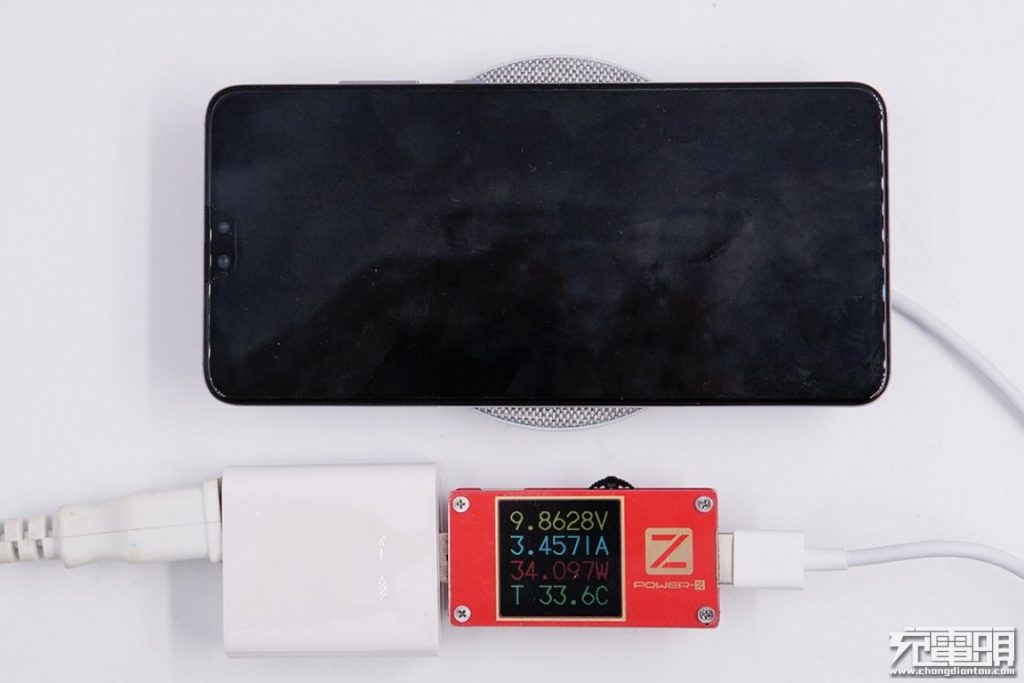

At this time, the input power is about 34.1W (9.9V/3.5A). So after efficiency conversion, the wireless charging power received at the phone end has indeed reached the 27W level.
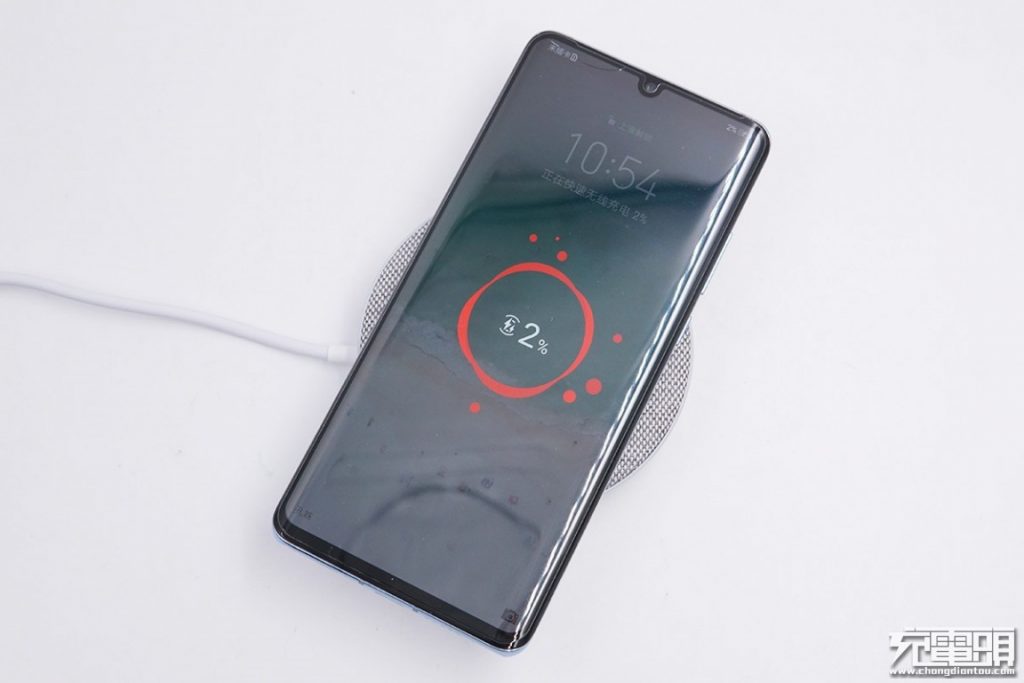

After we put the Huawei P30 Pro on top, two lightning bolts show up, indicating that fast wireless charging is in progress.
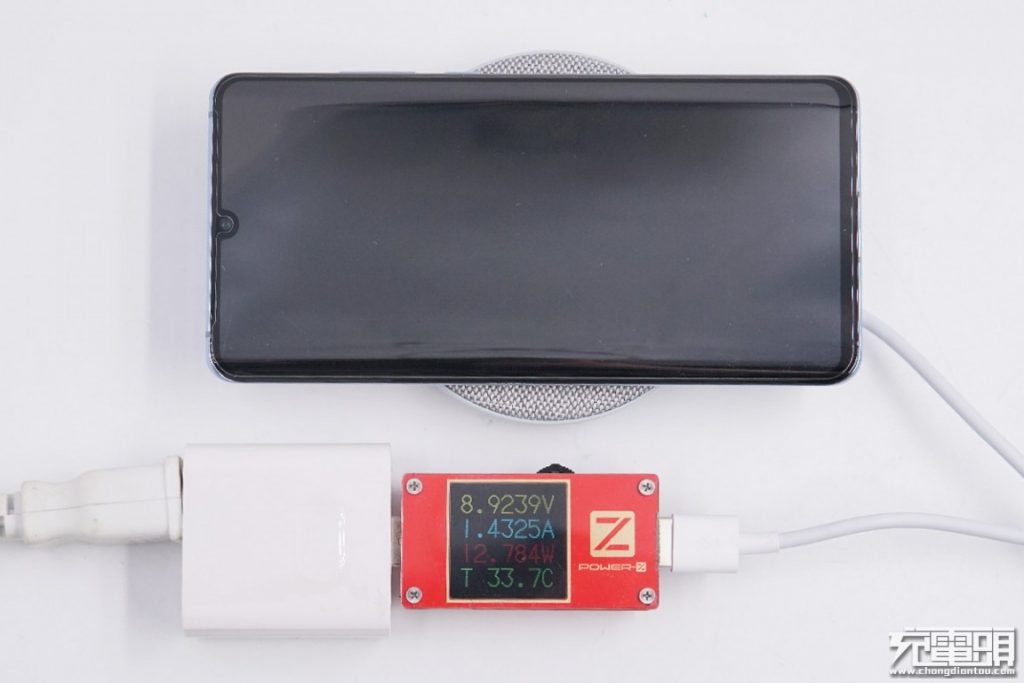

At this time, the input power is about 12.8W (8.9V/1.4A). So after efficiency conversion, the wireless charging power received at the phone end has indeed reached the 10W level.
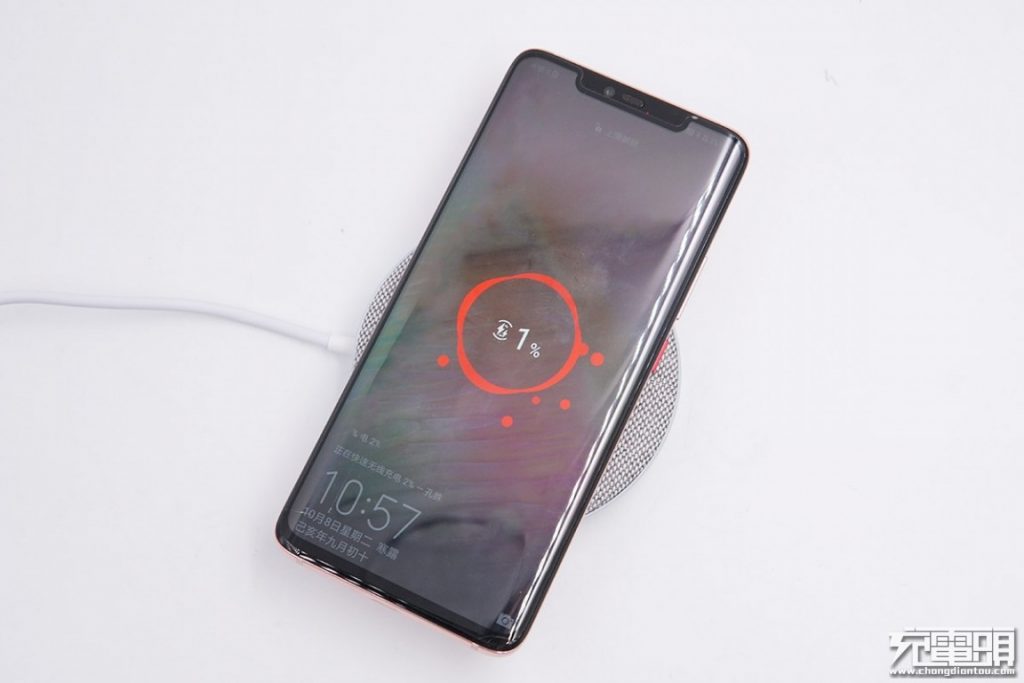

