Introduction
At ChargerLAB, we tested many devices every day, including mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and game consoles, and most of them adopt a USB-C connector. Moreover, the iPhone is about to switch from Lightning to USB-C. I believe it'll become the most common connector in our daily life in the future. But wait, what exactly is USB-C? Today, let's dive in and find out more about USB-C.
Back in 1994, Intel and Microsoft initiated the "USB-IF". It developed a set of specifications and transmission procedures for Universal Serial Bus. That's USB. They also made the standard physical interface based on the specification. So, the evolution process of the physical USB interface is always closely related to USB specification.

But, we need to clarify that the USB-C is a physical interface, emphasizing the shape of the interface, and the USB 2.0, 3.0, USB4 are different specifications of USB standard, emphasizing the transmission speed.
Types
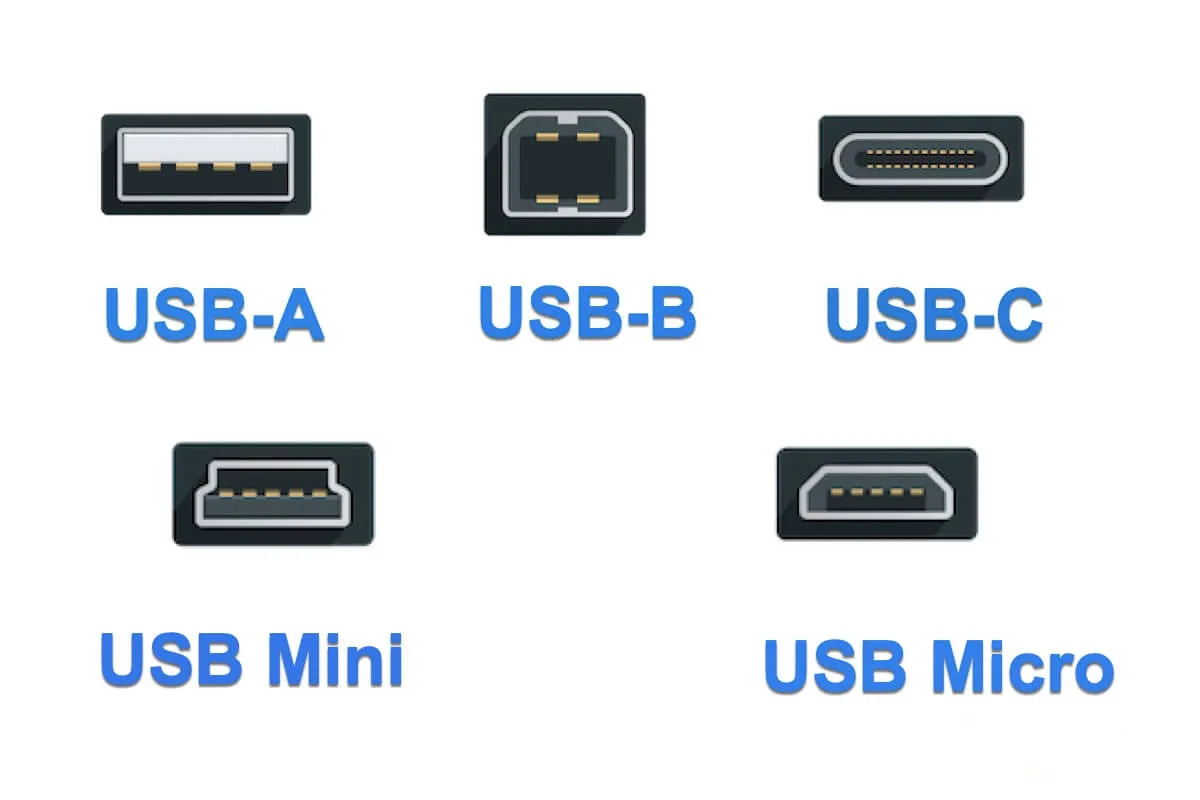

Firstly, let's talk about the physical interface of USB-C. From the name of USB Type-C, we know that there must be USB Type-B and USB Type-A. And we made a video before to talk about what is USB-B, you can click here check that out. As for USB-A, this is the most common interface in our daily life. Additionall, the A and B types have different sizes: Standard, Mini, and Micro. The standard size is the largest and is mainly used for desktop and larger peripheral equipment.

Next is the USB-C, the USB4 specification designates USB-C as the sole designated port, and this has been consistently maintained through the latest USB4 2.0 version. Compared with USB-A and USB-B, the biggest difference of USB-C is that the number of internal pins is greatly increased.
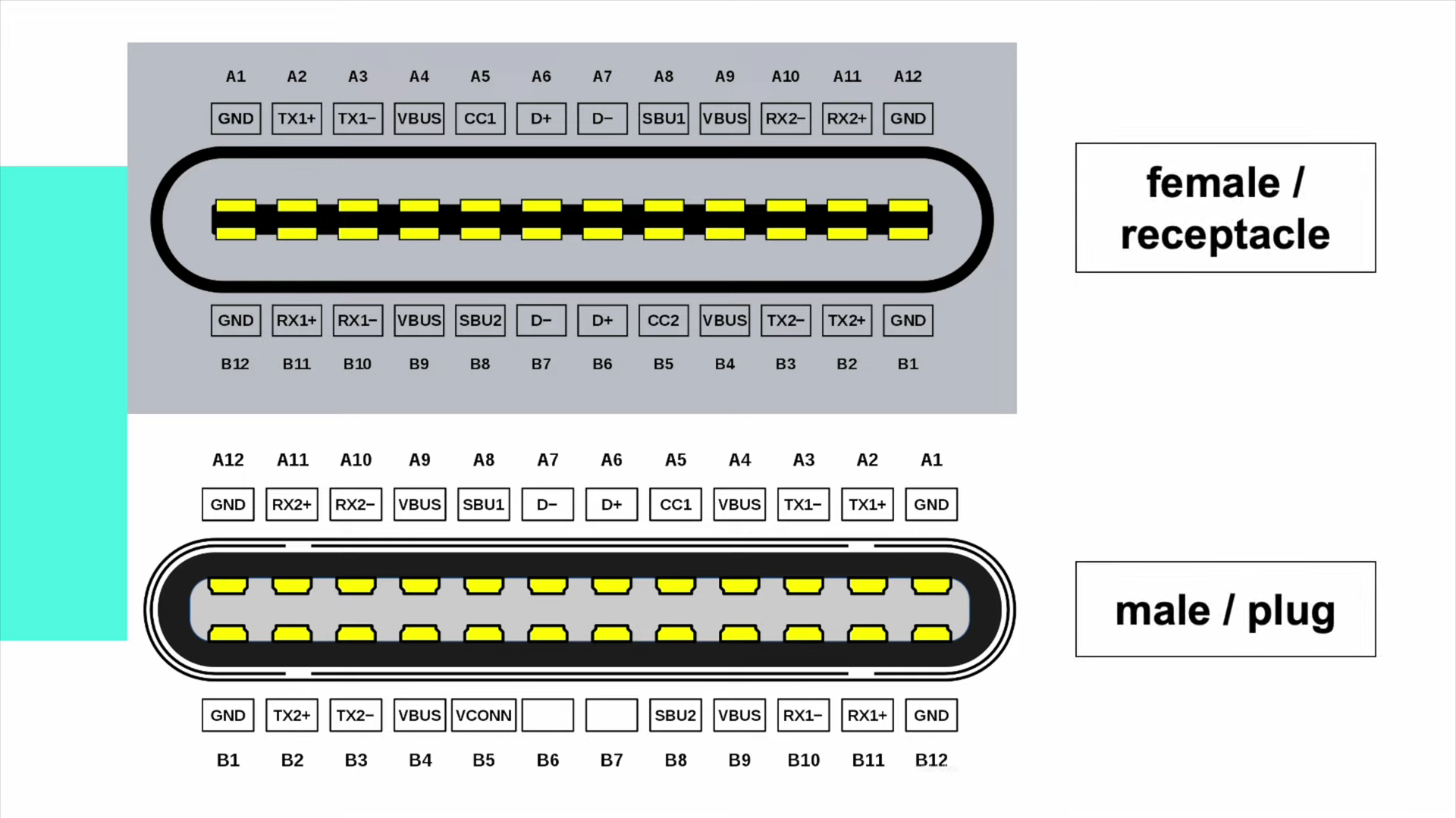
For standard USB-C connector, it has 24 pins in total. 12 pins in each row, and it can be divided into male and female, or plug and receptacle. Since the internal pins of the USB-C connector are center-symmetrical. It doesn't matter if it's plugged directly or reversed, those pins can be matched and work normally. That's another critical feature that differs from USB-A and USB-B.
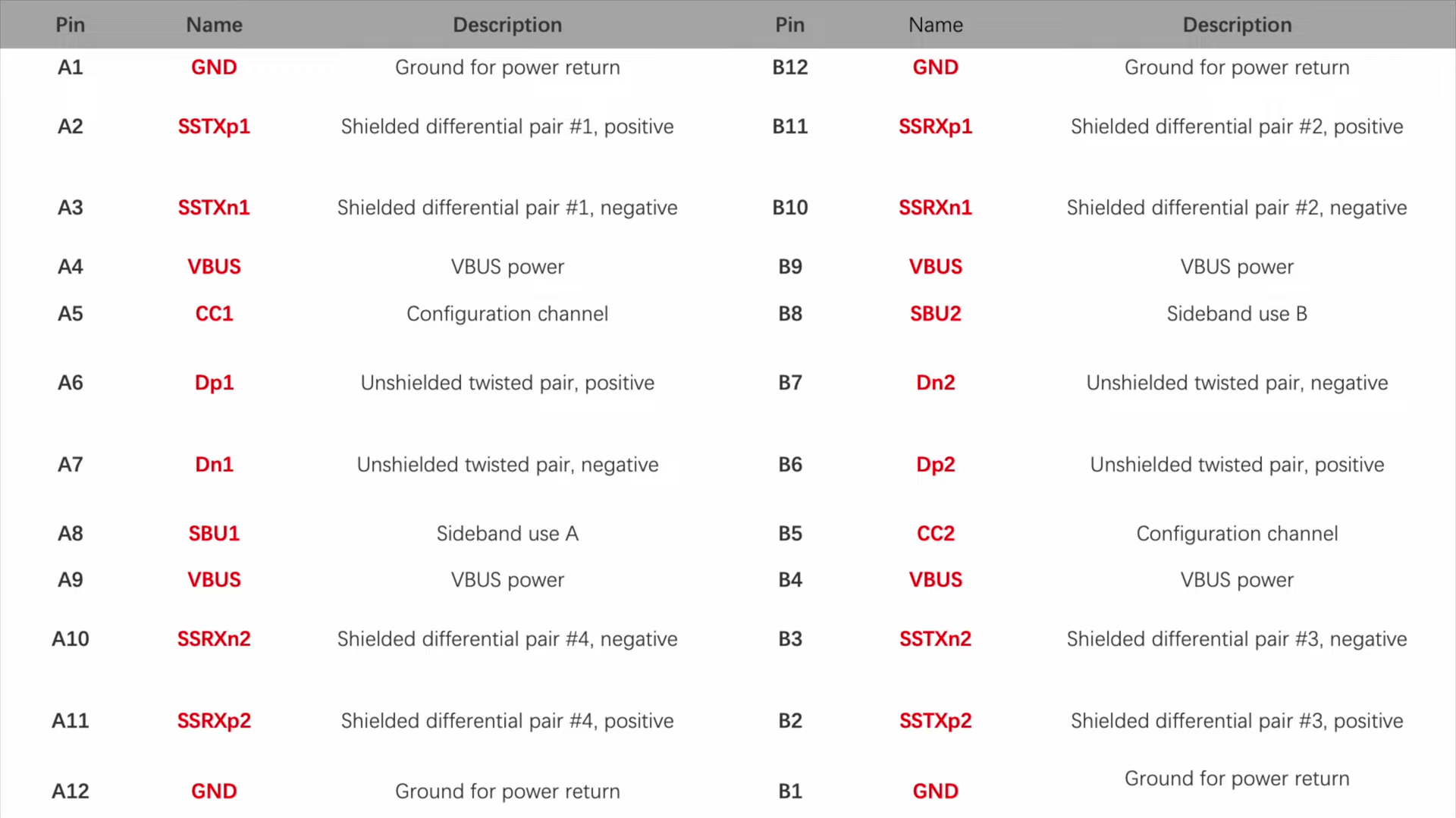
Different features require different pins inside the USB-C connector, which are drawn from the internal circuit. Only the full-pin, aka full-featured USB-C cable can support fast charging, video transmission, fast data transmission, etc.
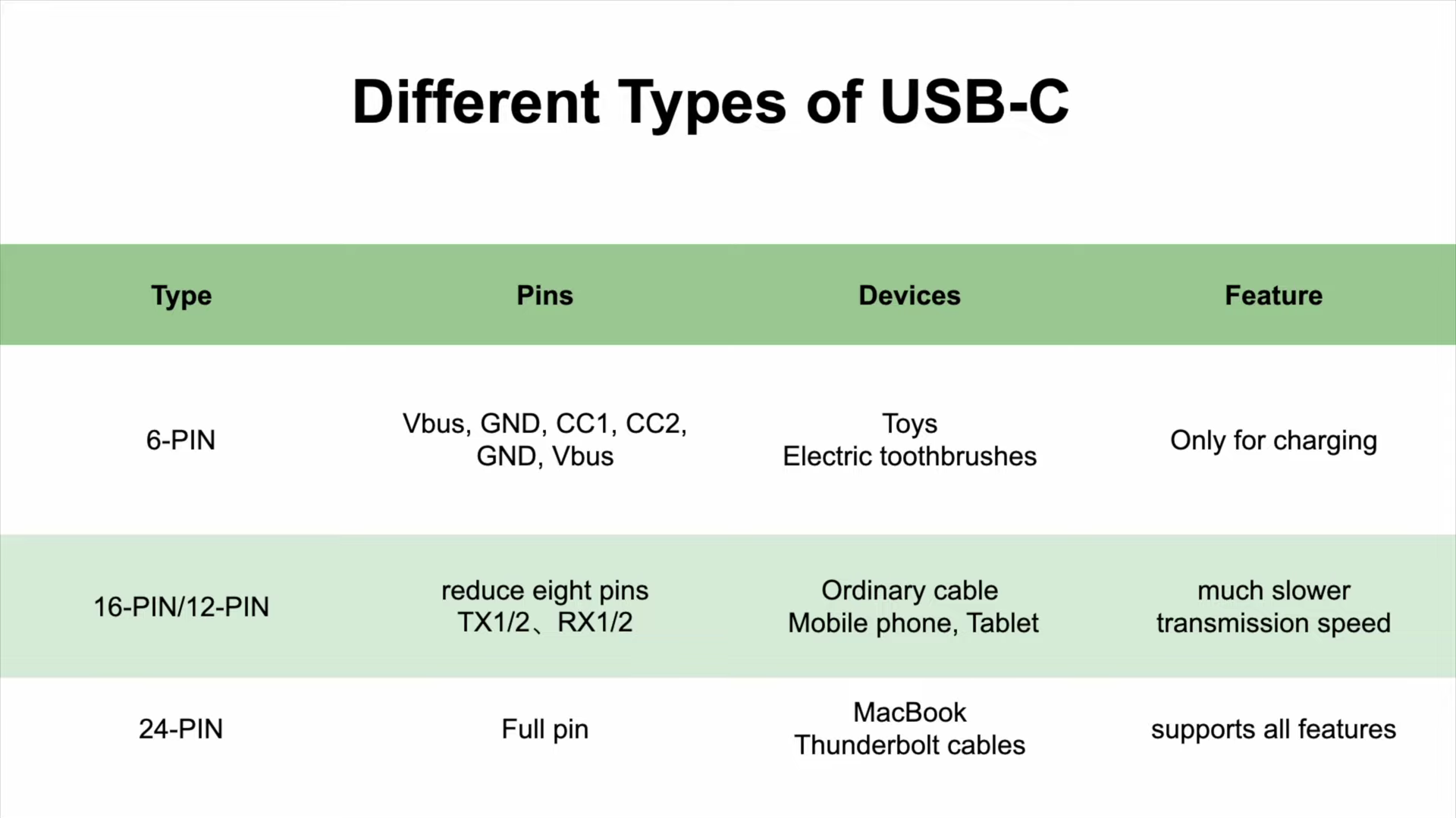
However, most of the USB-C connectors on the market are not equipped with 24 pins, manufacturers may reduce internal pins to reduce costs, some features will also be disabled. We found most USB-C connectors are equipped with 6-pin, 16-pin, or 24-pin.
Let's introduce them one by one.
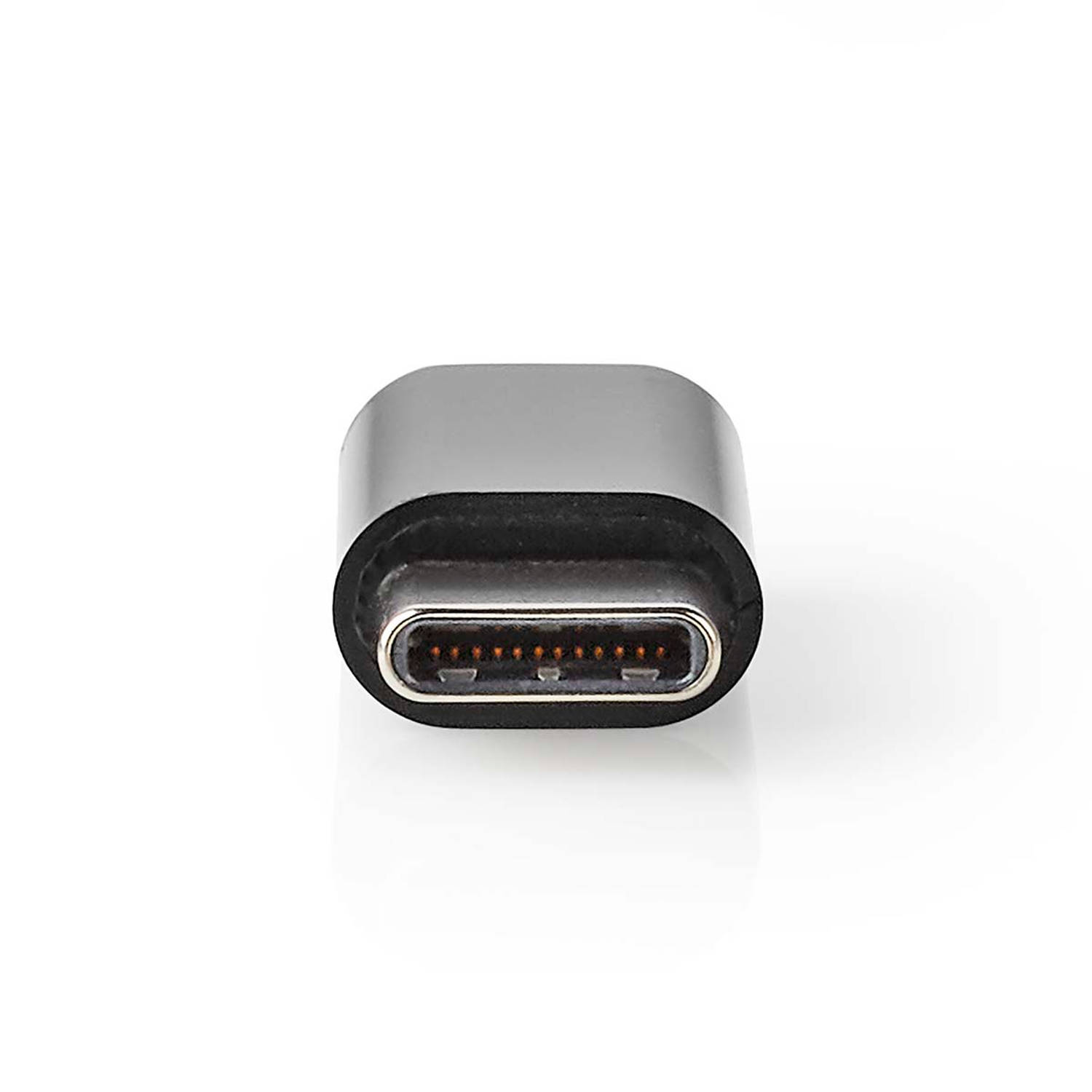