Huawei Mate 20 Pro on top, we have two lightning bolts show up, too, indicating that fast wireless charging is in progress.
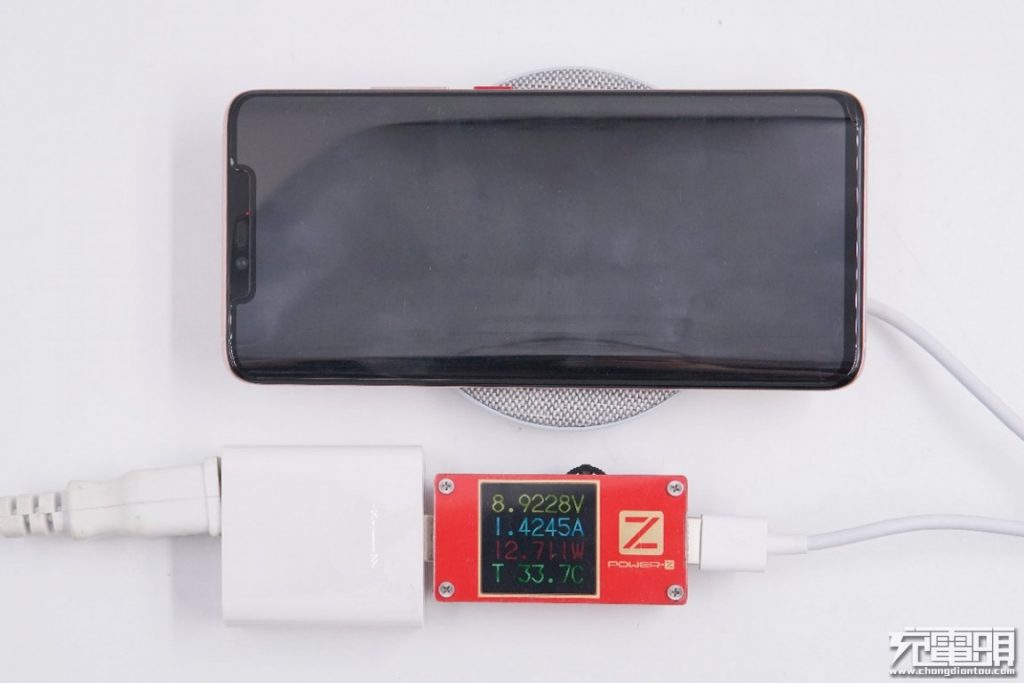

At this time, the input power is about 12.7W (8.9V/1.4A). So after efficiency conversion, the wireless charging power received at the phone end has indeed reached the 10W level.
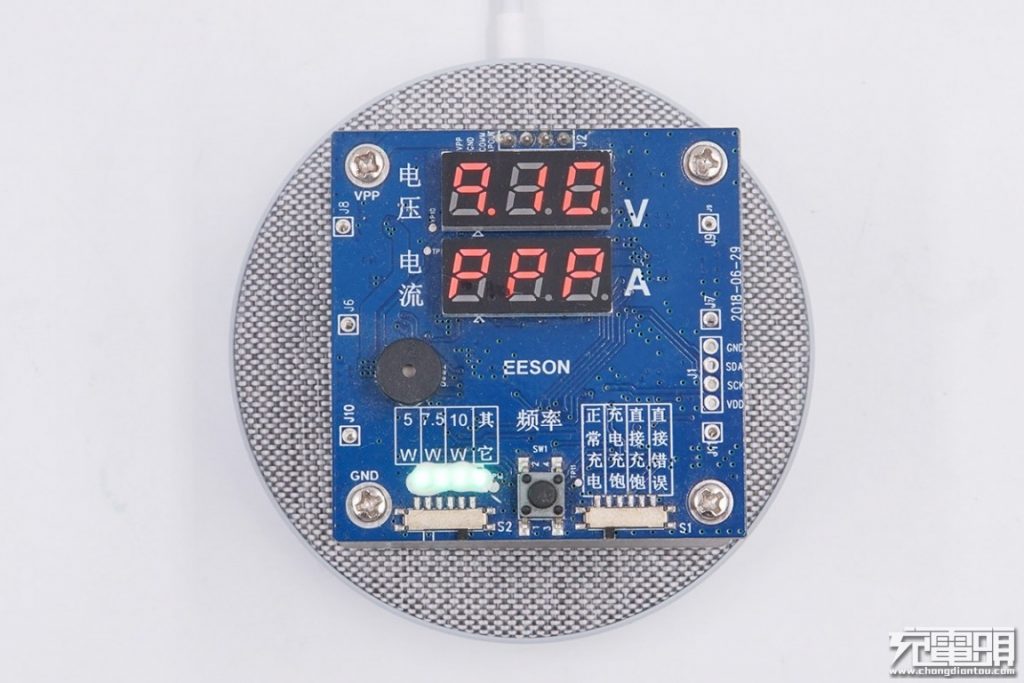

Using the wireless charging aging tester, we read a "PPP" which means it passed the 5W, 7.5W and 10W wireless charging. So it supports normal 5W, Apple 7.5W, and Samsung 10W wireless charging.

Our Samsung S10+ shows that it supports Samsung 10W wireless charging.

It also supports Apple's 7.5W wireless charging. It starts charging instantly when we put an iPhone on top.
II Teardown
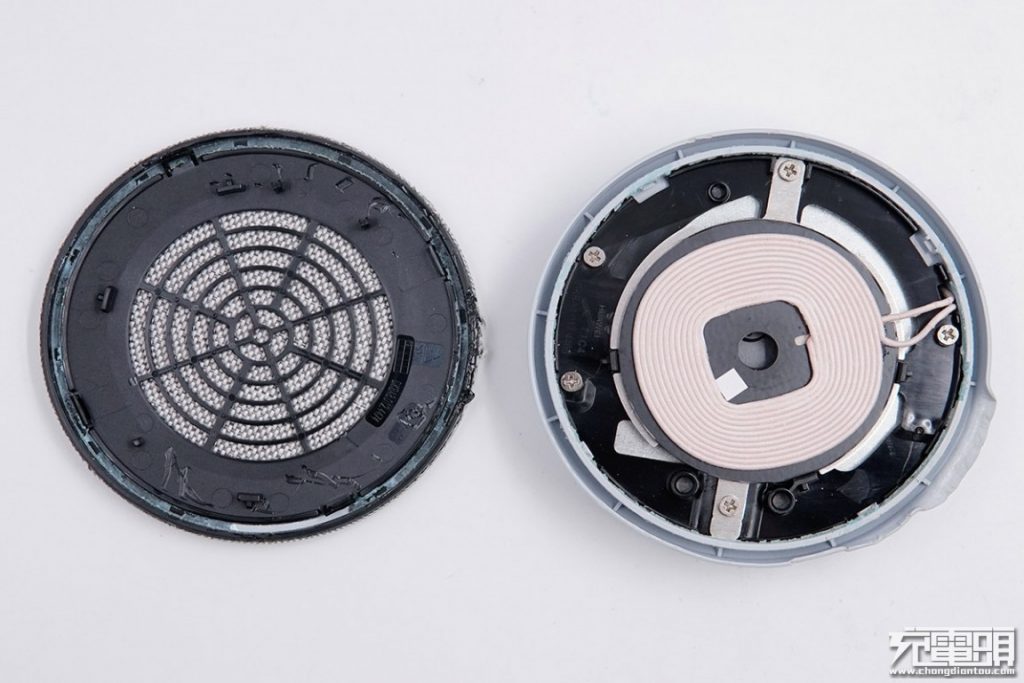
Remove the upper cover that is fixed with clips and adhesive, we can see the inner structure under the fabric cover is hollowed out for air intake. Below the vent is a wireless charging coil.
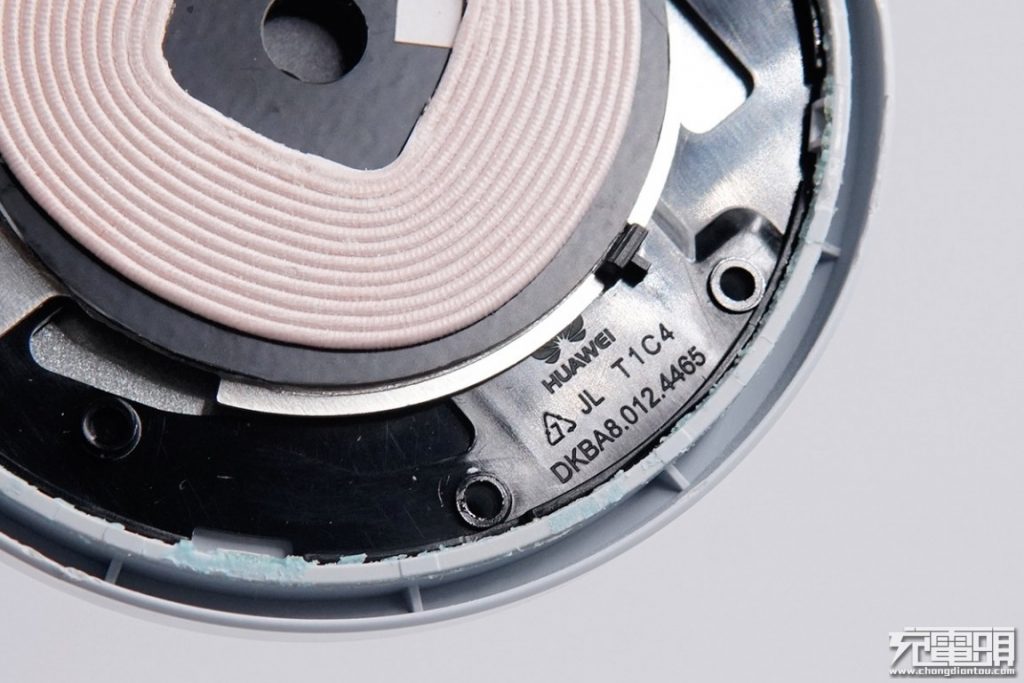

HUAWEI logo on the inner frame. (Nitpicking here: the logo is actually for Huawei's enterprise line, not consumer line).
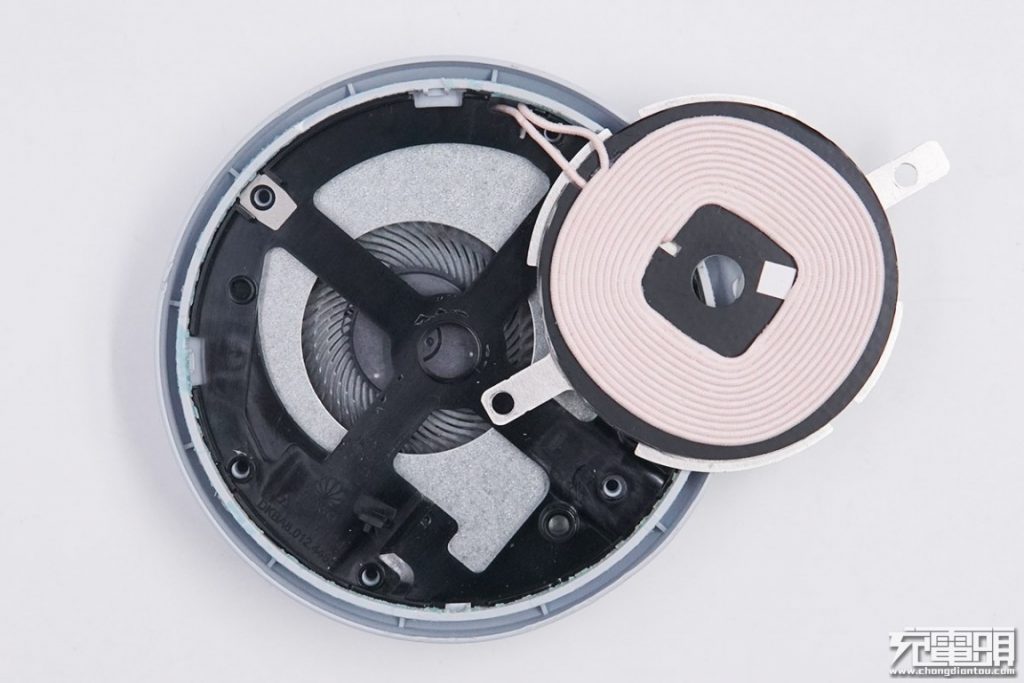
Remove the screws and the wireless charging coil and reveal a centrifugal fan underneath, which has very dense fan blades. The air is sucked through the opening of the magnetic shield to take away the heat generated by wireless charging.
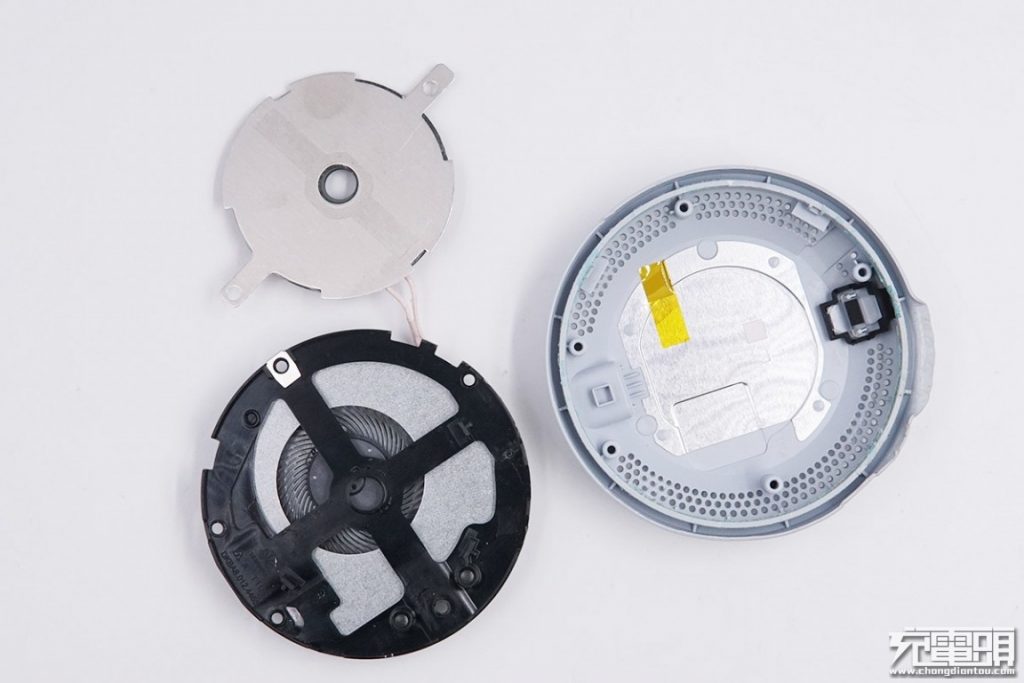