As mentioned, the 24-pin USB-C connector supports all features. We can find it in some high-end products, such as MacBook, Thunderbolt cables, etc.
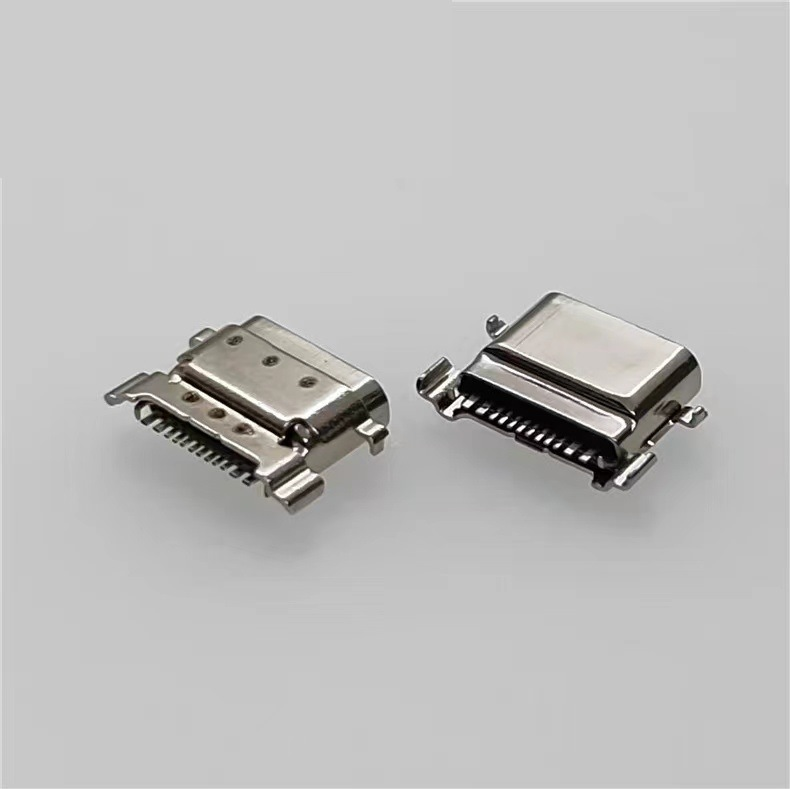

The 16-pin connector is the most common type of USB-C connector. Sometimes, two VBUS and two GND pins at both ends are soldered together. So, we also call it 12-pin USB-C connector. The transmission speed will be much slower, only for basic needs.
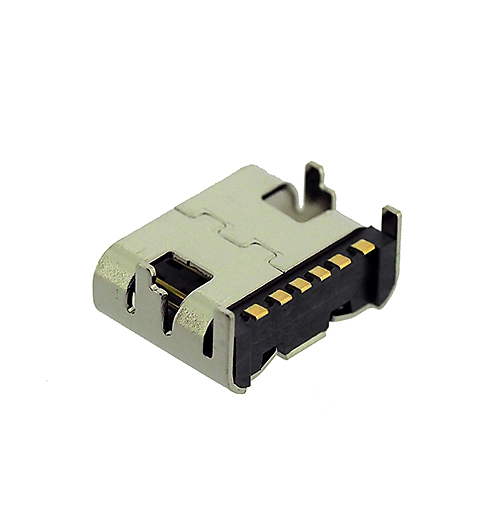