Remove the internal circuit board, the frame, and the fan.
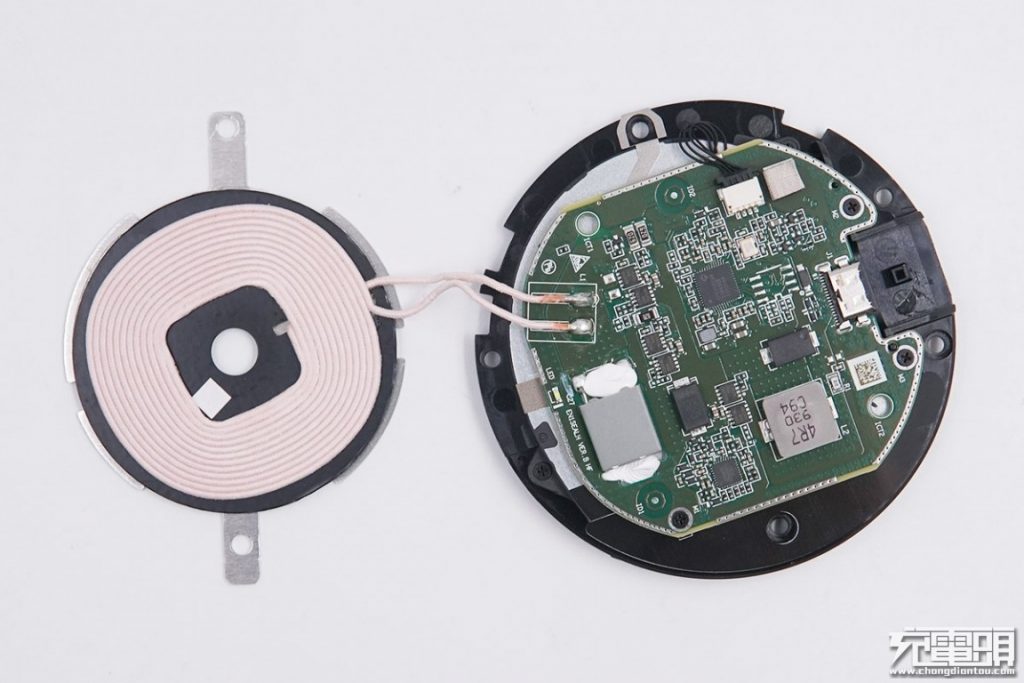
Taking a look at the wireless charging coil and circuit board, which adopt familiar edge perforation processes, for blocking electromagnetic radiation.
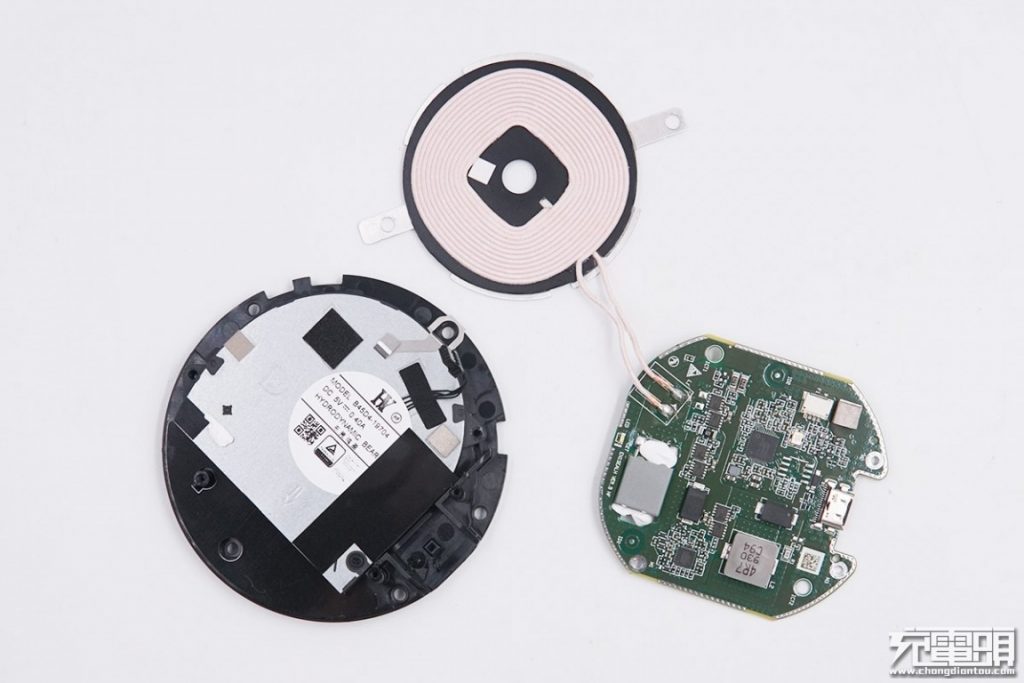
Underneath the PCB is a cooling fan.
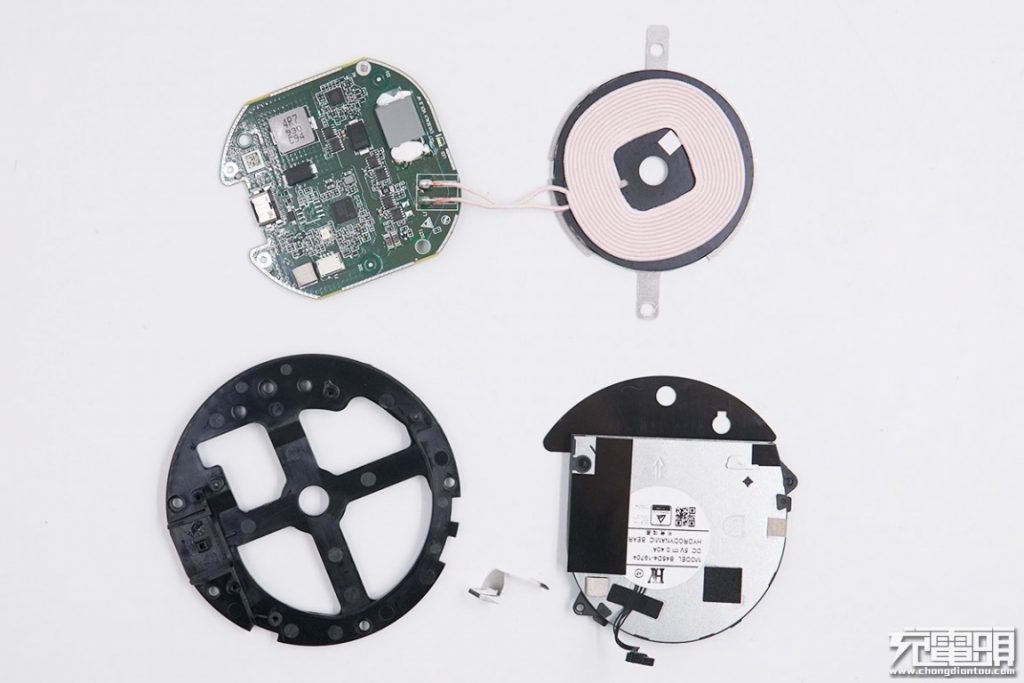
The wireless charging modual, fan and internal bracket.
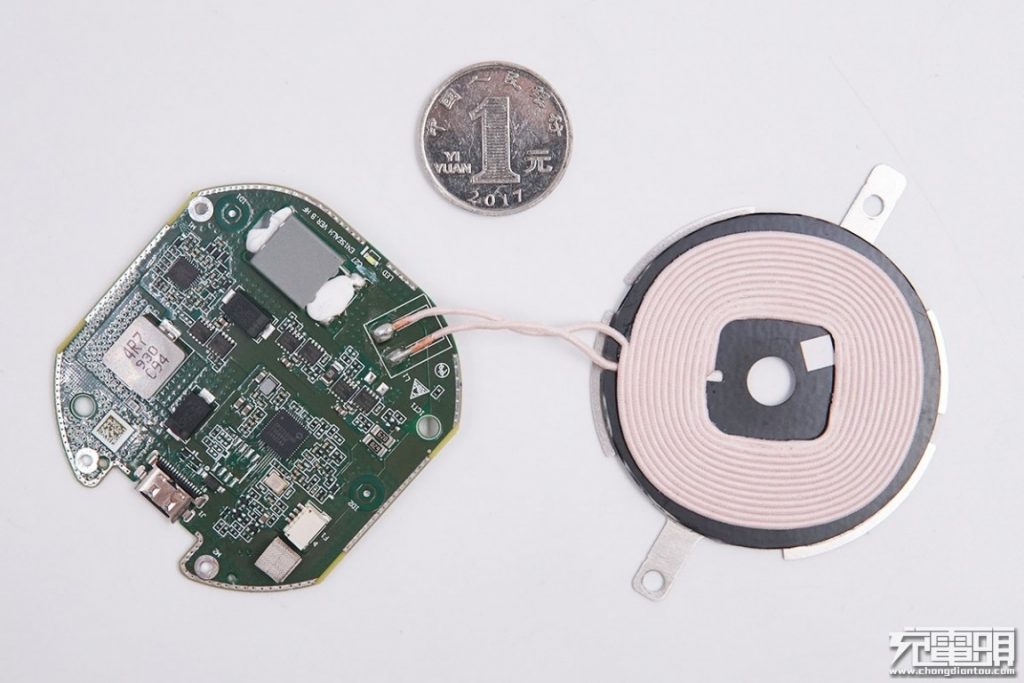
Compared to RMB 1 yuan coin.
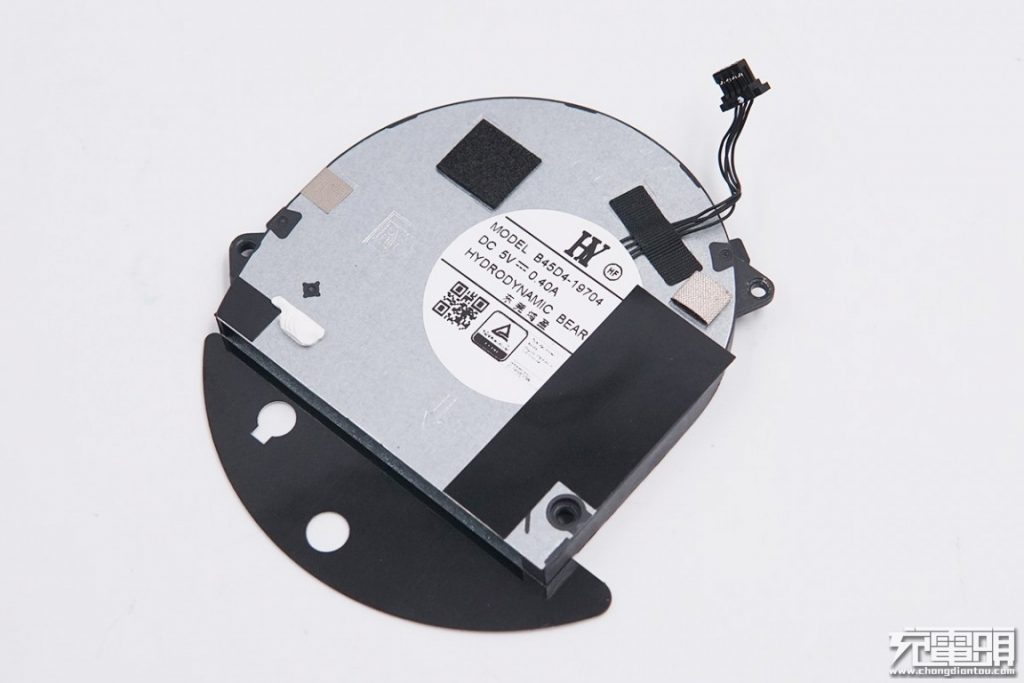

4-wire PWM temperature control fan by Dongguan Hongying, hydrodynamic bearing for lower noise and longevity, 5V/0.4A.
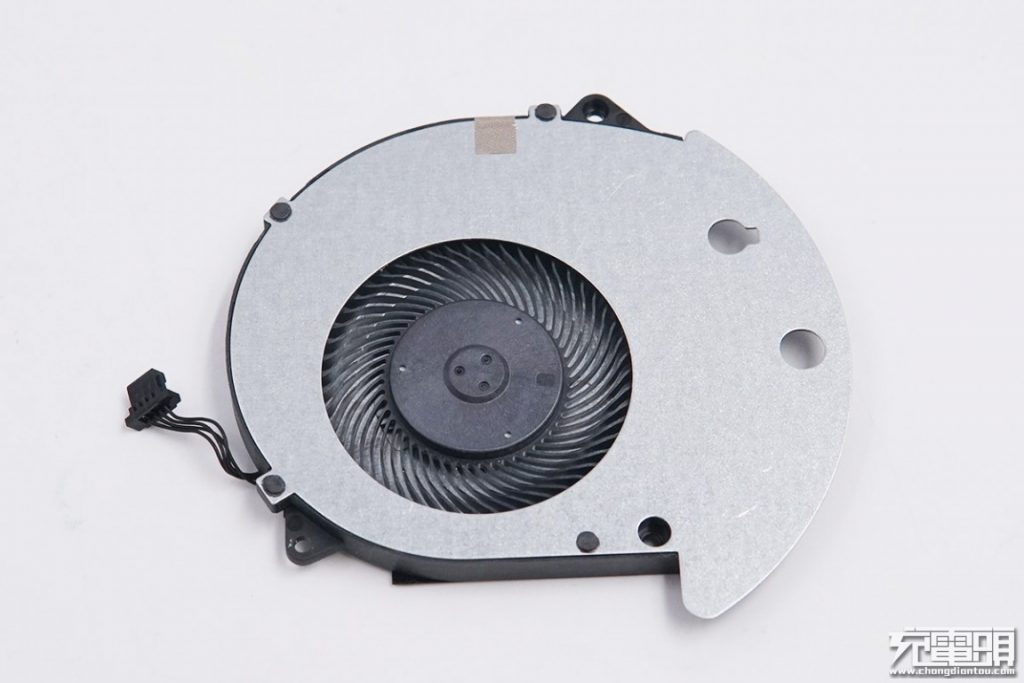

Taking a closer look at the fan blades.