Then, the 6-pin connector is designed for charging and cannot be used for data transmission. Specifically, in comparison to the 24-pin design, it retains only SBU1/2, CC1/2, and a pair of USB 2.0 pins, D+ and D-. We can see it on toys, electric toothbrushes, etc, because they do not need to transfer data.
Roles
Additionally, the USB-C port is defined differently based on various roles.
From a power perspective, USB-C can function as either a power source (Source) or a power sink (Sink), or even as a dual role port (DRP). In terms of communication functionality, USB-C can be a downstream-facing port (DFP) or an upstream-facing port (UFP), or again, serve as a dual role port. Regarding functional roles, these are determined during connection based on the power role. As a power source, the default functional role is DFP, while as a power sink, it defaults to UFP.
Classified by data roles, USB-C can function as DFP, which corresponds to the previous host side, or as UFP, representing the upstream interface.
When classified by power roles, it can operate as a pure power source, supplying power to a sink, or function as a pure power sink. It can also assume the dual role of a DRP.
Features
After introducing different types of USB-C connectors, let's take a deeper look at what kind of features it can support.
Fast Charging
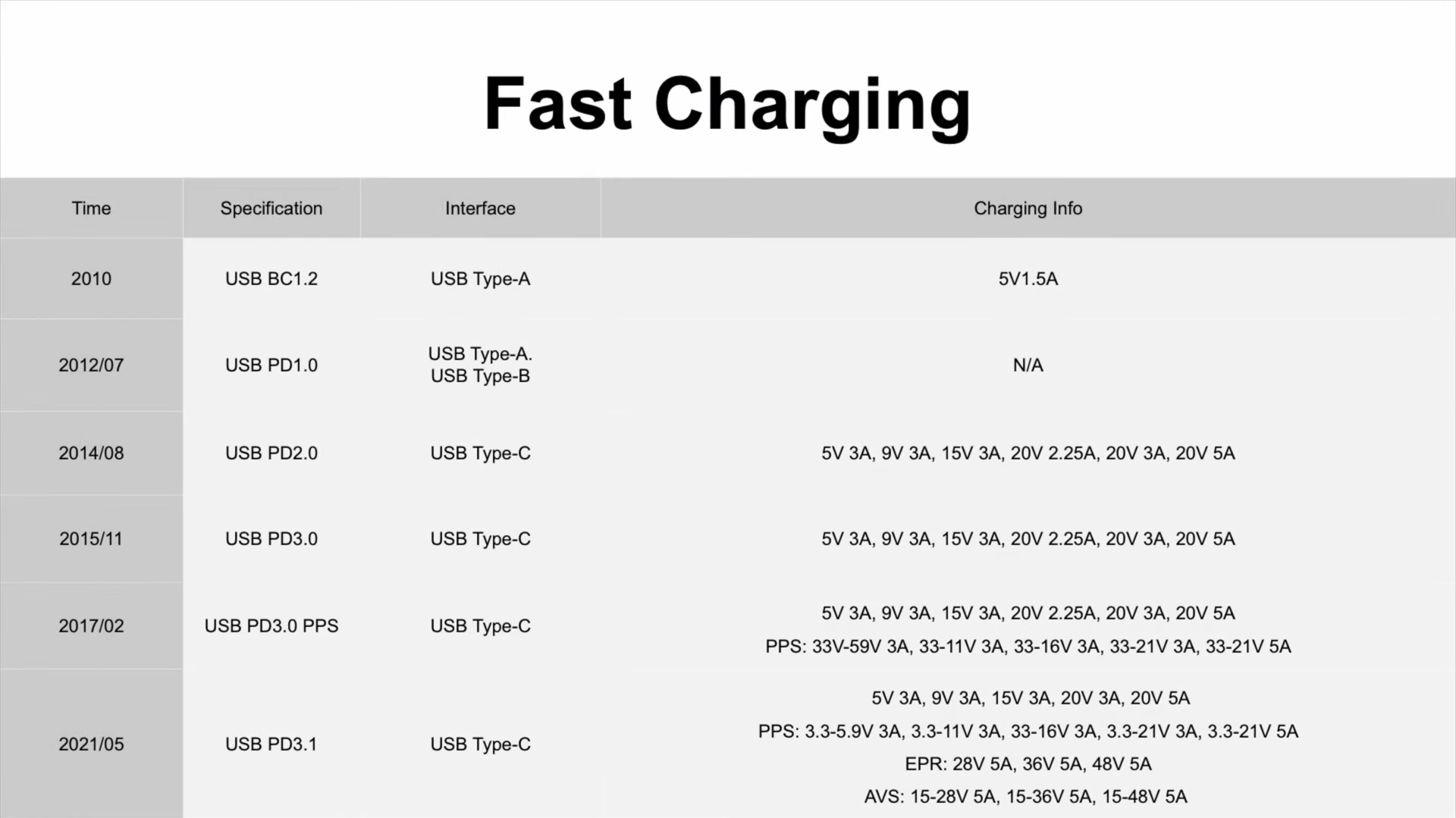
The most common fast charging protocol for now, the PD protocol is based on the USB-C. The PD2.0 is still very common in lots of GaN chargers we took apart, like Apple 20W. And PPS was added to PD3.0 in February 2017, your Samsung phone is using this protocol. Until now, the most powerful PD3.1 is also based on USB-C, which can deliver up to 240W charging power theoretically.
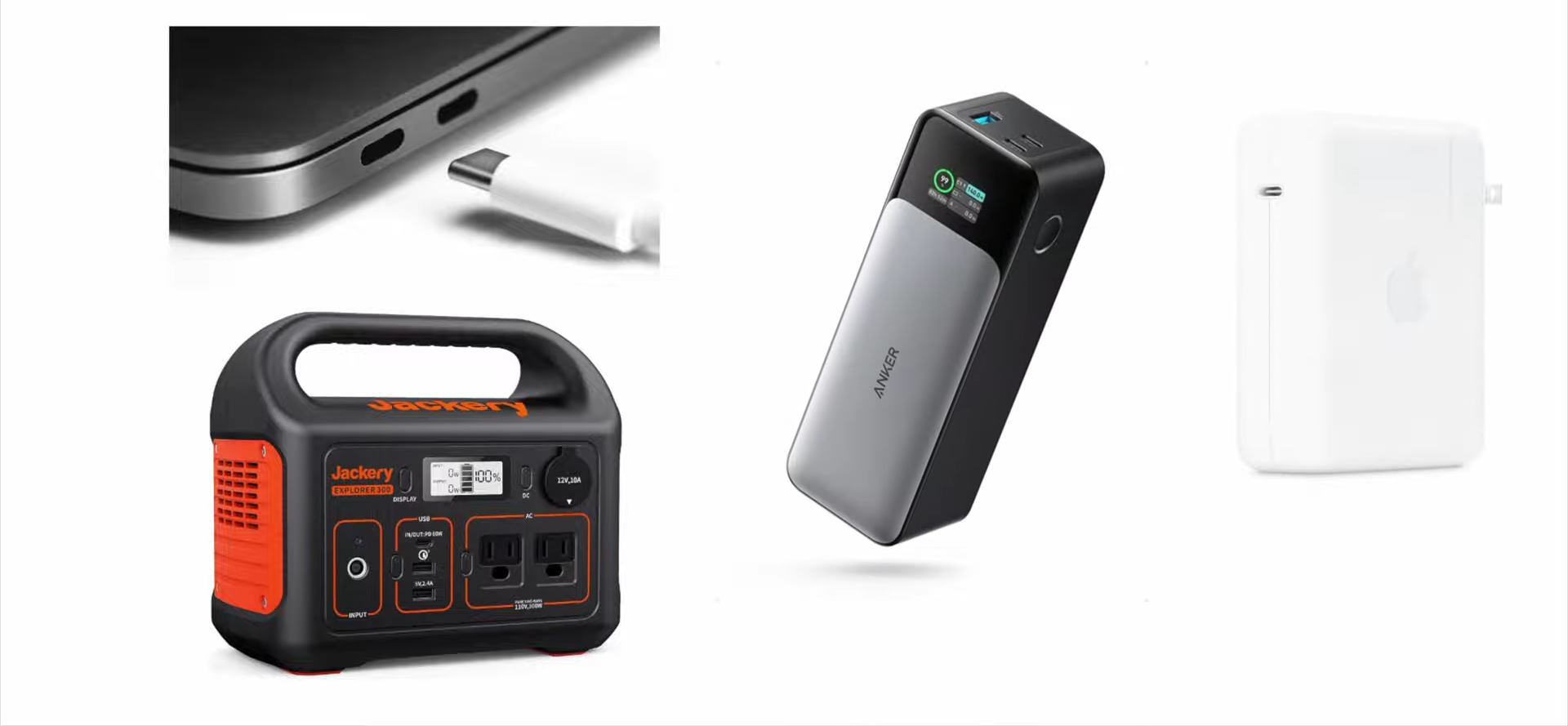