There is a hood on the outside of the indicator light.
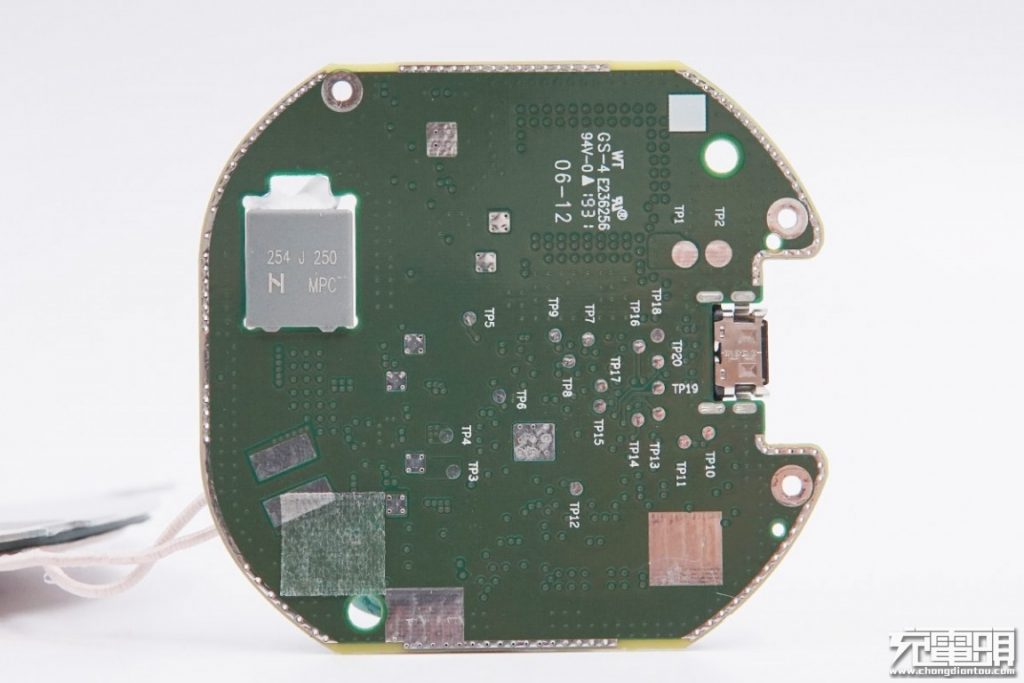
Next, let's take a look at the back of the PCB, which has a cut-out area with an MPC-CBB resonant capacitor.
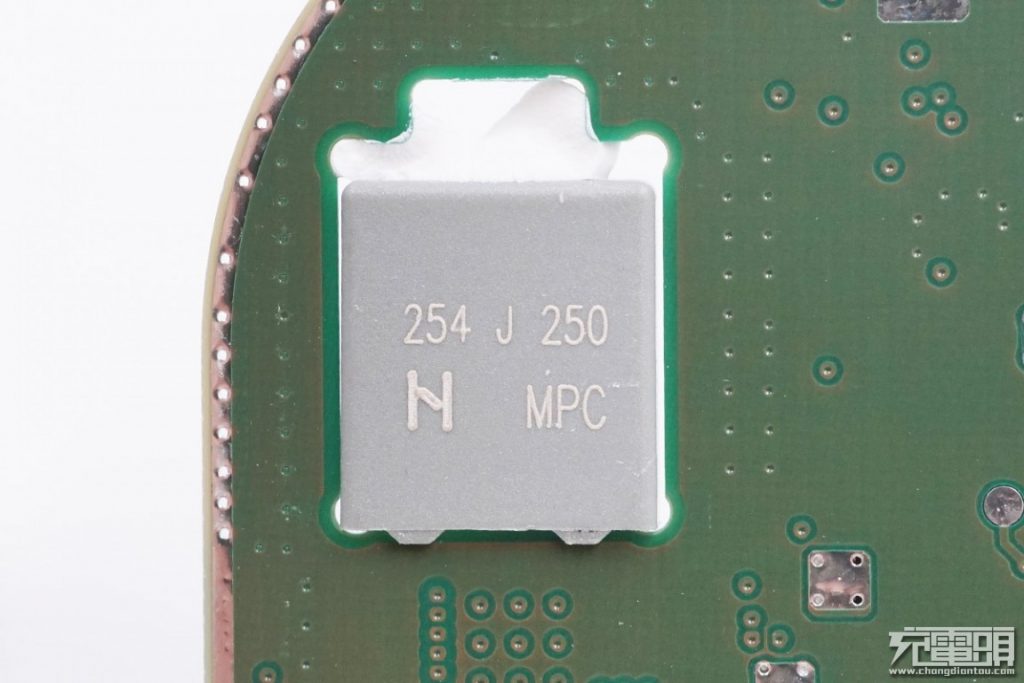
0.25μF 250V, grade J, the capacitor is reinforced with glue on both sides.
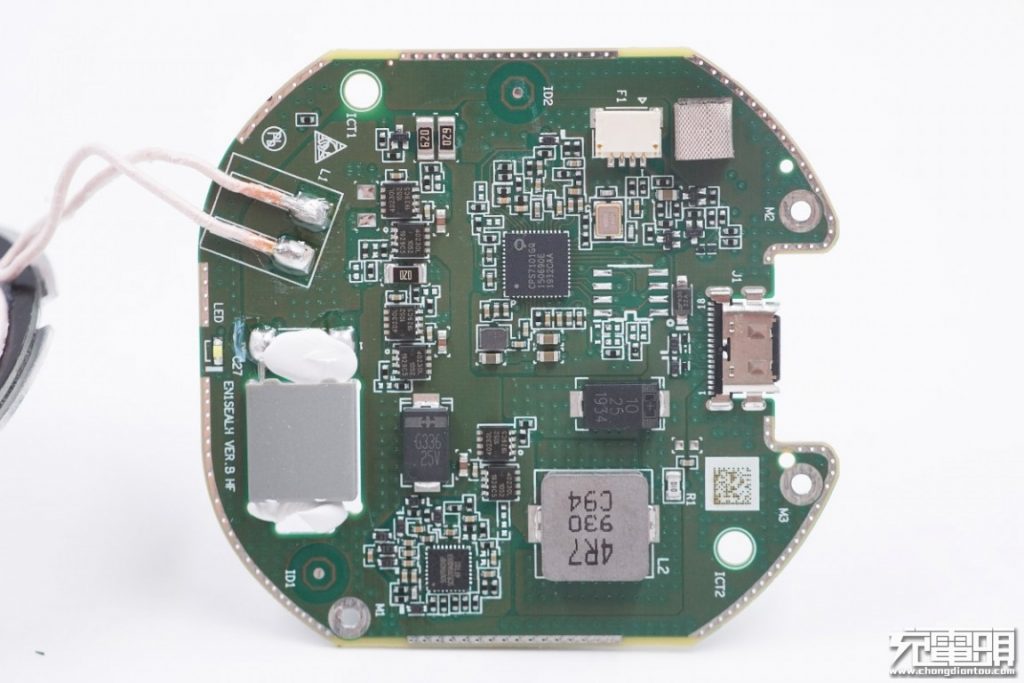

The front side of the PCB has two large tantalum capacitors (the two with a cross logo), an alloy inductor for boost and two controller chips.
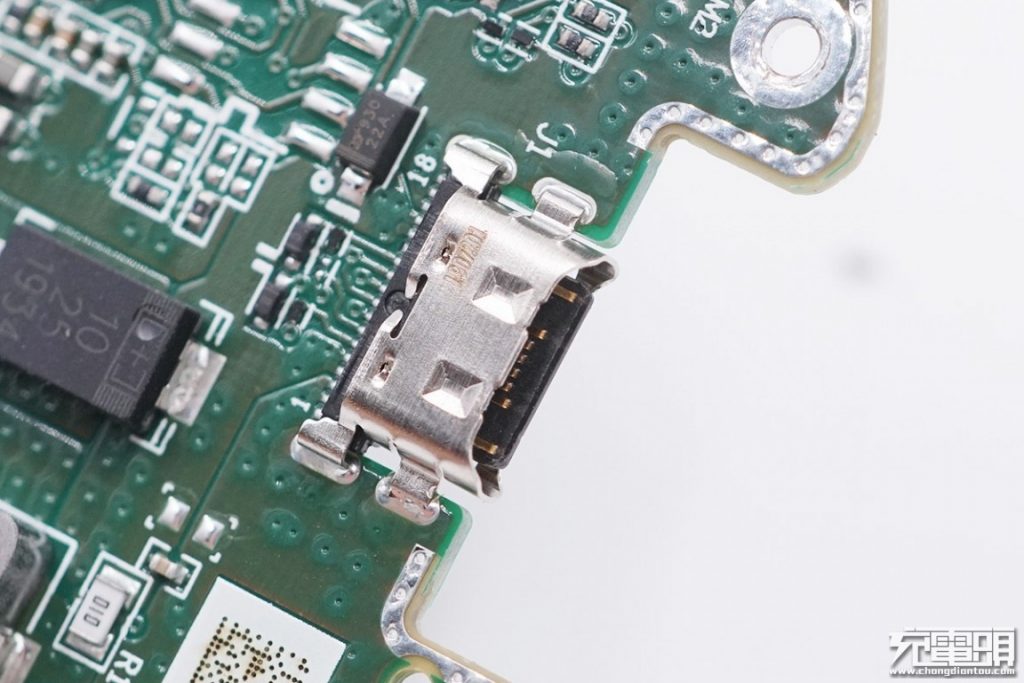

Input USB Type-C socket. Behind the socket is a TVS for input overvoltage protection. The data pins are also protected by TVS.
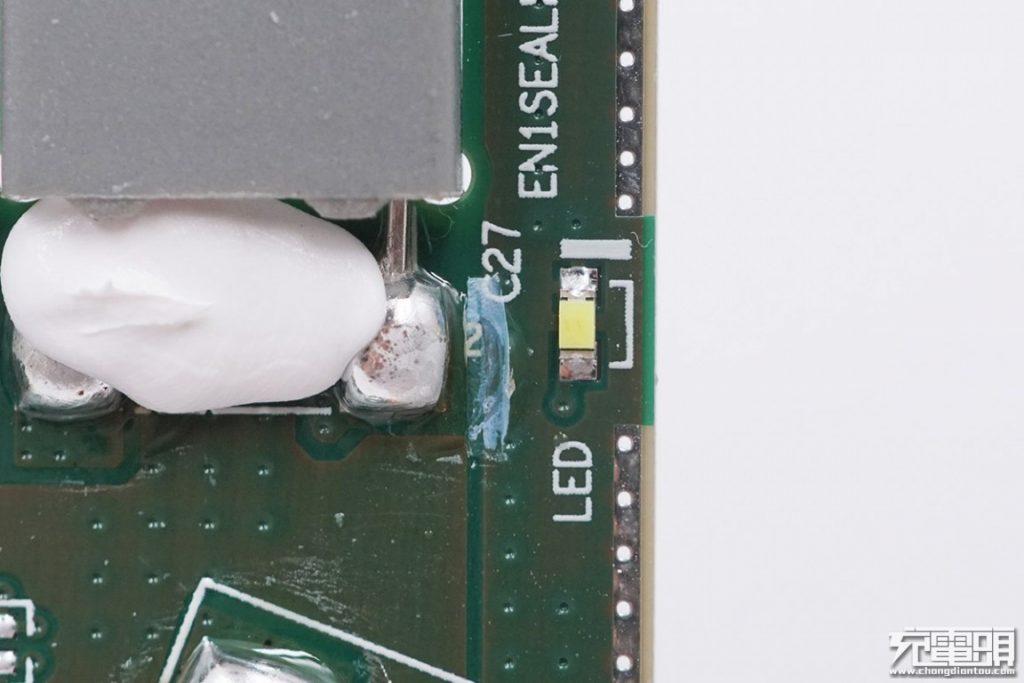

A white LED indicator on the side.
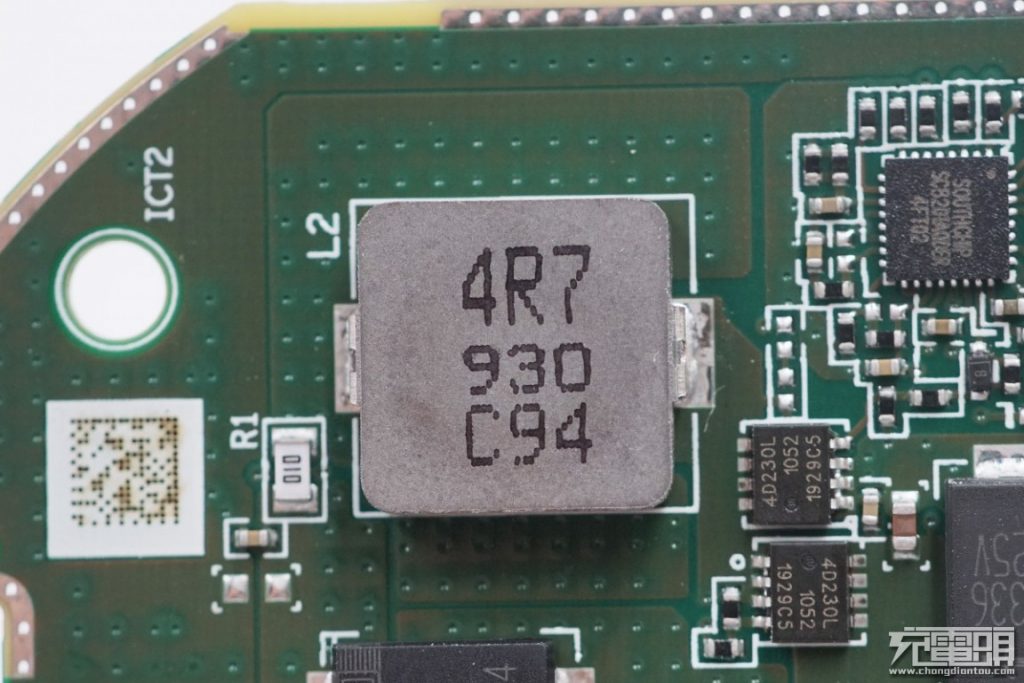
4R7 boost inductor. The white one with 010 marking in the lower left corner is the current sampling resistor.

10μF 25V tantalum capacitor for input filtering. Relatively premium stuff.
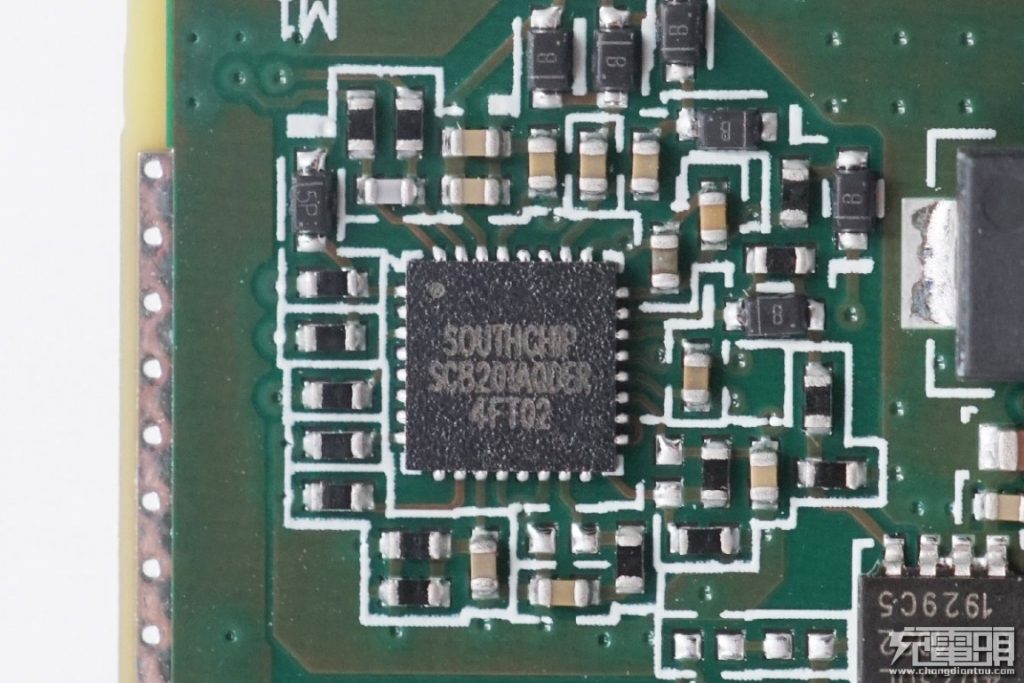
A Southchip SC8201A synchronous boost controller, which works with the main controller to adjust the voltage of wireless charging, and it has built-in MOS driver and multiple protection functions.
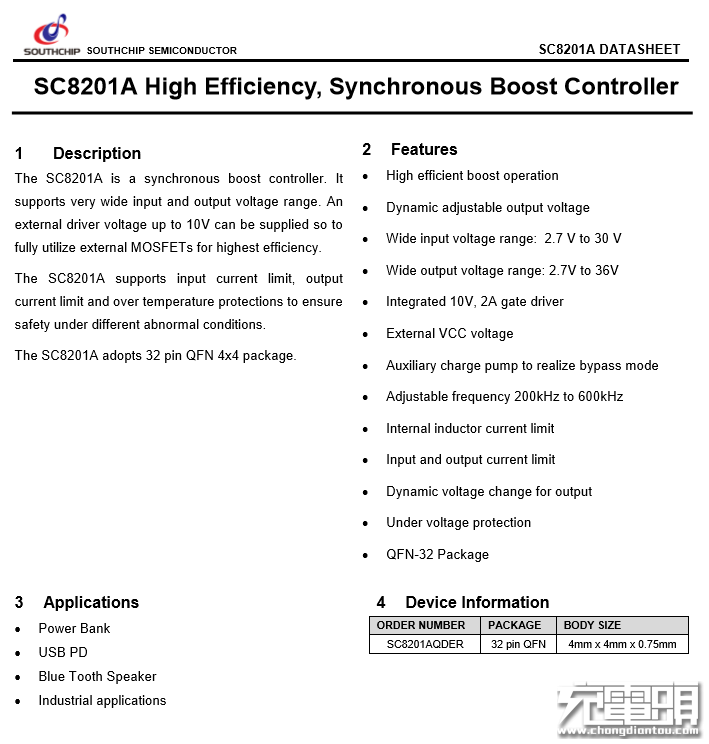
Detailed specifications of the Southchip SC8201A.
Nexperia PSMN4R2-30MLD, NMOS, two of them for synchronous rectification boost.