With such powerful performance, we can see USB-C in high-power laptops, fast chargers, and even outdoor power stations.
Data Transmission
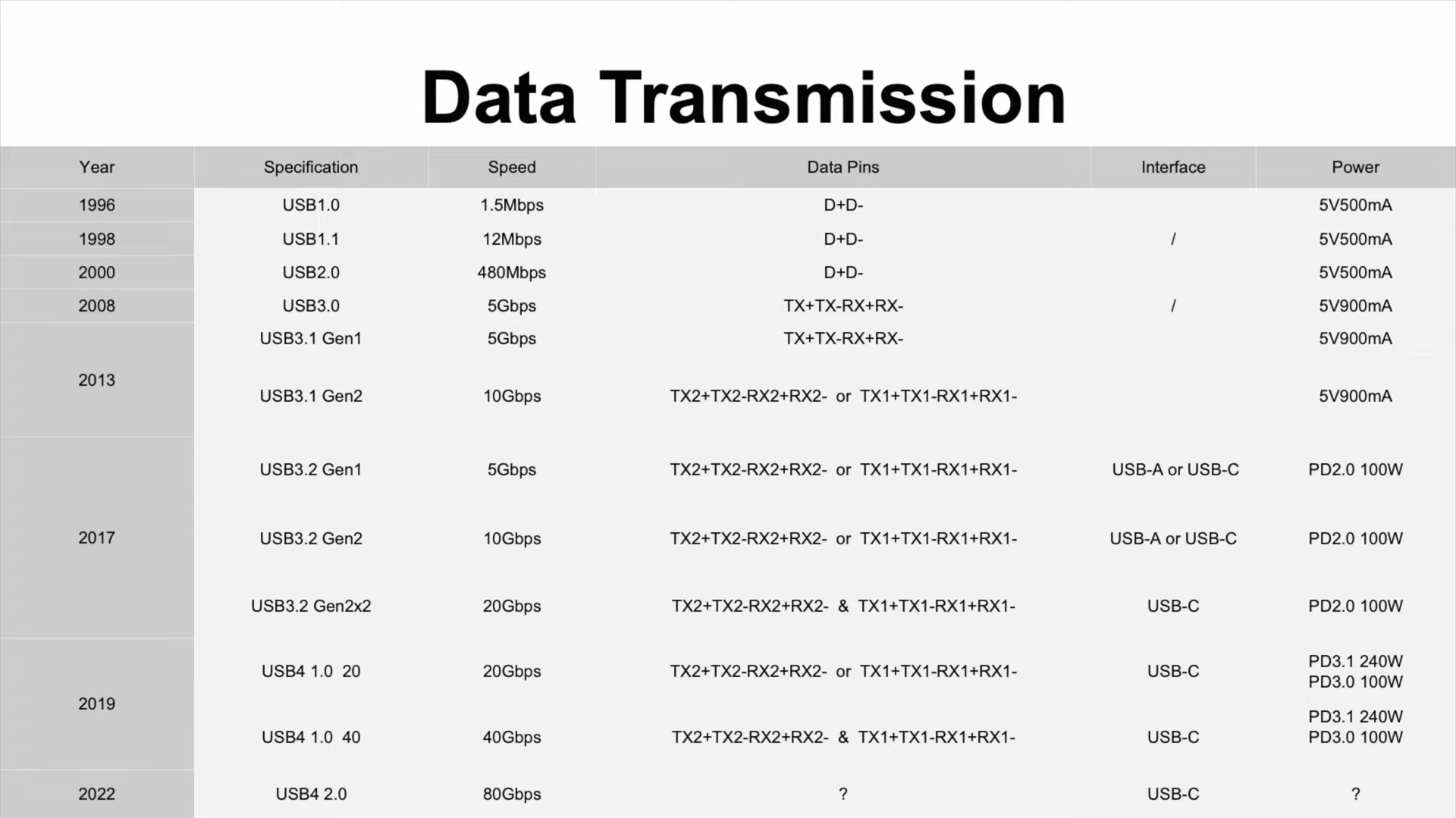
The second important feature is the data transmission. Before the release of USB-C, the data transfer speed of USB was relatively slow, but there're two pairs of high-speed differential signal channels inside the USB-C. With Thunderbolt 3 technology and USB-C, the transmission speed of USB is boosted to 40Gbps, and It will reach 80Gbps in the future.
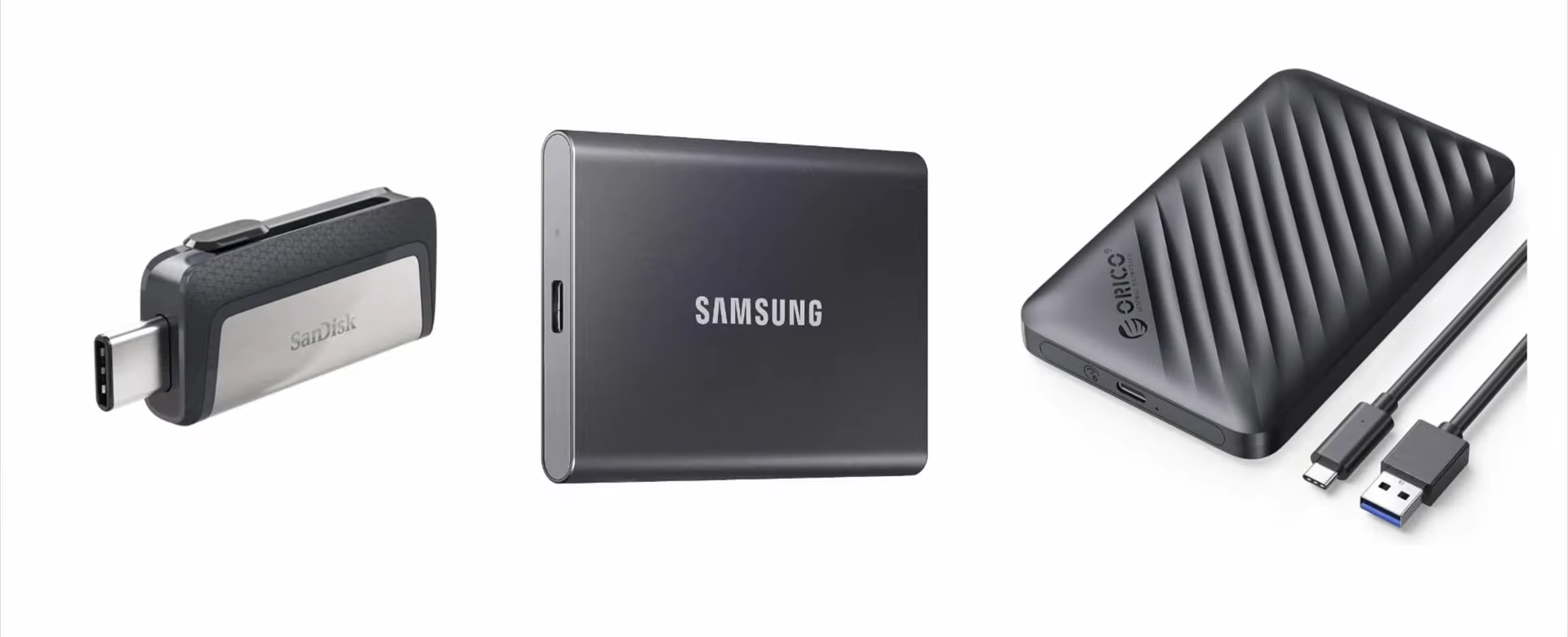

Some portable storage devices, such as USB flash drives, portable HDD, and SSD, now use USB-C.
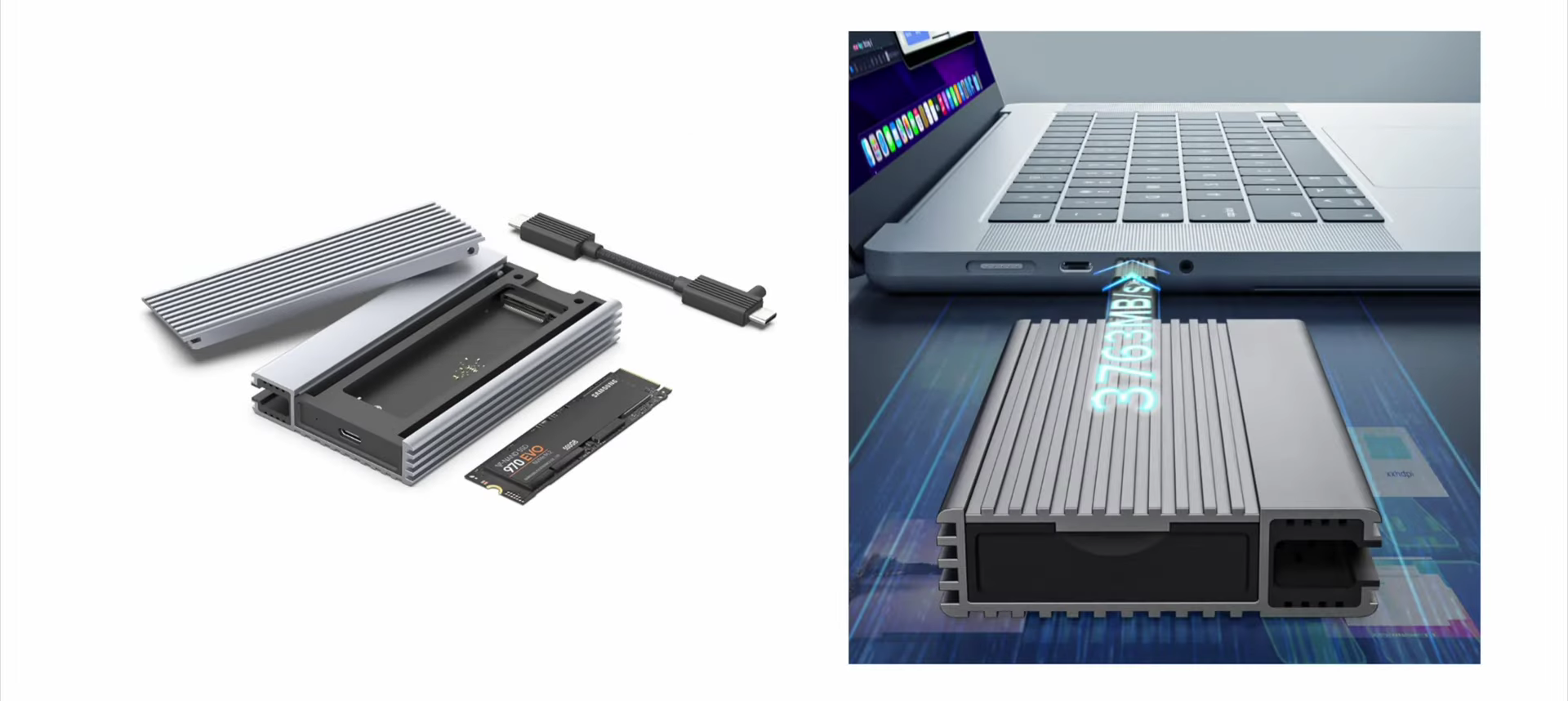