Detailed specifications of the Nexperia PSMN4R2-30MLD.
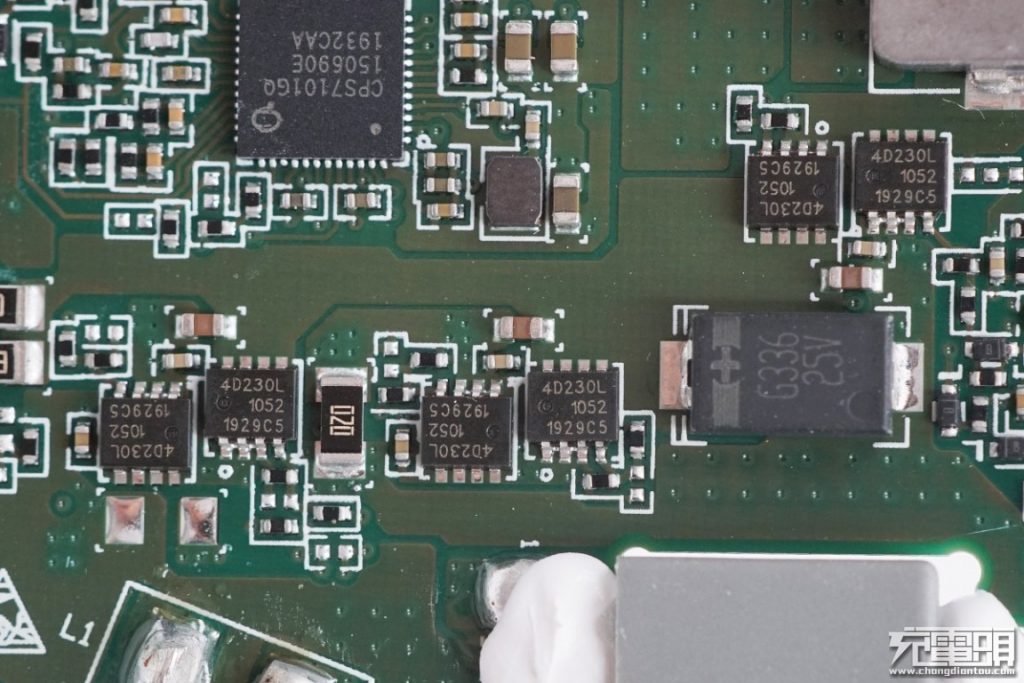
The wireless charging part also uses four PSMN4R2-30MLDs to form an H-bridge to drive the wireless charging coil.
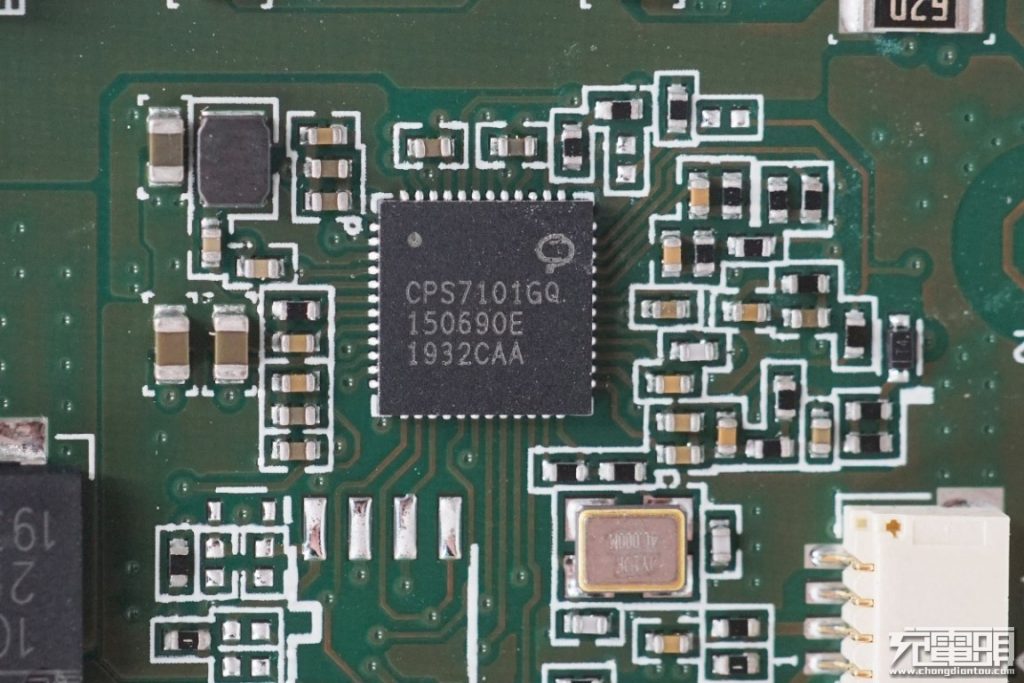
The CPS7101 is a highly efficient, Qi-compliant, magnetic inductive wireless power transmitter SoC. The system-on-chip integrates power controller, micro-controller, voltage regulator, foreign object detection (FOD), full bridge drivers and on-chip voltage and current demodulation. The chip is designed for wide input voltage range of 4.5V to 26V.
The CPS7101 integrates one full bridge driver and 2 PWM modules. Internal protection functions are provided for over current and over temperature.
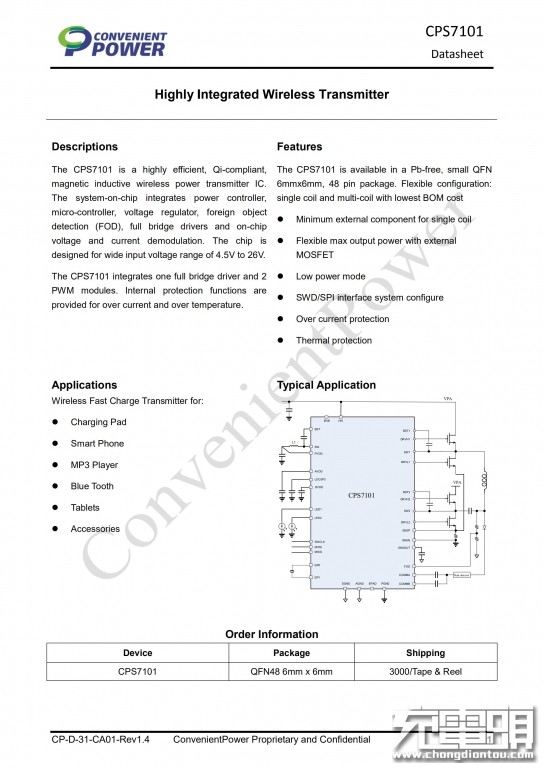
Detailed specifications of the CPS7101.
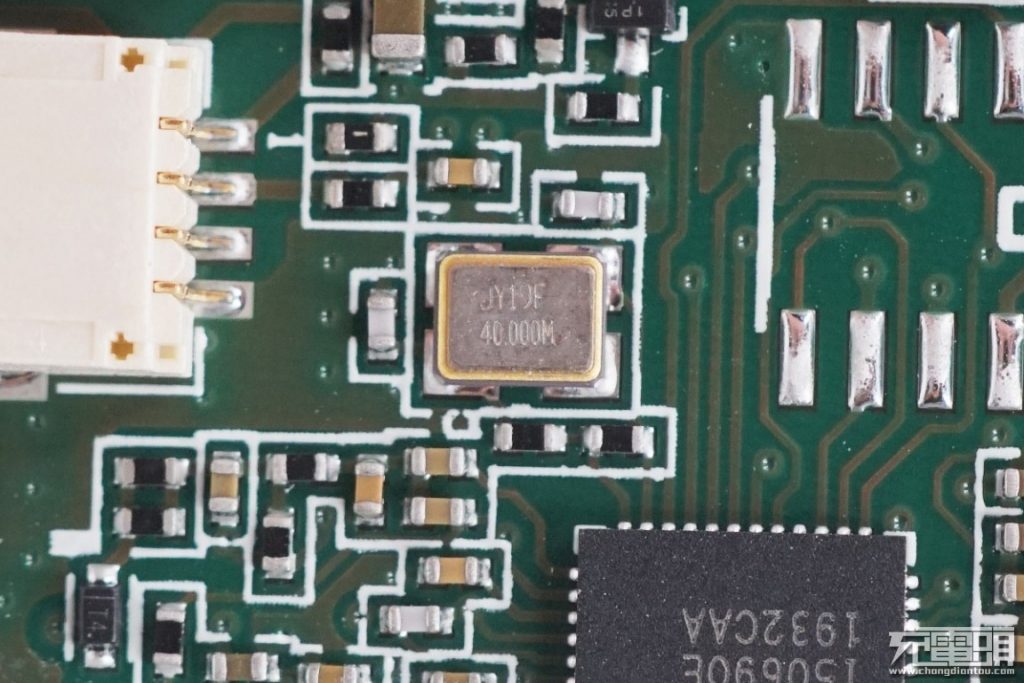