If you have an SSD enclosure that supports Thunderbolt 3/4, the transfer speed can even reach 3000MB/s.
Video Transmission
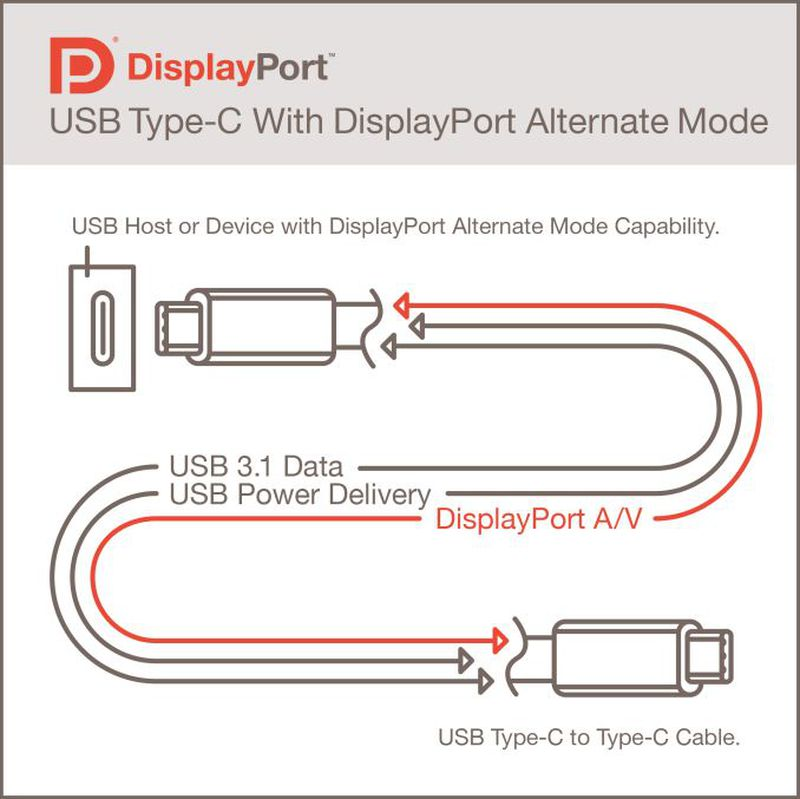
Another well-known feature of USB-C is video transmission. It can support up to 4K 60Hz.
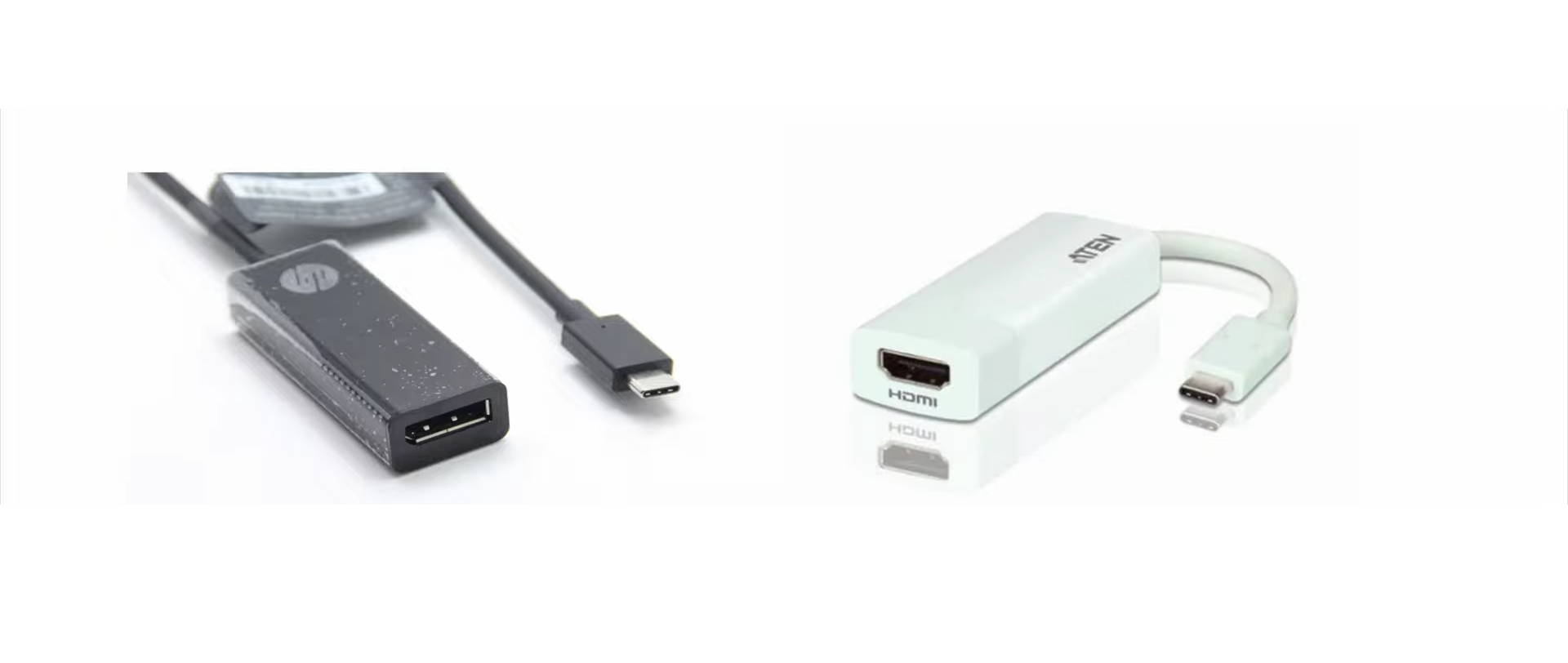

The method by which the USB-C port transmits video signals relies on switching to Alternative Modes to carry DP (DisplayPort) or HDMI signals. Currently, the highest supported protocols are DisplayPort 1.4 and HDMI 1.4.
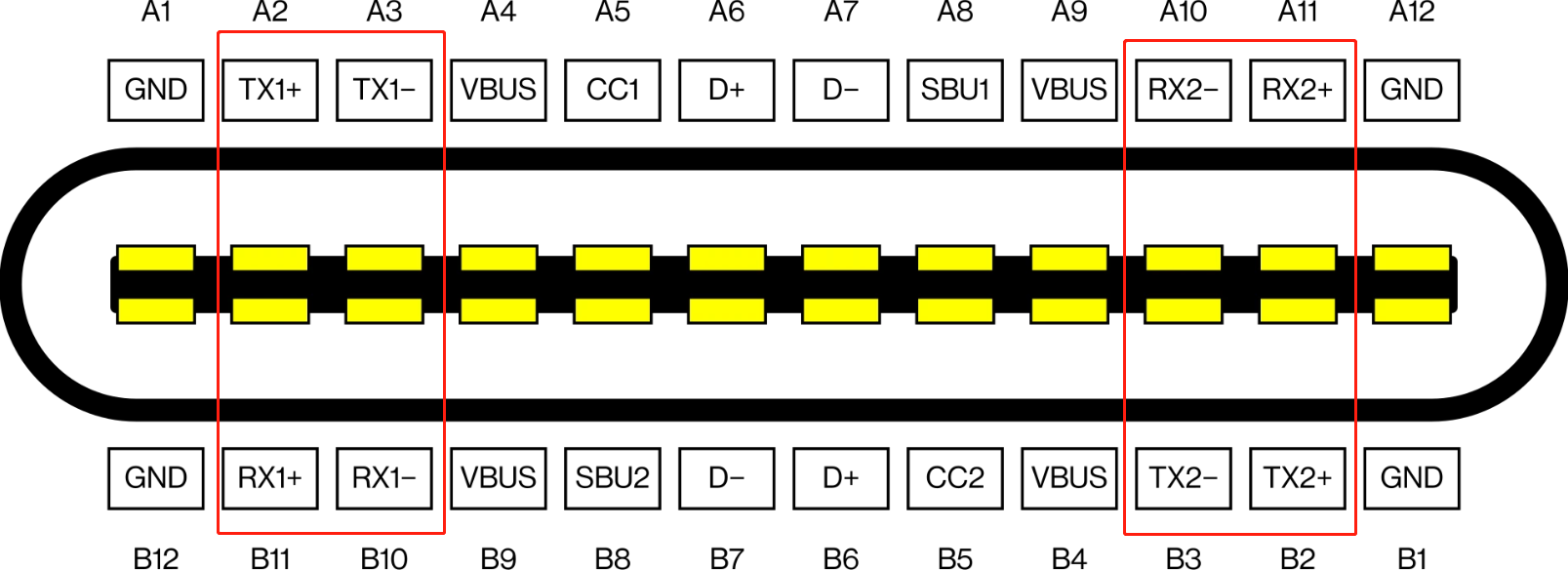
The underlying principle involves the TX1, TX2, RX1, and RX2 pins, corresponding to four pairs of differential signal transmission channels. In DP Alt-Mode, these four pairs of channels are utilized to transmit DP's four data channels.
When switched to HDMI Alt-Mode, these four pairs of differential signal transmission channels are repurposed for transmitting HDMI signals through its four data channels. However, due to its maximum support for HDMI 1.4b, in most cases, a converter chip is used to transform DP 1.4 into the more advanced HDMI 2.0 protocol, allowing support for 4K 60Hz displays.
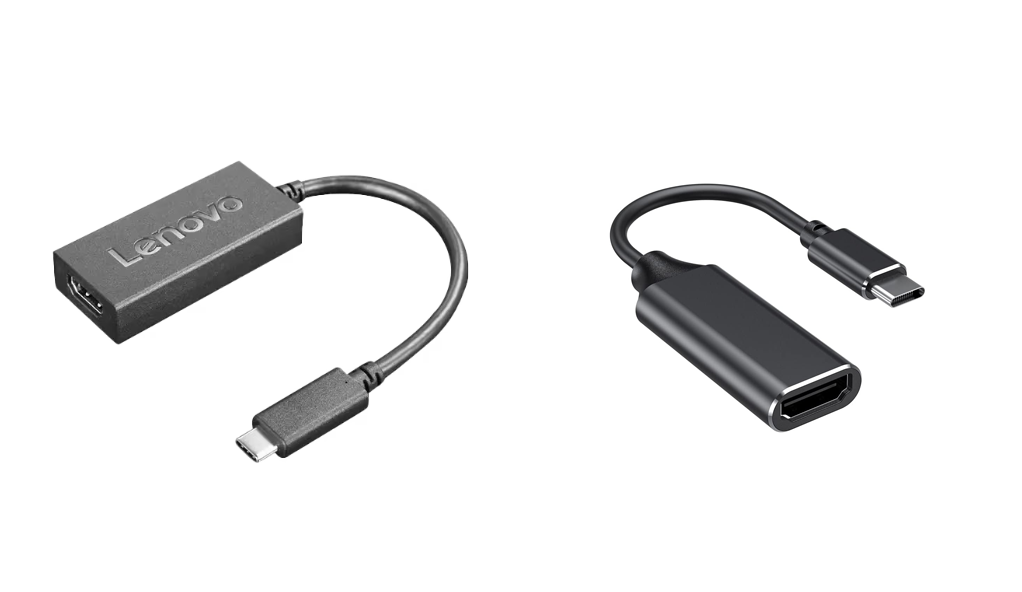