A 40.000MHz passive crystal oscillator that provides clocks for the CPS7101.
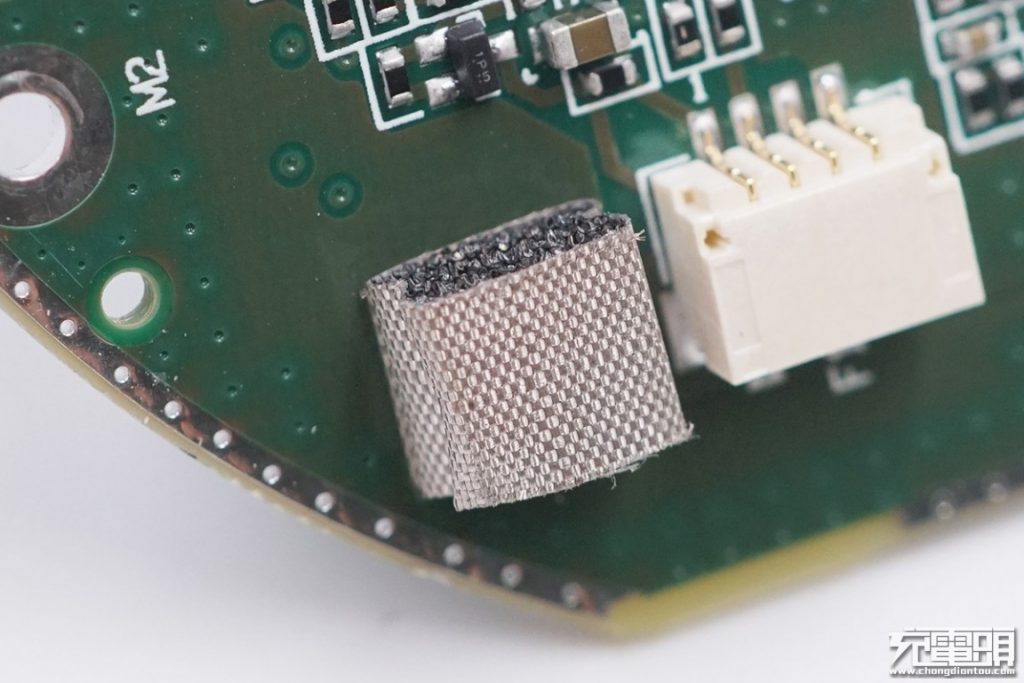
A conductive cloth for shielding and grounding.
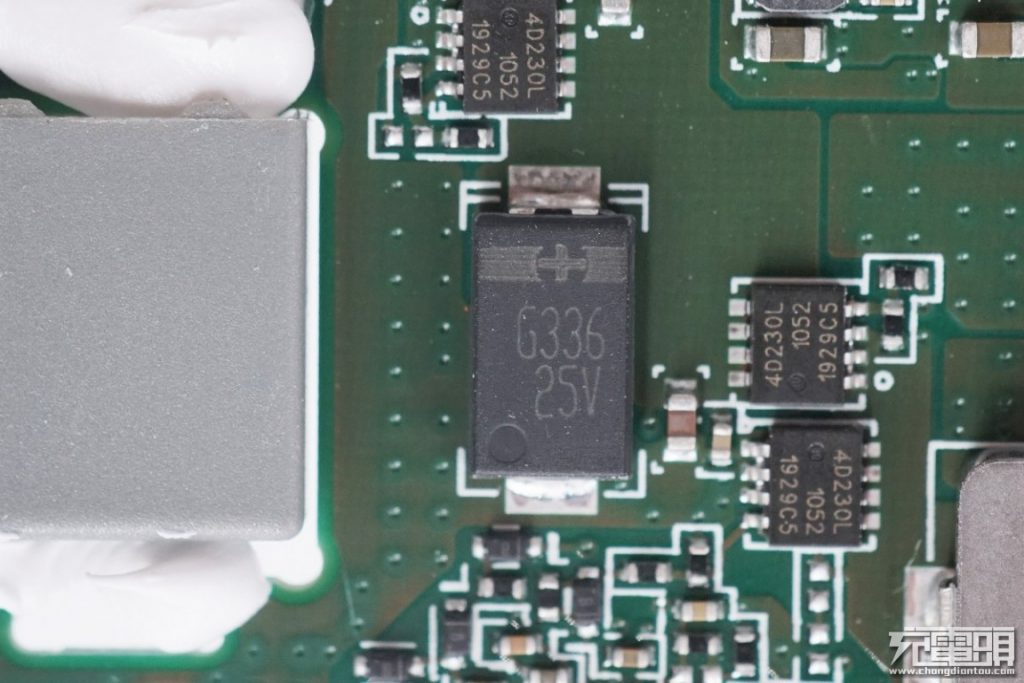
A 33μF 25V tantalum capacitor for synchronous rectified buck output.
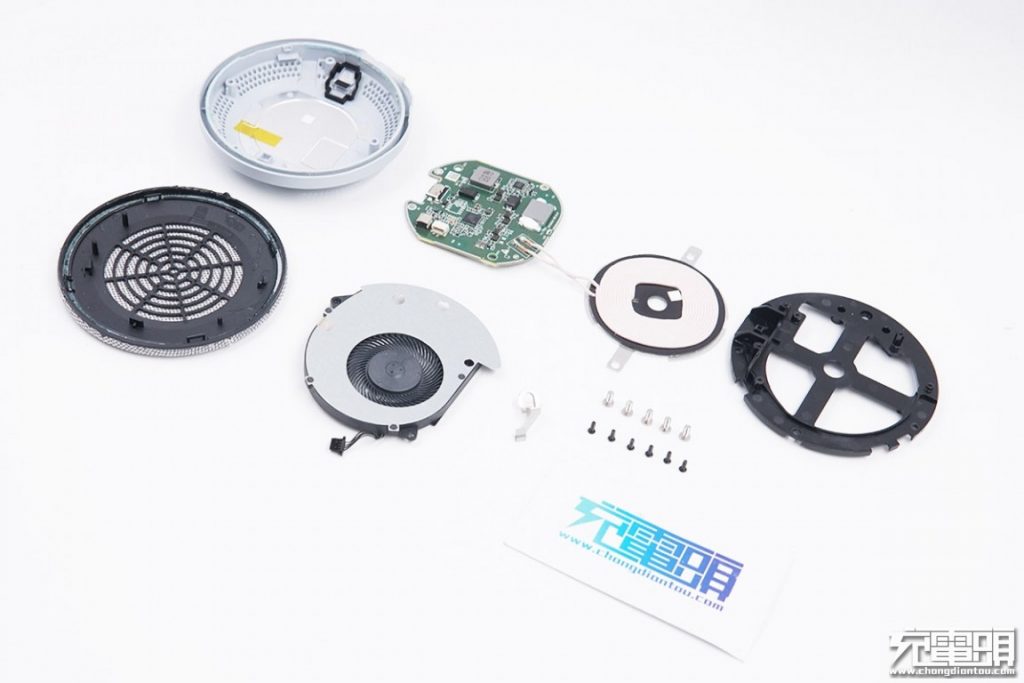

All the components.
III Conclusion
The Huawei 27W SuperCharge Wireless Charger (CP61) marks a new beginning for wireless charging.
We have had 5W/7.5W/10W wireless charging for quite some time now, which are perfectly fine for casual or overnight charging. But 27W wireless charging is a game changer.
With a speed faster than 18W wired PD/QC charging (which is the mainstream and the max charging speed for latest iPhones), wireless charging is becoming a practical and powerful solution not just for those who want to charge wirelessly, but also quickly. The era of high-wattage wireless charging is here.
In terms of internals, the Huawei 27W wireless charger continues the brand's neat fit and finish, with thoughtful design and layout, and high quality components to ensure performance and longevity of the unit. It has a unique internal design with a built-in centrifugal fan, which draws air through the fabric cover to take away the heat. On the PCBA side of things. A Southchip synchronous buck controller is used for boosting, working with a CPS SoC as the main controller. Nexperia's MOS tubes are used for high-voltage output, with the charge pump step-down inside the phone to achieve high-wattage wireless charging.
The Huawei 27W wireless charger also marks the first time, that CPS and Southchip, two companies from China, entering the supplying chain of Huawei with solid and reliable performance of their chips.
Pros:
27W wireless charging.
Thoughful design and high quality components.
Reasonably priced (199RMB/28USD in China).
Cons:
27W wireless charging requires a Huawei 40W SCP charger.
Source: chongdiantou