Many manufacturers nowadays prioritize aesthetic design and conserving the space occupied by peripheral ports in their products. Given USB-C's superior compatibility, it becomes the preferred choice for electronic device peripheral interfaces. Consequently, adapters that convert USB-C to DP or HDMI have become prevalent. Currently, these products typically support 4K 60Hz video signal output, fulfilling the basic requirements of the majority of users.
Audio Transmission
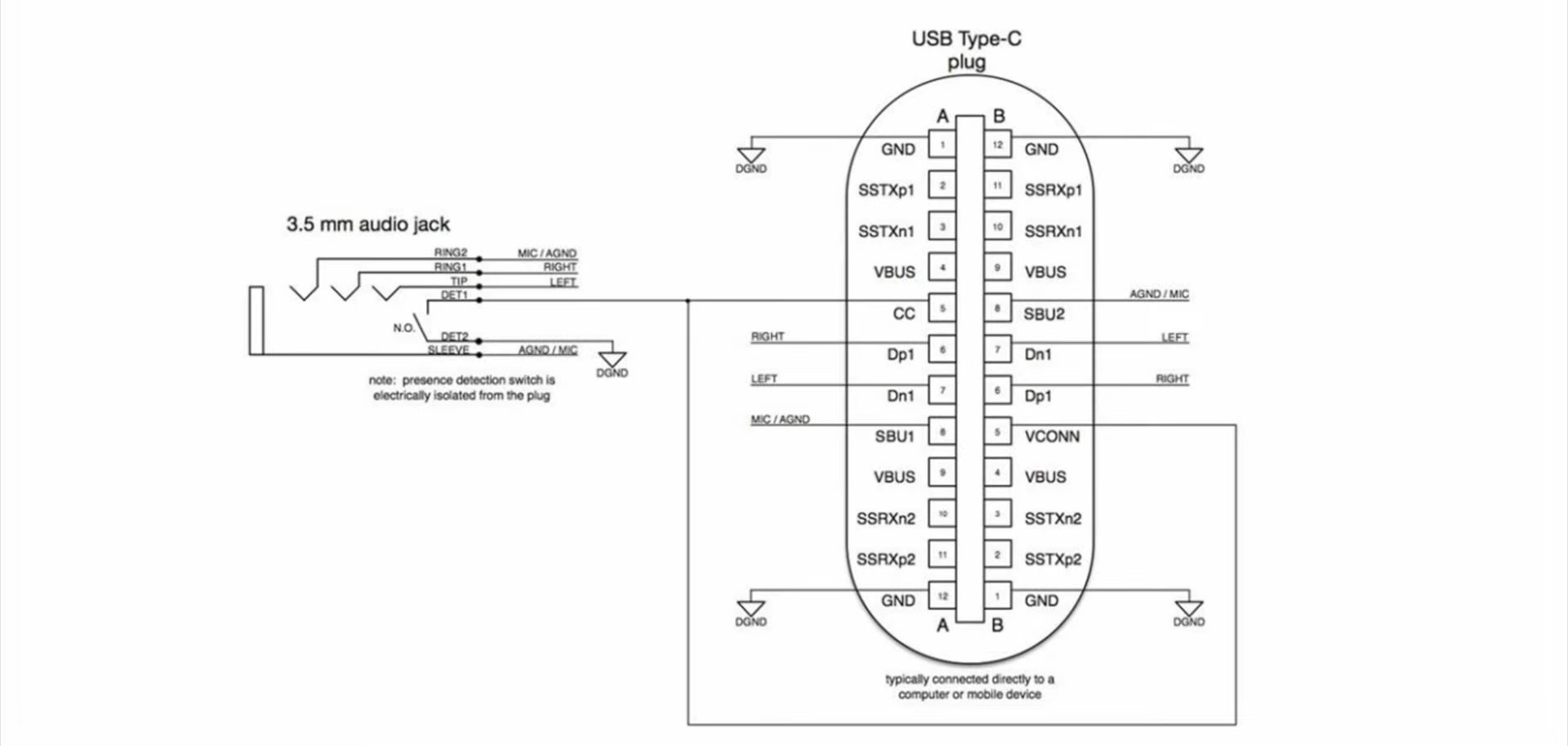
Another lesser-known feature is the audio transmission.
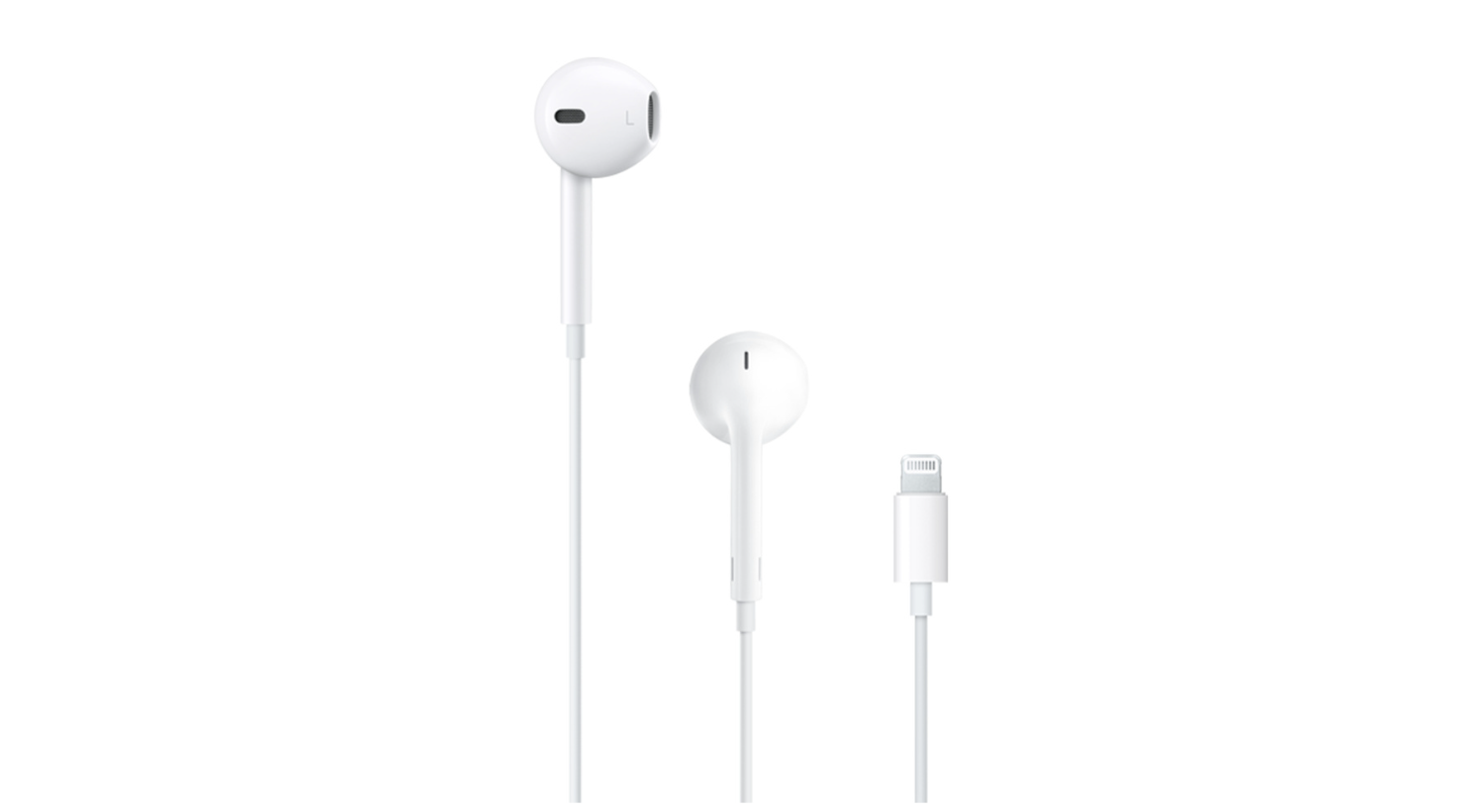

Since Apple canceled the 3.5mm headphone jack on the iPhone 7, it provided an alternative option inside the box, EarPods with Lightning connector.
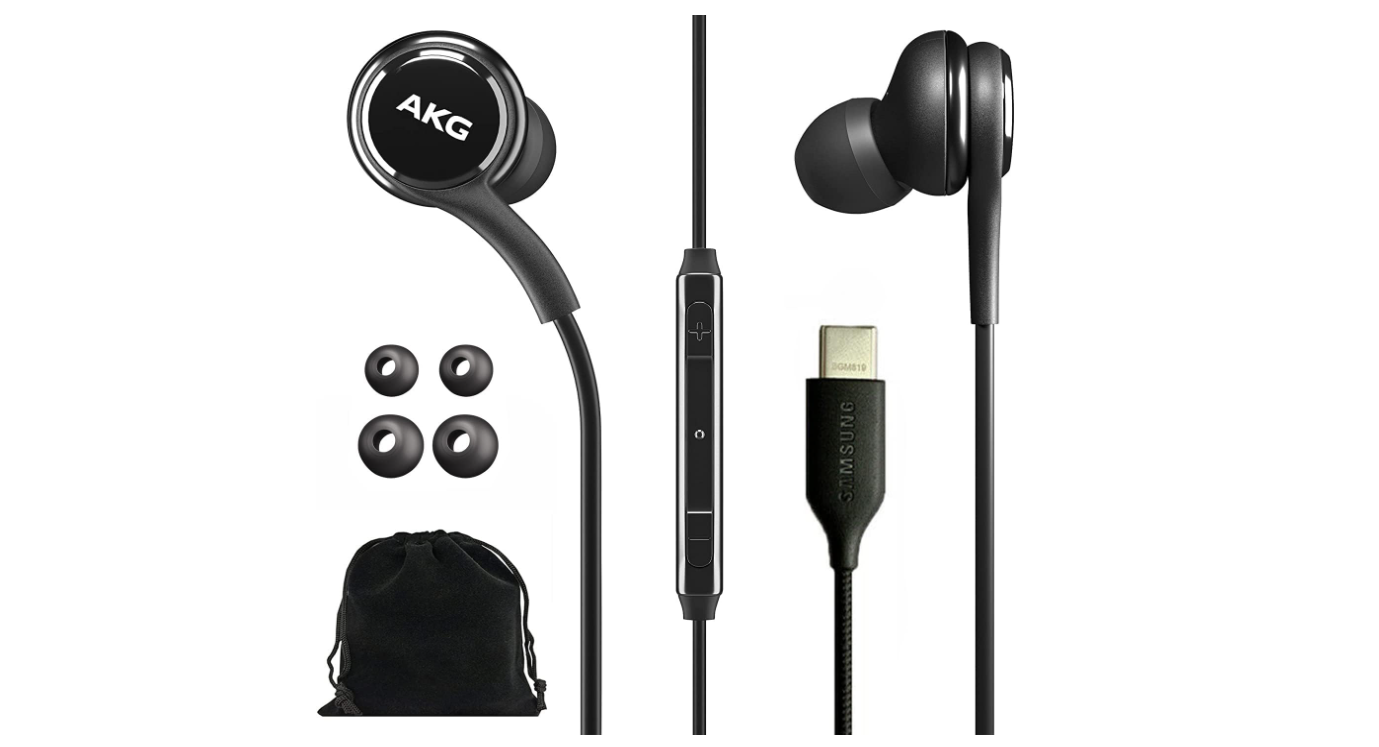

Subsequently, Android phones also canceled the 3.5mm jack and replaced it with earphones with USB-C connector.
This is mainly achieved through the USB-C port using PoE transmission (Power over Ethernet), which refers to a technology that transfers power over Ethernet cables. By leveraging the existing Ethernet infrastructure, PoE enables simultaneous data transmission and power supply to IP terminal devices (such as IP phones, access points, IP cameras, etc.) through the same network cable.

But now all kinds of Bluetooth earphones have replaced earphones with USB-C connector and become the most popular ones in our daily life.
The above are the main features of USB-C.
Q&A
Some people may wonder why some USB-A to USB-C cables can also support fast charging based on the PD protocol?
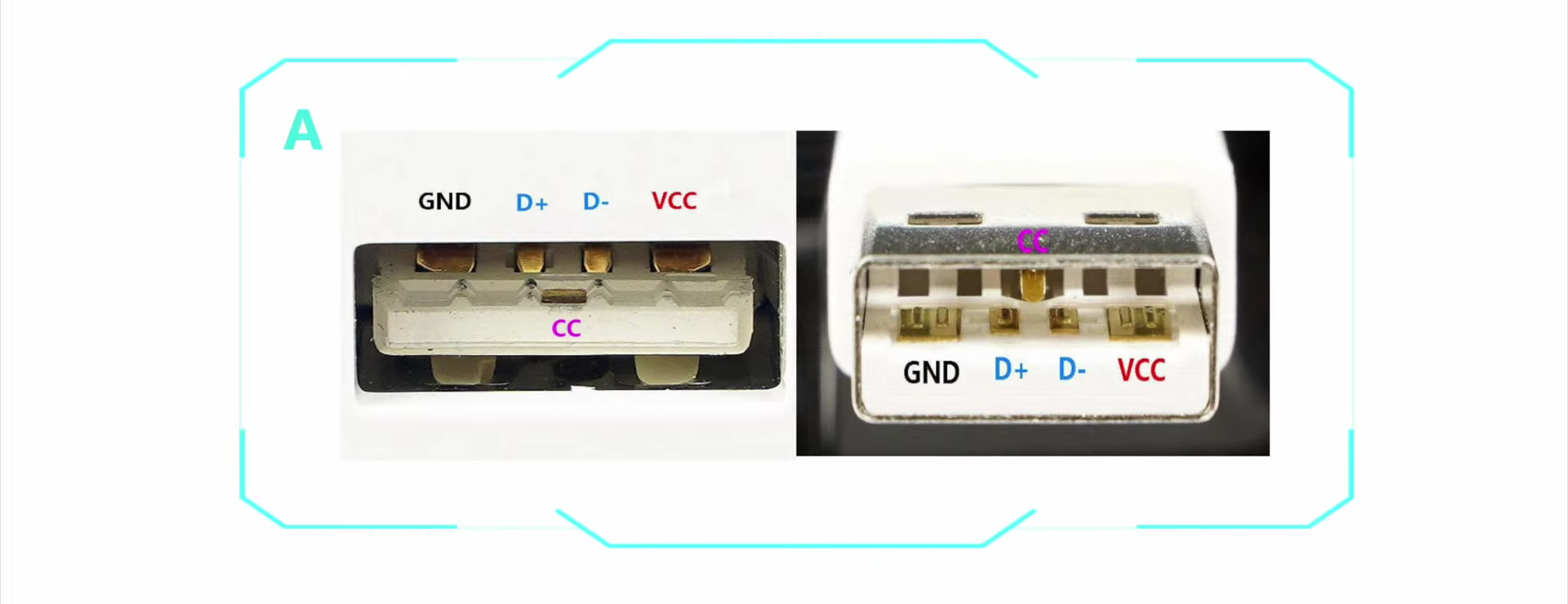
That's because some manufacturers, like Xiaomi, add a special pin inside the USB-A connector to achieve PD fast charging.
Secondly, as mentioned, different USB-C connectors support different charging power, so how do we know the specific supported power?

Users generally cannot know and need to use a tester, such as ChargerLAB POWER-Z KM003C to test.

However, the USB-IF has announced that new USB-C cables will add a certified power rating logo.
Summary of ChargerLAB
If you look around your electronic devices, more and more USB-C ports can be found. We believe in the future, USB-C will definitely replace USB-A and become the most common connector, but we can't say USB-C is perfect yet.
Two USB-C connectors that look the same may have completely different performance. That's because they may integrate different pins and support different protocols or standards. It's a total mess.
Hope today's video can answer some of your doubts. If you want to know more about USB-C, please leave your comments down below the article, and we may consider a new video to answer your questions.
Related Articles:
1. Why Gaming Laptops Don't Charge With USB-C?
2. What's USB Type-B Connector? | Introduction and Explained
3. Another Experiment | Will Wireless Charger Affect Multi-port USB Chargers?